Polina Kirichenko
What's in Common? Multimodal Models Hallucinate When Reasoning Across Scenes
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:Multimodal language models possess a remarkable ability to handle an open-vocabulary's worth of objects. Yet the best models still suffer from hallucinations when reasoning about scenes in the real world, revealing a gap between their seemingly strong performance on existing perception benchmarks that are saturating and their reasoning in the real world. To address this gap, we build a novel benchmark of in-the-wild scenes that we call Common-O. With more than 10.5k examples using exclusively new images not found in web training data to avoid contamination, Common-O goes beyond just perception, inspired by cognitive tests for humans, to probe reasoning across scenes by asking "what's in common?". We evaluate leading multimodal language models, including models specifically trained to perform chain-of-thought reasoning. We find that perceiving objects in single images is tractable for most models, yet reasoning across scenes is very challenging even for the best models, including reasoning models. Despite saturating many leaderboards focusing on perception, the best performing model only achieves 35% on Common-O -- and on Common-O Complex, consisting of more complex scenes, the best model achieves only 1%. Curiously, we find models are more prone to hallucinate when similar objects are present in the scene, suggesting models may be relying on object co-occurrence seen during training. Among the models we evaluated, we found scale can provide modest improvements while models explicitly trained with multi-image inputs show bigger improvements, suggesting scaled multi-image training may offer promise. We make our benchmark publicly available to spur research into the challenge of hallucination when reasoning across scenes.
The Impact of Coreset Selection on Spurious Correlations and Group Robustness
Jul 15, 2025
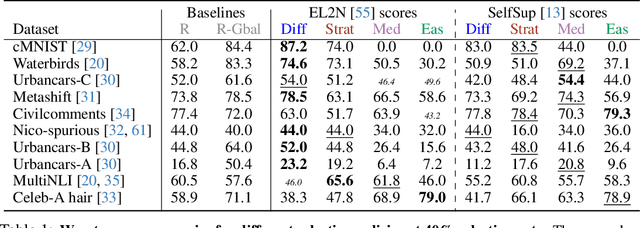

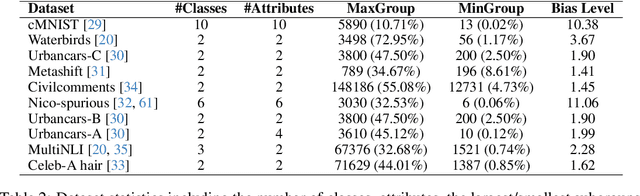
Abstract:Coreset selection methods have shown promise in reducing the training data size while maintaining model performance for data-efficient machine learning. However, as many datasets suffer from biases that cause models to learn spurious correlations instead of causal features, it is important to understand whether and how dataset reduction methods may perpetuate, amplify, or mitigate these biases. In this work, we conduct the first comprehensive analysis of the implications of data selection on the spurious bias levels of the selected coresets and the robustness of downstream models trained on them. We use an extensive experimental setting spanning ten different spurious correlations benchmarks, five score metrics to characterize sample importance/ difficulty, and five data selection policies across a broad range of coreset sizes. Thereby, we unravel a series of nontrivial nuances in interactions between sample difficulty and bias alignment, as well as dataset bias and resultant model robustness. For example, we find that selecting coresets using embedding-based sample characterization scores runs a comparatively lower risk of inadvertently exacerbating bias than selecting using characterizations based on learning dynamics. Most importantly, our analysis reveals that although some coreset selection methods could achieve lower bias levels by prioritizing difficult samples, they do not reliably guarantee downstream robustness.
Out-of-Distribution Detection Methods Answer the Wrong Questions
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:To detect distribution shifts and improve model safety, many out-of-distribution (OOD) detection methods rely on the predictive uncertainty or features of supervised models trained on in-distribution data. In this paper, we critically re-examine this popular family of OOD detection procedures, and we argue that these methods are fundamentally answering the wrong questions for OOD detection. There is no simple fix to this misalignment, since a classifier trained only on in-distribution classes cannot be expected to identify OOD points; for instance, a cat-dog classifier may confidently misclassify an airplane if it contains features that distinguish cats from dogs, despite generally appearing nothing alike. We find that uncertainty-based methods incorrectly conflate high uncertainty with being OOD, while feature-based methods incorrectly conflate far feature-space distance with being OOD. We show how these pathologies manifest as irreducible errors in OOD detection and identify common settings where these methods are ineffective. Additionally, interventions to improve OOD detection such as feature-logit hybrid methods, scaling of model and data size, epistemic uncertainty representation, and outlier exposure also fail to address this fundamental misalignment in objectives. We additionally consider unsupervised density estimation and generative models for OOD detection, which we show have their own fundamental limitations.
AbstentionBench: Reasoning LLMs Fail on Unanswerable Questions
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:For Large Language Models (LLMs) to be reliably deployed in both everyday and high-stakes domains, knowing when not to answer is equally critical as answering correctly. Real-world user queries, which can be underspecified, ill-posed, or fundamentally unanswerable, require LLMs to reason about uncertainty and selectively abstain -- i.e., refuse to answer definitively. However, abstention remains understudied, without a systematic evaluation framework for modern LLMs. In this work, we introduce AbstentionBench, a large-scale benchmark for holistically evaluating abstention across 20 diverse datasets, including questions with unknown answers, underspecification, false premises, subjective interpretations, and outdated information. Evaluating 20 frontier LLMs reveals abstention is an unsolved problem, and one where scaling models is of little use. While recent reasoning LLMs have shown impressive results in complex problem solving, surprisingly, we find that reasoning fine-tuning degrades abstention (by $24\%$ on average), even for math and science domains on which reasoning models are explicitly trained. We find that while a carefully crafted system prompt can boost abstention in practice, it does not resolve models' fundamental inability to reason about uncertainty. We release AbstentionBench to foster research into advancing LLM reliability.
COMPACT: COMPositional Atomic-to-Complex Visual Capability Tuning
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at simple vision-language tasks but struggle when faced with complex tasks that require multiple capabilities, such as simultaneously recognizing objects, counting them, and understanding their spatial relationships. This might be partially the result of the fact that Visual Instruction Tuning (VIT), a critical training step for MLLMs, has traditionally focused on scaling data volume, but not the compositional complexity of training examples. We propose COMPACT (COMPositional Atomic-to-complex visual Capability Tuning), which generates a training dataset explicitly controlling for the compositional complexity of the training examples. The data from COMPACT allows MLLMs to train on combinations of atomic capabilities to learn complex capabilities more efficiently. Across all benchmarks, COMPACT achieves comparable performance to the LLaVA-665k VIT while using less than 10% of its data budget, and even outperforms it on several, especially those involving complex multi-capability tasks. For example, COMPACT achieves substantial 83.3% improvement on MMStar and 94.0% improvement on MM-Vet compared to the full-scale VIT on particularly complex questions that require four or more atomic capabilities. COMPACT offers a scalable, data-efficient, visual compositional tuning recipe to improve on complex visual-language tasks.
Decomposed evaluations of geographic disparities in text-to-image models
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Recent work has identified substantial disparities in generated images of different geographic regions, including stereotypical depictions of everyday objects like houses and cars. However, existing measures for these disparities have been limited to either human evaluations, which are time-consuming and costly, or automatic metrics evaluating full images, which are unable to attribute these disparities to specific parts of the generated images. In this work, we introduce a new set of metrics, Decomposed Indicators of Disparities in Image Generation (Decomposed-DIG), that allows us to separately measure geographic disparities in the depiction of objects and backgrounds in generated images. Using Decomposed-DIG, we audit a widely used latent diffusion model and find that generated images depict objects with better realism than backgrounds and that backgrounds in generated images tend to contain larger regional disparities than objects. We use Decomposed-DIG to pinpoint specific examples of disparities, such as stereotypical background generation in Africa, struggling to generate modern vehicles in Africa, and unrealistically placing some objects in outdoor settings. Informed by our metric, we use a new prompting structure that enables a 52% worst-region improvement and a 20% average improvement in generated background diversity.
Modeling Caption Diversity in Contrastive Vision-Language Pretraining
Apr 30, 2024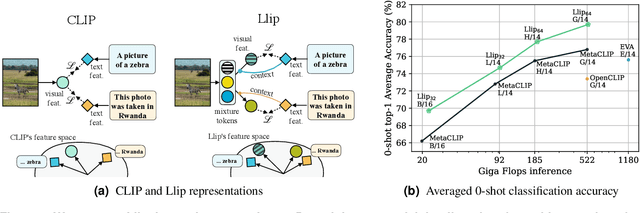
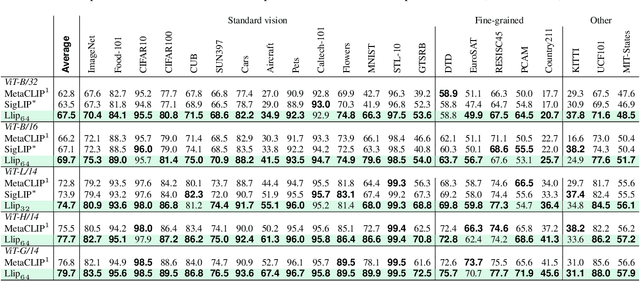
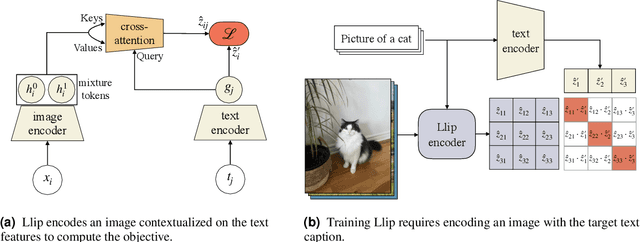
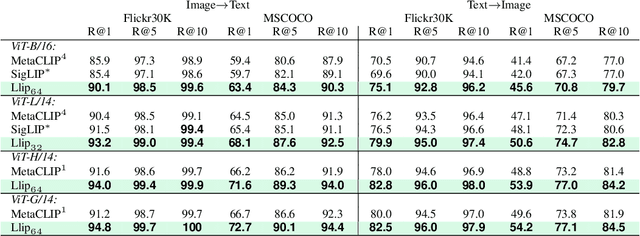
Abstract:There are a thousand ways to caption an image. Contrastive Language Pretraining (CLIP) on the other hand, works by mapping an image and its caption to a single vector -- limiting how well CLIP-like models can represent the diverse ways to describe an image. In this work, we introduce Llip, Latent Language Image Pretraining, which models the diversity of captions that could match an image. Llip's vision encoder outputs a set of visual features that are mixed into a final representation by conditioning on information derived from the text. We show that Llip outperforms non-contextualized baselines like CLIP and SigLIP on a variety of tasks even with large-scale encoders. Llip improves zero-shot classification by an average of 2.9% zero-shot classification benchmarks with a ViT-G/14 encoder. Specifically, Llip attains a zero-shot top-1 accuracy of 83.5% on ImageNet outperforming a similarly sized CLIP by 1.4%. We also demonstrate improvement on zero-shot retrieval on MS-COCO by 6.0%. We provide a comprehensive analysis of the components introduced by the method and demonstrate that Llip leads to richer visual representations.
Does Progress On Object Recognition Benchmarks Improve Real-World Generalization?
Jul 24, 2023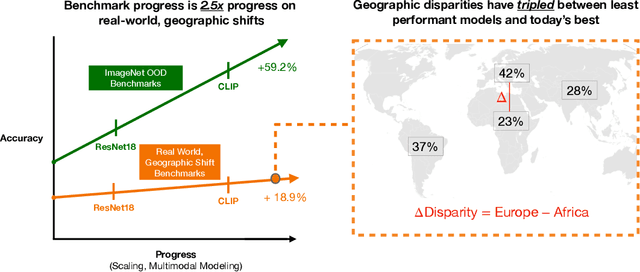
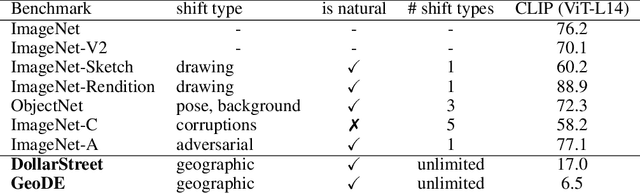
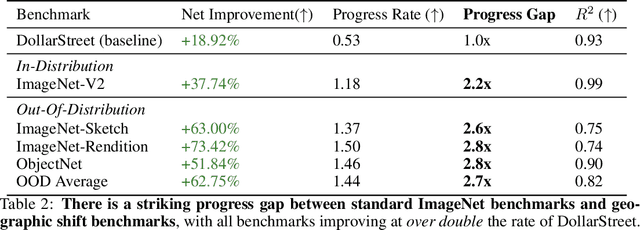
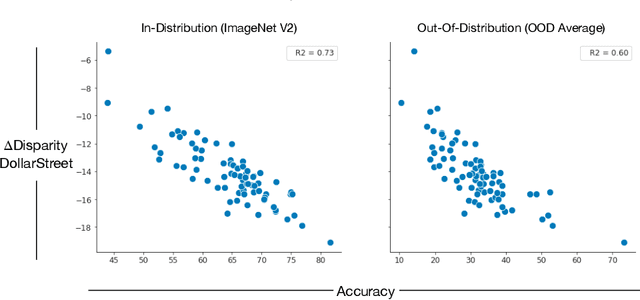
Abstract:For more than a decade, researchers have measured progress in object recognition on ImageNet-based generalization benchmarks such as ImageNet-A, -C, and -R. Recent advances in foundation models, trained on orders of magnitude more data, have begun to saturate these standard benchmarks, but remain brittle in practice. This suggests standard benchmarks, which tend to focus on predefined or synthetic changes, may not be sufficient for measuring real world generalization. Consequently, we propose studying generalization across geography as a more realistic measure of progress using two datasets of objects from households across the globe. We conduct an extensive empirical evaluation of progress across nearly 100 vision models up to most recent foundation models. We first identify a progress gap between standard benchmarks and real-world, geographical shifts: progress on ImageNet results in up to 2.5x more progress on standard generalization benchmarks than real-world distribution shifts. Second, we study model generalization across geographies by measuring the disparities in performance across regions, a more fine-grained measure of real world generalization. We observe all models have large geographic disparities, even foundation CLIP models, with differences of 7-20% in accuracy between regions. Counter to modern intuition, we discover progress on standard benchmarks fails to improve geographic disparities and often exacerbates them: geographic disparities between the least performant models and today's best models have more than tripled. Our results suggest scaling alone is insufficient for consistent robustness to real-world distribution shifts. Finally, we highlight in early experiments how simple last layer retraining on more representative, curated data can complement scaling as a promising direction of future work, reducing geographic disparity on both benchmarks by over two-thirds.
Chroma-VAE: Mitigating Shortcut Learning with Generative Classifiers
Nov 28, 2022



Abstract:Deep neural networks are susceptible to shortcut learning, using simple features to achieve low training loss without discovering essential semantic structure. Contrary to prior belief, we show that generative models alone are not sufficient to prevent shortcut learning, despite an incentive to recover a more comprehensive representation of the data than discriminative approaches. However, we observe that shortcuts are preferentially encoded with minimal information, a fact that generative models can exploit to mitigate shortcut learning. In particular, we propose Chroma-VAE, a two-pronged approach where a VAE classifier is initially trained to isolate the shortcut in a small latent subspace, allowing a secondary classifier to be trained on the complementary, shortcut-free latent subspace. In addition to demonstrating the efficacy of Chroma-VAE on benchmark and real-world shortcut learning tasks, our work highlights the potential for manipulating the latent space of generative classifiers to isolate or interpret specific correlations.
On Feature Learning in the Presence of Spurious Correlations
Oct 20, 2022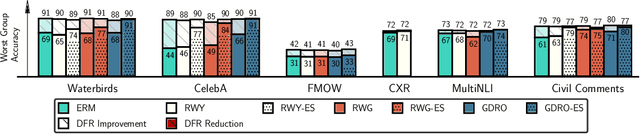
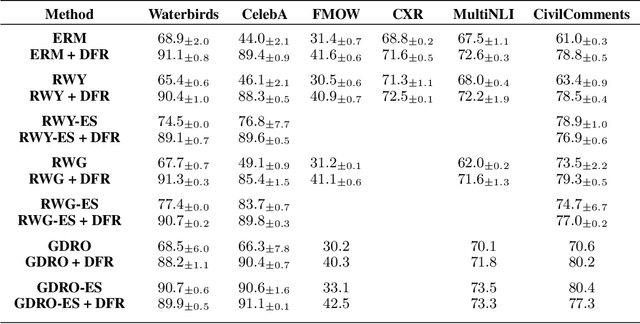
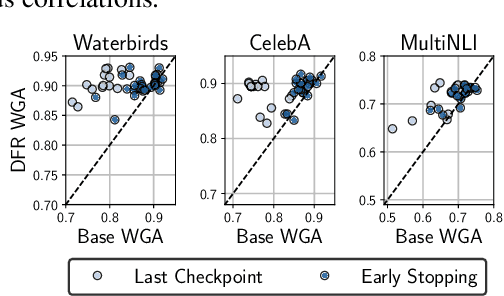
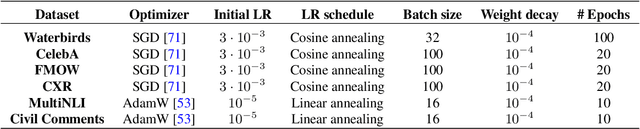
Abstract:Deep classifiers are known to rely on spurious features $\unicode{x2013}$ patterns which are correlated with the target on the training data but not inherently relevant to the learning problem, such as the image backgrounds when classifying the foregrounds. In this paper we evaluate the amount of information about the core (non-spurious) features that can be decoded from the representations learned by standard empirical risk minimization (ERM) and specialized group robustness training. Following recent work on Deep Feature Reweighting (DFR), we evaluate the feature representations by re-training the last layer of the model on a held-out set where the spurious correlation is broken. On multiple vision and NLP problems, we show that the features learned by simple ERM are highly competitive with the features learned by specialized group robustness methods targeted at reducing the effect of spurious correlations. Moreover, we show that the quality of learned feature representations is greatly affected by the design decisions beyond the training method, such as the model architecture and pre-training strategy. On the other hand, we find that strong regularization is not necessary for learning high quality feature representations. Finally, using insights from our analysis, we significantly improve upon the best results reported in the literature on the popular Waterbirds, CelebA hair color prediction and WILDS-FMOW problems, achieving 97%, 92% and 50% worst-group accuracies, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge