Marc Szafraniec
Disentangling the Factors of Convergence between Brains and Computer Vision Models
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Many AI models trained on natural images develop representations that resemble those of the human brain. However, the factors that drive this brain-model similarity remain poorly understood. To disentangle how the model, training and data independently lead a neural network to develop brain-like representations, we trained a family of self-supervised vision transformers (DINOv3) that systematically varied these different factors. We compare their representations of images to those of the human brain recorded with both fMRI and MEG, providing high resolution in spatial and temporal analyses. We assess the brain-model similarity with three complementary metrics focusing on overall representational similarity, topographical organization, and temporal dynamics. We show that all three factors - model size, training amount, and image type - independently and interactively impact each of these brain similarity metrics. In particular, the largest DINOv3 models trained with the most human-centric images reach the highest brain-similarity. This emergence of brain-like representations in AI models follows a specific chronology during training: models first align with the early representations of the sensory cortices, and only align with the late and prefrontal representations of the brain with considerably more training. Finally, this developmental trajectory is indexed by both structural and functional properties of the human cortex: the representations that are acquired last by the models specifically align with the cortical areas with the largest developmental expansion, thickness, least myelination, and slowest timescales. Overall, these findings disentangle the interplay between architecture and experience in shaping how artificial neural networks come to see the world as humans do, thus offering a promising framework to understand how the human brain comes to represent its visual world.
DINOv3
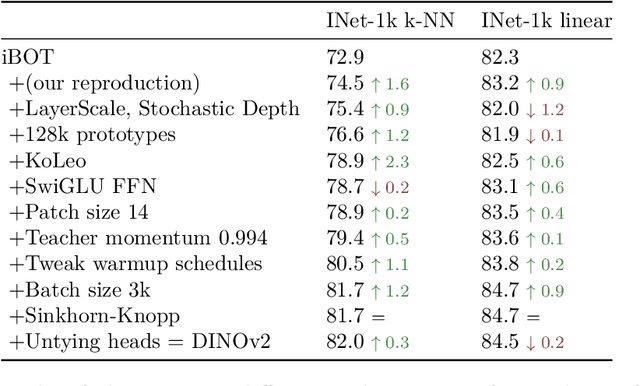
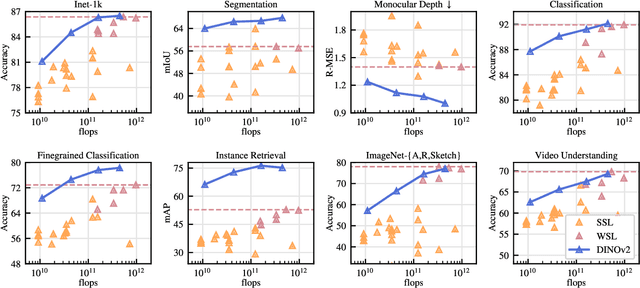
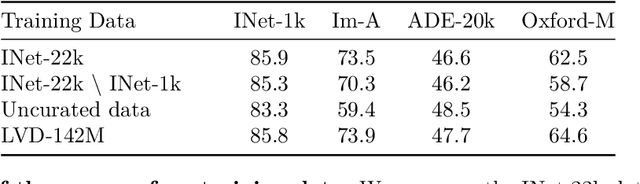
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Self-supervised learning holds the promise of eliminating the need for manual data annotation, enabling models to scale effortlessly to massive datasets and larger architectures. By not being tailored to specific tasks or domains, this training paradigm has the potential to learn visual representations from diverse sources, ranging from natural to aerial images -- using a single algorithm. This technical report introduces DINOv3, a major milestone toward realizing this vision by leveraging simple yet effective strategies. First, we leverage the benefit of scaling both dataset and model size by careful data preparation, design, and optimization. Second, we introduce a new method called Gram anchoring, which effectively addresses the known yet unsolved issue of dense feature maps degrading during long training schedules. Finally, we apply post-hoc strategies that further enhance our models' flexibility with respect to resolution, model size, and alignment with text. As a result, we present a versatile vision foundation model that outperforms the specialized state of the art across a broad range of settings, without fine-tuning. DINOv3 produces high-quality dense features that achieve outstanding performance on various vision tasks, significantly surpassing previous self- and weakly-supervised foundation models. We also share the DINOv3 suite of vision models, designed to advance the state of the art on a wide spectrum of tasks and data by providing scalable solutions for diverse resource constraints and deployment scenarios.
V-JEPA 2: Self-Supervised Video Models Enable Understanding, Prediction and Planning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:A major challenge for modern AI is to learn to understand the world and learn to act largely by observation. This paper explores a self-supervised approach that combines internet-scale video data with a small amount of interaction data (robot trajectories), to develop models capable of understanding, predicting, and planning in the physical world. We first pre-train an action-free joint-embedding-predictive architecture, V-JEPA 2, on a video and image dataset comprising over 1 million hours of internet video. V-JEPA 2 achieves strong performance on motion understanding (77.3 top-1 accuracy on Something-Something v2) and state-of-the-art performance on human action anticipation (39.7 recall-at-5 on Epic-Kitchens-100) surpassing previous task-specific models. Additionally, after aligning V-JEPA 2 with a large language model, we demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on multiple video question-answering tasks at the 8 billion parameter scale (e.g., 84.0 on PerceptionTest, 76.9 on TempCompass). Finally, we show how self-supervised learning can be applied to robotic planning tasks by post-training a latent action-conditioned world model, V-JEPA 2-AC, using less than 62 hours of unlabeled robot videos from the Droid dataset. We deploy V-JEPA 2-AC zero-shot on Franka arms in two different labs and enable picking and placing of objects using planning with image goals. Notably, this is achieved without collecting any data from the robots in these environments, and without any task-specific training or reward. This work demonstrates how self-supervised learning from web-scale data and a small amount of robot interaction data can yield a world model capable of planning in the physical world.
DINOv2 Meets Text: A Unified Framework for Image- and Pixel-Level Vision-Language Alignment
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Self-supervised visual foundation models produce powerful embeddings that achieve remarkable performance on a wide range of downstream tasks. However, unlike vision-language models such as CLIP, self-supervised visual features are not readily aligned with language, hindering their adoption in open-vocabulary tasks. Our method, named dino.txt, unlocks this new ability for DINOv2, a widely used self-supervised visual encoder. We build upon the LiT training strategy, which trains a text encoder to align with a frozen vision model but leads to unsatisfactory results on dense tasks. We propose several key ingredients to improve performance on both global and dense tasks, such as concatenating the [CLS] token with the patch average to train the alignment and curating data using both text and image modalities. With these, we successfully train a CLIP-like model with only a fraction of the computational cost compared to CLIP while achieving state-of-the-art results in zero-shot classification and open-vocabulary semantic segmentation.
You Don't Need Data-Augmentation in Self-Supervised Learning
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Self-Supervised learning (SSL) with Joint-Embedding Architectures (JEA) has led to outstanding performances. All instantiations of this paradigm were trained using strong and well-established hand-crafted data augmentations, leading to the general belief that they are required for the proper training and performance of such models. On the other hand, generative reconstruction-based models such as BEIT and MAE or Joint-Embedding Predictive Architectures such as I-JEPA have shown strong performance without using data augmentations except masking. In this work, we challenge the importance of invariance and data-augmentation in JEAs at scale. By running a case-study on a recent SSL foundation model - DINOv2 - we show that strong image representations can be obtained with JEAs and only cropping without resizing provided the training data is large enough, reaching state-of-the-art results and using the least amount of augmentation in the literature. Through this study, we also discuss the impact of compute constraints on the outcomes of experimental deep learning research, showing that they can lead to very different conclusions.
Automatic Data Curation for Self-Supervised Learning: A Clustering-Based Approach
May 24, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised features are the cornerstone of modern machine learning systems. They are typically pre-trained on data collections whose construction and curation typically require extensive human effort. This manual process has some limitations similar to those encountered in supervised learning, e.g., the crowd-sourced selection of data is costly and time-consuming, preventing scaling the dataset size. In this work, we consider the problem of automatic curation of high-quality datasets for self-supervised pre-training. We posit that such datasets should be large, diverse and balanced, and propose a clustering-based approach for building ones satisfying all these criteria. Our method involves successive and hierarchical applications of $k$-means on a large and diverse data repository to obtain clusters that distribute uniformly among data concepts, followed by a hierarchical, balanced sampling step from these clusters. Extensive experiments on three different data domains including web-based images, satellite images and text show that features trained on our automatically curated datasets outperform those trained on uncurated data while being on par or better than ones trained on manually curated data.
Better (pseudo-)labels for semi-supervised instance segmentation
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:Despite the availability of large datasets for tasks like image classification and image-text alignment, labeled data for more complex recognition tasks, such as detection and segmentation, is less abundant. In particular, for instance segmentation annotations are time-consuming to produce, and the distribution of instances is often highly skewed across classes. While semi-supervised teacher-student distillation methods show promise in leveraging vast amounts of unlabeled data, they suffer from miscalibration, resulting in overconfidence in frequently represented classes and underconfidence in rarer ones. Additionally, these methods encounter difficulties in efficiently learning from a limited set of examples. We introduce a dual-strategy to enhance the teacher model's training process, substantially improving the performance on few-shot learning. Secondly, we propose a calibration correction mechanism that that enables the student model to correct the teacher's calibration errors. Using our approach, we observed marked improvements over a state-of-the-art supervised baseline performance on the LVIS dataset, with an increase of 2.8% in average precision (AP) and 10.3% gain in AP for rare classes.
DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision
Apr 14, 2023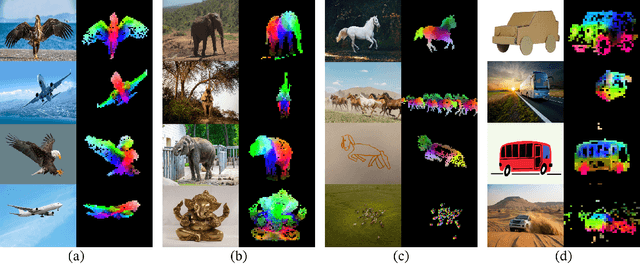
Abstract:The recent breakthroughs in natural language processing for model pretraining on large quantities of data have opened the way for similar foundation models in computer vision. These models could greatly simplify the use of images in any system by producing all-purpose visual features, i.e., features that work across image distributions and tasks without finetuning. This work shows that existing pretraining methods, especially self-supervised methods, can produce such features if trained on enough curated data from diverse sources. We revisit existing approaches and combine different techniques to scale our pretraining in terms of data and model size. Most of the technical contributions aim at accelerating and stabilizing the training at scale. In terms of data, we propose an automatic pipeline to build a dedicated, diverse, and curated image dataset instead of uncurated data, as typically done in the self-supervised literature. In terms of models, we train a ViT model (Dosovitskiy et al., 2020) with 1B parameters and distill it into a series of smaller models that surpass the best available all-purpose features, OpenCLIP (Ilharco et al., 2021) on most of the benchmarks at image and pixel levels.
Code Translation with Compiler Representations
Jul 13, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we leverage low-level compiler intermediate representations (IR) to improve code translation. Traditional transpilers rely on syntactic information and handcrafted rules, which limits their applicability and produces unnatural-looking code. Applying neural machine translation (NMT) approaches to code has successfully broadened the set of programs on which one can get a natural-looking translation. However, they treat the code as sequences of text tokens, and still do not differentiate well enough between similar pieces of code which have different semantics in different languages. The consequence is low quality translation, reducing the practicality of NMT, and stressing the need for an approach significantly increasing its accuracy. Here we propose to augment code translation with IRs, specifically LLVM IR, with results on the C++, Java, Rust, and Go languages. Our method improves upon the state of the art for unsupervised code translation, increasing the number of correct translations by 11% on average, and up to 79% for the Java - Rust pair. We extend previous test sets for code translation, by adding hundreds of Go and Rust functions. Additionally, we train models with high performance on the problem of IR decompilation, generating programming source code from IR, and study using IRs as intermediary pivot for translation.
DOBF: A Deobfuscation Pre-Training Objective for Programming Languages
Feb 16, 2021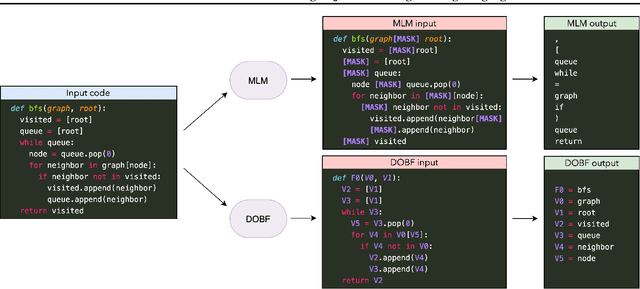
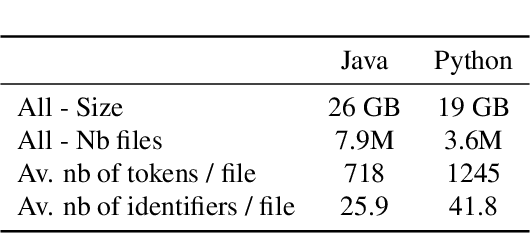

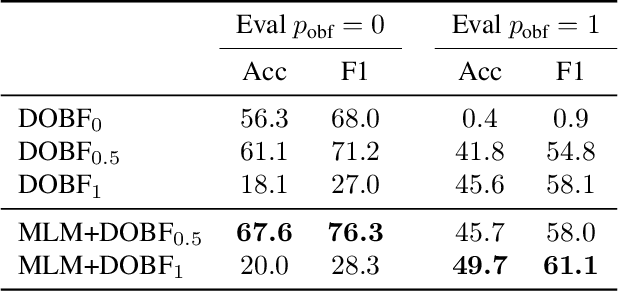
Abstract:Recent advances in self-supervised learning have dramatically improved the state of the art on a wide variety of tasks. However, research in language model pre-training has mostly focused on natural languages, and it is unclear whether models like BERT and its variants provide the best pre-training when applied to other modalities, such as source code. In this paper, we introduce a new pre-training objective, DOBF, that leverages the structural aspect of programming languages and pre-trains a model to recover the original version of obfuscated source code. We show that models pre-trained with DOBF significantly outperform existing approaches on multiple downstream tasks, providing relative improvements of up to 13% in unsupervised code translation, and 24% in natural language code search. Incidentally, we found that our pre-trained model is able to de-obfuscate fully obfuscated source files, and to suggest descriptive variable names.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge