Melissa Hall
Inference-time Physics Alignment of Video Generative Models with Latent World Models
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:State-of-the-art video generative models produce promising visual content yet often violate basic physics principles, limiting their utility. While some attribute this deficiency to insufficient physics understanding from pre-training, we find that the shortfall in physics plausibility also stems from suboptimal inference strategies. We therefore introduce WMReward and treat improving physics plausibility of video generation as an inference-time alignment problem. In particular, we leverage the strong physics prior of a latent world model (here, VJEPA-2) as a reward to search and steer multiple candidate denoising trajectories, enabling scaling test-time compute for better generation performance. Empirically, our approach substantially improves physics plausibility across image-conditioned, multiframe-conditioned, and text-conditioned generation settings, with validation from human preference study. Notably, in the ICCV 2025 Perception Test PhysicsIQ Challenge, we achieve a final score of 62.64%, winning first place and outperforming the previous state of the art by 7.42%. Our work demonstrates the viability of using latent world models to improve physics plausibility of video generation, beyond this specific instantiation or parameterization.
Multimodal RewardBench 2: Evaluating Omni Reward Models for Interleaved Text and Image
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Reward models (RMs) are essential for training large language models (LLMs), but remain underexplored for omni models that handle interleaved image and text sequences. We introduce Multimodal RewardBench 2 (MMRB2), the first comprehensive benchmark for reward models on multimodal understanding and (interleaved) generation. MMRB2 spans four tasks: text-to-image, image editing, interleaved generation, and multimodal reasoning ("thinking-with-images"), providing 1,000 expert-annotated preference pairs per task from 23 models and agents across 21 source tasks. MMRB2 is designed with: (1) practical but challenging prompts; (2) responses from state-of-the-art models and agents; and (3) preference pairs with strong human-expert consensus, curated via an ensemble filtering strategy. Using MMRB2, we study existing judges for each subtask, including multimodal LLM-as-a-judge and models trained with human preferences. The latest Gemini 3 Pro attains 75-80% accuracy. GPT-5 and Gemini 2.5 Pro reach 66-75% accuracy, compared to >90% for humans, yet surpass the widely used GPT-4o (59%). The best performing open-source model Qwen3-VL-32B achieves similar accuracies as Gemini 2.5 Flash (64%). We also show that MMRB2 performance strongly correlates with downstream task success using Best-of-N sampling and conduct an in-depth analysis that shows key areas to improve the reward models going forward.
DIMCIM: A Quantitative Evaluation Framework for Default-mode Diversity and Generalization in Text-to-Image Generative Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-image (T2I) models have achieved impressive quality and consistency. However, this has come at the cost of representation diversity. While automatic evaluation methods exist for benchmarking model diversity, they either require reference image datasets or lack specificity about the kind of diversity measured, limiting their adaptability and interpretability. To address this gap, we introduce the Does-it/Can-it framework, DIM-CIM, a reference-free measurement of default-mode diversity ("Does" the model generate images with expected attributes?) and generalization capacity ("Can" the model generate diverse attributes for a particular concept?). We construct the COCO-DIMCIM benchmark, which is seeded with COCO concepts and captions and augmented by a large language model. With COCO-DIMCIM, we find that widely-used models improve in generalization at the cost of default-mode diversity when scaling from 1.5B to 8.1B parameters. DIMCIM also identifies fine-grained failure cases, such as attributes that are generated with generic prompts but are rarely generated when explicitly requested. Finally, we use DIMCIM to evaluate the training data of a T2I model and observe a correlation of 0.85 between diversity in training images and default-mode diversity. Our work provides a flexible and interpretable framework for assessing T2I model diversity and generalization, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of model performance.
Multi-Modal Language Models as Text-to-Image Model Evaluators
May 01, 2025Abstract:The steady improvements of text-to-image (T2I) generative models lead to slow deprecation of automatic evaluation benchmarks that rely on static datasets, motivating researchers to seek alternative ways to evaluate the T2I progress. In this paper, we explore the potential of multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) as evaluator agents that interact with a T2I model, with the objective of assessing prompt-generation consistency and image aesthetics. We present Multimodal Text-to-Image Eval (MT2IE), an evaluation framework that iteratively generates prompts for evaluation, scores generated images and matches T2I evaluation of existing benchmarks with a fraction of the prompts used in existing static benchmarks. Moreover, we show that MT2IE's prompt-generation consistency scores have higher correlation with human judgment than scores previously introduced in the literature. MT2IE generates prompts that are efficient at probing T2I model performance, producing the same relative T2I model rankings as existing benchmarks while using only 1/80th the number of prompts for evaluation.
Improving the Scaling Laws of Synthetic Data with Deliberate Practice
Feb 21, 2025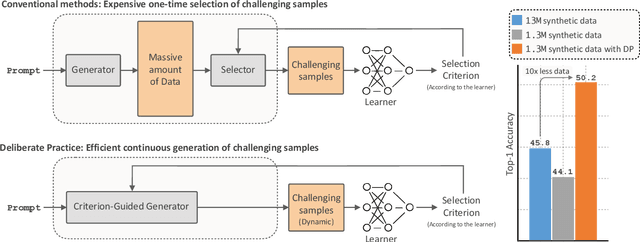
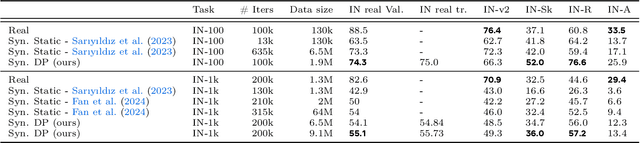
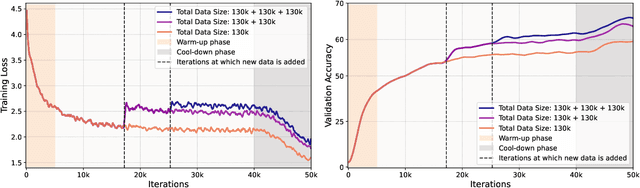
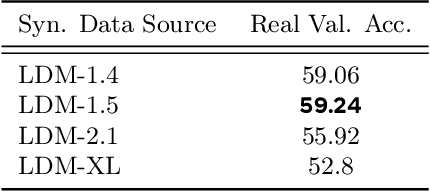
Abstract:Inspired by the principle of deliberate practice in human learning, we propose Deliberate Practice for Synthetic Data Generation (DP), a novel framework that improves sample efficiency through dynamic synthetic data generation. Prior work has shown that scaling synthetic data is inherently challenging, as naively adding new data leads to diminishing returns. To address this, pruning has been identified as a key mechanism for improving scaling, enabling models to focus on the most informative synthetic samples. Rather than generating a large dataset and pruning it afterward, DP efficiently approximates the direct generation of informative samples. We theoretically show how training on challenging, informative examples improves scaling laws and empirically validate that DP achieves better scaling performance with significantly fewer training samples and iterations. On ImageNet-100, DP generates 3.4x fewer samples and requires six times fewer iterations, while on ImageNet-1k, it generates 8x fewer samples with a 30 percent reduction in iterations, all while achieving superior performance compared to prior work.
EvalGIM: A Library for Evaluating Generative Image Models
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:As the use of text-to-image generative models increases, so does the adoption of automatic benchmarking methods used in their evaluation. However, while metrics and datasets abound, there are few unified benchmarking libraries that provide a framework for performing evaluations across many datasets and metrics. Furthermore, the rapid introduction of increasingly robust benchmarking methods requires that evaluation libraries remain flexible to new datasets and metrics. Finally, there remains a gap in synthesizing evaluations in order to deliver actionable takeaways about model performance. To enable unified, flexible, and actionable evaluations, we introduce EvalGIM (pronounced ''EvalGym''), a library for evaluating generative image models. EvalGIM contains broad support for datasets and metrics used to measure quality, diversity, and consistency of text-to-image generative models. In addition, EvalGIM is designed with flexibility for user customization as a top priority and contains a structure that allows plug-and-play additions of new datasets and metrics. To enable actionable evaluation insights, we introduce ''Evaluation Exercises'' that highlight takeaways for specific evaluation questions. The Evaluation Exercises contain easy-to-use and reproducible implementations of two state-of-the-art evaluation methods of text-to-image generative models: consistency-diversity-realism Pareto Fronts and disaggregated measurements of performance disparities across groups. EvalGIM also contains Evaluation Exercises that introduce two new analysis methods for text-to-image generative models: robustness analyses of model rankings and balanced evaluations across different prompt styles. We encourage text-to-image model exploration with EvalGIM and invite contributions at https://github.com/facebookresearch/EvalGIM/.
What makes a good metric? Evaluating automatic metrics for text-to-image consistency
Dec 18, 2024
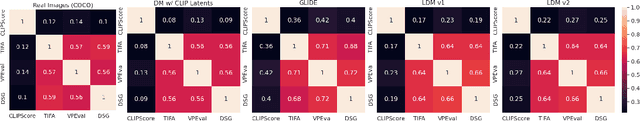

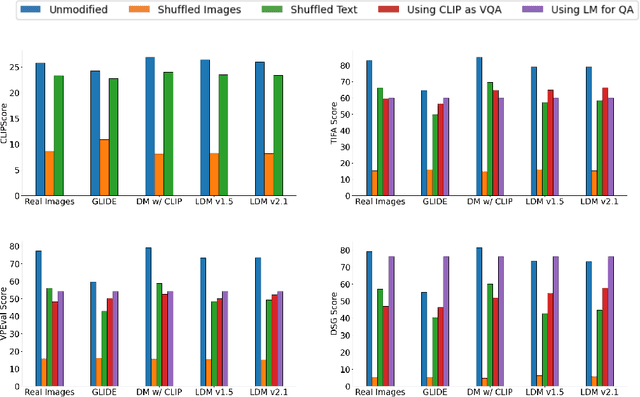
Abstract:Language models are increasingly being incorporated as components in larger AI systems for various purposes, from prompt optimization to automatic evaluation. In this work, we analyze the construct validity of four recent, commonly used methods for measuring text-to-image consistency - CLIPScore, TIFA, VPEval, and DSG - which rely on language models and/or VQA models as components. We define construct validity for text-image consistency metrics as a set of desiderata that text-image consistency metrics should have, and find that no tested metric satisfies all of them. We find that metrics lack sufficient sensitivity to language and visual properties. Next, we find that TIFA, VPEval and DSG contribute novel information above and beyond CLIPScore, but also that they correlate highly with each other. We also ablate different aspects of the text-image consistency metrics and find that not all model components are strictly necessary, also a symptom of insufficient sensitivity to visual information. Finally, we show that all three VQA-based metrics likely rely on familiar text shortcuts (such as yes-bias in QA) that call their aptitude as quantitative evaluations of model performance into question.
Boosting Latent Diffusion with Perceptual Objectives
Nov 06, 2024Abstract:Latent diffusion models (LDMs) power state-of-the-art high-resolution generative image models. LDMs learn the data distribution in the latent space of an autoencoder (AE) and produce images by mapping the generated latents into RGB image space using the AE decoder. While this approach allows for efficient model training and sampling, it induces a disconnect between the training of the diffusion model and the decoder, resulting in a loss of detail in the generated images. To remediate this disconnect, we propose to leverage the internal features of the decoder to define a latent perceptual loss (LPL). This loss encourages the models to create sharper and more realistic images. Our loss can be seamlessly integrated with common autoencoders used in latent diffusion models, and can be applied to different generative modeling paradigms such as DDPM with epsilon and velocity prediction, as well as flow matching. Extensive experiments with models trained on three datasets at 256 and 512 resolution show improved quantitative -- with boosts between 6% and 20% in FID -- and qualitative results when using our perceptual loss.
On Improved Conditioning Mechanisms and Pre-training Strategies for Diffusion Models
Nov 05, 2024Abstract:Large-scale training of latent diffusion models (LDMs) has enabled unprecedented quality in image generation. However, the key components of the best performing LDM training recipes are oftentimes not available to the research community, preventing apple-to-apple comparisons and hindering the validation of progress in the field. In this work, we perform an in-depth study of LDM training recipes focusing on the performance of models and their training efficiency. To ensure apple-to-apple comparisons, we re-implement five previously published models with their corresponding recipes. Through our study, we explore the effects of (i)~the mechanisms used to condition the generative model on semantic information (e.g., text prompt) and control metadata (e.g., crop size, random flip flag, etc.) on the model performance, and (ii)~the transfer of the representations learned on smaller and lower-resolution datasets to larger ones on the training efficiency and model performance. We then propose a novel conditioning mechanism that disentangles semantic and control metadata conditionings and sets a new state-of-the-art in class-conditional generation on the ImageNet-1k dataset -- with FID improvements of 7% on 256 and 8% on 512 resolutions -- as well as text-to-image generation on the CC12M dataset -- with FID improvements of 8% on 256 and 23% on 512 resolution.
Decomposed evaluations of geographic disparities in text-to-image models
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Recent work has identified substantial disparities in generated images of different geographic regions, including stereotypical depictions of everyday objects like houses and cars. However, existing measures for these disparities have been limited to either human evaluations, which are time-consuming and costly, or automatic metrics evaluating full images, which are unable to attribute these disparities to specific parts of the generated images. In this work, we introduce a new set of metrics, Decomposed Indicators of Disparities in Image Generation (Decomposed-DIG), that allows us to separately measure geographic disparities in the depiction of objects and backgrounds in generated images. Using Decomposed-DIG, we audit a widely used latent diffusion model and find that generated images depict objects with better realism than backgrounds and that backgrounds in generated images tend to contain larger regional disparities than objects. We use Decomposed-DIG to pinpoint specific examples of disparities, such as stereotypical background generation in Africa, struggling to generate modern vehicles in Africa, and unrealistically placing some objects in outdoor settings. Informed by our metric, we use a new prompting structure that enables a 52% worst-region improvement and a 20% average improvement in generated background diversity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge