Gautier Marti
Interpreting LLMs as Credit Risk Classifiers: Do Their Feature Explanations Align with Classical ML?
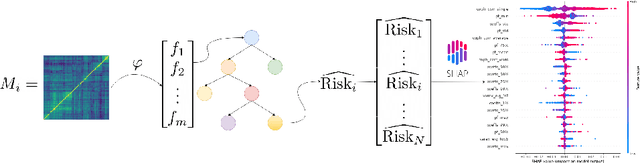
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly explored as flexible alternatives to classical machine learning models for classification tasks through zero-shot prompting. However, their suitability for structured tabular data remains underexplored, especially in high-stakes financial applications such as financial risk assessment. This study conducts a systematic comparison between zero-shot LLM-based classifiers and LightGBM, a state-of-the-art gradient-boosting model, on a real-world loan default prediction task. We evaluate their predictive performance, analyze feature attributions using SHAP, and assess the reliability of LLM-generated self-explanations. While LLMs are able to identify key financial risk indicators, their feature importance rankings diverge notably from LightGBM, and their self-explanations often fail to align with empirical SHAP attributions. These findings highlight the limitations of LLMs as standalone models for structured financial risk prediction and raise concerns about the trustworthiness of their self-generated explanations. Our results underscore the need for explainability audits, baseline comparisons with interpretable models, and human-in-the-loop oversight when deploying LLMs in risk-sensitive financial environments.
Residual Speech Embeddings for Tone Classification: Removing Linguistic Content to Enhance Paralinguistic Analysis
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Self-supervised learning models for speech processing, such as wav2vec2, HuBERT, WavLM, and Whisper, generate embeddings that capture both linguistic and paralinguistic information, making it challenging to analyze tone independently of spoken content. In this work, we introduce a method for disentangling paralinguistic features from linguistic content by regressing speech embeddings onto their corresponding text embeddings and using the residuals as a representation of vocal tone. We evaluate this approach across multiple self-supervised speech embeddings, demonstrating that residual embeddings significantly improve tone classification performance compared to raw speech embeddings. Our results show that this method enhances linear separability, enabling improved classification even with simple models such as logistic regression. Visualization of the residual embeddings further confirms the successful removal of linguistic information while preserving tone-related features. These findings highlight the potential of residual embeddings for applications in sentiment analysis, speaker characterization, and paralinguistic speech processing.
Enriching Datasets with Demographics through Large Language Models: What's in a Name?
Sep 17, 2024Abstract:Enriching datasets with demographic information, such as gender, race, and age from names, is a critical task in fields like healthcare, public policy, and social sciences. Such demographic insights allow for more precise and effective engagement with target populations. Despite previous efforts employing hidden Markov models and recurrent neural networks to predict demographics from names, significant limitations persist: the lack of large-scale, well-curated, unbiased, publicly available datasets, and the lack of an approach robust across datasets. This scarcity has hindered the development of traditional supervised learning approaches. In this paper, we demonstrate that the zero-shot capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) can perform as well as, if not better than, bespoke models trained on specialized data. We apply these LLMs to a variety of datasets, including a real-life, unlabelled dataset of licensed financial professionals in Hong Kong, and critically assess the inherent demographic biases in these models. Our work not only advances the state-of-the-art in demographic enrichment but also opens avenues for future research in mitigating biases in LLMs.
cCorrGAN: Conditional Correlation GAN for Learning Empirical Conditional Distributions in the Elliptope
Jul 22, 2021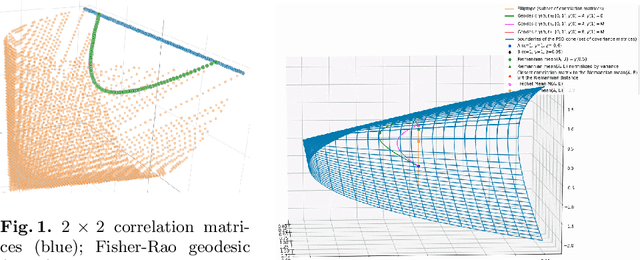
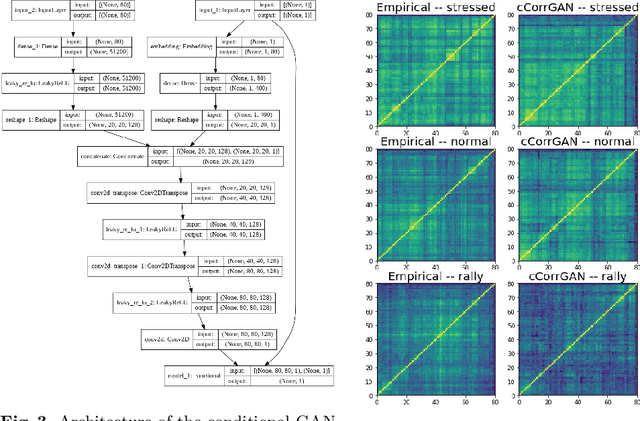
Abstract:We propose a methodology to approximate conditional distributions in the elliptope of correlation matrices based on conditional generative adversarial networks. We illustrate the methodology with an application from quantitative finance: Monte Carlo simulations of correlated returns to compare risk-based portfolio construction methods. Finally, we discuss about current limitations and advocate for further exploration of the elliptope geometry to improve results.
* International Conference on Geometric Science of Information
CorrGAN: Sampling Realistic Financial Correlation Matrices Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Oct 21, 2019



Abstract:We propose a novel approach for sampling realistic financial correlation matrices. This approach is based on generative adversarial networks. Experiments demonstrate that generative adversarial networks are able to recover most of the known stylized facts about empirical correlation matrices estimated on asset returns. This is the first time such results are documented in the literature. Practical financial applications range from trading strategies enhancement to risk and portfolio stress testing. Such generative models can also help ground empirical finance deeper into science by allowing for falsifiability of statements and more objective comparison of empirical methods.
Autoregressive Convolutional Neural Networks for Asynchronous Time Series
Jun 12, 2018



Abstract:We propose Significance-Offset Convolutional Neural Network, a deep convolutional network architecture for regression of multivariate asynchronous time series. The model is inspired by standard autoregressive (AR) models and gating mechanisms used in recurrent neural networks. It involves an AR-like weighting system, where the final predictor is obtained as a weighted sum of adjusted regressors, while the weights are datadependent functions learnt through a convolutional network. The architecture was designed for applications on asynchronous time series and is evaluated on such datasets: a hedge fund proprietary dataset of over 2 million quotes for a credit derivative index, an artificially generated noisy autoregressive series and UCI household electricity consumption dataset. The proposed architecture achieves promising results as compared to convolutional and recurrent neural networks.
Putting Self-Supervised Token Embedding on the Tables
Oct 25, 2017



Abstract:Information distribution by electronic messages is a privileged means of transmission for many businesses and individuals, often under the form of plain-text tables. As their number grows, it becomes necessary to use an algorithm to extract text and numbers instead of a human. Usual methods are focused on regular expressions or on a strict structure in the data, but are not efficient when we have many variations, fuzzy structure or implicit labels. In this paper we introduce SC2T, a totally self-supervised model for constructing vector representations of tokens in semi-structured messages by using characters and context levels that address these issues. It can then be used for an unsupervised labeling of tokens, or be the basis for a semi-supervised information extraction system.
Optimal Transport vs. Fisher-Rao distance between Copulas for Clustering Multivariate Time Series
Nov 14, 2016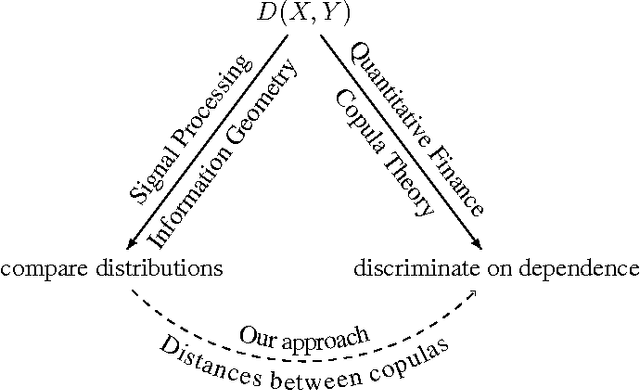
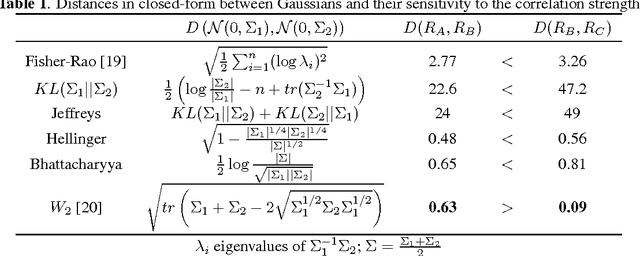
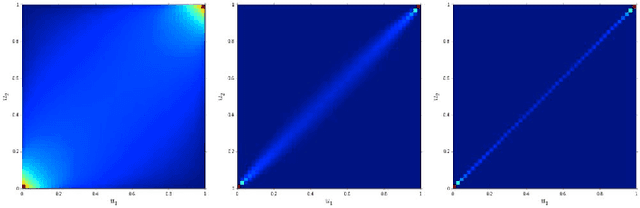
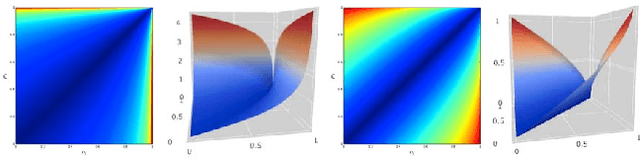
Abstract:We present a methodology for clustering N objects which are described by multivariate time series, i.e. several sequences of real-valued random variables. This clustering methodology leverages copulas which are distributions encoding the dependence structure between several random variables. To take fully into account the dependence information while clustering, we need a distance between copulas. In this work, we compare renowned distances between distributions: the Fisher-Rao geodesic distance, related divergences and optimal transport, and discuss their advantages and disadvantages. Applications of such methodology can be found in the clustering of financial assets. A tutorial, experiments and implementation for reproducible research can be found at www.datagrapple.com/Tech.
Exploring and measuring non-linear correlations: Copulas, Lightspeed Transportation and Clustering
Oct 30, 2016



Abstract:We propose a methodology to explore and measure the pairwise correlations that exist between variables in a dataset. The methodology leverages copulas for encoding dependence between two variables, state-of-the-art optimal transport for providing a relevant geometry to the copulas, and clustering for summarizing the main dependence patterns found between the variables. Some of the clusters centers can be used to parameterize a novel dependence coefficient which can target or forget specific dependence patterns. Finally, we illustrate and benchmark the methodology on several datasets. Code and numerical experiments are available online for reproducible research.
Clustering Financial Time Series: How Long is Enough?
Apr 14, 2016



Abstract:Researchers have used from 30 days to several years of daily returns as source data for clustering financial time series based on their correlations. This paper sets up a statistical framework to study the validity of such practices. We first show that clustering correlated random variables from their observed values is statistically consistent. Then, we also give a first empirical answer to the much debated question: How long should the time series be? If too short, the clusters found can be spurious; if too long, dynamics can be smoothed out.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge