Hugo Flores Garcia
HARP 2.0: Expanding Hosted, Asynchronous, Remote Processing for Deep Learning in the DAW
Mar 04, 2025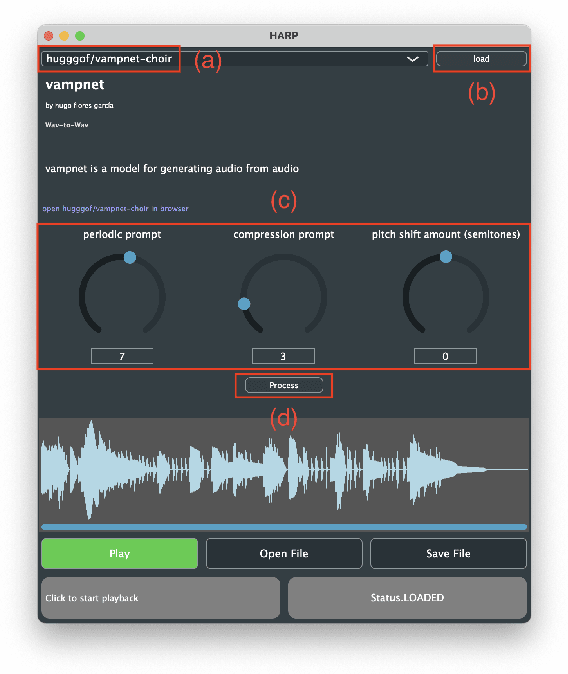
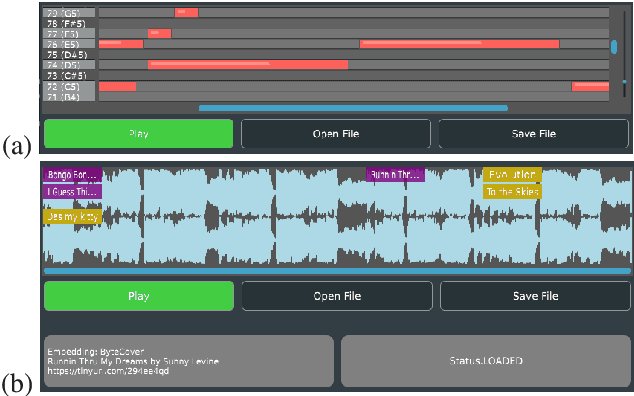
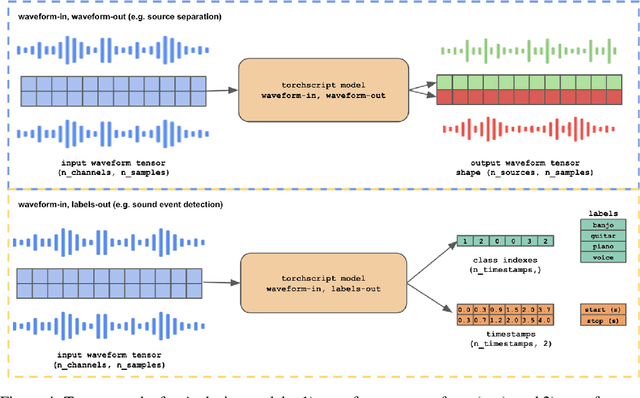
Abstract:HARP 2.0 brings deep learning models to digital audio workstation (DAW) software through hosted, asynchronous, remote processing, allowing users to route audio from a plug-in interface through any compatible Gradio endpoint to perform arbitrary transformations. HARP renders endpoint-defined controls and processed audio in-plugin, meaning users can explore a variety of cutting-edge deep learning models without ever leaving the DAW. In the 2.0 release we introduce support for MIDI-based models and audio/MIDI labeling models, provide a streamlined pyharp Python API for model developers, and implement numerous interface and stability improvements. Through this work, we hope to bridge the gap between model developers and creatives, improving access to deep learning models by seamlessly integrating them into DAW workflows.
Exploring Musical Roots: Applying Audio Embeddings to Empower Influence Attribution for a Generative Music Model
Jan 25, 2024



Abstract:Every artist has a creative process that draws inspiration from previous artists and their works. Today, "inspiration" has been automated by generative music models. The black box nature of these models obscures the identity of the works that influence their creative output. As a result, users may inadvertently appropriate, misuse, or copy existing artists' works. We establish a replicable methodology to systematically identify similar pieces of music audio in a manner that is useful for understanding training data attribution. A key aspect of our approach is to harness an effective music audio similarity measure. We compare the effect of applying CLMR and CLAP embeddings to similarity measurement in a set of 5 million audio clips used to train VampNet, a recent open source generative music model. We validate this approach with a human listening study. We also explore the effect that modifications of an audio example (e.g., pitch shifting, time stretching, background noise) have on similarity measurements. This work is foundational to incorporating automated influence attribution into generative modeling, which promises to let model creators and users move from ignorant appropriation to informed creation. Audio samples that accompany this paper are available at https://tinyurl.com/exploring-musical-roots.
VampNet: Music Generation via Masked Acoustic Token Modeling
Jul 12, 2023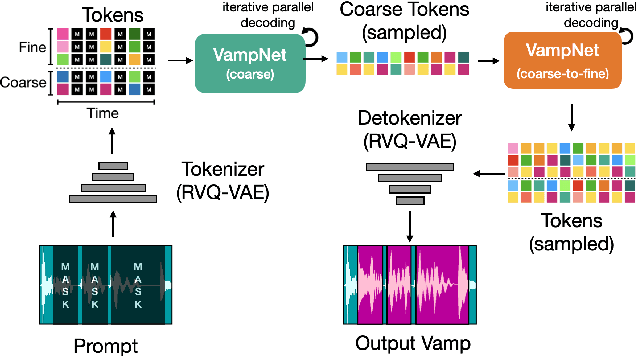
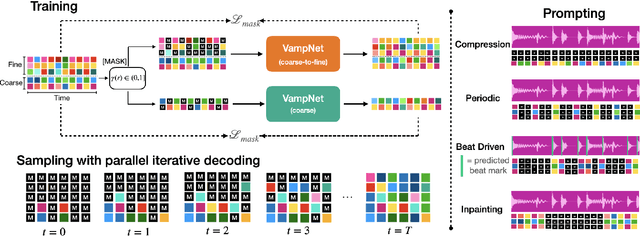
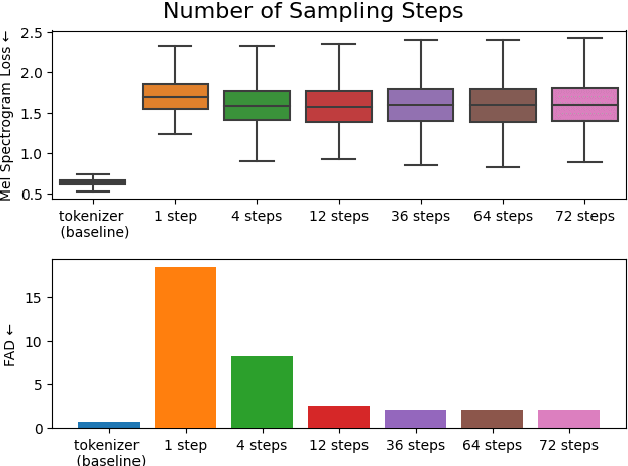
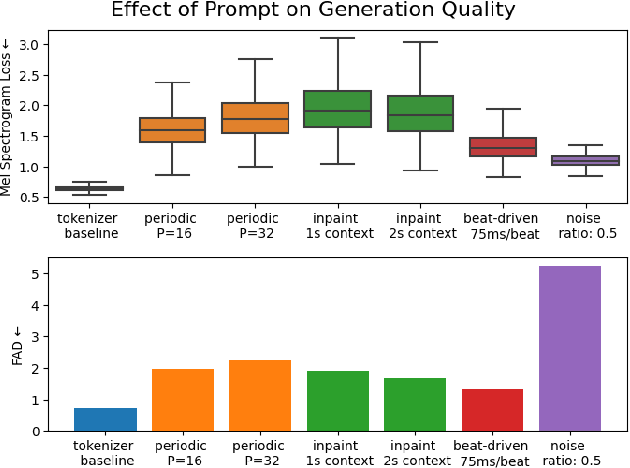
Abstract:We introduce VampNet, a masked acoustic token modeling approach to music synthesis, compression, inpainting, and variation. We use a variable masking schedule during training which allows us to sample coherent music from the model by applying a variety of masking approaches (called prompts) during inference. VampNet is non-autoregressive, leveraging a bidirectional transformer architecture that attends to all tokens in a forward pass. With just 36 sampling passes, VampNet can generate coherent high-fidelity musical waveforms. We show that by prompting VampNet in various ways, we can apply it to tasks like music compression, inpainting, outpainting, continuation, and looping with variation (vamping). Appropriately prompted, VampNet is capable of maintaining style, genre, instrumentation, and other high-level aspects of the music. This flexible prompting capability makes VampNet a powerful music co-creation tool. Code and audio samples are available online.
Deep Learning Tools for Audacity: Helping Researchers Expand the Artist's Toolkit
Oct 28, 2021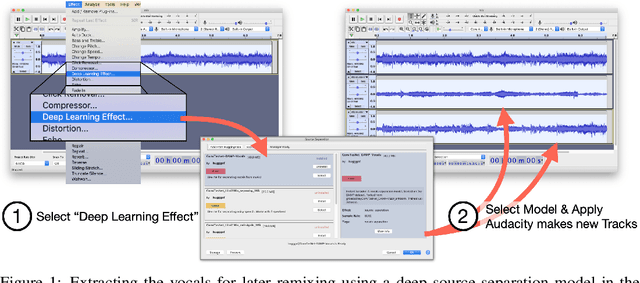
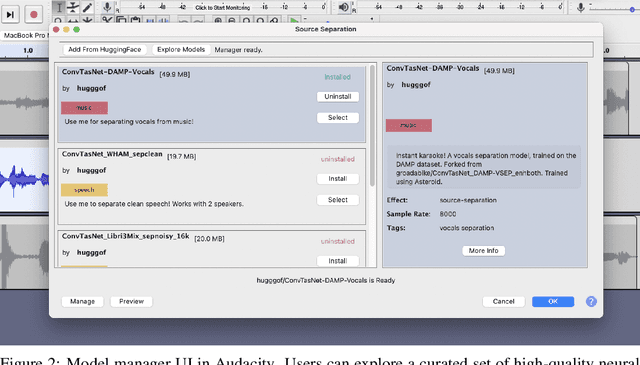
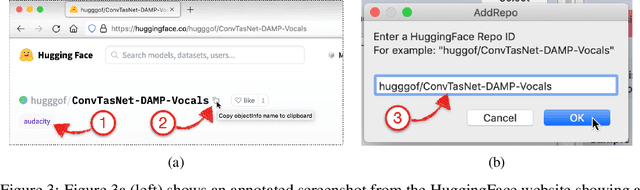
Abstract:We present a software framework that integrates neural networks into the popular open-source audio editing software, Audacity, with a minimal amount of developer effort. In this paper, we showcase some example use cases for both end-users and neural network developers. We hope that this work fosters a new level of interactivity between deep learning practitioners and end-users.
Leveraging Hierarchical Structures for Few-Shot Musical Instrument Recognition
Jul 29, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning work on musical instrument recognition has generally focused on instrument classes for which we have abundant data. In this work, we exploit hierarchical relationships between instruments in a few-shot learning setup to enable classification of a wider set of musical instruments, given a few examples at inference. We apply a hierarchical loss function to the training of prototypical networks, combined with a method to aggregate prototypes hierarchically, mirroring the structure of a predefined musical instrument hierarchy. These extensions require no changes to the network architecture and new levels can be easily added or removed. Compared to a non-hierarchical few-shot baseline, our method leads to a significant increase in classification accuracy and significant decrease mistake severity on instrument classes unseen in training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge