Abhishek Sureddy
Safe to Serve: Aligning Instruction-Tuned Models for Safety and Helpfulness
Nov 26, 2024
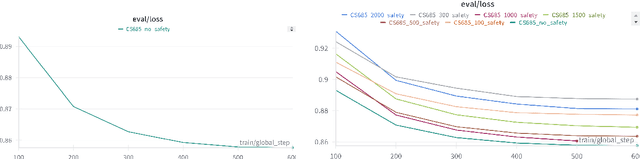
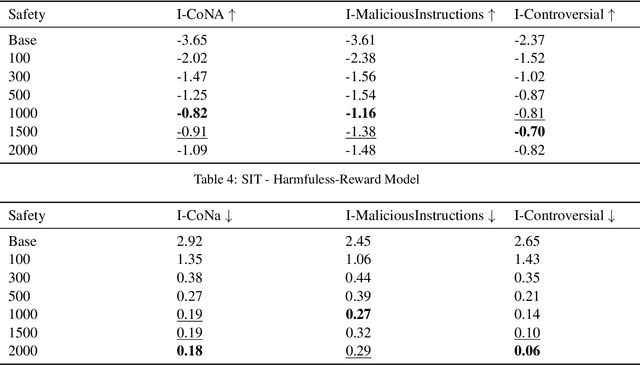
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex reasoning and text generation. However, these models can inadvertently generate unsafe or biased responses when prompted with problematic inputs, raising significant ethical and practical concerns for real-world deployment. This research addresses the critical challenge of developing language models that generate both helpful and harmless content, navigating the delicate balance between model performance and safety. We demonstrate that incorporating safety-related instructions during the instruction-tuning of pre-trained models significantly reduces toxic responses to unsafe prompts without compromising performance on helpfulness datasets. We found Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to be particularly effective, outperforming both SIT and RAFT by leveraging both chosen and rejected responses for learning. Our approach increased safe responses from 40$\%$ to over 90$\%$ across various harmfulness benchmarks. In addition, we discuss a rigorous evaluation framework encompassing specialized metrics and diverse datasets for safety and helpfulness tasks ensuring a comprehensive assessment of the model's capabilities.
Decomposed evaluations of geographic disparities in text-to-image models
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Recent work has identified substantial disparities in generated images of different geographic regions, including stereotypical depictions of everyday objects like houses and cars. However, existing measures for these disparities have been limited to either human evaluations, which are time-consuming and costly, or automatic metrics evaluating full images, which are unable to attribute these disparities to specific parts of the generated images. In this work, we introduce a new set of metrics, Decomposed Indicators of Disparities in Image Generation (Decomposed-DIG), that allows us to separately measure geographic disparities in the depiction of objects and backgrounds in generated images. Using Decomposed-DIG, we audit a widely used latent diffusion model and find that generated images depict objects with better realism than backgrounds and that backgrounds in generated images tend to contain larger regional disparities than objects. We use Decomposed-DIG to pinpoint specific examples of disparities, such as stereotypical background generation in Africa, struggling to generate modern vehicles in Africa, and unrealistically placing some objects in outdoor settings. Informed by our metric, we use a new prompting structure that enables a 52% worst-region improvement and a 20% average improvement in generated background diversity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge