Pavel Izmailov
Reliable and Responsible Foundation Models: A Comprehensive Survey
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Foundation models, including Large Language Models (LLMs), Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), Image Generative Models (i.e, Text-to-Image Models and Image-Editing Models), and Video Generative Models, have become essential tools with broad applications across various domains such as law, medicine, education, finance, science, and beyond. As these models see increasing real-world deployment, ensuring their reliability and responsibility has become critical for academia, industry, and government. This survey addresses the reliable and responsible development of foundation models. We explore critical issues, including bias and fairness, security and privacy, uncertainty, explainability, and distribution shift. Our research also covers model limitations, such as hallucinations, as well as methods like alignment and Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content (AIGC) detection. For each area, we review the current state of the field and outline concrete future research directions. Additionally, we discuss the intersections between these areas, highlighting their connections and shared challenges. We hope our survey fosters the development of foundation models that are not only powerful but also ethical, trustworthy, reliable, and socially responsible.
From Entropy to Epiplexity: Rethinking Information for Computationally Bounded Intelligence
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Can we learn more from data than existed in the generating process itself? Can new and useful information be constructed from merely applying deterministic transformations to existing data? Can the learnable content in data be evaluated without considering a downstream task? On these questions, Shannon information and Kolmogorov complexity come up nearly empty-handed, in part because they assume observers with unlimited computational capacity and fail to target the useful information content. In this work, we identify and exemplify three seeming paradoxes in information theory: (1) information cannot be increased by deterministic transformations; (2) information is independent of the order of data; (3) likelihood modeling is merely distribution matching. To shed light on the tension between these results and modern practice, and to quantify the value of data, we introduce epiplexity, a formalization of information capturing what computationally bounded observers can learn from data. Epiplexity captures the structural content in data while excluding time-bounded entropy, the random unpredictable content exemplified by pseudorandom number generators and chaotic dynamical systems. With these concepts, we demonstrate how information can be created with computation, how it depends on the ordering of the data, and how likelihood modeling can produce more complex programs than present in the data generating process itself. We also present practical procedures to estimate epiplexity which we show capture differences across data sources, track with downstream performance, and highlight dataset interventions that improve out-of-distribution generalization. In contrast to principles of model selection, epiplexity provides a theoretical foundation for data selection, guiding how to select, generate, or transform data for learning systems.
Improving Semantic Uncertainty Quantification in LVLMs with Semantic Gaussian Processes
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) often produce plausible but unreliable outputs, making robust uncertainty estimation essential. Recent work on semantic uncertainty estimates relies on external models to cluster multiple sampled responses and measure their semantic consistency. However, these clustering methods are often fragile, highly sensitive to minor phrasing variations, and can incorrectly group or separate semantically similar answers, leading to unreliable uncertainty estimates. We propose Semantic Gaussian Process Uncertainty (SGPU), a Bayesian framework that quantifies semantic uncertainty by analyzing the geometric structure of answer embeddings, avoiding brittle clustering. SGPU maps generated answers into a dense semantic space, computes the Gram matrix of their embeddings, and summarizes their semantic configuration via the eigenspectrum. This spectral representation is then fed into a Gaussian Process Classifier that learns to map patterns of semantic consistency to predictive uncertainty, and that can be applied in both black-box and white-box settings. Across six LLMs and LVLMs on eight datasets spanning VQA, image classification, and textual QA, SGPU consistently achieves state-of-the-art calibration (ECE) and discriminative (AUROC, AUARC) performance. We further show that SGPU transfers across models and modalities, indicating that its spectral representation captures general patterns of semantic uncertainty.
Closing the Train-Test Gap in World Models for Gradient-Based Planning
Dec 10, 2025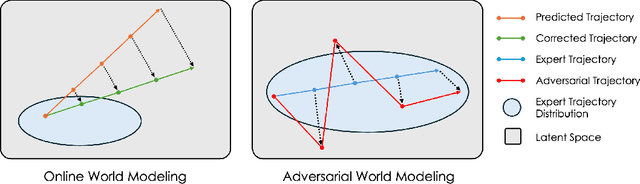
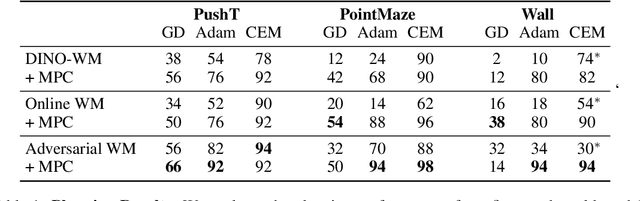
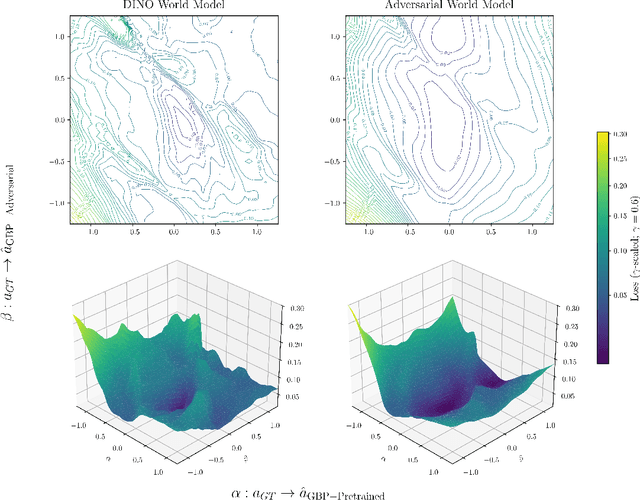
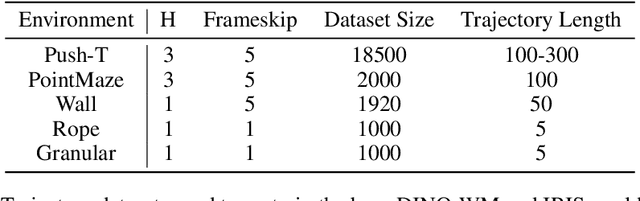
Abstract:World models paired with model predictive control (MPC) can be trained offline on large-scale datasets of expert trajectories and enable generalization to a wide range of planning tasks at inference time. Compared to traditional MPC procedures, which rely on slow search algorithms or on iteratively solving optimization problems exactly, gradient-based planning offers a computationally efficient alternative. However, the performance of gradient-based planning has thus far lagged behind that of other approaches. In this paper, we propose improved methods for training world models that enable efficient gradient-based planning. We begin with the observation that although a world model is trained on a next-state prediction objective, it is used at test-time to instead estimate a sequence of actions. The goal of our work is to close this train-test gap. To that end, we propose train-time data synthesis techniques that enable significantly improved gradient-based planning with existing world models. At test time, our approach outperforms or matches the classical gradient-free cross-entropy method (CEM) across a variety of object manipulation and navigation tasks in 10% of the time budget.
OpenAI o1 System Card
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:The o1 model series is trained with large-scale reinforcement learning to reason using chain of thought. These advanced reasoning capabilities provide new avenues for improving the safety and robustness of our models. In particular, our models can reason about our safety policies in context when responding to potentially unsafe prompts, through deliberative alignment. This leads to state-of-the-art performance on certain benchmarks for risks such as generating illicit advice, choosing stereotyped responses, and succumbing to known jailbreaks. Training models to incorporate a chain of thought before answering has the potential to unlock substantial benefits, while also increasing potential risks that stem from heightened intelligence. Our results underscore the need for building robust alignment methods, extensively stress-testing their efficacy, and maintaining meticulous risk management protocols. This report outlines the safety work carried out for the OpenAI o1 and OpenAI o1-mini models, including safety evaluations, external red teaming, and Preparedness Framework evaluations.
Can a Confident Prior Replace a Cold Posterior?
Mar 02, 2024Abstract:Benchmark datasets used for image classification tend to have very low levels of label noise. When Bayesian neural networks are trained on these datasets, they often underfit, misrepresenting the aleatoric uncertainty of the data. A common solution is to cool the posterior, which improves fit to the training data but is challenging to interpret from a Bayesian perspective. We explore whether posterior tempering can be replaced by a confidence-inducing prior distribution. First, we introduce a "DirClip" prior that is practical to sample and nearly matches the performance of a cold posterior. Second, we introduce a "confidence prior" that directly approximates a cold likelihood in the limit of decreasing temperature but cannot be easily sampled. Lastly, we provide several general insights into confidence-inducing priors, such as when they might diverge and how fine-tuning can mitigate numerical instability.
Weak-to-Strong Generalization: Eliciting Strong Capabilities With Weak Supervision
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:Widely used alignment techniques, such as reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), rely on the ability of humans to supervise model behavior - for example, to evaluate whether a model faithfully followed instructions or generated safe outputs. However, future superhuman models will behave in complex ways too difficult for humans to reliably evaluate; humans will only be able to weakly supervise superhuman models. We study an analogy to this problem: can weak model supervision elicit the full capabilities of a much stronger model? We test this using a range of pretrained language models in the GPT-4 family on natural language processing (NLP), chess, and reward modeling tasks. We find that when we naively finetune strong pretrained models on labels generated by a weak model, they consistently perform better than their weak supervisors, a phenomenon we call weak-to-strong generalization. However, we are still far from recovering the full capabilities of strong models with naive finetuning alone, suggesting that techniques like RLHF may scale poorly to superhuman models without further work. We find that simple methods can often significantly improve weak-to-strong generalization: for example, when finetuning GPT-4 with a GPT-2-level supervisor and an auxiliary confidence loss, we can recover close to GPT-3.5-level performance on NLP tasks. Our results suggest that it is feasible to make empirical progress today on a fundamental challenge of aligning superhuman models.
Simple and Fast Group Robustness by Automatic Feature Reweighting
Jun 19, 2023Abstract:A major challenge to out-of-distribution generalization is reliance on spurious features -- patterns that are predictive of the class label in the training data distribution, but not causally related to the target. Standard methods for reducing the reliance on spurious features typically assume that we know what the spurious feature is, which is rarely true in the real world. Methods that attempt to alleviate this limitation are complex, hard to tune, and lead to a significant computational overhead compared to standard training. In this paper, we propose Automatic Feature Reweighting (AFR), an extremely simple and fast method for updating the model to reduce the reliance on spurious features. AFR retrains the last layer of a standard ERM-trained base model with a weighted loss that emphasizes the examples where the ERM model predicts poorly, automatically upweighting the minority group without group labels. With this simple procedure, we improve upon the best reported results among competing methods trained without spurious attributes on several vision and natural language classification benchmarks, using only a fraction of their compute.
* ICML 23. Code available at https://github.com/AndPotap/afr
FlexiViT: One Model for All Patch Sizes
Dec 15, 2022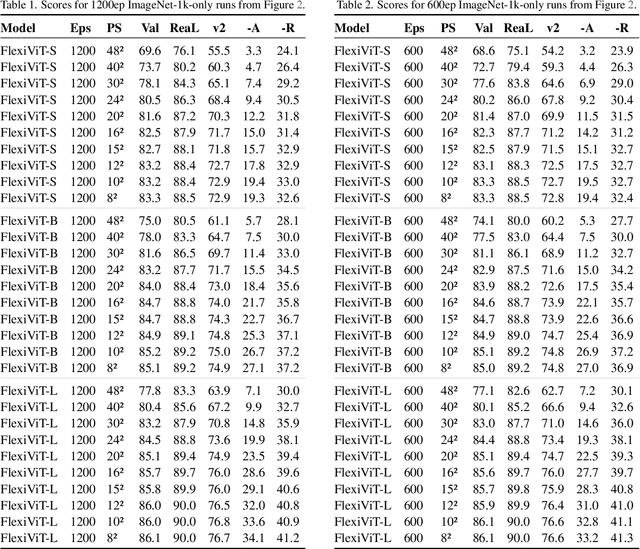
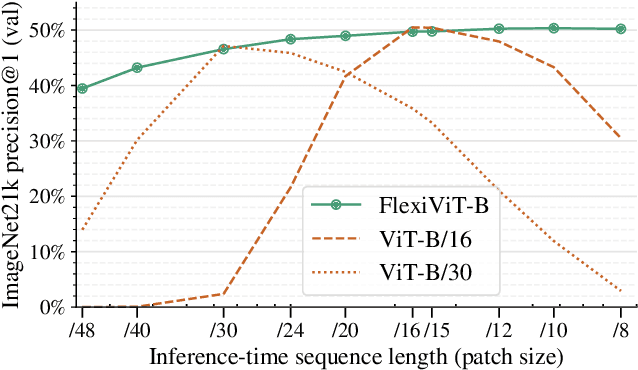
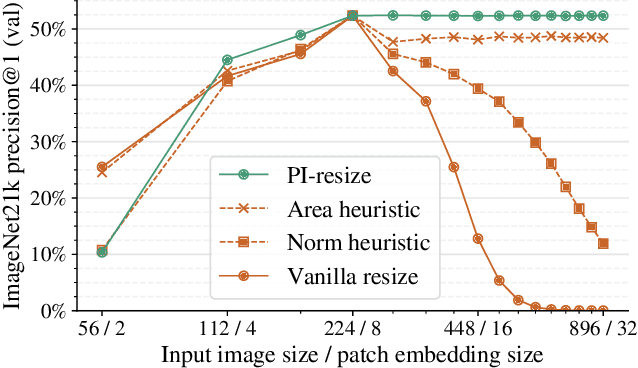
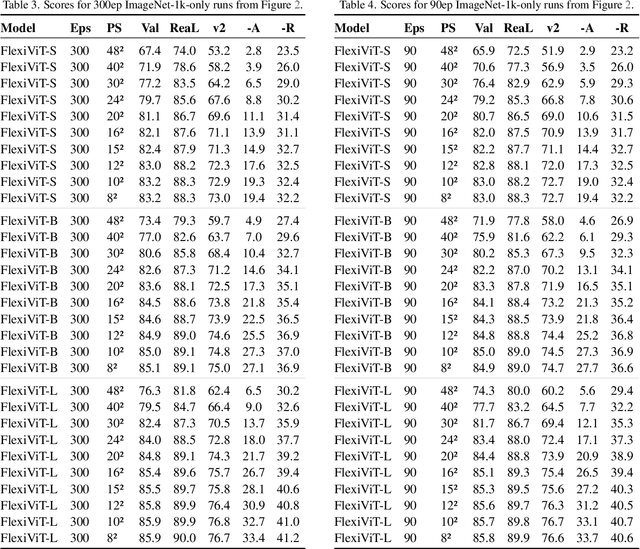
Abstract:Vision Transformers convert images to sequences by slicing them into patches. The size of these patches controls a speed/accuracy tradeoff, with smaller patches leading to higher accuracy at greater computational cost, but changing the patch size typically requires retraining the model. In this paper, we demonstrate that simply randomizing the patch size at training time leads to a single set of weights that performs well across a wide range of patch sizes, making it possible to tailor the model to different compute budgets at deployment time. We extensively evaluate the resulting model, which we call FlexiViT, on a wide range of tasks, including classification, image-text retrieval, open-world detection, panoptic segmentation, and semantic segmentation, concluding that it usually matches, and sometimes outperforms, standard ViT models trained at a single patch size in an otherwise identical setup. Hence, FlexiViT training is a simple drop-in improvement for ViT that makes it easy to add compute-adaptive capabilities to most models relying on a ViT backbone architecture. Code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/google-research/big_vision
On Feature Learning in the Presence of Spurious Correlations
Oct 20, 2022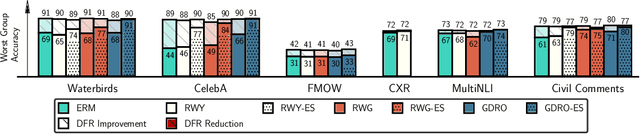
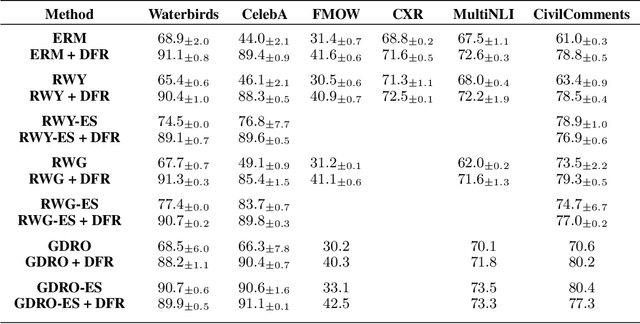
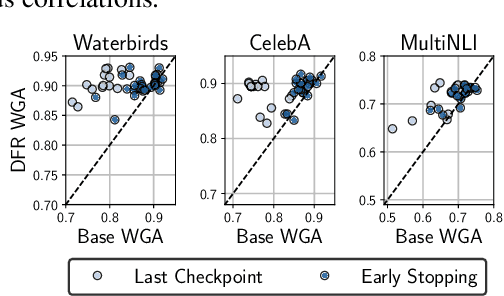
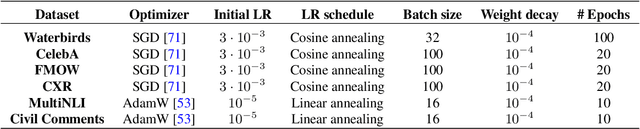
Abstract:Deep classifiers are known to rely on spurious features $\unicode{x2013}$ patterns which are correlated with the target on the training data but not inherently relevant to the learning problem, such as the image backgrounds when classifying the foregrounds. In this paper we evaluate the amount of information about the core (non-spurious) features that can be decoded from the representations learned by standard empirical risk minimization (ERM) and specialized group robustness training. Following recent work on Deep Feature Reweighting (DFR), we evaluate the feature representations by re-training the last layer of the model on a held-out set where the spurious correlation is broken. On multiple vision and NLP problems, we show that the features learned by simple ERM are highly competitive with the features learned by specialized group robustness methods targeted at reducing the effect of spurious correlations. Moreover, we show that the quality of learned feature representations is greatly affected by the design decisions beyond the training method, such as the model architecture and pre-training strategy. On the other hand, we find that strong regularization is not necessary for learning high quality feature representations. Finally, using insights from our analysis, we significantly improve upon the best results reported in the literature on the popular Waterbirds, CelebA hair color prediction and WILDS-FMOW problems, achieving 97%, 92% and 50% worst-group accuracies, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge