Prem Seetharaman
PromptSep: Generative Audio Separation via Multimodal Prompting
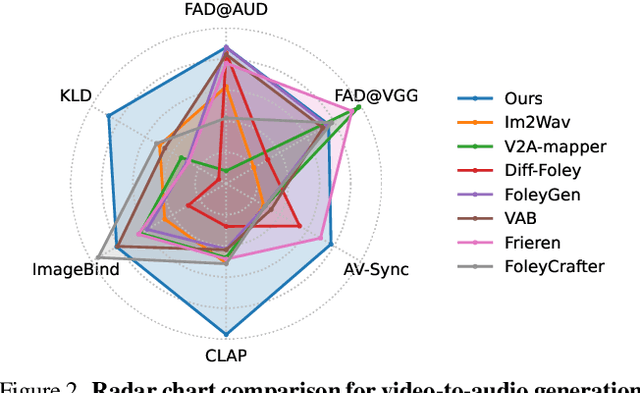
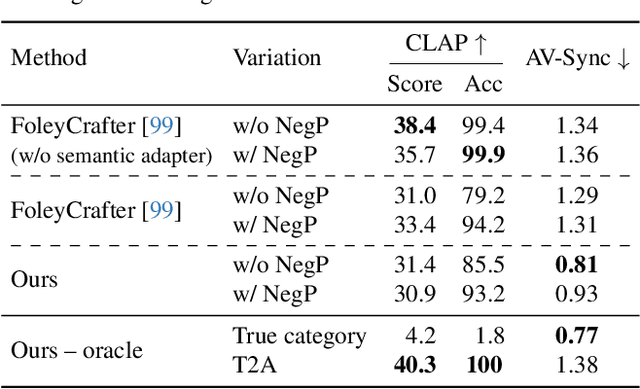
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in language-queried audio source separation (LASS) have shown that generative models can achieve higher separation audio quality than traditional masking-based approaches. However, two key limitations restrict their practical use: (1) users often require operations beyond separation, such as sound removal; and (2) relying solely on text prompts can be unintuitive for specifying sound sources. In this paper, we propose PromptSep to extend LASS into a broader framework for general-purpose sound separation. PromptSep leverages a conditional diffusion model enhanced with elaborated data simulation to enable both audio extraction and sound removal. To move beyond text-only queries, we incorporate vocal imitation as an additional and more intuitive conditioning modality for our model, by incorporating Sketch2Sound as a data augmentation strategy. Both objective and subjective evaluations on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that PromptSep achieves state-of-the-art performance in sound removal and vocal-imitation-guided source separation, while maintaining competitive results on language-queried source separation.
The Rhythm In Anything: Audio-Prompted Drums Generation with Masked Language Modeling
Sep 19, 2025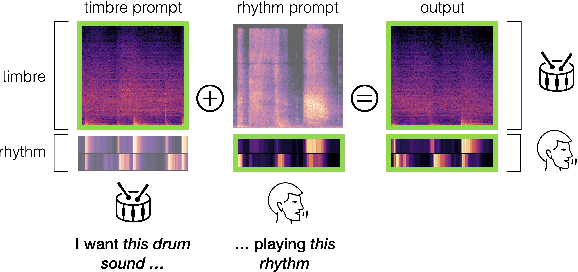
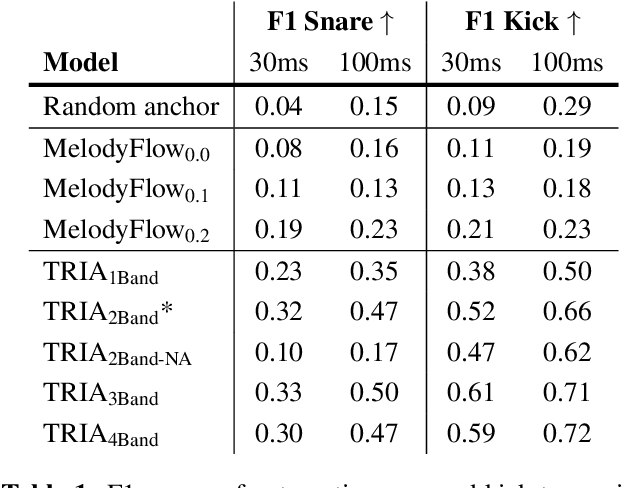
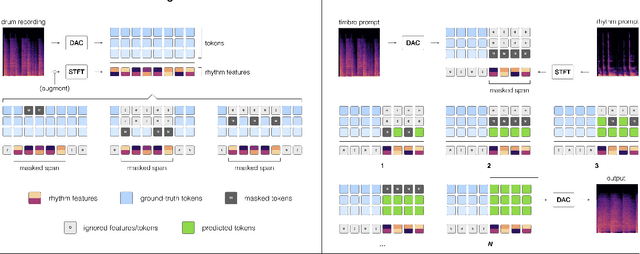
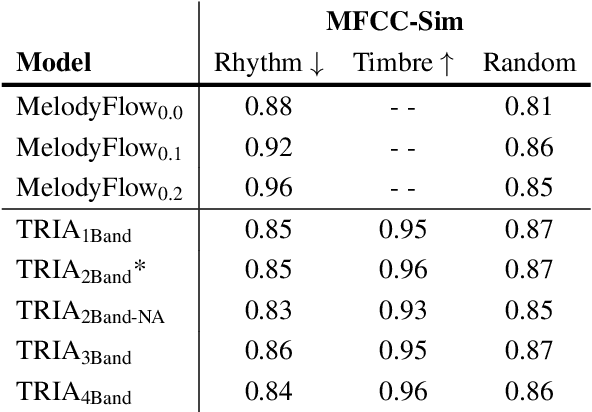
Abstract:Musicians and nonmusicians alike use rhythmic sound gestures, such as tapping and beatboxing, to express drum patterns. While these gestures effectively communicate musical ideas, realizing these ideas as fully-produced drum recordings can be time-consuming, potentially disrupting many creative workflows. To bridge this gap, we present TRIA (The Rhythm In Anything), a masked transformer model for mapping rhythmic sound gestures to high-fidelity drum recordings. Given an audio prompt of the desired rhythmic pattern and a second prompt to represent drumkit timbre, TRIA produces audio of a drumkit playing the desired rhythm (with appropriate elaborations) in the desired timbre. Subjective and objective evaluations show that a TRIA model trained on less than 10 hours of publicly-available drum data can generate high-quality, faithful realizations of sound gestures across a wide range of timbres in a zero-shot manner.
FLAM: Frame-Wise Language-Audio Modeling
May 08, 2025Abstract:Recent multi-modal audio-language models (ALMs) excel at text-audio retrieval but struggle with frame-wise audio understanding. Prior works use temporal-aware labels or unsupervised training to improve frame-wise capabilities, but they still lack fine-grained labeling capability to pinpoint when an event occurs. While traditional sound event detection models can precisely localize events, they are limited to pre-defined categories, making them ineffective for real-world scenarios with out-of-distribution events. In this work, we introduce FLAM, an open-vocabulary contrastive audio-language model capable of localizing specific sound events. FLAM employs a memory-efficient and calibrated frame-wise objective with logit adjustment to address spurious correlations, such as event dependencies and label imbalances during training. To enable frame-wise supervision, we leverage a large-scale dataset with diverse audio events, LLM-generated captions and simulation. Experimental results and case studies demonstrate that FLAM significantly improves the open-vocabulary localization capability while maintaining strong performance in global retrieval and downstream tasks.
SILA: Signal-to-Language Augmentation for Enhanced Control in Text-to-Audio Generation
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:The field of text-to-audio generation has seen significant advancements, and yet the ability to finely control the acoustic characteristics of generated audio remains under-explored. In this paper, we introduce a novel yet simple approach to generate sound effects with control over key acoustic parameters such as loudness, pitch, reverb, fade, brightness, noise and duration, enabling creative applications in sound design and content creation. These parameters extend beyond traditional Digital Signal Processing (DSP) techniques, incorporating learned representations that capture the subtleties of how sound characteristics can be shaped in context, enabling a richer and more nuanced control over the generated audio. Our approach is model-agnostic and is based on learning the disentanglement between audio semantics and its acoustic features. Our approach not only enhances the versatility and expressiveness of text-to-audio generation but also opens new avenues for creative audio production and sound design. Our objective and subjective evaluation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in producing high-quality, customizable audio outputs that align closely with user specifications.
Sketch2Sound: Controllable Audio Generation via Time-Varying Signals and Sonic Imitations
Dec 11, 2024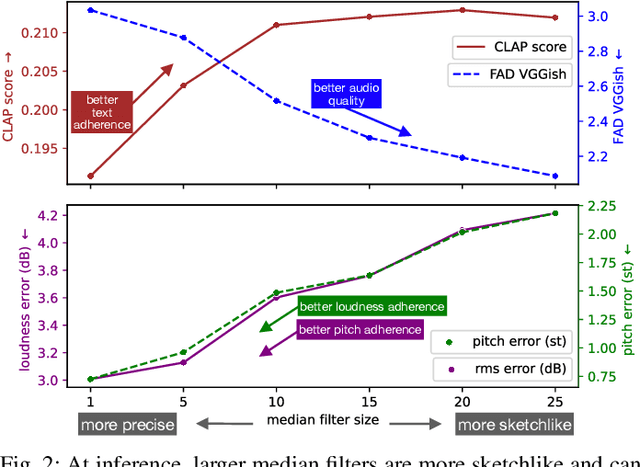
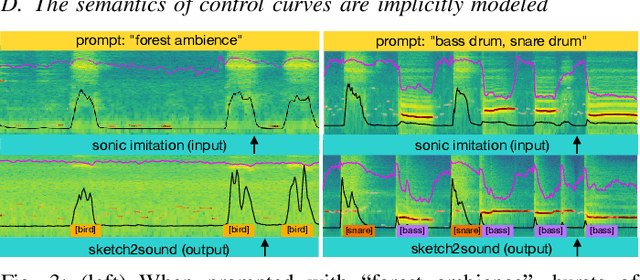
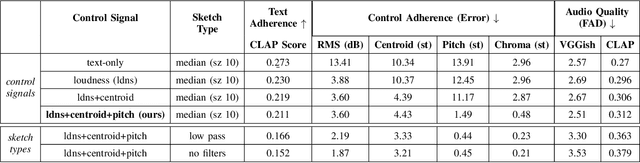
Abstract:We present Sketch2Sound, a generative audio model capable of creating high-quality sounds from a set of interpretable time-varying control signals: loudness, brightness, and pitch, as well as text prompts. Sketch2Sound can synthesize arbitrary sounds from sonic imitations (i.e.,~a vocal imitation or a reference sound-shape). Sketch2Sound can be implemented on top of any text-to-audio latent diffusion transformer (DiT), and requires only 40k steps of fine-tuning and a single linear layer per control, making it more lightweight than existing methods like ControlNet. To synthesize from sketchlike sonic imitations, we propose applying random median filters to the control signals during training, allowing Sketch2Sound to be prompted using controls with flexible levels of temporal specificity. We show that Sketch2Sound can synthesize sounds that follow the gist of input controls from a vocal imitation while retaining the adherence to an input text prompt and audio quality compared to a text-only baseline. Sketch2Sound allows sound artists to create sounds with the semantic flexibility of text prompts and the expressivity and precision of a sonic gesture or vocal imitation. Sound examples are available at https://hugofloresgarcia.art/sketch2sound/.
Video-Guided Foley Sound Generation with Multimodal Controls
Nov 26, 2024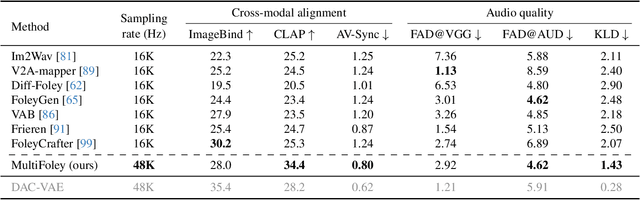
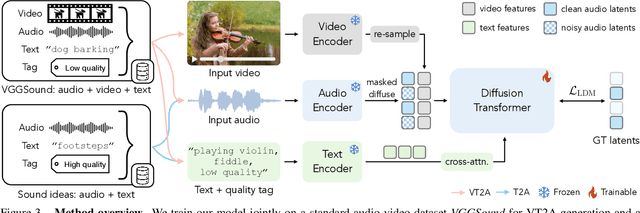
Abstract:Generating sound effects for videos often requires creating artistic sound effects that diverge significantly from real-life sources and flexible control in the sound design. To address this problem, we introduce MultiFoley, a model designed for video-guided sound generation that supports multimodal conditioning through text, audio, and video. Given a silent video and a text prompt, MultiFoley allows users to create clean sounds (e.g., skateboard wheels spinning without wind noise) or more whimsical sounds (e.g., making a lion's roar sound like a cat's meow). MultiFoley also allows users to choose reference audio from sound effects (SFX) libraries or partial videos for conditioning. A key novelty of our model lies in its joint training on both internet video datasets with low-quality audio and professional SFX recordings, enabling high-quality, full-bandwidth (48kHz) audio generation. Through automated evaluations and human studies, we demonstrate that MultiFoley successfully generates synchronized high-quality sounds across varied conditional inputs and outperforms existing methods. Please see our project page for video results: https://ificl.github.io/MultiFoley/
Code Drift: Towards Idempotent Neural Audio Codecs
Oct 14, 2024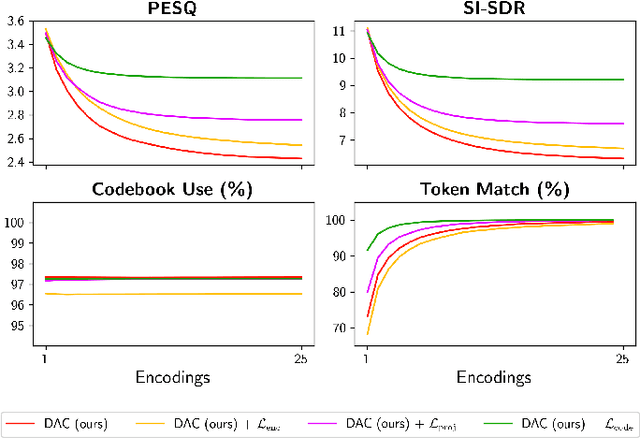
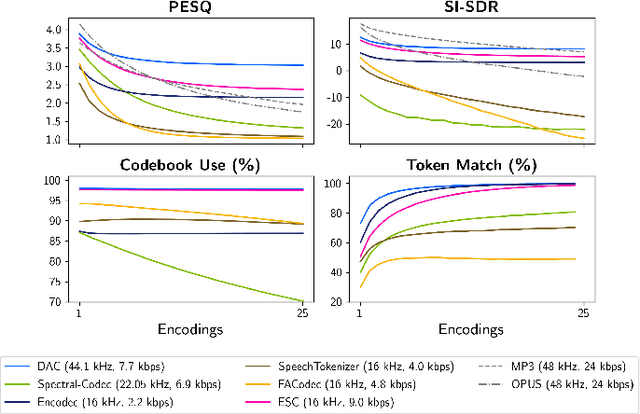
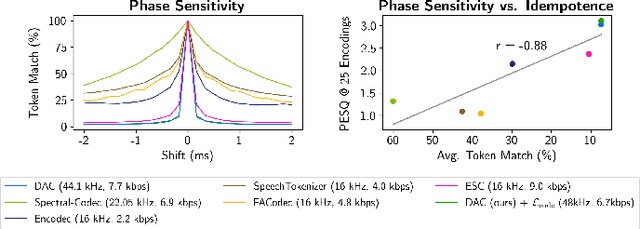
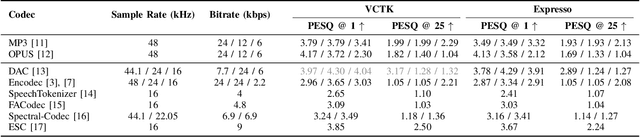
Abstract:Neural codecs have demonstrated strong performance in high-fidelity compression of audio signals at low bitrates. The token-based representations produced by these codecs have proven particularly useful for generative modeling. While much research has focused on improvements in compression ratio and perceptual transparency, recent works have largely overlooked another desirable codec property -- idempotence, the stability of compressed outputs under multiple rounds of encoding. We find that state-of-the-art neural codecs exhibit varied degrees of idempotence, with some degrading audio outputs significantly after as few as three encodings. We investigate possible causes of low idempotence and devise a method for improving idempotence through fine-tuning a codec model. We then examine the effect of idempotence on a simple conditional generative modeling task, and find that increased idempotence can be achieved without negatively impacting downstream modeling performance -- potentially extending the usefulness of neural codecs for practical file compression and iterative generative modeling workflows.
VampNet: Music Generation via Masked Acoustic Token Modeling
Jul 12, 2023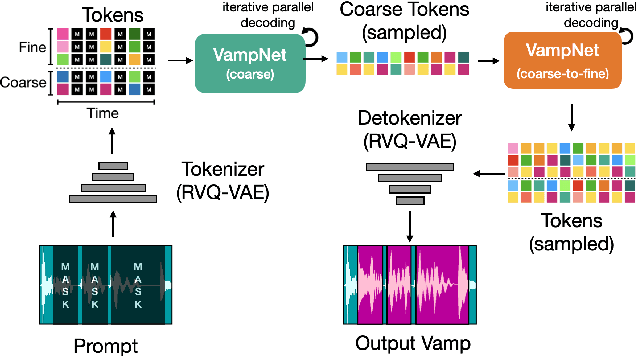
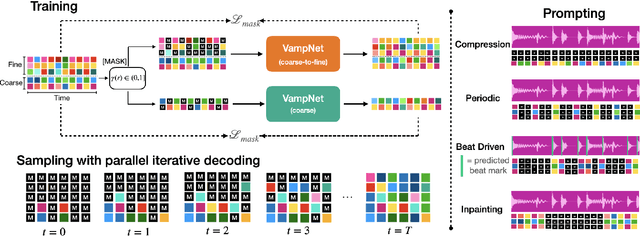
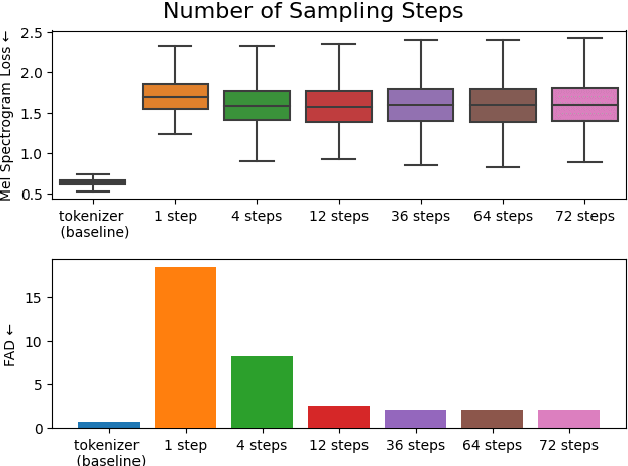
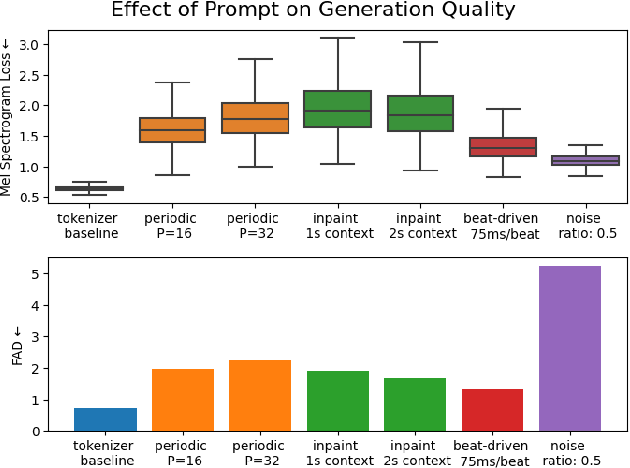
Abstract:We introduce VampNet, a masked acoustic token modeling approach to music synthesis, compression, inpainting, and variation. We use a variable masking schedule during training which allows us to sample coherent music from the model by applying a variety of masking approaches (called prompts) during inference. VampNet is non-autoregressive, leveraging a bidirectional transformer architecture that attends to all tokens in a forward pass. With just 36 sampling passes, VampNet can generate coherent high-fidelity musical waveforms. We show that by prompting VampNet in various ways, we can apply it to tasks like music compression, inpainting, outpainting, continuation, and looping with variation (vamping). Appropriately prompted, VampNet is capable of maintaining style, genre, instrumentation, and other high-level aspects of the music. This flexible prompting capability makes VampNet a powerful music co-creation tool. Code and audio samples are available online.
High-Fidelity Audio Compression with Improved RVQGAN
Jun 11, 2023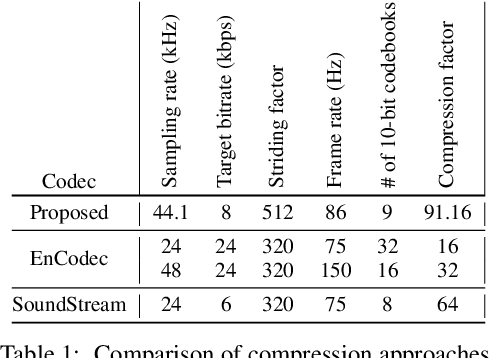
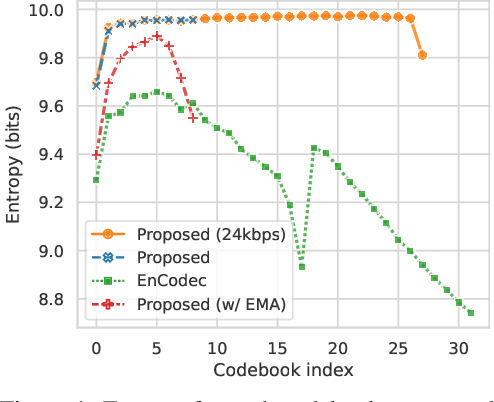
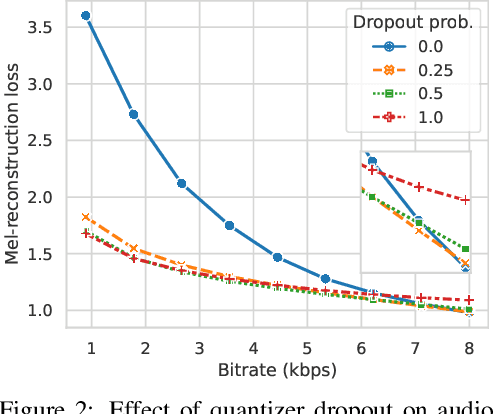
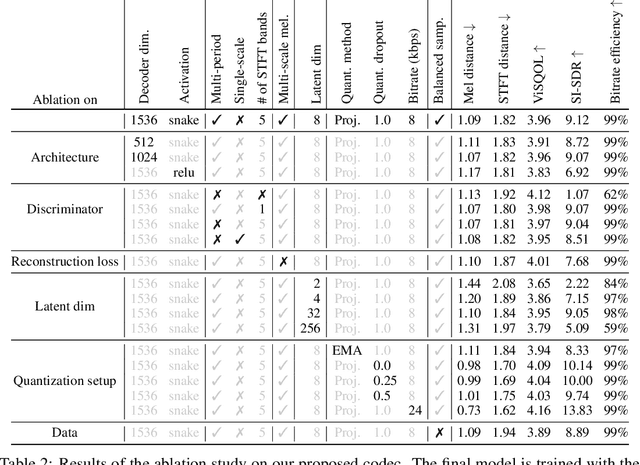
Abstract:Language models have been successfully used to model natural signals, such as images, speech, and music. A key component of these models is a high quality neural compression model that can compress high-dimensional natural signals into lower dimensional discrete tokens. To that end, we introduce a high-fidelity universal neural audio compression algorithm that achieves ~90x compression of 44.1 KHz audio into tokens at just 8kbps bandwidth. We achieve this by combining advances in high-fidelity audio generation with better vector quantization techniques from the image domain, along with improved adversarial and reconstruction losses. We compress all domains (speech, environment, music, etc.) with a single universal model, making it widely applicable to generative modeling of all audio. We compare with competing audio compression algorithms, and find our method outperforms them significantly. We provide thorough ablations for every design choice, as well as open-source code and trained model weights. We hope our work can lay the foundation for the next generation of high-fidelity audio modeling.
Music Separation Enhancement with Generative Modeling
Aug 26, 2022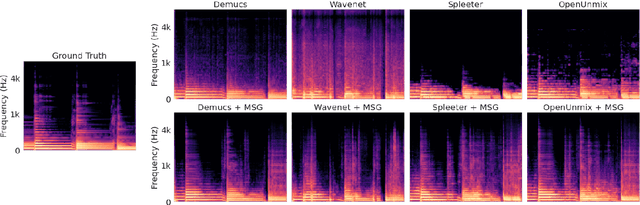
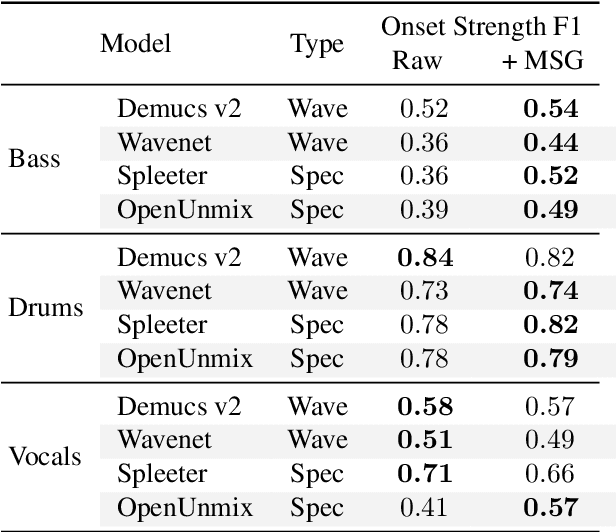
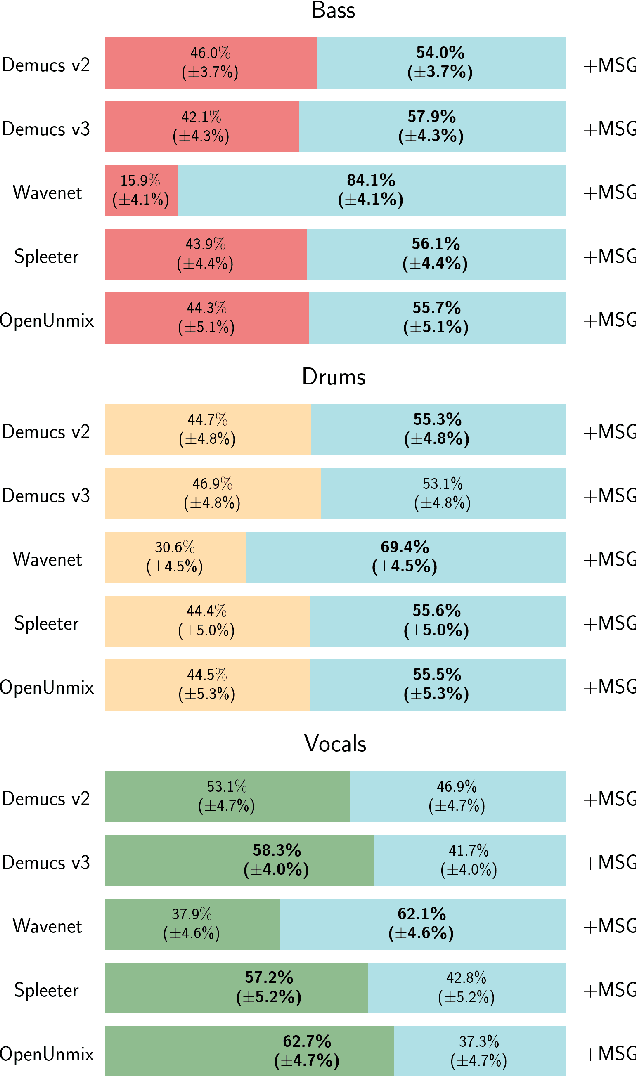
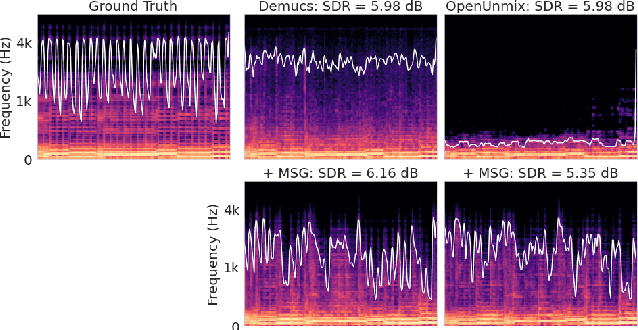
Abstract:Despite phenomenal progress in recent years, state-of-the-art music separation systems produce source estimates with significant perceptual shortcomings, such as adding extraneous noise or removing harmonics. We propose a post-processing model (the Make it Sound Good (MSG) post-processor) to enhance the output of music source separation systems. We apply our post-processing model to state-of-the-art waveform-based and spectrogram-based music source separators, including a separator unseen by MSG during training. Our analysis of the errors produced by source separators shows that waveform models tend to introduce more high-frequency noise, while spectrogram models tend to lose transients and high frequency content. We introduce objective measures to quantify both kinds of errors and show MSG improves the source reconstruction of both kinds of errors. Crowdsourced subjective evaluations demonstrate that human listeners prefer source estimates of bass and drums that have been post-processed by MSG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge