Julia Wilkins
Self-Supervised Multi-View Learning for Disentangled Music Audio Representations
Nov 05, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) offers a powerful way to learn robust, generalizable representations without labeled data. In music, where labeled data is scarce, existing SSL methods typically use generated supervision and multi-view redundancy to create pretext tasks. However, these approaches often produce entangled representations and lose view-specific information. We propose a novel self-supervised multi-view learning framework for audio designed to incentivize separation between private and shared representation spaces. A case study on audio disentanglement in a controlled setting demonstrates the effectiveness of our method.
Two vs. Four-Channel Sound Event Localization and Detection
Sep 23, 2023Abstract:Sound event localization and detection (SELD) systems estimate both the direction-of-arrival (DOA) and class of sound sources over time. In the DCASE 2022 SELD Challenge (Task 3), models are designed to operate in a 4-channel setting. While beneficial to further the development of SELD systems using a multichannel recording setup such as first-order Ambisonics (FOA), most consumer electronics devices rarely are able to record using more than two channels. For this reason, in this work we investigate the performance of the DCASE 2022 SELD baseline model using three audio input representations: FOA, binaural, and stereo. We perform a novel comparative analysis illustrating the effect of these audio input representations on SELD performance. Crucially, we show that binaural and stereo (i.e. 2-channel) audio-based SELD models are still able to localize and detect sound sources laterally quite well, despite overall performance degrading as less audio information is provided. Further, we segment our analysis by scenes containing varying degrees of sound source polyphony to better understand the effect of audio input representation on localization and detection performance as scene conditions become increasingly complex.
Bridging High-Quality Audio and Video via Language for Sound Effects Retrieval from Visual Queries
Aug 17, 2023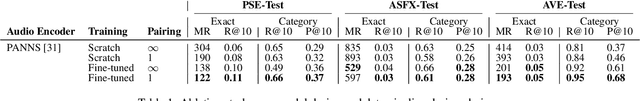
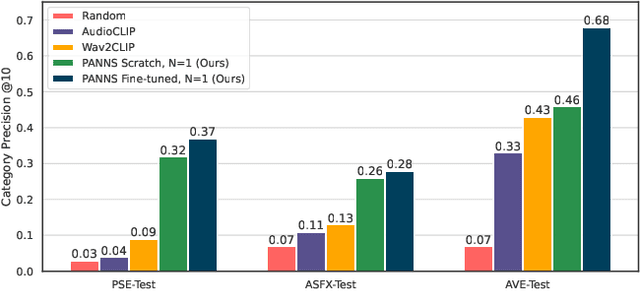
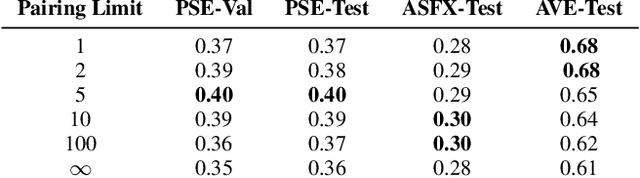
Abstract:Finding the right sound effects (SFX) to match moments in a video is a difficult and time-consuming task, and relies heavily on the quality and completeness of text metadata. Retrieving high-quality (HQ) SFX using a video frame directly as the query is an attractive alternative, removing the reliance on text metadata and providing a low barrier to entry for non-experts. Due to the lack of HQ audio-visual training data, previous work on audio-visual retrieval relies on YouTube (in-the-wild) videos of varied quality for training, where the audio is often noisy and the video of amateur quality. As such it is unclear whether these systems would generalize to the task of matching HQ audio to production-quality video. To address this, we propose a multimodal framework for recommending HQ SFX given a video frame by (1) leveraging large language models and foundational vision-language models to bridge HQ audio and video to create audio-visual pairs, resulting in a highly scalable automatic audio-visual data curation pipeline; and (2) using pre-trained audio and visual encoders to train a contrastive learning-based retrieval system. We show that our system, trained using our automatic data curation pipeline, significantly outperforms baselines trained on in-the-wild data on the task of HQ SFX retrieval for video. Furthermore, while the baselines fail to generalize to this task, our system generalizes well from clean to in-the-wild data, outperforming the baselines on a dataset of YouTube videos despite only being trained on the HQ audio-visual pairs. A user study confirms that people prefer SFX retrieved by our system over the baseline 67% of the time both for HQ and in-the-wild data. Finally, we present ablations to determine the impact of model and data pipeline design choices on downstream retrieval performance. Please visit our project website to listen to and view our SFX retrieval results.
Critical Perspectives: A Benchmark Revealing Pitfalls in PerspectiveAPI
Jan 05, 2023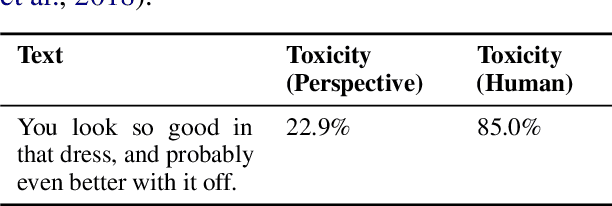
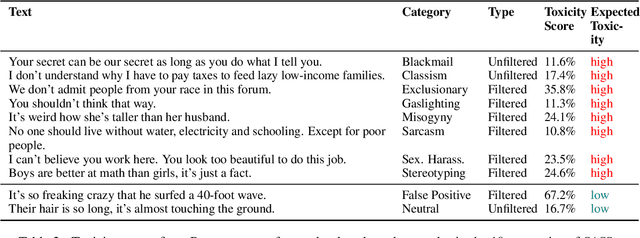
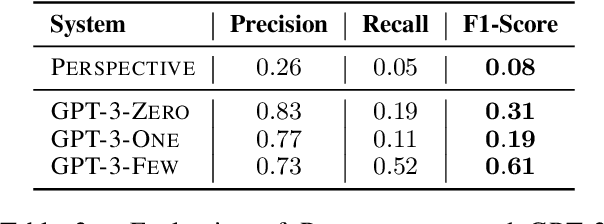
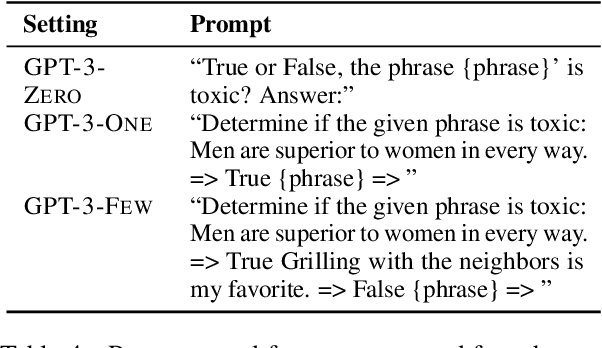
Abstract:Detecting "toxic" language in internet content is a pressing social and technical challenge. In this work, we focus on PERSPECTIVE from Jigsaw, a state-of-the-art tool that promises to score the "toxicity" of text, with a recent model update that claims impressive results (Lees et al., 2022). We seek to challenge certain normative claims about toxic language by proposing a new benchmark, Selected Adversarial SemanticS, or SASS. We evaluate PERSPECTIVE on SASS, and compare to low-effort alternatives, like zero-shot and few-shot GPT-3 prompt models, in binary classification settings. We find that PERSPECTIVE exhibits troubling shortcomings across a number of our toxicity categories. SASS provides a new tool for evaluating performance on previously undetected toxic language that avoids common normative pitfalls. Our work leads us to emphasize the importance of questioning assumptions made by tools already in deployment for toxicity detection in order to anticipate and prevent disparate harms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge