Kevin Murphy
Google Brain
Joint Learning of Hierarchical Neural Options and Abstract World Model
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Building agents that can perform new skills by composing existing skills is a long-standing goal of AI agent research. Towards this end, we investigate how to efficiently acquire a sequence of skills, formalized as hierarchical neural options. However, existing model-free hierarchical reinforcement algorithms need a lot of data. We propose a novel method, which we call AgentOWL (Option and World model Learning Agent), that jointly learns -- in a sample efficient way -- an abstract world model (abstracting across both states and time) and a set of hierarchical neural options. We show, on a subset of Object-Centric Atari games, that our method can learn more skills using much less data than baseline methods.
Scalable Generalized Bayesian Online Neural Network Training for Sequential Decision Making
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:We introduce scalable algorithms for online learning and generalized Bayesian inference of neural network parameters, designed for sequential decision making tasks. Our methods combine the strengths of frequentist and Bayesian filtering, which include fast low-rank updates via a block-diagonal approximation of the parameter error covariance, and a well-defined posterior predictive distribution that we use for decision making. More precisely, our main method updates a low-rank error covariance for the hidden layers parameters, and a full-rank error covariance for the final layer parameters. Although this characterizes an improper posterior, we show that the resulting posterior predictive distribution is well-defined. Our methods update all network parameters online, with no need for replay buffers or offline retraining. We show, empirically, that our methods achieve a competitive tradeoff between speed and accuracy on (non-stationary) contextual bandit problems and Bayesian optimization problems.
Direct Motion Models for Assessing Generated Videos
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:A current limitation of video generative video models is that they generate plausible looking frames, but poor motion -- an issue that is not well captured by FVD and other popular methods for evaluating generated videos. Here we go beyond FVD by developing a metric which better measures plausible object interactions and motion. Our novel approach is based on auto-encoding point tracks and yields motion features that can be used to not only compare distributions of videos (as few as one generated and one ground truth, or as many as two datasets), but also for evaluating motion of single videos. We show that using point tracks instead of pixel reconstruction or action recognition features results in a metric which is markedly more sensitive to temporal distortions in synthetic data, and can predict human evaluations of temporal consistency and realism in generated videos obtained from open-source models better than a wide range of alternatives. We also show that by using a point track representation, we can spatiotemporally localize generative video inconsistencies, providing extra interpretability of generated video errors relative to prior work. An overview of the results and link to the code can be found on the project page: http://trajan-paper.github.io.
Distributional Diffusion Models with Scoring Rules
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models generate high-quality synthetic data. They operate by defining a continuous-time forward process which gradually adds Gaussian noise to data until fully corrupted. The corresponding reverse process progressively "denoises" a Gaussian sample into a sample from the data distribution. However, generating high-quality outputs requires many discretization steps to obtain a faithful approximation of the reverse process. This is expensive and has motivated the development of many acceleration methods. We propose to accomplish sample generation by learning the posterior {\em distribution} of clean data samples given their noisy versions, instead of only the mean of this distribution. This allows us to sample from the probability transitions of the reverse process on a coarse time scale, significantly accelerating inference with minimal degradation of the quality of the output. This is accomplished by replacing the standard regression loss used to estimate conditional means with a scoring rule. We validate our method on image and robot trajectory generation, where we consistently outperform standard diffusion models at few discretization steps.
Reinforcement Learning: An Overview
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:This manuscript gives a big-picture, up-to-date overview of the field of (deep) reinforcement learning and sequential decision making, covering value-based RL, policy-gradient methods, model-based methods, and various other topics (including a very brief discussion of RL+LLMs).
Towards a Mechanistic Explanation of Diffusion Model Generalization
Nov 28, 2024Abstract:We propose a mechanism for diffusion generalization based on local denoising operations. Through analysis of network and empirical denoisers, we identify local inductive biases in diffusion models. We demonstrate that local denoising operations can be used to approximate the optimal diffusion denoiser. Using a collection of patch-based, local empirical denoisers, we construct a denoiser which approximates the generalization behaviour of diffusion model denoisers over forward and reverse diffusion processes.
BONE: a unifying framework for Bayesian online learning in non-stationary environments
Nov 15, 2024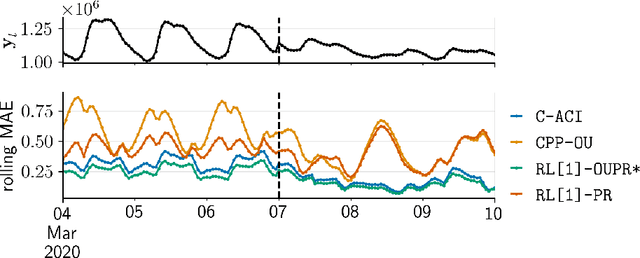
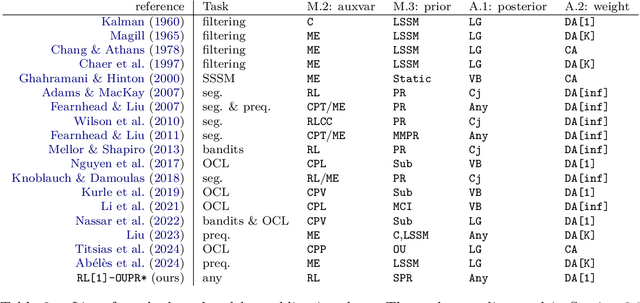
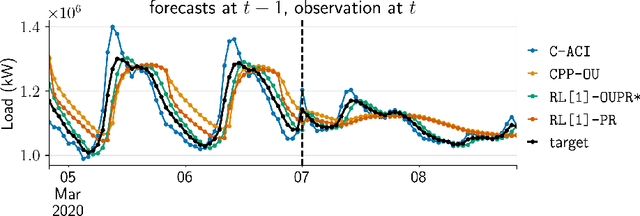
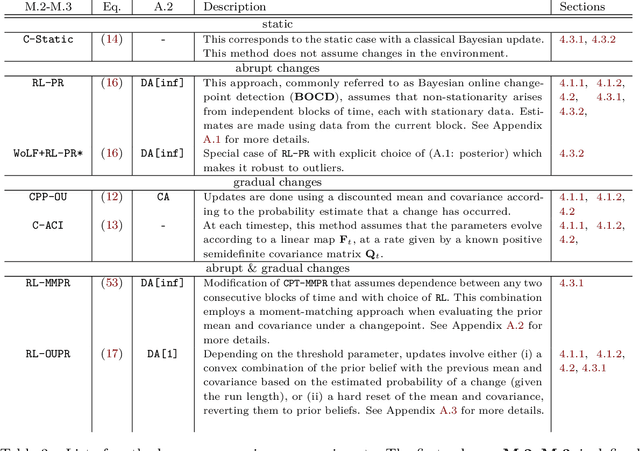
Abstract:We propose a unifying framework for methods that perform Bayesian online learning in non-stationary environments. We call the framework BONE, which stands for (B)ayesian (O)nline learning in (N)on-stationary (E)nvironments. BONE provides a common structure to tackle a variety of problems, including online continual learning, prequential forecasting, and contextual bandits. The framework requires specifying three modelling choices: (i) a model for measurements (e.g., a neural network), (ii) an auxiliary process to model non-stationarity (e.g., the time since the last changepoint), and (iii) a conditional prior over model parameters (e.g., a multivariate Gaussian). The framework also requires two algorithmic choices, which we use to carry out approximate inference under this framework: (i) an algorithm to estimate beliefs (posterior distribution) about the model parameters given the auxiliary variable, and (ii) an algorithm to estimate beliefs about the auxiliary variable. We show how this modularity allows us to write many different existing methods as instances of BONE; we also use this framework to propose a new method. We then experimentally compare existing methods with our proposed new method on several datasets; we provide insights into the situations that make one method more suitable than another for a given task.
Collage: Decomposable Rapid Prototyping for Information Extraction on Scientific PDFs
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Recent years in NLP have seen the continued development of domain-specific information extraction tools for scientific documents, alongside the release of increasingly multimodal pretrained transformer models. While the opportunity for scientists outside of NLP to evaluate and apply such systems to their own domains has never been clearer, these models are difficult to compare: they accept different input formats, are often black-box and give little insight into processing failures, and rarely handle PDF documents, the most common format of scientific publication. In this work, we present Collage, a tool designed for rapid prototyping, visualization, and evaluation of different information extraction models on scientific PDFs. Collage allows the use and evaluation of any HuggingFace token classifier, several LLMs, and multiple other task-specific models out of the box, and provides extensible software interfaces to accelerate experimentation with new models. Further, we enable both developers and users of NLP-based tools to inspect, debug, and better understand modeling pipelines by providing granular views of intermediate states of processing. We demonstrate our system in the context of information extraction to assist with literature review in materials science.
Diffusion Model Predictive Control
Oct 07, 2024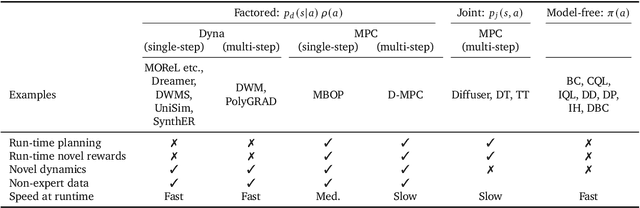
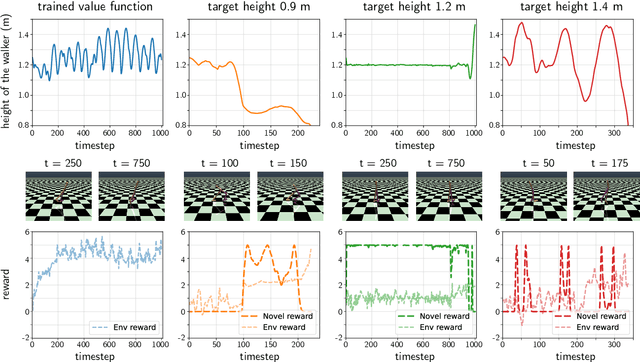
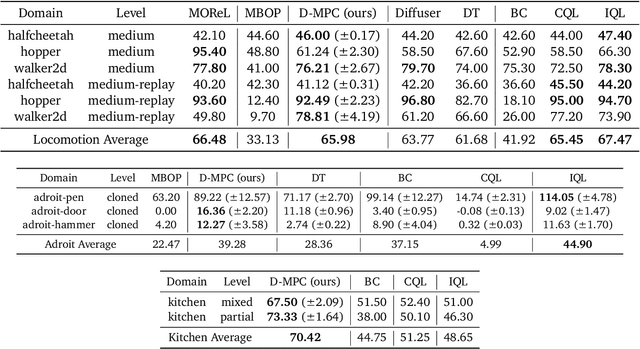
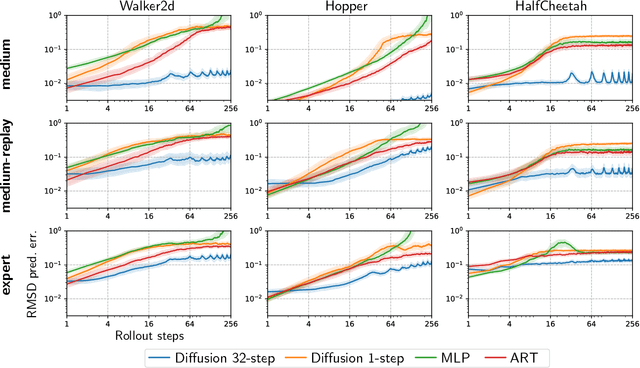
Abstract:We propose Diffusion Model Predictive Control (D-MPC), a novel MPC approach that learns a multi-step action proposal and a multi-step dynamics model, both using diffusion models, and combines them for use in online MPC. On the popular D4RL benchmark, we show performance that is significantly better than existing model-based offline planning methods using MPC and competitive with state-of-the-art (SOTA) model-based and model-free reinforcement learning methods. We additionally illustrate D-MPC's ability to optimize novel reward functions at run time and adapt to novel dynamics, and highlight its advantages compared to existing diffusion-based planning baselines.
DMC-VB: A Benchmark for Representation Learning for Control with Visual Distractors
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Learning from previously collected data via behavioral cloning or offline reinforcement learning (RL) is a powerful recipe for scaling generalist agents by avoiding the need for expensive online learning. Despite strong generalization in some respects, agents are often remarkably brittle to minor visual variations in control-irrelevant factors such as the background or camera viewpoint. In this paper, we present theDeepMind Control Visual Benchmark (DMC-VB), a dataset collected in the DeepMind Control Suite to evaluate the robustness of offline RL agents for solving continuous control tasks from visual input in the presence of visual distractors. In contrast to prior works, our dataset (a) combines locomotion and navigation tasks of varying difficulties, (b) includes static and dynamic visual variations, (c) considers data generated by policies with different skill levels, (d) systematically returns pairs of state and pixel observation, (e) is an order of magnitude larger, and (f) includes tasks with hidden goals. Accompanying our dataset, we propose three benchmarks to evaluate representation learning methods for pretraining, and carry out experiments on several recently proposed methods. First, we find that pretrained representations do not help policy learning on DMC-VB, and we highlight a large representation gap between policies learned on pixel observations and on states. Second, we demonstrate when expert data is limited, policy learning can benefit from representations pretrained on (a) suboptimal data, and (b) tasks with stochastic hidden goals. Our dataset and benchmark code to train and evaluate agents are available at: https://github.com/google-deepmind/dmc_vision_benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge