Justin Salamon
PromptSep: Generative Audio Separation via Multimodal Prompting
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in language-queried audio source separation (LASS) have shown that generative models can achieve higher separation audio quality than traditional masking-based approaches. However, two key limitations restrict their practical use: (1) users often require operations beyond separation, such as sound removal; and (2) relying solely on text prompts can be unintuitive for specifying sound sources. In this paper, we propose PromptSep to extend LASS into a broader framework for general-purpose sound separation. PromptSep leverages a conditional diffusion model enhanced with elaborated data simulation to enable both audio extraction and sound removal. To move beyond text-only queries, we incorporate vocal imitation as an additional and more intuitive conditioning modality for our model, by incorporating Sketch2Sound as a data augmentation strategy. Both objective and subjective evaluations on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that PromptSep achieves state-of-the-art performance in sound removal and vocal-imitation-guided source separation, while maintaining competitive results on language-queried source separation.
FLAM: Frame-Wise Language-Audio Modeling
May 08, 2025Abstract:Recent multi-modal audio-language models (ALMs) excel at text-audio retrieval but struggle with frame-wise audio understanding. Prior works use temporal-aware labels or unsupervised training to improve frame-wise capabilities, but they still lack fine-grained labeling capability to pinpoint when an event occurs. While traditional sound event detection models can precisely localize events, they are limited to pre-defined categories, making them ineffective for real-world scenarios with out-of-distribution events. In this work, we introduce FLAM, an open-vocabulary contrastive audio-language model capable of localizing specific sound events. FLAM employs a memory-efficient and calibrated frame-wise objective with logit adjustment to address spurious correlations, such as event dependencies and label imbalances during training. To enable frame-wise supervision, we leverage a large-scale dataset with diverse audio events, LLM-generated captions and simulation. Experimental results and case studies demonstrate that FLAM significantly improves the open-vocabulary localization capability while maintaining strong performance in global retrieval and downstream tasks.
SILA: Signal-to-Language Augmentation for Enhanced Control in Text-to-Audio Generation
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:The field of text-to-audio generation has seen significant advancements, and yet the ability to finely control the acoustic characteristics of generated audio remains under-explored. In this paper, we introduce a novel yet simple approach to generate sound effects with control over key acoustic parameters such as loudness, pitch, reverb, fade, brightness, noise and duration, enabling creative applications in sound design and content creation. These parameters extend beyond traditional Digital Signal Processing (DSP) techniques, incorporating learned representations that capture the subtleties of how sound characteristics can be shaped in context, enabling a richer and more nuanced control over the generated audio. Our approach is model-agnostic and is based on learning the disentanglement between audio semantics and its acoustic features. Our approach not only enhances the versatility and expressiveness of text-to-audio generation but also opens new avenues for creative audio production and sound design. Our objective and subjective evaluation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in producing high-quality, customizable audio outputs that align closely with user specifications.
Sketch2Sound: Controllable Audio Generation via Time-Varying Signals and Sonic Imitations
Dec 11, 2024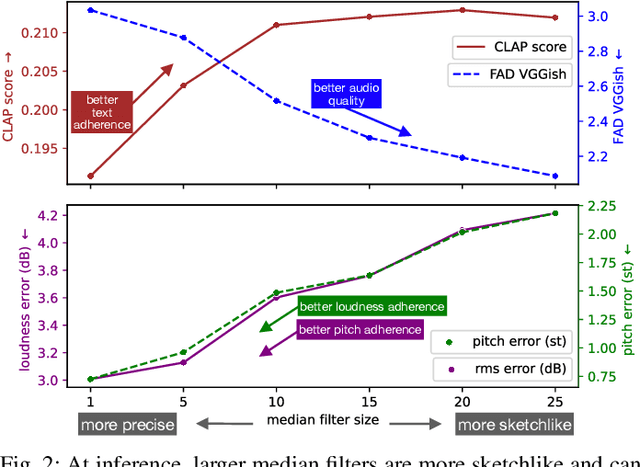
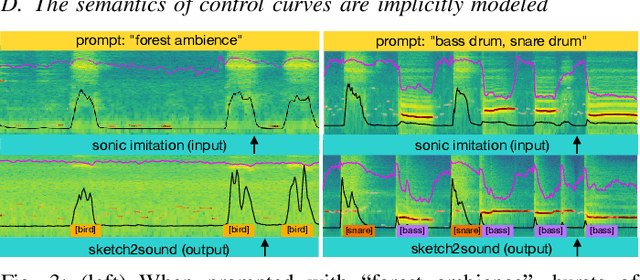
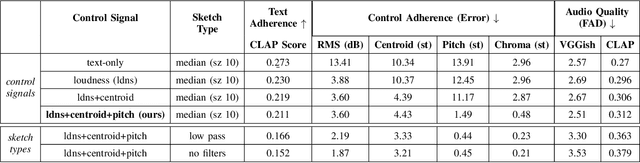
Abstract:We present Sketch2Sound, a generative audio model capable of creating high-quality sounds from a set of interpretable time-varying control signals: loudness, brightness, and pitch, as well as text prompts. Sketch2Sound can synthesize arbitrary sounds from sonic imitations (i.e.,~a vocal imitation or a reference sound-shape). Sketch2Sound can be implemented on top of any text-to-audio latent diffusion transformer (DiT), and requires only 40k steps of fine-tuning and a single linear layer per control, making it more lightweight than existing methods like ControlNet. To synthesize from sketchlike sonic imitations, we propose applying random median filters to the control signals during training, allowing Sketch2Sound to be prompted using controls with flexible levels of temporal specificity. We show that Sketch2Sound can synthesize sounds that follow the gist of input controls from a vocal imitation while retaining the adherence to an input text prompt and audio quality compared to a text-only baseline. Sketch2Sound allows sound artists to create sounds with the semantic flexibility of text prompts and the expressivity and precision of a sonic gesture or vocal imitation. Sound examples are available at https://hugofloresgarcia.art/sketch2sound/.
Video-Guided Foley Sound Generation with Multimodal Controls
Nov 26, 2024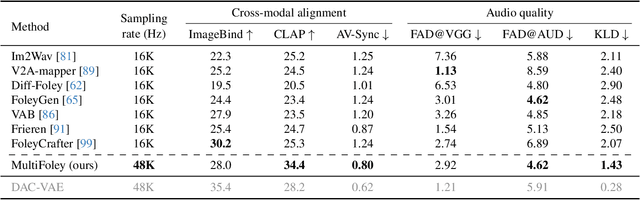
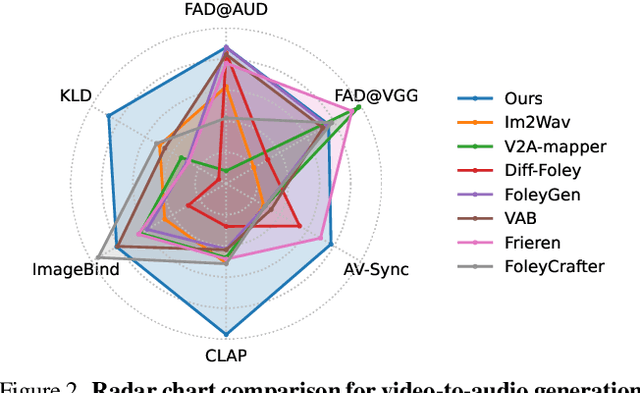
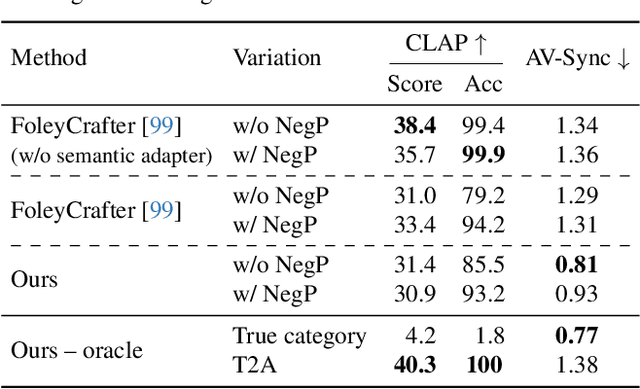
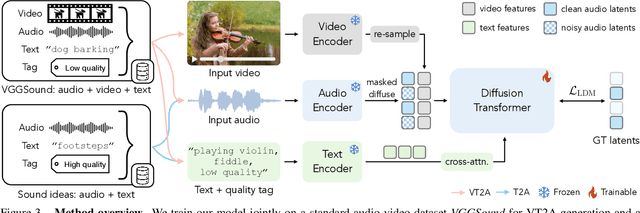
Abstract:Generating sound effects for videos often requires creating artistic sound effects that diverge significantly from real-life sources and flexible control in the sound design. To address this problem, we introduce MultiFoley, a model designed for video-guided sound generation that supports multimodal conditioning through text, audio, and video. Given a silent video and a text prompt, MultiFoley allows users to create clean sounds (e.g., skateboard wheels spinning without wind noise) or more whimsical sounds (e.g., making a lion's roar sound like a cat's meow). MultiFoley also allows users to choose reference audio from sound effects (SFX) libraries or partial videos for conditioning. A key novelty of our model lies in its joint training on both internet video datasets with low-quality audio and professional SFX recordings, enabling high-quality, full-bandwidth (48kHz) audio generation. Through automated evaluations and human studies, we demonstrate that MultiFoley successfully generates synchronized high-quality sounds across varied conditional inputs and outperforms existing methods. Please see our project page for video results: https://ificl.github.io/MultiFoley/
Augment, Drop & Swap: Improving Diversity in LLM Captions for Efficient Music-Text Representation Learning
Sep 17, 2024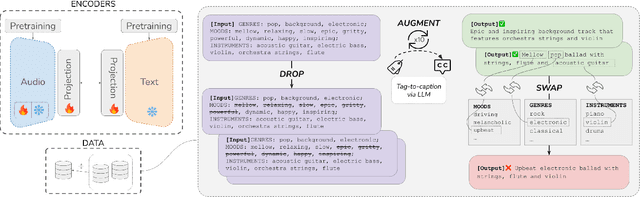
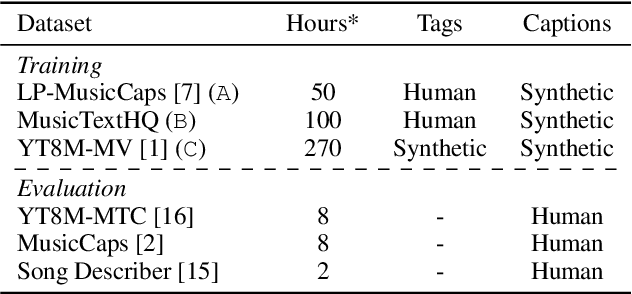
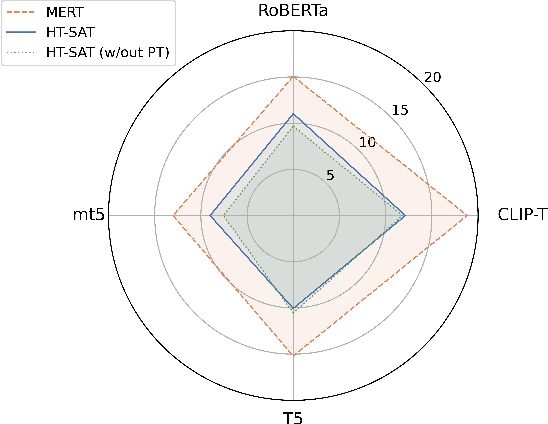
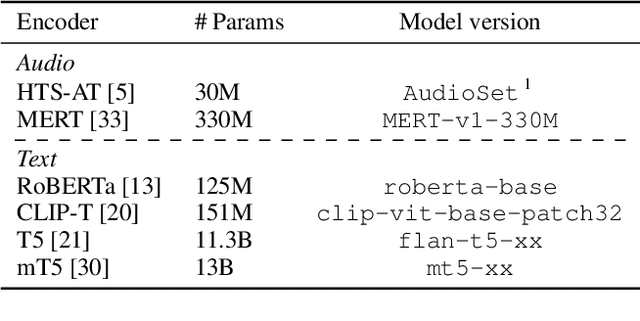
Abstract:Audio-text contrastive models have become a powerful approach in music representation learning. Despite their empirical success, however, little is known about the influence of key design choices on the quality of music-text representations learnt through this framework. In this work, we expose these design choices within the constraints of limited data and computation budgets, and establish a more solid understanding of their impact grounded in empirical observations along three axes: the choice of base encoders, the level of curation in training data, and the use of text augmentation. We find that data curation is the single most important factor for music-text contrastive training in resource-constrained scenarios. Motivated by this insight, we introduce two novel techniques, Augmented View Dropout and TextSwap, which increase the diversity and descriptiveness of text inputs seen in training. Through our experiments we demonstrate that these are effective at boosting performance across different pre-training regimes, model architectures, and downstream data distributions, without incurring higher computational costs or requiring additional training data.
Bridging High-Quality Audio and Video via Language for Sound Effects Retrieval from Visual Queries
Aug 17, 2023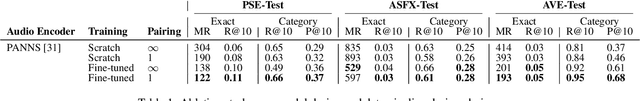
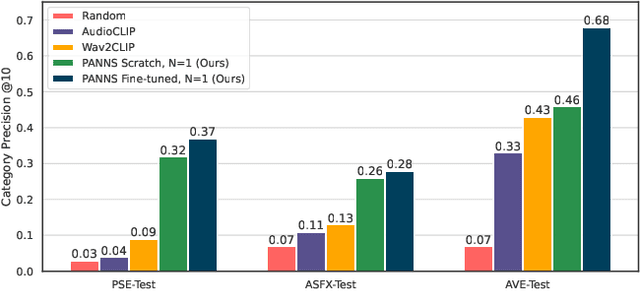
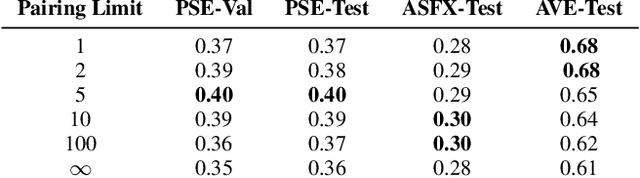
Abstract:Finding the right sound effects (SFX) to match moments in a video is a difficult and time-consuming task, and relies heavily on the quality and completeness of text metadata. Retrieving high-quality (HQ) SFX using a video frame directly as the query is an attractive alternative, removing the reliance on text metadata and providing a low barrier to entry for non-experts. Due to the lack of HQ audio-visual training data, previous work on audio-visual retrieval relies on YouTube (in-the-wild) videos of varied quality for training, where the audio is often noisy and the video of amateur quality. As such it is unclear whether these systems would generalize to the task of matching HQ audio to production-quality video. To address this, we propose a multimodal framework for recommending HQ SFX given a video frame by (1) leveraging large language models and foundational vision-language models to bridge HQ audio and video to create audio-visual pairs, resulting in a highly scalable automatic audio-visual data curation pipeline; and (2) using pre-trained audio and visual encoders to train a contrastive learning-based retrieval system. We show that our system, trained using our automatic data curation pipeline, significantly outperforms baselines trained on in-the-wild data on the task of HQ SFX retrieval for video. Furthermore, while the baselines fail to generalize to this task, our system generalizes well from clean to in-the-wild data, outperforming the baselines on a dataset of YouTube videos despite only being trained on the HQ audio-visual pairs. A user study confirms that people prefer SFX retrieved by our system over the baseline 67% of the time both for HQ and in-the-wild data. Finally, we present ablations to determine the impact of model and data pipeline design choices on downstream retrieval performance. Please visit our project website to listen to and view our SFX retrieval results.
Language-Guided Music Recommendation for Video via Prompt Analogies
Jun 15, 2023



Abstract:We propose a method to recommend music for an input video while allowing a user to guide music selection with free-form natural language. A key challenge of this problem setting is that existing music video datasets provide the needed (video, music) training pairs, but lack text descriptions of the music. This work addresses this challenge with the following three contributions. First, we propose a text-synthesis approach that relies on an analogy-based prompting procedure to generate natural language music descriptions from a large-scale language model (BLOOM-176B) given pre-trained music tagger outputs and a small number of human text descriptions. Second, we use these synthesized music descriptions to train a new trimodal model, which fuses text and video input representations to query music samples. For training, we introduce a text dropout regularization mechanism which we show is critical to model performance. Our model design allows for the retrieved music audio to agree with the two input modalities by matching visual style depicted in the video and musical genre, mood, or instrumentation described in the natural language query. Third, to evaluate our approach, we collect a testing dataset for our problem by annotating a subset of 4k clips from the YT8M-MusicVideo dataset with natural language music descriptions which we make publicly available. We show that our approach can match or exceed the performance of prior methods on video-to-music retrieval while significantly improving retrieval accuracy when using text guidance.
Efficient Spoken Language Recognition via Multilabel Classification
Jun 02, 2023


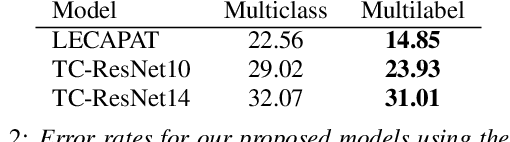
Abstract:Spoken language recognition (SLR) is the task of automatically identifying the language present in a speech signal. Existing SLR models are either too computationally expensive or too large to run effectively on devices with limited resources. For real-world deployment, a model should also gracefully handle unseen languages outside of the target language set, yet prior work has focused on closed-set classification where all input languages are known a-priori. In this paper we address these two limitations: we explore efficient model architectures for SLR based on convolutional networks, and propose a multilabel training strategy to handle non-target languages at inference time. Using the VoxLingua107 dataset, we show that our models obtain competitive results while being orders of magnitude smaller and faster than current state-of-the-art methods, and that our multilabel strategy is more robust to unseen non-target languages compared to multiclass classification.
Conditional Generation of Audio from Video via Foley Analogies
Apr 17, 2023Abstract:The sound effects that designers add to videos are designed to convey a particular artistic effect and, thus, may be quite different from a scene's true sound. Inspired by the challenges of creating a soundtrack for a video that differs from its true sound, but that nonetheless matches the actions occurring on screen, we propose the problem of conditional Foley. We present the following contributions to address this problem. First, we propose a pretext task for training our model to predict sound for an input video clip using a conditional audio-visual clip sampled from another time within the same source video. Second, we propose a model for generating a soundtrack for a silent input video, given a user-supplied example that specifies what the video should "sound like". We show through human studies and automated evaluation metrics that our model successfully generates sound from video, while varying its output according to the content of a supplied example. Project site: https://xypb.github.io/CondFoleyGen/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge