Mahmoud Assran
A Shortcut-aware Video-QA Benchmark for Physical Understanding via Minimal Video Pairs
Jun 11, 2025



Abstract:Existing benchmarks for assessing the spatio-temporal understanding and reasoning abilities of video language models are susceptible to score inflation due to the presence of shortcut solutions based on superficial visual or textual cues. This paper mitigates the challenges in accurately assessing model performance by introducing the Minimal Video Pairs (MVP) benchmark, a simple shortcut-aware video QA benchmark for assessing the physical understanding of video language models. The benchmark is comprised of 55K high-quality multiple-choice video QA examples focusing on physical world understanding. Examples are curated from nine video data sources, spanning first-person egocentric and exocentric videos, robotic interaction data, and cognitive science intuitive physics benchmarks. To mitigate shortcut solutions that rely on superficial visual or textual cues and biases, each sample in MVP has a minimal-change pair -- a visually similar video accompanied by an identical question but an opposing answer. To answer a question correctly, a model must provide correct answers for both examples in the minimal-change pair; as such, models that solely rely on visual or textual biases would achieve below random performance. Human performance on MVP is 92.9\%, while the best open-source state-of-the-art video-language model achieves 40.2\% compared to random performance at 25\%.
Intuitive physics understanding emerges from self-supervised pretraining on natural videos
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:We investigate the emergence of intuitive physics understanding in general-purpose deep neural network models trained to predict masked regions in natural videos. Leveraging the violation-of-expectation framework, we find that video prediction models trained to predict outcomes in a learned representation space demonstrate an understanding of various intuitive physics properties, such as object permanence and shape consistency. In contrast, video prediction in pixel space and multimodal large language models, which reason through text, achieve performance closer to chance. Our comparisons of these architectures reveal that jointly learning an abstract representation space while predicting missing parts of sensory input, akin to predictive coding, is sufficient to acquire an understanding of intuitive physics, and that even models trained on one week of unique video achieve above chance performance. This challenges the idea that core knowledge -- a set of innate systems to help understand the world -- needs to be hardwired to develop an understanding of intuitive physics.
An Image is Worth More Than 16x16 Patches: Exploring Transformers on Individual Pixels
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:This work does not introduce a new method. Instead, we present an interesting finding that questions the necessity of the inductive bias -- locality in modern computer vision architectures. Concretely, we find that vanilla Transformers can operate by directly treating each individual pixel as a token and achieve highly performant results. This is substantially different from the popular design in Vision Transformer, which maintains the inductive bias from ConvNets towards local neighborhoods (e.g. by treating each 16x16 patch as a token). We mainly showcase the effectiveness of pixels-as-tokens across three well-studied tasks in computer vision: supervised learning for object classification, self-supervised learning via masked autoencoding, and image generation with diffusion models. Although directly operating on individual pixels is less computationally practical, we believe the community must be aware of this surprising piece of knowledge when devising the next generation of neural architectures for computer vision.
Modeling Caption Diversity in Contrastive Vision-Language Pretraining
Apr 30, 2024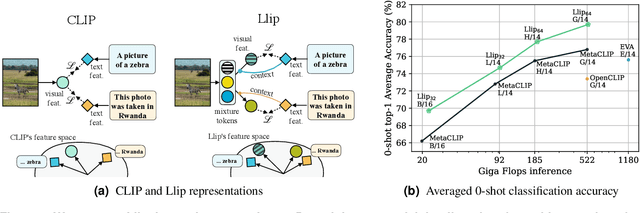
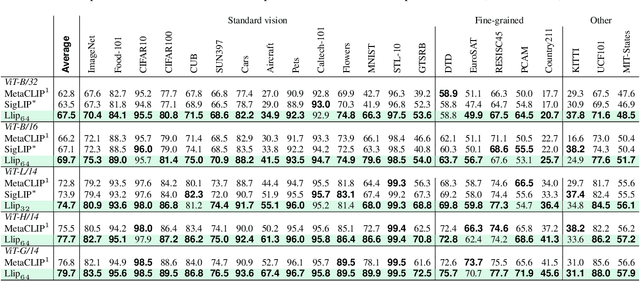
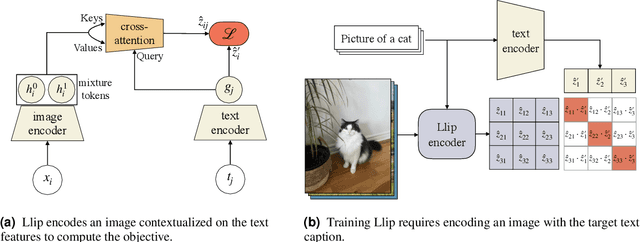
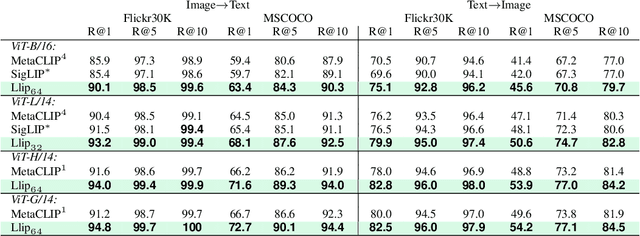
Abstract:There are a thousand ways to caption an image. Contrastive Language Pretraining (CLIP) on the other hand, works by mapping an image and its caption to a single vector -- limiting how well CLIP-like models can represent the diverse ways to describe an image. In this work, we introduce Llip, Latent Language Image Pretraining, which models the diversity of captions that could match an image. Llip's vision encoder outputs a set of visual features that are mixed into a final representation by conditioning on information derived from the text. We show that Llip outperforms non-contextualized baselines like CLIP and SigLIP on a variety of tasks even with large-scale encoders. Llip improves zero-shot classification by an average of 2.9% zero-shot classification benchmarks with a ViT-G/14 encoder. Specifically, Llip attains a zero-shot top-1 accuracy of 83.5% on ImageNet outperforming a similarly sized CLIP by 1.4%. We also demonstrate improvement on zero-shot retrieval on MS-COCO by 6.0%. We provide a comprehensive analysis of the components introduced by the method and demonstrate that Llip leads to richer visual representations.
Learning and Leveraging World Models in Visual Representation Learning
Mar 01, 2024


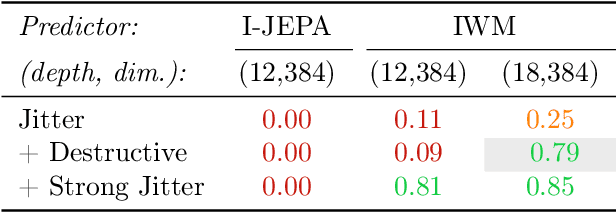
Abstract:Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA) has emerged as a promising self-supervised approach that learns by leveraging a world model. While previously limited to predicting missing parts of an input, we explore how to generalize the JEPA prediction task to a broader set of corruptions. We introduce Image World Models, an approach that goes beyond masked image modeling and learns to predict the effect of global photometric transformations in latent space. We study the recipe of learning performant IWMs and show that it relies on three key aspects: conditioning, prediction difficulty, and capacity. Additionally, we show that the predictive world model learned by IWM can be adapted through finetuning to solve diverse tasks; a fine-tuned IWM world model matches or surpasses the performance of previous self-supervised methods. Finally, we show that learning with an IWM allows one to control the abstraction level of the learned representations, learning invariant representations such as contrastive methods, or equivariant representations such as masked image modelling.
Predicting masked tokens in stochastic locations improves masked image modeling
Jul 31, 2023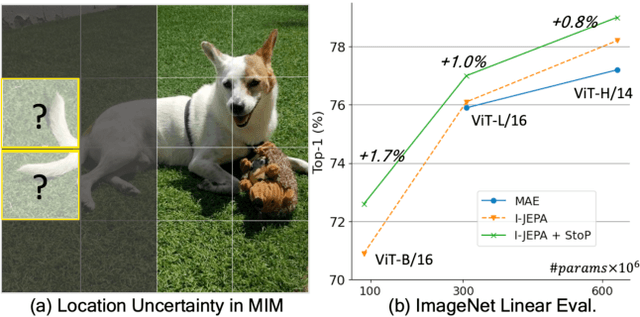
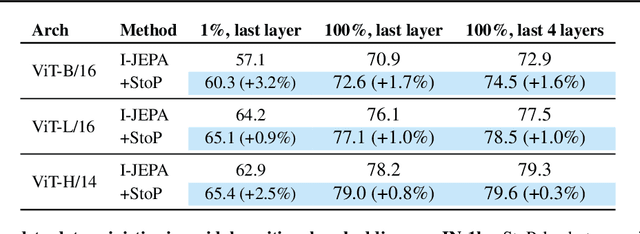
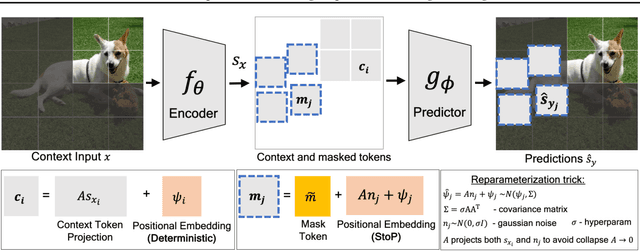
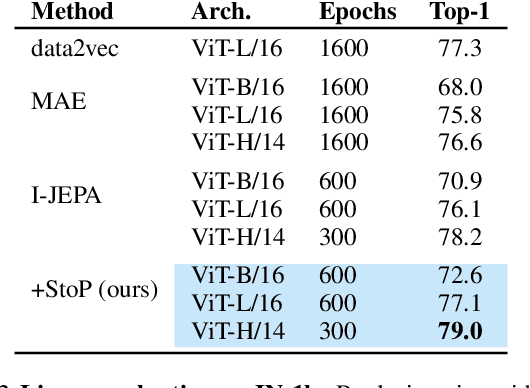
Abstract:Self-supervised learning is a promising paradigm in deep learning that enables learning from unlabeled data by constructing pretext tasks that require learning useful representations. In natural language processing, the dominant pretext task has been masked language modeling (MLM), while in computer vision there exists an equivalent called Masked Image Modeling (MIM). However, MIM is challenging because it requires predicting semantic content in accurate locations. E.g, given an incomplete picture of a dog, we can guess that there is a tail, but we cannot determine its exact location. In this work, we propose FlexPredict, a stochastic model that addresses this challenge by incorporating location uncertainty into the model. Specifically, we condition the model on stochastic masked token positions to guide the model toward learning features that are more robust to location uncertainties. Our approach improves downstream performance on a range of tasks, e.g, compared to MIM baselines, FlexPredict boosts ImageNet linear probing by 1.6% with ViT-B and by 2.5% for semi-supervised video segmentation using ViT-L.
DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision
Apr 14, 2023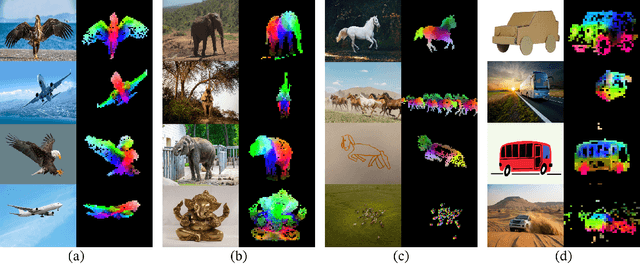
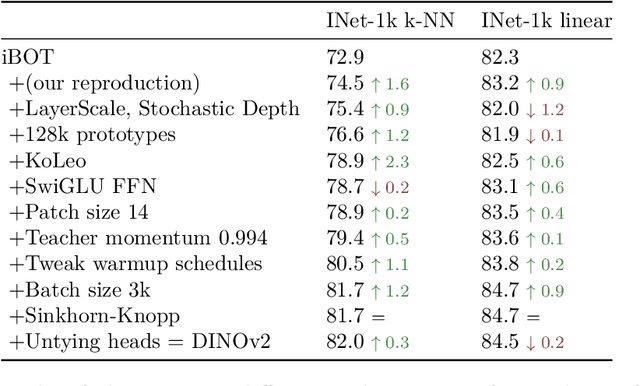
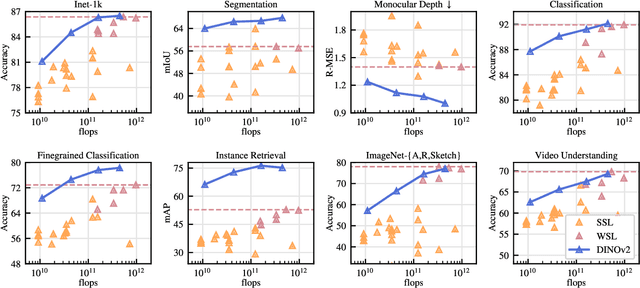
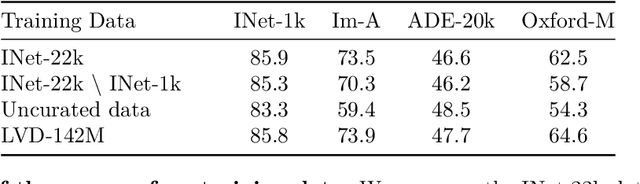
Abstract:The recent breakthroughs in natural language processing for model pretraining on large quantities of data have opened the way for similar foundation models in computer vision. These models could greatly simplify the use of images in any system by producing all-purpose visual features, i.e., features that work across image distributions and tasks without finetuning. This work shows that existing pretraining methods, especially self-supervised methods, can produce such features if trained on enough curated data from diverse sources. We revisit existing approaches and combine different techniques to scale our pretraining in terms of data and model size. Most of the technical contributions aim at accelerating and stabilizing the training at scale. In terms of data, we propose an automatic pipeline to build a dedicated, diverse, and curated image dataset instead of uncurated data, as typically done in the self-supervised literature. In terms of models, we train a ViT model (Dosovitskiy et al., 2020) with 1B parameters and distill it into a series of smaller models that surpass the best available all-purpose features, OpenCLIP (Ilharco et al., 2021) on most of the benchmarks at image and pixel levels.
Self-Supervised Learning from Images with a Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture
Jan 19, 2023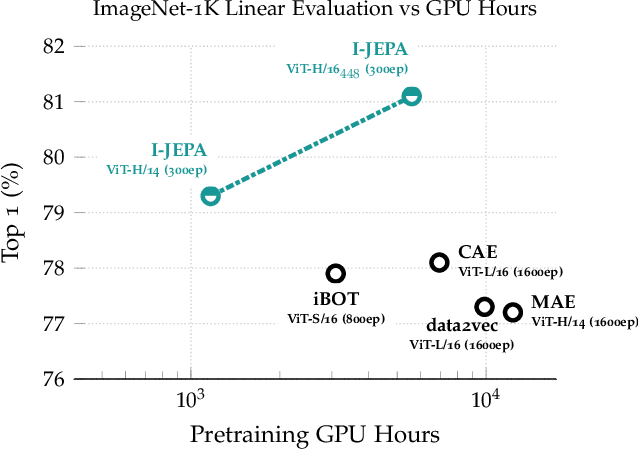
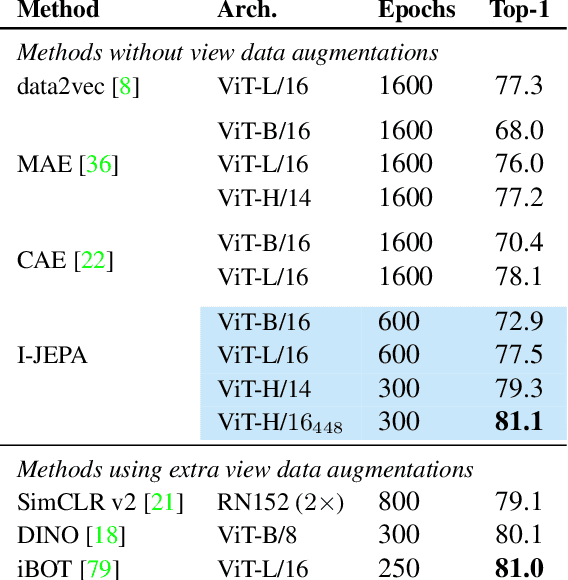
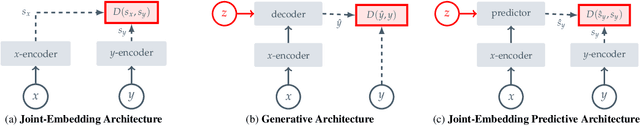
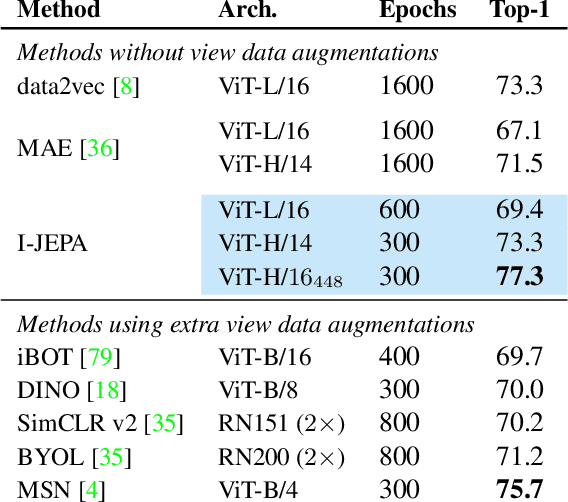
Abstract:This paper demonstrates an approach for learning highly semantic image representations without relying on hand-crafted data-augmentations. We introduce the Image-based Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (I-JEPA), a non-generative approach for self-supervised learning from images. The idea behind I-JEPA is simple: from a single context block, predict the representations of various target blocks in the same image. A core design choice to guide I-JEPA towards producing semantic representations is the masking strategy; specifically, it is crucial to (a) predict several target blocks in the image, (b) sample target blocks with sufficiently large scale (occupying 15%-20% of the image), and (c) use a sufficiently informative (spatially distributed) context block. Empirically, when combined with Vision Transformers, we find I-JEPA to be highly scalable. For instance, we train a ViT-Huge/16 on ImageNet using 32 A100 GPUs in under 38 hours to achieve strong downstream performance across a wide range of tasks requiring various levels of abstraction, from linear classification to object counting and depth prediction.
The Hidden Uniform Cluster Prior in Self-Supervised Learning
Oct 13, 2022



Abstract:A successful paradigm in representation learning is to perform self-supervised pretraining using tasks based on mini-batch statistics (e.g., SimCLR, VICReg, SwAV, MSN). We show that in the formulation of all these methods is an overlooked prior to learn features that enable uniform clustering of the data. While this prior has led to remarkably semantic representations when pretraining on class-balanced data, such as ImageNet, we demonstrate that it can hamper performance when pretraining on class-imbalanced data. By moving away from conventional uniformity priors and instead preferring power-law distributed feature clusters, we show that one can improve the quality of the learned representations on real-world class-imbalanced datasets. To demonstrate this, we develop an extension of the Masked Siamese Networks (MSN) method to support the use of arbitrary features priors.
Masked Siamese Networks for Label-Efficient Learning
Apr 14, 2022



Abstract:We propose Masked Siamese Networks (MSN), a self-supervised learning framework for learning image representations. Our approach matches the representation of an image view containing randomly masked patches to the representation of the original unmasked image. This self-supervised pre-training strategy is particularly scalable when applied to Vision Transformers since only the unmasked patches are processed by the network. As a result, MSNs improve the scalability of joint-embedding architectures, while producing representations of a high semantic level that perform competitively on low-shot image classification. For instance, on ImageNet-1K, with only 5,000 annotated images, our base MSN model achieves 72.4% top-1 accuracy, and with 1% of ImageNet-1K labels, we achieve 75.7% top-1 accuracy, setting a new state-of-the-art for self-supervised learning on this benchmark. Our code is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge