Peisen Zhao
UMG-CLIP: A Unified Multi-Granularity Vision Generalist for Open-World Understanding
Jan 18, 2024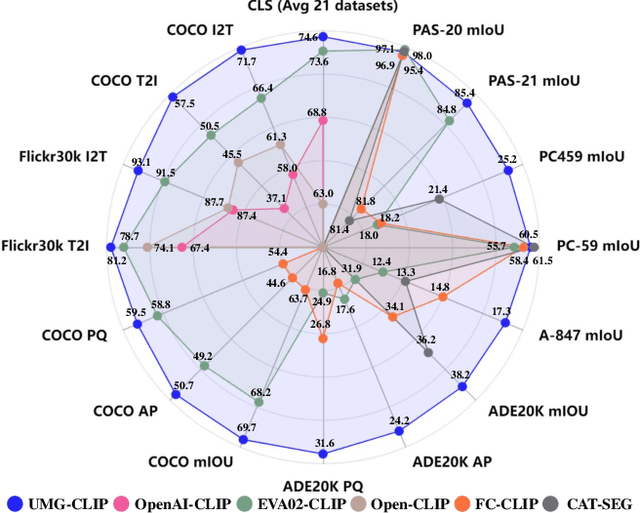
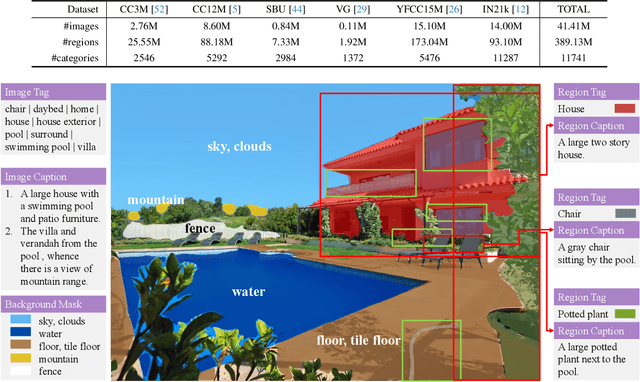
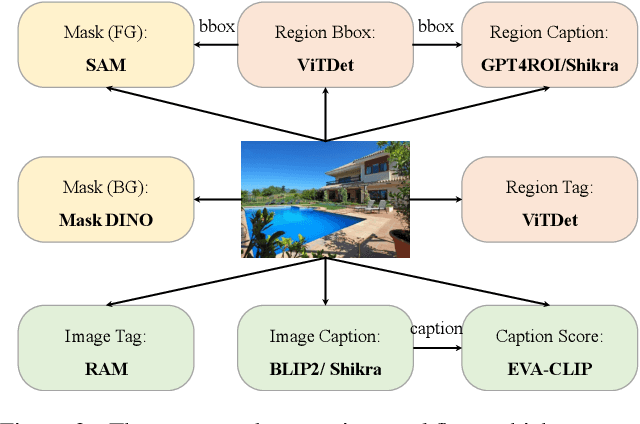
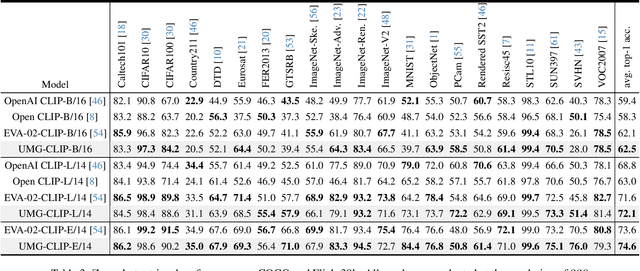
Abstract:Vision-language foundation models, represented by Contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP), have gained increasing attention for jointly understanding both vision and textual tasks. However, existing approaches primarily focus on training models to match global image representations with textual descriptions, thereby overlooking the critical alignment between local regions and corresponding text tokens. This paper extends CLIP with multi-granularity alignment. Notably, we deliberately construct a new dataset comprising pseudo annotations at various levels of granularities, encompassing image-level, region-level, and pixel-level captions/tags. Accordingly, we develop a unified multi-granularity learning framework, named UMG-CLIP, that simultaneously empowers the model with versatile perception abilities across different levels of detail. Equipped with parameter efficient tuning, UMG-CLIP surpasses current widely used CLIP models and achieves state-of-the-art performance on diverse image understanding benchmarks, including open-world recognition, retrieval, semantic segmentation, and panoptic segmentation tasks. We hope UMG-CLIP can serve as a valuable option for advancing vision-language foundation models.
Prune Spatio-temporal Tokens by Semantic-aware Temporal Accumulation
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Transformers have become the primary backbone of the computer vision community due to their impressive performance. However, the unfriendly computation cost impedes their potential in the video recognition domain. To optimize the speed-accuracy trade-off, we propose Semantic-aware Temporal Accumulation score (STA) to prune spatio-temporal tokens integrally. STA score considers two critical factors: temporal redundancy and semantic importance. The former depicts a specific region based on whether it is a new occurrence or a seen entity by aggregating token-to-token similarity in consecutive frames while the latter evaluates each token based on its contribution to the overall prediction. As a result, tokens with higher scores of STA carry more temporal redundancy as well as lower semantics thus being pruned. Based on the STA score, we are able to progressively prune the tokens without introducing any additional parameters or requiring further re-training. We directly apply the STA module to off-the-shelf ViT and VideoSwin backbones, and the empirical results on Kinetics-400 and Something-Something V2 achieve over 30% computation reduction with a negligible ~0.2% accuracy drop. The code is released at https://github.com/Mark12Ding/STA.
Multi-modal Prompting for Low-Shot Temporal Action Localization
Mar 21, 2023
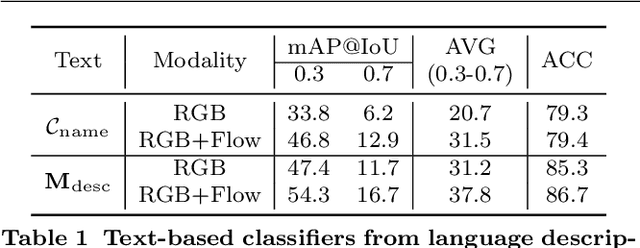
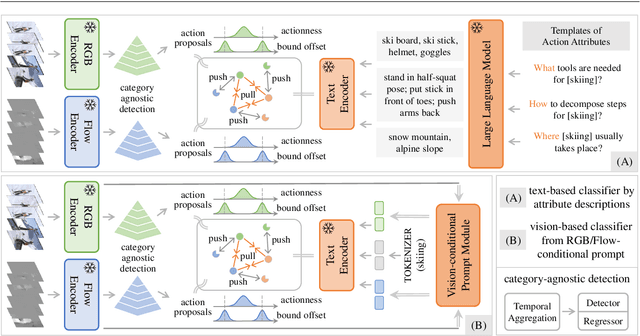
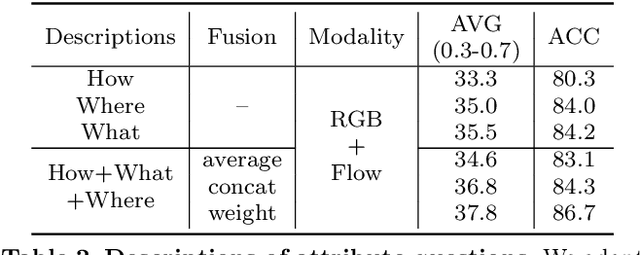
Abstract:In this paper, we consider the problem of temporal action localization under low-shot (zero-shot & few-shot) scenario, with the goal of detecting and classifying the action instances from arbitrary categories within some untrimmed videos, even not seen at training time. We adopt a Transformer-based two-stage action localization architecture with class-agnostic action proposal, followed by open-vocabulary classification. We make the following contributions. First, to compensate image-text foundation models with temporal motions, we improve category-agnostic action proposal by explicitly aligning embeddings of optical flows, RGB and texts, which has largely been ignored in existing low-shot methods. Second, to improve open-vocabulary action classification, we construct classifiers with strong discriminative power, i.e., avoid lexical ambiguities. To be specific, we propose to prompt the pre-trained CLIP text encoder either with detailed action descriptions (acquired from large-scale language models), or visually-conditioned instance-specific prompt vectors. Third, we conduct thorough experiments and ablation studies on THUMOS14 and ActivityNet1.3, demonstrating the superior performance of our proposed model, outperforming existing state-of-the-art approaches by one significant margin.
Constraint and Union for Partially-Supervised Temporal Sentence Grounding
Feb 20, 2023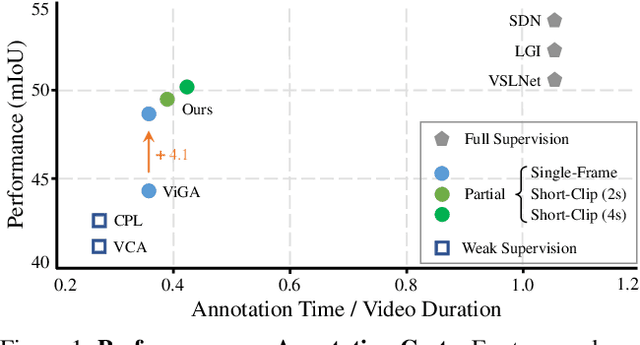

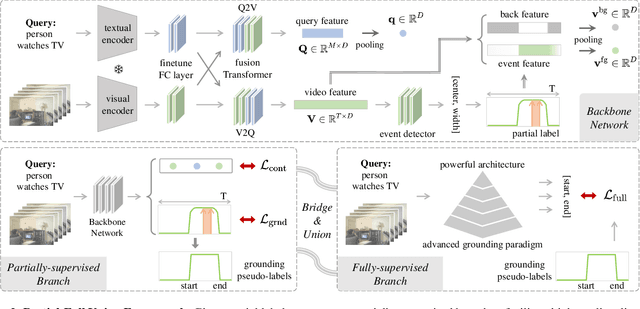

Abstract:Temporal sentence grounding aims to detect the event timestamps described by the natural language query from given untrimmed videos. The existing fully-supervised setting achieves great performance but requires expensive annotation costs; while the weakly-supervised setting adopts cheap labels but performs poorly. To pursue high performance with less annotation cost, this paper introduces an intermediate partially-supervised setting, i.e., only short-clip or even single-frame labels are available during training. To take full advantage of partial labels, we propose a novel quadruple constraint pipeline to comprehensively shape event-query aligned representations, covering intra- and inter-samples, uni- and multi-modalities. The former raises intra-cluster compactness and inter-cluster separability; while the latter enables event-background separation and event-query gather. To achieve more powerful performance with explicit grounding optimization, we further introduce a partial-full union framework, i.e., bridging with an additional fully-supervised branch, to enjoy its impressive grounding bonus, and be robust to partial annotations. Extensive experiments and ablations on Charades-STA and ActivityNet Captions demonstrate the significance of partial supervision and our superior performance.
Distilling Vision-Language Pre-training to Collaborate with Weakly-Supervised Temporal Action Localization
Dec 19, 2022



Abstract:Weakly-supervised temporal action localization (WTAL) learns to detect and classify action instances with only category labels. Most methods widely adopt the off-the-shelf Classification-Based Pre-training (CBP) to generate video features for action localization. However, the different optimization objectives between classification and localization, make temporally localized results suffer from the serious incomplete issue. To tackle this issue without additional annotations, this paper considers to distill free action knowledge from Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP), since we surprisingly observe that the localization results of vanilla VLP have an over-complete issue, which is just complementary to the CBP results. To fuse such complementarity, we propose a novel distillation-collaboration framework with two branches acting as CBP and VLP respectively. The framework is optimized through a dual-branch alternate training strategy. Specifically, during the B step, we distill the confident background pseudo-labels from the CBP branch; while during the F step, the confident foreground pseudo-labels are distilled from the VLP branch. And as a result, the dual-branch complementarity is effectively fused to promote a strong alliance. Extensive experiments and ablation studies on THUMOS14 and ActivityNet1.2 reveal that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Adaptive Mutual Supervision for Weakly-Supervised Temporal Action Localization
Apr 06, 2021



Abstract:Weakly-supervised temporal action localization aims to localize actions in untrimmed videos with only video-level action category labels. Most of previous methods ignore the incompleteness issue of Class Activation Sequences (CAS), suffering from trivial localization results. To solve this issue, we introduce an adaptive mutual supervision framework (AMS) with two branches, where the base branch adopts CAS to localize the most discriminative action regions, while the supplementary branch localizes the less discriminative action regions through a novel adaptive sampler. The adaptive sampler dynamically updates the input of the supplementary branch with a sampling weight sequence negatively correlated with the CAS from the base branch, thereby prompting the supplementary branch to localize the action regions underestimated by the base branch. To promote mutual enhancement between these two branches, we construct mutual location supervision. Each branch leverages location pseudo-labels generated from the other branch as localization supervision. By alternately optimizing the two branches in multiple iterations, we progressively complete action regions. Extensive experiments on THUMOS14 and ActivityNet1.2 demonstrate that the proposed AMS method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods.
Point-Level Temporal Action Localization: Bridging Fully-supervised Proposals to Weakly-supervised Losses
Dec 15, 2020



Abstract:Point-Level temporal action localization (PTAL) aims to localize actions in untrimmed videos with only one timestamp annotation for each action instance. Existing methods adopt the frame-level prediction paradigm to learn from the sparse single-frame labels. However, such a framework inevitably suffers from a large solution space. This paper attempts to explore the proposal-based prediction paradigm for point-level annotations, which has the advantage of more constrained solution space and consistent predictions among neighboring frames. The point-level annotations are first used as the keypoint supervision to train a keypoint detector. At the location prediction stage, a simple but effective mapper module, which enables back-propagation of training errors, is then introduced to bridge the fully-supervised framework with weak supervision. To our best of knowledge, this is the first work to leverage the fully-supervised paradigm for the point-level setting. Experiments on THUMOS14, BEOID, and GTEA verify the effectiveness of our proposed method both quantitatively and qualitatively, and demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Privileged Knowledge Distillation for Online Action Detection
Dec 03, 2020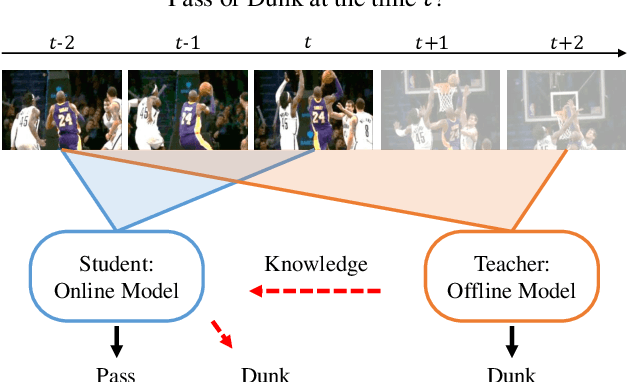
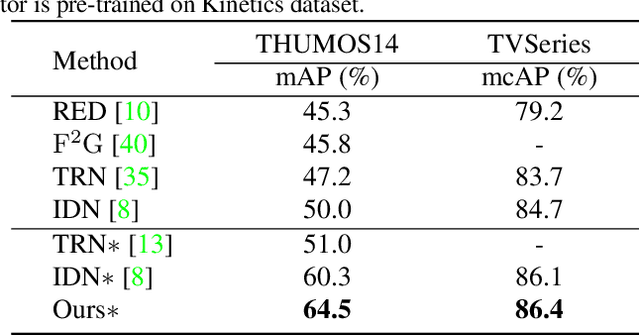
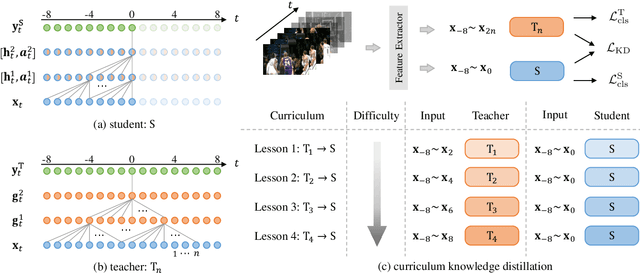
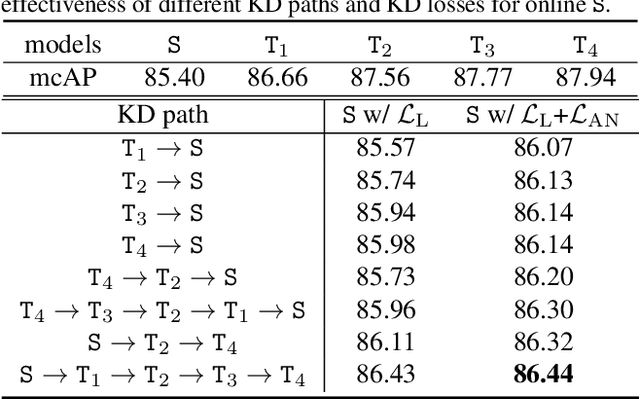
Abstract:Online Action Detection (OAD) in videos is proposed as a per-frame labeling task to address the real-time prediction tasks that can only obtain the previous and current video frames. This paper presents a novel learning-with-privileged based framework for online action detection where the future frames only observable at the training stages are considered as a form of privileged information. Knowledge distillation is employed to transfer the privileged information from the offline teacher to the online student. We note that this setting is different from conventional KD because the difference between the teacher and student models mostly lies in input data rather than the network architecture. We propose Privileged Knowledge Distillation (PKD) which (i) schedules a curriculum learning procedure and (ii) inserts auxiliary nodes to the student model, both for shrinking the information gap and improving learning performance. Compared to other OAD methods that explicitly predict future frames, our approach avoids learning unpredictable unnecessary yet inconsistent visual contents and achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on two popular OAD benchmarks, TVSeries and THUMOS14.
Universal-to-Specific Framework for Complex Action Recognition
Jul 13, 2020



Abstract:Video-based action recognition has recently attracted much attention in the field of computer vision. To solve more complex recognition tasks, it has become necessary to distinguish different levels of interclass variations. Inspired by a common flowchart based on the human decision-making process that first narrows down the probable classes and then applies a "rethinking" process for finer-level recognition, we propose an effective universal-to-specific (U2S) framework for complex action recognition. The U2S framework is composed of three subnetworks: a universal network, a category-specific network, and a mask network. The universal network first learns universal feature representations. The mask network then generates attention masks for confusing classes through category regularization based on the output of the universal network. The mask is further used to guide the category-specific network for class-specific feature representations. The entire framework is optimized in an end-to-end manner. Experiments on a variety of benchmark datasets, e.g., the Something-Something, UCF101, and HMDB51 datasets, demonstrate the effectiveness of the U2S framework; i.e., U2S can focus on discriminative spatiotemporal regions for confusing categories. We further visualize the relationship between different classes, showing that U2S indeed improves the discriminability of learned features. Moreover, the proposed U2S model is a general framework and may adopt any base recognition network.
Constraining Temporal Relationship for Action Localization
Feb 18, 2020



Abstract:Recently, temporal action localization (TAL), i.e., finding specific action segments in untrimmed videos, has attracted increasing attentions of the computer vision community. State-of-the-art solutions for TAL involves predicting three values at each time point, corresponding to the probabilities that the action starts, continues and ends, and post-processing these curves for the final localization. This paper delves deep into this mechanism, and argues that existing approaches mostly ignored the potential relationship of these curves, and results in low quality of action proposals. To alleviate this problem, we add extra constraints to these curves, e.g., the probability of ''action continues'' should be relatively high between probability peaks of ''action starts'' and ''action ends'', so that the entire framework is aware of these latent constraints during an end-to-end optimization process. Experiments are performed on two popular TAL datasets, THUMOS14 and ActivityNet1.3. Our approach clearly outperforms the baseline both quantitatively (in terms of the AR@AN and mAP) and qualitatively (the curves in the testing stage become much smoother). In particular, when we build our constraints beyond TSA-Net and PGCN, we achieve the state-of-the-art performance especially at strict high IoU settings. The code will be available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge