Jianlong Chang
A Survey of Generative Techniques for Spatial-Temporal Data Mining
May 15, 2024



Abstract:This paper focuses on the integration of generative techniques into spatial-temporal data mining, considering the significant growth and diverse nature of spatial-temporal data. With the advancements in RNNs, CNNs, and other non-generative techniques, researchers have explored their application in capturing temporal and spatial dependencies within spatial-temporal data. However, the emergence of generative techniques such as LLMs, SSL, Seq2Seq and diffusion models has opened up new possibilities for enhancing spatial-temporal data mining further. The paper provides a comprehensive analysis of generative technique-based spatial-temporal methods and introduces a standardized framework specifically designed for the spatial-temporal data mining pipeline. By offering a detailed review and a novel taxonomy of spatial-temporal methodology utilizing generative techniques, the paper enables a deeper understanding of the various techniques employed in this field. Furthermore, the paper highlights promising future research directions, urging researchers to delve deeper into spatial-temporal data mining. It emphasizes the need to explore untapped opportunities and push the boundaries of knowledge to unlock new insights and improve the effectiveness and efficiency of spatial-temporal data mining. By integrating generative techniques and providing a standardized framework, the paper contributes to advancing the field and encourages researchers to explore the vast potential of generative techniques in spatial-temporal data mining.
When Parameter-efficient Tuning Meets General-purpose Vision-language Models
Dec 16, 2023



Abstract:Instruction tuning has shown promising potential for developing general-purpose AI capabilities by using large-scale pre-trained models and boosts growing research to integrate multimodal information for creative applications. However, existing works still face two main limitations: the high training costs and heavy computing resource dependence of full model fine-tuning, and the lack of semantic information in instructions, which hinders multimodal alignment. Addressing these challenges, this paper proposes a novel approach to utilize Parameter-Efficient Tuning for generAl-purpose vision-Language models, namely PETAL. PETAL revolutionizes the training process by requiring only 0.5% of the total parameters, achieved through a unique mode approximation technique, which significantly reduces the training costs and reliance on heavy computing resources. Furthermore, PETAL enhances the semantic depth of instructions in two innovative ways: 1) by introducing adaptive instruction mixture-of-experts(MOEs), and 2) by fortifying the score-based linkage between parameter-efficient tuning and mutual information. Our extensive experiments across five multimodal downstream benchmarks reveal that PETAL not only outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in most scenarios but also surpasses full fine-tuning models in effectiveness. Additionally, our approach demonstrates remarkable advantages in few-shot settings, backed by comprehensive visualization analyses. Our source code is available at: https://github. com/melonking32/PETAL.
Towards AGI in Computer Vision: Lessons Learned from GPT and Large Language Models
Jun 14, 2023



Abstract:The AI community has been pursuing algorithms known as artificial general intelligence (AGI) that apply to any kind of real-world problem. Recently, chat systems powered by large language models (LLMs) emerge and rapidly become a promising direction to achieve AGI in natural language processing (NLP), but the path towards AGI in computer vision (CV) remains unclear. One may owe the dilemma to the fact that visual signals are more complex than language signals, yet we are interested in finding concrete reasons, as well as absorbing experiences from GPT and LLMs to solve the problem. In this paper, we start with a conceptual definition of AGI and briefly review how NLP solves a wide range of tasks via a chat system. The analysis inspires us that unification is the next important goal of CV. But, despite various efforts in this direction, CV is still far from a system like GPT that naturally integrates all tasks. We point out that the essential weakness of CV lies in lacking a paradigm to learn from environments, yet NLP has accomplished the task in the text world. We then imagine a pipeline that puts a CV algorithm (i.e., an agent) in world-scale, interactable environments, pre-trains it to predict future frames with respect to its action, and then fine-tunes it with instruction to accomplish various tasks. We expect substantial research and engineering efforts to push the idea forward and scale it up, for which we share our perspectives on future research directions.
Mode Approximation Makes Good Multimodal Prompts
May 23, 2023Abstract:Driven by the progress of large-scale pre-training, parameter-efficient transfer learning has gained immense popularity across different subfields of Artificial Intelligence. The core is to adapt the model to downstream tasks with only a small set of parameters. Recently, researchers have leveraged such proven techniques in multimodal tasks and achieve promising results. However, two critical issues remain unresolved: how to further reduce the complexity with lightweight design and how to boost alignment between modalities under extremely low parameters. In this paper, we propose A graceful prompt framework for cross-modal transfer (Aurora) to overcome these challenges. Considering the redundancy in existing architectures, we first utilize the mode approximation to generate 0.1M trainable parameters to implement the multimodal prompt tuning, which explores the low intrinsic dimension with only 0.04% parameters of the pre-trained model. Then, for better modality alignment, we propose the Informative Context Enhancement and Gated Query Transformation module under extremely few parameters scenes. A thorough evaluation on six cross-modal benchmarks shows that it not only outperforms the state-of-the-art but even outperforms the full fine-tuning approach. Our code is available at: https://github.com/WillDreamer/Aurora.
Visual Tuning
May 10, 2023Abstract:Fine-tuning visual models has been widely shown promising performance on many downstream visual tasks. With the surprising development of pre-trained visual foundation models, visual tuning jumped out of the standard modus operandi that fine-tunes the whole pre-trained model or just the fully connected layer. Instead, recent advances can achieve superior performance than full-tuning the whole pre-trained parameters by updating far fewer parameters, enabling edge devices and downstream applications to reuse the increasingly large foundation models deployed on the cloud. With the aim of helping researchers get the full picture and future directions of visual tuning, this survey characterizes a large and thoughtful selection of recent works, providing a systematic and comprehensive overview of existing work and models. Specifically, it provides a detailed background of visual tuning and categorizes recent visual tuning techniques into five groups: prompt tuning, adapter tuning, parameter tuning, and remapping tuning. Meanwhile, it offers some exciting research directions for prospective pre-training and various interactions in visual tuning.
LION: Implicit Vision Prompt Tuning
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Despite recent competitive performance across a range of vision tasks, vision Transformers still have an issue of heavy computational costs. Recently, vision prompt learning has provided an economic solution to this problem without fine-tuning the whole large-scale models. However, the efficiency of existing models are still far from satisfactory due to insertion of extensive prompts blocks and trick prompt designs. In this paper, we propose an efficient vision model named impLicit vIsion prOmpt tuNing (LION), which is motivated by deep implicit models with stable memory costs for various complex tasks. In particular, we merely insect two equilibrium implicit layers in two ends of the pre-trained main backbone with parameters in the backbone frozen. Moreover, we prune the parameters in these two layers according to lottery hypothesis. The performance obtained by our LION are promising on a wide range of datasets. In particular, our LION reduces up to 11.5% of training parameter numbers while obtaining higher performance compared with the state-of-the-art baseline VPT, especially under challenging scenes. Furthermore, we find that our proposed LION had a good generalization performance, making it an easy way to boost transfer learning in the future.
Constraint and Union for Partially-Supervised Temporal Sentence Grounding
Feb 20, 2023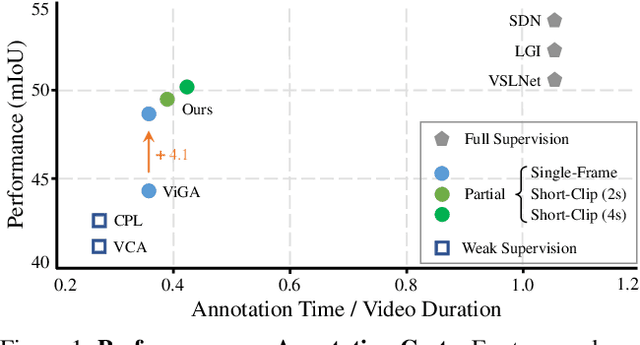

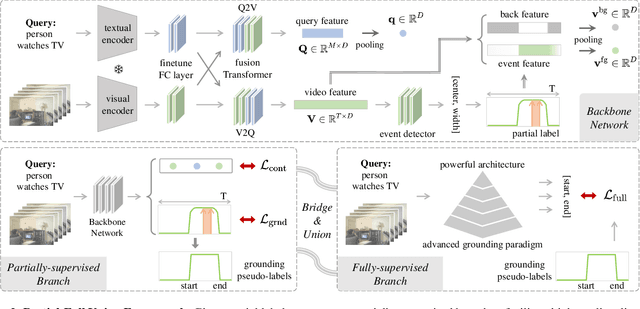

Abstract:Temporal sentence grounding aims to detect the event timestamps described by the natural language query from given untrimmed videos. The existing fully-supervised setting achieves great performance but requires expensive annotation costs; while the weakly-supervised setting adopts cheap labels but performs poorly. To pursue high performance with less annotation cost, this paper introduces an intermediate partially-supervised setting, i.e., only short-clip or even single-frame labels are available during training. To take full advantage of partial labels, we propose a novel quadruple constraint pipeline to comprehensively shape event-query aligned representations, covering intra- and inter-samples, uni- and multi-modalities. The former raises intra-cluster compactness and inter-cluster separability; while the latter enables event-background separation and event-query gather. To achieve more powerful performance with explicit grounding optimization, we further introduce a partial-full union framework, i.e., bridging with an additional fully-supervised branch, to enjoy its impressive grounding bonus, and be robust to partial annotations. Extensive experiments and ablations on Charades-STA and ActivityNet Captions demonstrate the significance of partial supervision and our superior performance.
Distilling Vision-Language Pre-training to Collaborate with Weakly-Supervised Temporal Action Localization
Dec 19, 2022



Abstract:Weakly-supervised temporal action localization (WTAL) learns to detect and classify action instances with only category labels. Most methods widely adopt the off-the-shelf Classification-Based Pre-training (CBP) to generate video features for action localization. However, the different optimization objectives between classification and localization, make temporally localized results suffer from the serious incomplete issue. To tackle this issue without additional annotations, this paper considers to distill free action knowledge from Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP), since we surprisingly observe that the localization results of vanilla VLP have an over-complete issue, which is just complementary to the CBP results. To fuse such complementarity, we propose a novel distillation-collaboration framework with two branches acting as CBP and VLP respectively. The framework is optimized through a dual-branch alternate training strategy. Specifically, during the B step, we distill the confident background pseudo-labels from the CBP branch; while during the F step, the confident foreground pseudo-labels are distilled from the VLP branch. And as a result, the dual-branch complementarity is effectively fused to promote a strong alliance. Extensive experiments and ablation studies on THUMOS14 and ActivityNet1.2 reveal that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
OhMG: Zero-shot Open-vocabulary Human Motion Generation
Oct 28, 2022



Abstract:Generating motion in line with text has attracted increasing attention nowadays. However, open-vocabulary human motion generation still remains touchless and undergoes the lack of diverse labeled data. The good news is that, recent studies of large multi-model foundation models (e.g., CLIP) have demonstrated superior performance on few/zero-shot image-text alignment, largely reducing the need for manually labeled data. In this paper, we take advantage of CLIP for open-vocabulary 3D human motion generation in a zero-shot manner. Specifically, our model is composed of two stages, i.e., text2pose and pose2motion. For text2pose, to address the difficulty of optimization with direct supervision from CLIP, we propose to carve the versatile CLIP model into a slimmer but more specific model for aligning 3D poses and texts, via a novel pipeline distillation strategy. Optimizing with the distilled 3D pose-text model, we manage to concretize the text-pose knowledge of CLIP into a text2pose generator effectively and efficiently. As for pose2motion, drawing inspiration from the advanced language model, we pretrain a transformer-based motion model, which makes up for the lack of motion dynamics of CLIP. After that, by formulating the generated poses from the text2pose stage as prompts, the motion generator can generate motions referring to the poses in a controllable and flexible manner. Our method is validated against advanced baselines and obtains sharp improvements. The code will be released here.
Towards a Unified View on Visual Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning
Oct 03, 2022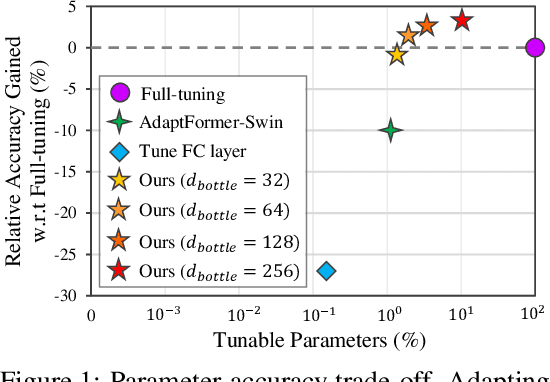
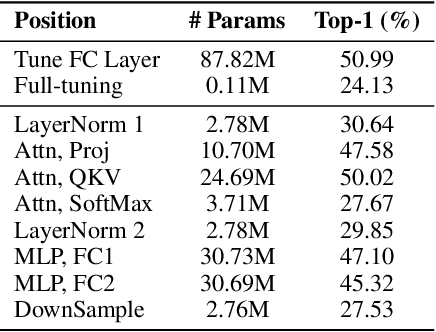
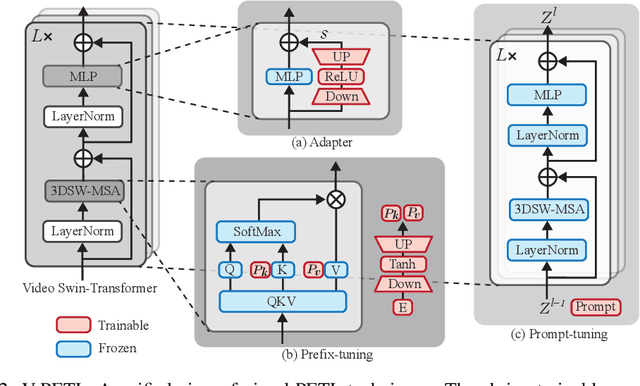
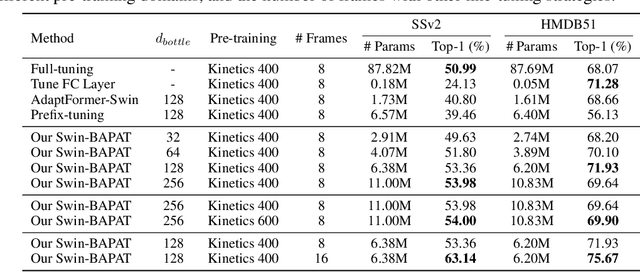
Abstract:Since the release of various large-scale natural language processing (NLP) pre-trained models, parameter efficient transfer learning (PETL) has become a popular paradigm capable of achieving impressive performance on various downstream tasks. PETL aims at making good use of the representation knowledge in the pre-trained large models by fine-tuning a small number of parameters. Recently, it has also attracted increasing attention to developing various PETL techniques for vision tasks. Popular PETL techniques such as Prompt-tuning and Adapter have been proposed for high-level visual downstream tasks such as image classification and video recognition. However, Prefix-tuning remains under-explored for vision tasks. In this work, we intend to adapt large video-based models to downstream tasks with a good parameter-accuracy trade-off. Towards this goal, we propose a framework with a unified view called visual-PETL (V-PETL) to investigate the different aspects affecting the trade-off. Specifically, we analyze the positional importance of trainable parameters and differences between NLP and vision tasks in terms of data structures and pre-training mechanisms while implementing various PETL techniques, especially for the under-explored prefix-tuning technique. Based on a comprehensive understanding of differences between NLP and video data, we propose a new variation of prefix-tuning module called parallel attention (PATT) for video-based downstream tasks. An extensive empirical analysis on two video datasets via different frozen backbones has been carried and the findings show that the proposed PATT can effectively contribute to other PETL techniques. An effective scheme Swin-BAPAT derived from the proposed V-PETL framework achieves significantly better performance than the state-of-the-art AdaptFormer-Swin with slightly more parameters and outperforms full-tuning with far less parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge