Matthew J. Muckley
DIMCIM: A Quantitative Evaluation Framework for Default-mode Diversity and Generalization in Text-to-Image Generative Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-image (T2I) models have achieved impressive quality and consistency. However, this has come at the cost of representation diversity. While automatic evaluation methods exist for benchmarking model diversity, they either require reference image datasets or lack specificity about the kind of diversity measured, limiting their adaptability and interpretability. To address this gap, we introduce the Does-it/Can-it framework, DIM-CIM, a reference-free measurement of default-mode diversity ("Does" the model generate images with expected attributes?) and generalization capacity ("Can" the model generate diverse attributes for a particular concept?). We construct the COCO-DIMCIM benchmark, which is seeded with COCO concepts and captions and augmented by a large language model. With COCO-DIMCIM, we find that widely-used models improve in generalization at the cost of default-mode diversity when scaling from 1.5B to 8.1B parameters. DIMCIM also identifies fine-grained failure cases, such as attributes that are generated with generic prompts but are rarely generated when explicitly requested. Finally, we use DIMCIM to evaluate the training data of a T2I model and observe a correlation of 0.85 between diversity in training images and default-mode diversity. Our work provides a flexible and interpretable framework for assessing T2I model diversity and generalization, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of model performance.
Towards image compression with perfect realism at ultra-low bitrates
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:Image codecs are typically optimized to trade-off bitrate vs, distortion metrics. At low bitrates, this leads to compression artefacts which are easily perceptible, even when training with perceptual or adversarial losses. To improve image quality, and to make it less dependent on the bitrate, we propose to decode with iterative diffusion models, instead of feed-forward decoders trained using MSE or LPIPS distortions used in most neural codecs. In addition to conditioning the model on a vector-quantized image representation, we also condition on a global textual image description to provide additional context. We dub our model PerCo for 'perceptual compression', and compare it to state-of-the-art codecs at rates from 0.1 down to 0.003 bits per pixel. The latter rate is an order of magnitude smaller than those considered in most prior work. At this bitrate a 512x768 Kodak image is encoded in less than 153 bytes. Despite this ultra-low bitrate, our approach maintains the ability to reconstruct realistic images. We find that our model leads to reconstructions with state-of-the-art visual quality as measured by FID and KID, and that the visual quality is less dependent on the bitrate than previous methods.
Improving Statistical Fidelity for Neural Image Compression with Implicit Local Likelihood Models
Jan 28, 2023



Abstract:Lossy image compression aims to represent images in as few bits as possible while maintaining fidelity to the original. Theoretical results indicate that optimizing distortion metrics such as PSNR or MS-SSIM necessarily leads to a discrepancy in the statistics of original images from those of reconstructions, in particular at low bitrates, often manifested by the blurring of the compressed images. Previous work has leveraged adversarial discriminators to improve statistical fidelity. Yet these binary discriminators adopted from generative modeling tasks may not be ideal for image compression. In this paper, we introduce a non-binary discriminator that is conditioned on quantized local image representations obtained via VQ-VAE autoencoders. Our evaluations on the CLIC2020, DIV2K and Kodak datasets show that our discriminator is more effective for jointly optimizing distortion (e.g., PSNR) and statistical fidelity (e.g., FID) than the state-of-the-art HiFiC model. On the CLIC2020 test set, we obtain the same FID as HiFiC with 30-40% fewer bits.
Image Compression with Product Quantized Masked Image Modeling
Dec 14, 2022

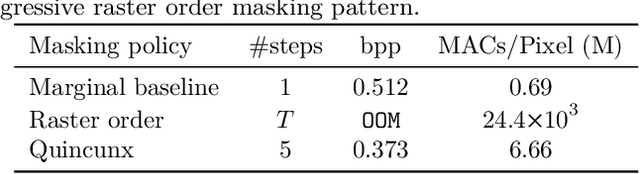

Abstract:Recent neural compression methods have been based on the popular hyperprior framework. It relies on Scalar Quantization and offers a very strong compression performance. This contrasts from recent advances in image generation and representation learning, where Vector Quantization is more commonly employed. In this work, we attempt to bring these lines of research closer by revisiting vector quantization for image compression. We build upon the VQ-VAE framework and introduce several modifications. First, we replace the vanilla vector quantizer by a product quantizer. This intermediate solution between vector and scalar quantization allows for a much wider set of rate-distortion points: It implicitly defines high-quality quantizers that would otherwise require intractably large codebooks. Second, inspired by the success of Masked Image Modeling (MIM) in the context of self-supervised learning and generative image models, we propose a novel conditional entropy model which improves entropy coding by modelling the co-dependencies of the quantized latent codes. The resulting PQ-MIM model is surprisingly effective: its compression performance on par with recent hyperprior methods. It also outperforms HiFiC in terms of FID and KID metrics when optimized with perceptual losses (e.g. adversarial). Finally, since PQ-MIM is compatible with image generation frameworks, we show qualitatively that it can operate under a hybrid mode between compression and generation, with no further training or finetuning. As a result, we explore the extreme compression regime where an image is compressed into 200 bytes, i.e., less than a tweet.
State-of-the-Art Machine Learning MRI Reconstruction in 2020: Results of the Second fastMRI Challenge
Dec 28, 2020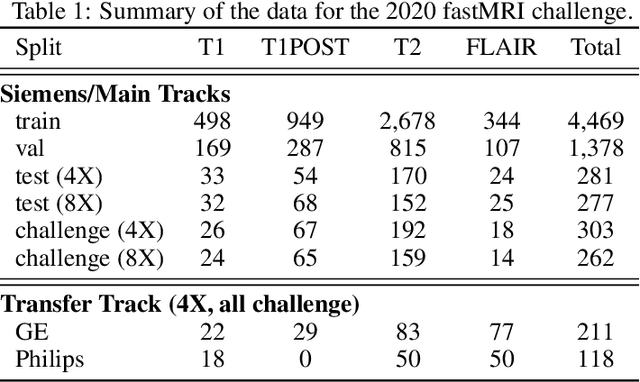
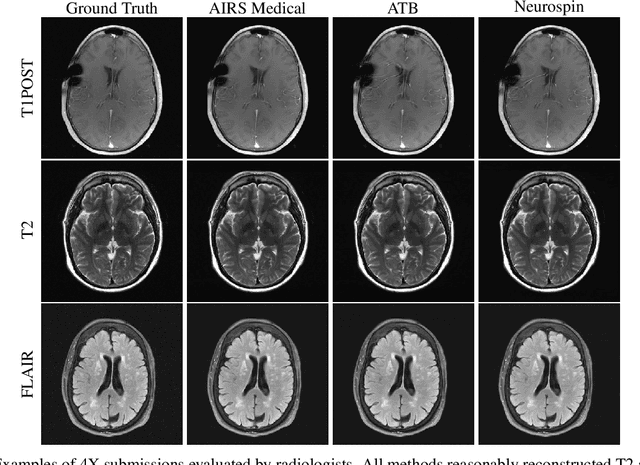
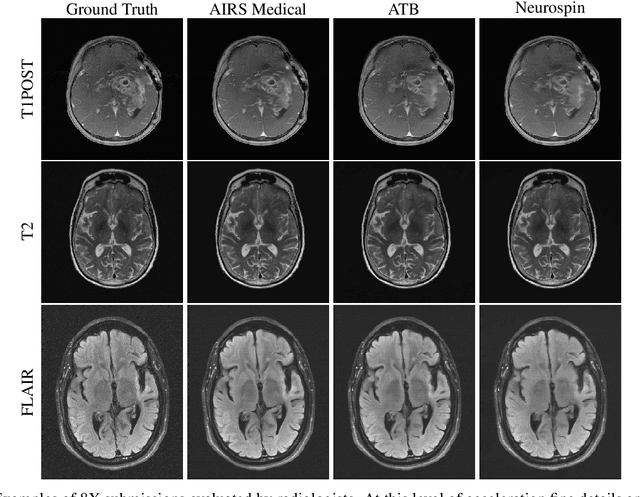
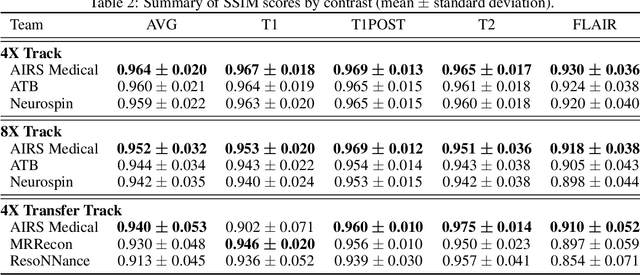
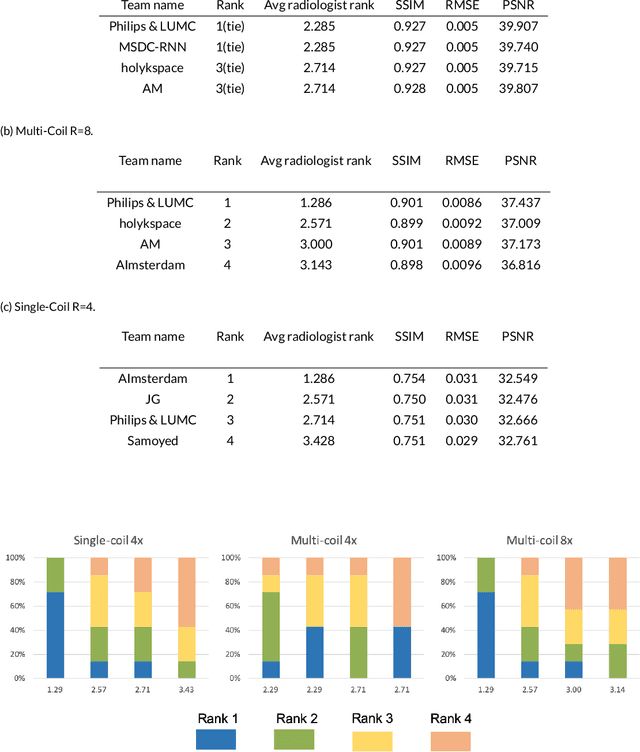
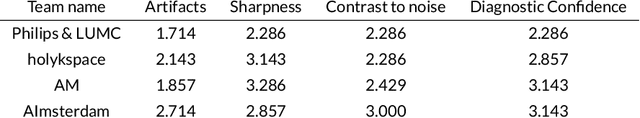
Abstract:Accelerating MRI scans is one of the principal outstanding problems in the MRI research community. Towards this goal, we hosted the second fastMRI competition targeted towards reconstructing MR images with subsampled k-space data. We provided participants with data from 7,299 clinical brain scans (de-identified via a HIPAA-compliant procedure by NYU Langone Health), holding back the fully-sampled data from 894 of these scans for challenge evaluation purposes. In contrast to the 2019 challenge, we focused our radiologist evaluations on pathological assessment in brain images. We also debuted a new Transfer track that required participants to submit models evaluated on MRI scanners from outside the training set. We received 19 submissions from eight different groups. Results showed one team scoring best in both SSIM scores and qualitative radiologist evaluations. We also performed analysis on alternative metrics to mitigate the effects of background noise and collected feedback from the participants to inform future challenges. Lastly, we identify common failure modes across the submissions, highlighting areas of need for future research in the MRI reconstruction community.
Advancing machine learning for MR image reconstruction with an open competition: Overview of the 2019 fastMRI challenge
Jan 06, 2020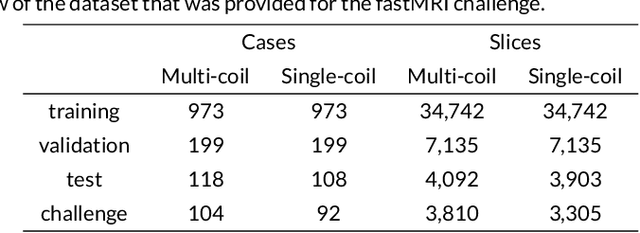
Abstract:Purpose: To advance research in the field of machine learning for MR image reconstruction with an open challenge. Methods: We provided participants with a dataset of raw k-space data from 1,594 consecutive clinical exams of the knee. The goal of the challenge was to reconstruct images from these data. In order to strike a balance between realistic data and a shallow learning curve for those not already familiar with MR image reconstruction, we ran multiple tracks for multi-coil and single-coil data. We performed a two-stage evaluation based on quantitative image metrics followed by evaluation by a panel of radiologists. The challenge ran from June to December of 2019. Results: We received a total of 33 challenge submissions. All participants chose to submit results from supervised machine learning approaches. Conclusion: The challenge led to new developments in machine learning for image reconstruction, provided insight into the current state of the art in the field, and highlighted remaining hurdles for clinical adoption.
Reducing Uncertainty in Undersampled MRI Reconstruction with Active Acquisition
Feb 08, 2019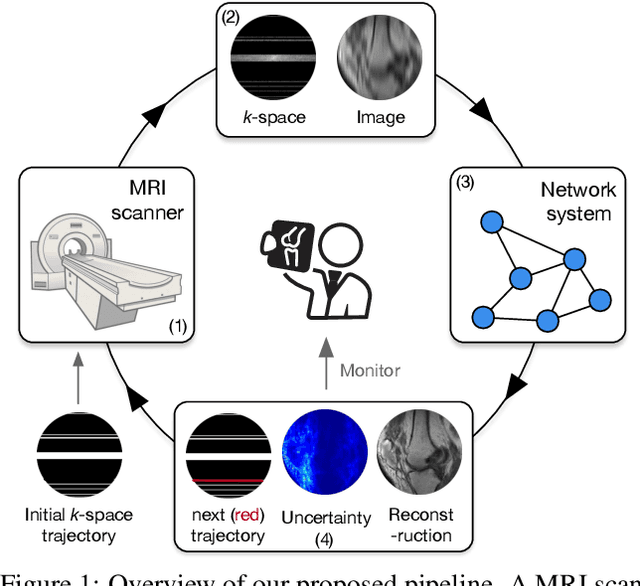
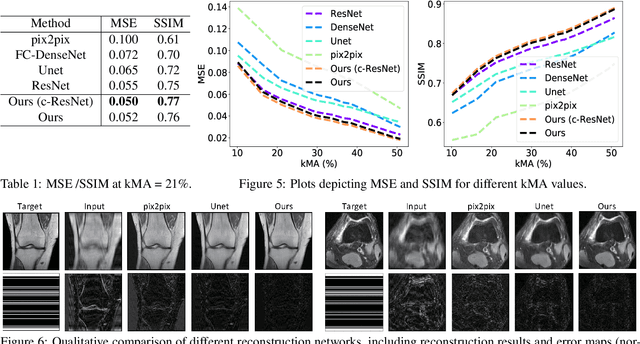
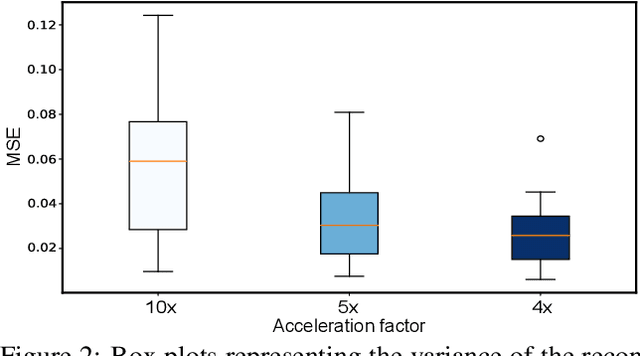
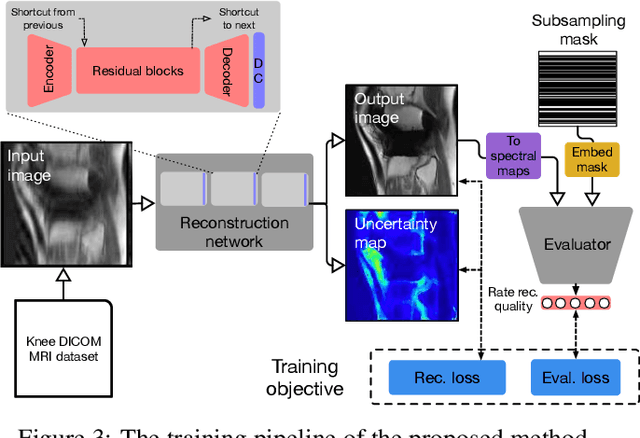
Abstract:The goal of MRI reconstruction is to restore a high fidelity image from partially observed measurements. This partial view naturally induces reconstruction uncertainty that can only be reduced by acquiring additional measurements. In this paper, we present a novel method for MRI reconstruction that, at inference time, dynamically selects the measurements to take and iteratively refines the prediction in order to best reduce the reconstruction error and, thus, its uncertainty. We validate our method on a large scale knee MRI dataset, as well as on ImageNet. Results show that (1) our system successfully outperforms active acquisition baselines; (2) our uncertainty estimates correlate with error maps; and (3) our ResNet-based architecture surpasses standard pixel-to-pixel models in the task of MRI reconstruction. The proposed method not only shows high-quality reconstructions but also paves the road towards more applicable solutions for accelerating MRI.
fastMRI: An Open Dataset and Benchmarks for Accelerated MRI
Nov 21, 2018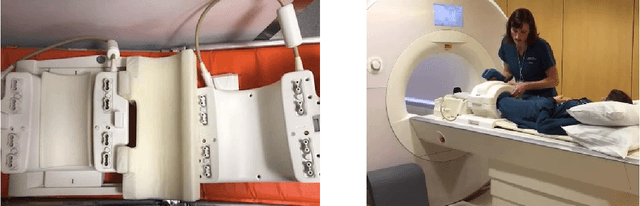
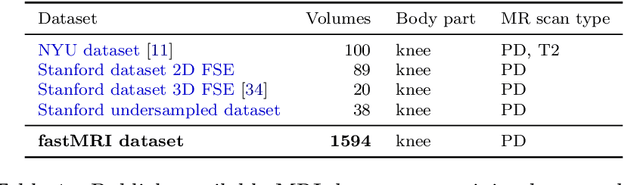
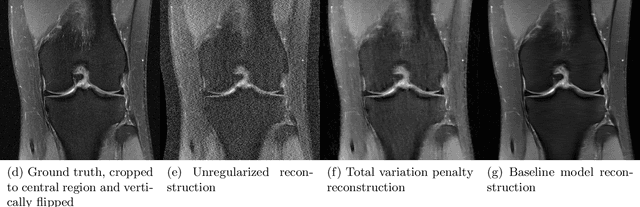
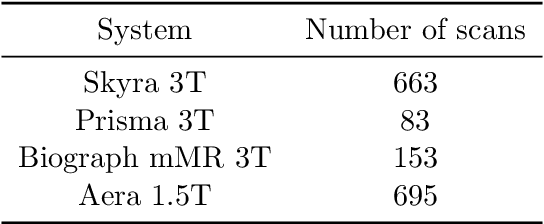
Abstract:Accelerating Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) by taking fewer measurements has the potential to reduce medical costs, minimize stress to patients and make MRI possible in applications where it is currently prohibitively slow or expensive. We introduce the fastMRI dataset, a large-scale collection of both raw MR measurements and clinical MR images, that can be used for training and evaluation of machine-learning approaches to MR image reconstruction. By introducing standardized evaluation criteria and a freely-accessible dataset, our goal is to help the community make rapid advances in the state of the art for MR image reconstruction. We also provide a self-contained introduction to MRI for machine learning researchers with no medical imaging background.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge