Aaron Courville
Universite de Montreal
Towards Sustainable Investment Policies Informed by Opponent Shaping
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Addressing climate change requires global coordination, yet rational economic actors often prioritize immediate gains over collective welfare, resulting in social dilemmas. InvestESG is a recently proposed multi-agent simulation that captures the dynamic interplay between investors and companies under climate risk. We provide a formal characterization of the conditions under which InvestESG exhibits an intertemporal social dilemma, deriving theoretical thresholds at which individual incentives diverge from collective welfare. Building on this, we apply Advantage Alignment, a scalable opponent shaping algorithm shown to be effective in general-sum games, to influence agent learning in InvestESG. We offer theoretical insights into why Advantage Alignment systematically favors socially beneficial equilibria by biasing learning dynamics toward cooperative outcomes. Our results demonstrate that strategically shaping the learning processes of economic agents can result in better outcomes that could inform policy mechanisms to better align market incentives with long-term sustainability goals.
A Comedy of Estimators: On KL Regularization in RL Training of LLMs
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:The reasoning performance of large language models (LLMs) can be substantially improved by training them with reinforcement learning (RL). The RL objective for LLM training involves a regularization term, which is the reverse Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between the trained policy and the reference policy. Since computing the KL divergence exactly is intractable, various estimators are used in practice to estimate it from on-policy samples. Despite its wide adoption, including in several open-source libraries, there is no systematic study analyzing the numerous ways of incorporating KL estimators in the objective and their effect on the downstream performance of RL-trained models. Recent works show that prevailing practices for incorporating KL regularization do not provide correct gradients for stated objectives, creating a discrepancy between the objective and its implementation. In this paper, we further analyze these practices and study the gradients of several estimators configurations, revealing how design choices shape gradient bias. We substantiate these findings with empirical observations by RL fine-tuning \texttt{Qwen2.5-7B}, \texttt{Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct} and \texttt{Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507} with different configurations and evaluating their performance on both in- and out-of-distribution tasks. Through our analysis, we observe that, in on-policy settings: (1) estimator configurations with biased gradients can result in training instabilities; and (2) using estimator configurations resulting in unbiased gradients leads to better performance on in-domain as well as out-of-domain tasks. We also investigate the performance resulting from different KL configurations in off-policy settings and observe that KL regularization can help stabilize off-policy RL training resulting from asynchronous setups.
Shape of Thought: When Distribution Matters More than Correctness in Reasoning Tasks
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:We present the surprising finding that a language model's reasoning capabilities can be improved by training on synthetic datasets of chain-of-thought (CoT) traces from more capable models, even when all of those traces lead to an incorrect final answer. Our experiments show this approach can yield better performance on reasoning tasks than training on human-annotated datasets. We hypothesize that two key factors explain this phenomenon: first, the distribution of synthetic data is inherently closer to the language model's own distribution, making it more amenable to learning. Second, these `incorrect' traces are often only partially flawed and contain valid reasoning steps from which the model can learn. To further test the first hypothesis, we use a language model to paraphrase human-annotated traces -- shifting their distribution closer to the model's own distribution -- and show that this improves performance. For the second hypothesis, we introduce increasingly flawed CoT traces and study to what extent models are tolerant to these flaws. We demonstrate our findings across various reasoning domains like math, algorithmic reasoning and code generation using MATH, GSM8K, Countdown and MBPP datasets on various language models ranging from 1.5B to 9B across Qwen, Llama, and Gemma models. Our study shows that curating datasets that are closer to the model's distribution is a critical aspect to consider. We also show that a correct final answer is not always a reliable indicator of a faithful reasoning process.
Asymmetric Proximal Policy Optimization: mini-critics boost LLM reasoning
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Most recent RL for LLMs (RL4LLM) methods avoid explicit critics, replacing them with average advantage baselines. This shift is largely pragmatic: conventional value functions are computationally expensive to train at LLM scale and often fail under sparse rewards and long reasoning horizons. We revisit this bottleneck from an architectural perspective and introduce Asymmetric Proximal Policy Optimization (AsyPPO), a simple and scalable framework that restores the critics role while remaining efficient in large-model settings. AsyPPO employs a set of lightweight mini-critics, each trained on disjoint prompt shards. This design encourages diversity while preserving calibration, reducing value-estimation bias. Beyond robust estimation, AsyPPO leverages inter-critic uncertainty to refine the policy update: (i) masking advantages in states where critics agree and gradients add little learning signal, and (ii) filtering high-divergence states from entropy regularization, suppressing spurious exploration. After training on open-source data with only 5,000 samples, AsyPPO consistently improves learning stability and performance across multiple benchmarks over strong baselines, such as GRPO, achieving performance gains of more than six percent on Qwen3-4b-Base and about three percent on Qwen3-8b-Base and Qwen3-14b-Base over classic PPO, without additional tricks. These results highlight the importance of architectural innovations for scalable, efficient algorithms.
Compositional Discrete Latent Code for High Fidelity, Productive Diffusion Models
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:We argue that diffusion models' success in modeling complex distributions is, for the most part, coming from their input conditioning. This paper investigates the representation used to condition diffusion models from the perspective that ideal representations should improve sample fidelity, be easy to generate, and be compositional to allow out-of-training samples generation. We introduce Discrete Latent Code (DLC), an image representation derived from Simplicial Embeddings trained with a self-supervised learning objective. DLCs are sequences of discrete tokens, as opposed to the standard continuous image embeddings. They are easy to generate and their compositionality enables sampling of novel images beyond the training distribution. Diffusion models trained with DLCs have improved generation fidelity, establishing a new state-of-the-art for unconditional image generation on ImageNet. Additionally, we show that composing DLCs allows the image generator to produce out-of-distribution samples that coherently combine the semantics of images in diverse ways. Finally, we showcase how DLCs can enable text-to-image generation by leveraging large-scale pretrained language models. We efficiently finetune a text diffusion language model to generate DLCs that produce novel samples outside of the image generator training distribution.
Stable Gradients for Stable Learning at Scale in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 18, 2025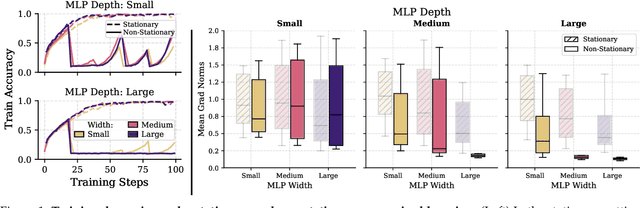
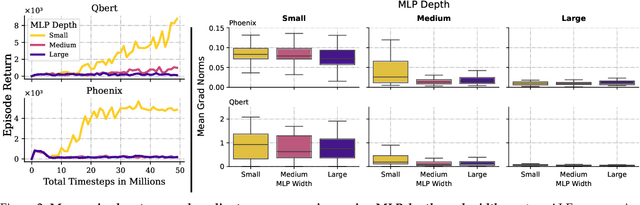
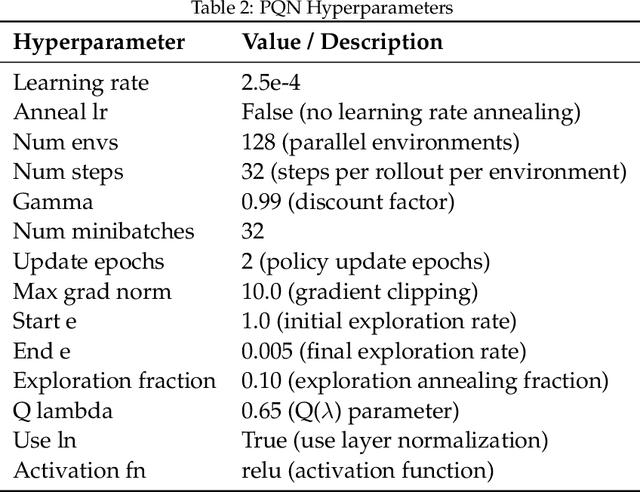
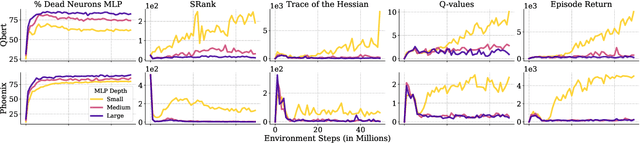
Abstract:Scaling deep reinforcement learning networks is challenging and often results in degraded performance, yet the root causes of this failure mode remain poorly understood. Several recent works have proposed mechanisms to address this, but they are often complex and fail to highlight the causes underlying this difficulty. In this work, we conduct a series of empirical analyses which suggest that the combination of non-stationarity with gradient pathologies, due to suboptimal architectural choices, underlie the challenges of scale. We propose a series of direct interventions that stabilize gradient flow, enabling robust performance across a range of network depths and widths. Our interventions are simple to implement and compatible with well-established algorithms, and result in an effective mechanism that enables strong performance even at large scales. We validate our findings on a variety of agents and suites of environments.
Adaptive Accompaniment with ReaLchords
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Jamming requires coordination, anticipation, and collaborative creativity between musicians. Current generative models of music produce expressive output but are not able to generate in an \emph{online} manner, meaning simultaneously with other musicians (human or otherwise). We propose ReaLchords, an online generative model for improvising chord accompaniment to user melody. We start with an online model pretrained by maximum likelihood, and use reinforcement learning to finetune the model for online use. The finetuning objective leverages both a novel reward model that provides feedback on both harmonic and temporal coherency between melody and chord, and a divergence term that implements a novel type of distillation from a teacher model that can see the future melody. Through quantitative experiments and listening tests, we demonstrate that the resulting model adapts well to unfamiliar input and produce fitting accompaniment. ReaLchords opens the door to live jamming, as well as simultaneous co-creation in other modalities.
The Courage to Stop: Overcoming Sunk Cost Fallacy in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 16, 2025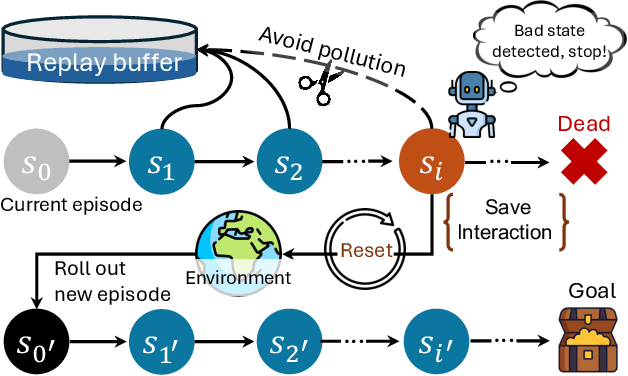
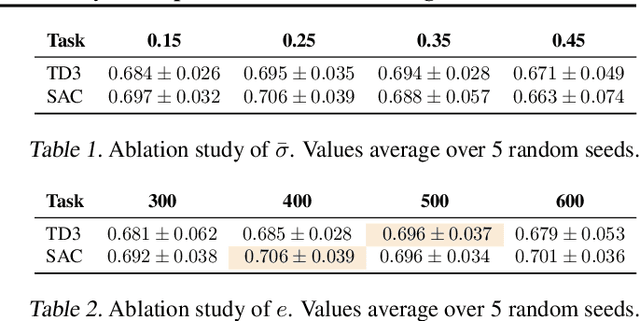
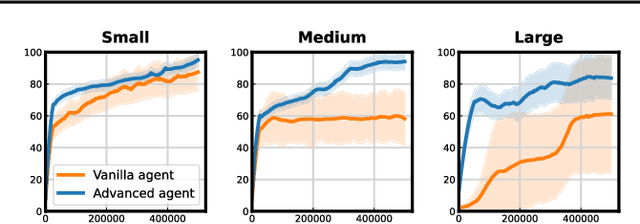
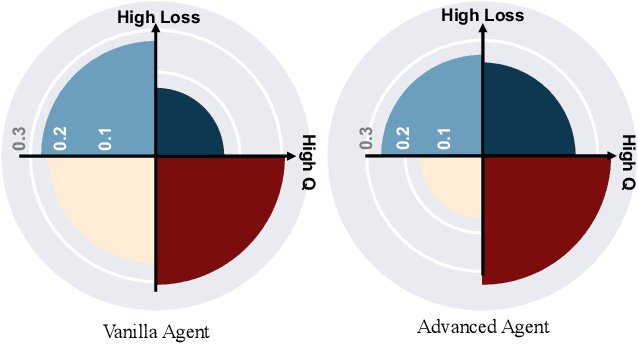
Abstract:Off-policy deep reinforcement learning (RL) typically leverages replay buffers for reusing past experiences during learning. This can help improve sample efficiency when the collected data is informative and aligned with the learning objectives; when that is not the case, it can have the effect of "polluting" the replay buffer with data which can exacerbate optimization challenges in addition to wasting environment interactions due to wasteful sampling. We argue that sampling these uninformative and wasteful transitions can be avoided by addressing the sunk cost fallacy, which, in the context of deep RL, is the tendency towards continuing an episode until termination. To address this, we propose learn to stop (LEAST), a lightweight mechanism that enables strategic early episode termination based on Q-value and gradient statistics, which helps agents recognize when to terminate unproductive episodes early. We demonstrate that our method improves learning efficiency on a variety of RL algorithms, evaluated on both the MuJoCo and DeepMind Control Suite benchmarks.
Bias Analysis in Unconditional Image Generative Models
Jun 10, 2025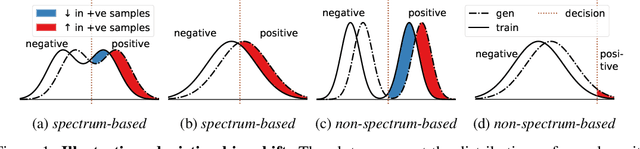
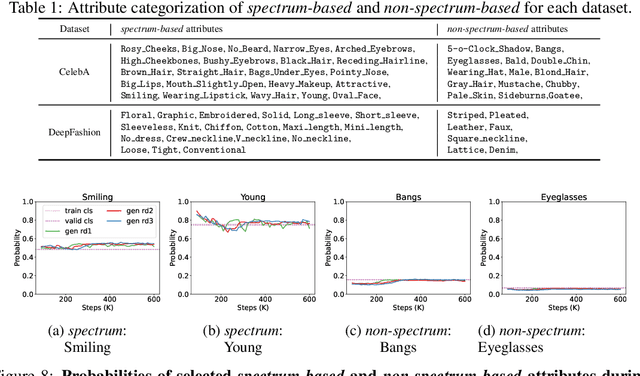
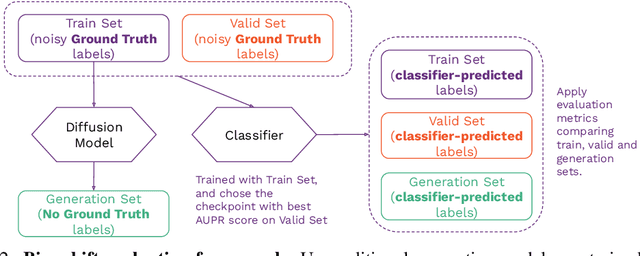
Abstract:The widespread adoption of generative AI models has raised growing concerns about representational harm and potential discriminatory outcomes. Yet, despite growing literature on this topic, the mechanisms by which bias emerges - especially in unconditional generation - remain disentangled. We define the bias of an attribute as the difference between the probability of its presence in the observed distribution and its expected proportion in an ideal reference distribution. In our analysis, we train a set of unconditional image generative models and adopt a commonly used bias evaluation framework to study bias shift between training and generated distributions. Our experiments reveal that the detected attribute shifts are small. We find that the attribute shifts are sensitive to the attribute classifier used to label generated images in the evaluation framework, particularly when its decision boundaries fall in high-density regions. Our empirical analysis indicates that this classifier sensitivity is often observed in attributes values that lie on a spectrum, as opposed to exhibiting a binary nature. This highlights the need for more representative labeling practices, understanding the shortcomings through greater scrutiny of evaluation frameworks, and recognizing the socially complex nature of attributes when evaluating bias.
Measure gradients, not activations! Enhancing neuronal activity in deep reinforcement learning
May 29, 2025Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (RL) agents frequently suffer from neuronal activity loss, which impairs their ability to adapt to new data and learn continually. A common method to quantify and address this issue is the tau-dormant neuron ratio, which uses activation statistics to measure the expressive ability of neurons. While effective for simple MLP-based agents, this approach loses statistical power in more complex architectures. To address this, we argue that in advanced RL agents, maintaining a neuron's learning capacity, its ability to adapt via gradient updates, is more critical than preserving its expressive ability. Based on this insight, we shift the statistical objective from activations to gradients, and introduce GraMa (Gradient Magnitude Neural Activity Metric), a lightweight, architecture-agnostic metric for quantifying neuron-level learning capacity. We show that GraMa effectively reveals persistent neuron inactivity across diverse architectures, including residual networks, diffusion models, and agents with varied activation functions. Moreover, resetting neurons guided by GraMa (ReGraMa) consistently improves learning performance across multiple deep RL algorithms and benchmarks, such as MuJoCo and the DeepMind Control Suite.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge