IEEE
Shallow Network Based on Depthwise Over-Parameterized Convolution for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Dec 01, 2021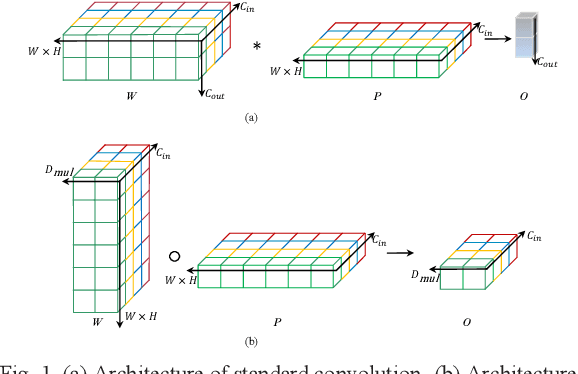
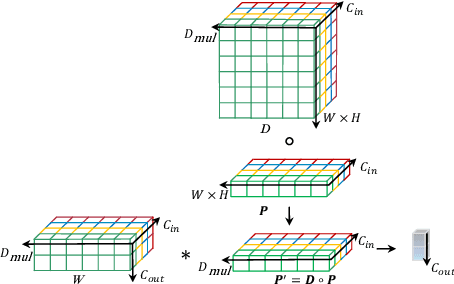
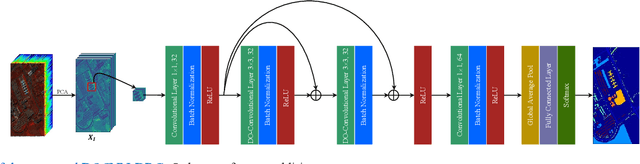
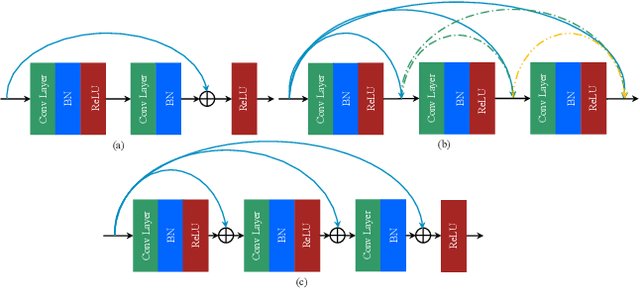
Abstract:Recently, convolutional neural network (CNN) techniques have gained popularity as a tool for hyperspectral image classification (HSIC). To improve the feature extraction efficiency of HSIC under the condition of limited samples, the current methods generally use deep models with plenty of layers. However, deep network models are prone to overfitting and gradient vanishing problems when samples are limited. In addition, the spatial resolution decreases severely with deeper depth, which is very detrimental to spatial edge feature extraction. Therefore, this letter proposes a shallow model for HSIC, which is called depthwise over-parameterized convolutional neural network (DOCNN). To ensure the effective extraction of the shallow model, the depthwise over-parameterized convolution (DO-Conv) kernel is introduced to extract the discriminative features. The depthwise over-parameterized Convolution kernel is composed of a standard convolution kernel and a depthwise convolution kernel, which can extract the spatial feature of the different channels individually and fuse the spatial features of the whole channels simultaneously. Moreover, to further reduce the loss of spatial edge features due to the convolution operation, a dense residual connection (DRC) structure is proposed to apply to the feature extraction part of the whole network. Experimental results obtained from three benchmark data sets show that the proposed method outperforms other state-of-the-art methods in terms of classification accuracy and computational efficiency.
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Using Custom-Designed Convolutional Neural Network
Oct 08, 2021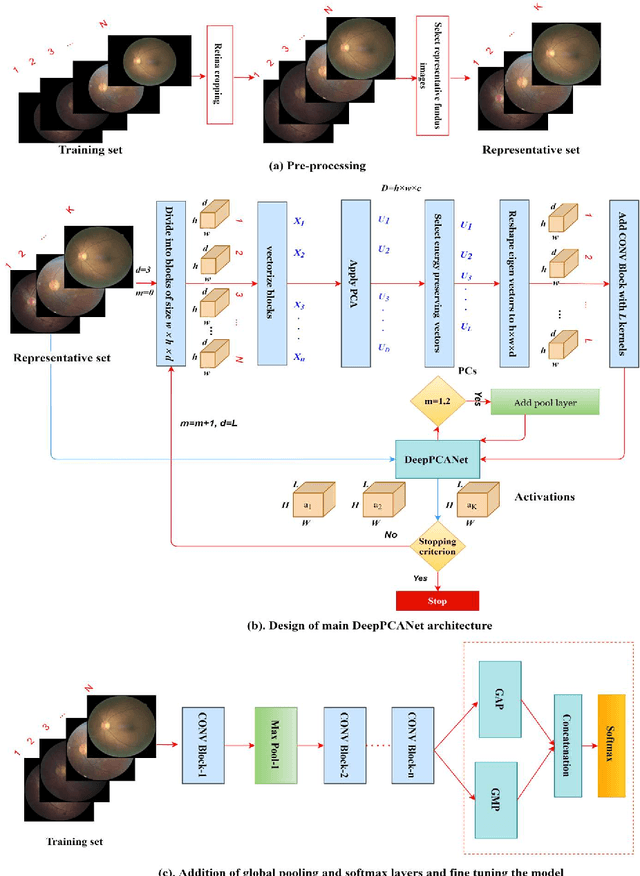
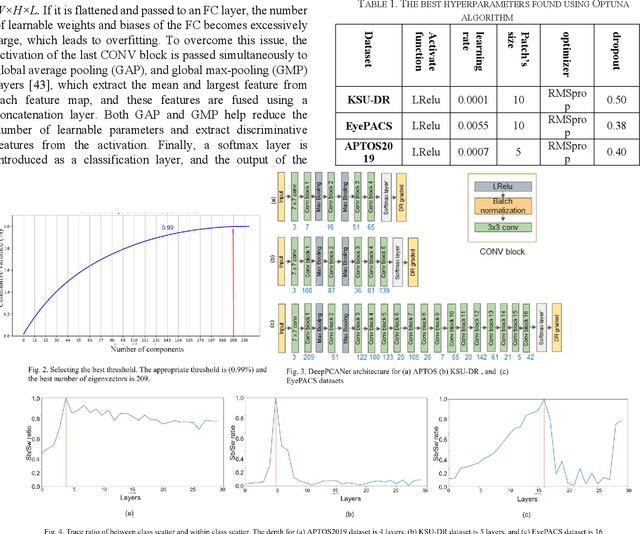
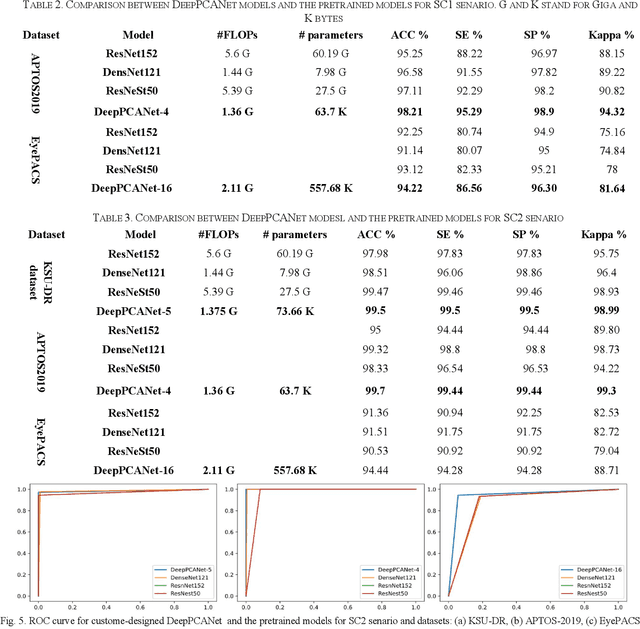
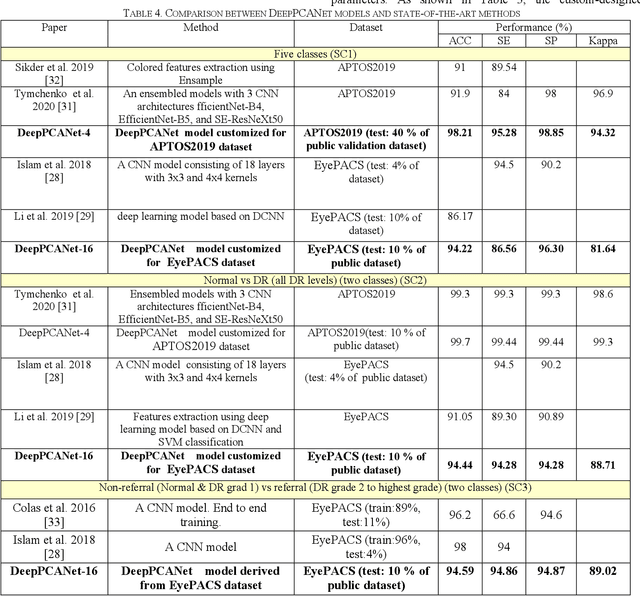
Abstract:The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (DR) has reached 34.6% worldwide and is a major cause of blindness among middle-aged diabetic patients. Regular DR screening using fundus photography helps detect its complications and prevent its progression to advanced levels. As manual screening is time-consuming and subjective, machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) have been employed to aid graders. However, the existing CNN-based methods use either pre-trained CNN models or a brute force approach to design new CNN models, which are not customized to the complexity of fundus images. To overcome this issue, we introduce an approach for custom-design of CNN models, whose architectures are adapted to the structural patterns of fundus images and better represent the DR-relevant features. It takes the leverage of k-medoid clustering, principal component analysis (PCA), and inter-class and intra-class variations to automatically determine the depth and width of a CNN model. The designed models are lightweight, adapted to the internal structures of fundus images, and encode the discriminative patterns of DR lesions. The technique is validated on a local dataset from King Saud University Medical City, Saudi Arabia, and two challenging benchmark datasets from Kaggle: EyePACS and APTOS2019. The custom-designed models outperform the famous pre-trained CNN models like ResNet152, Densnet121, and ResNeSt50 with a significant decrease in the number of parameters and compete well with the state-of-the-art CNN-based DR screening methods. The proposed approach is helpful for DR screening under diverse clinical settings and referring the patients who may need further assessment and treatment to expert ophthalmologists.
A Novel Deep Learning Method for Thermal to Annotated Thermal-Optical Fused Images
Jul 13, 2021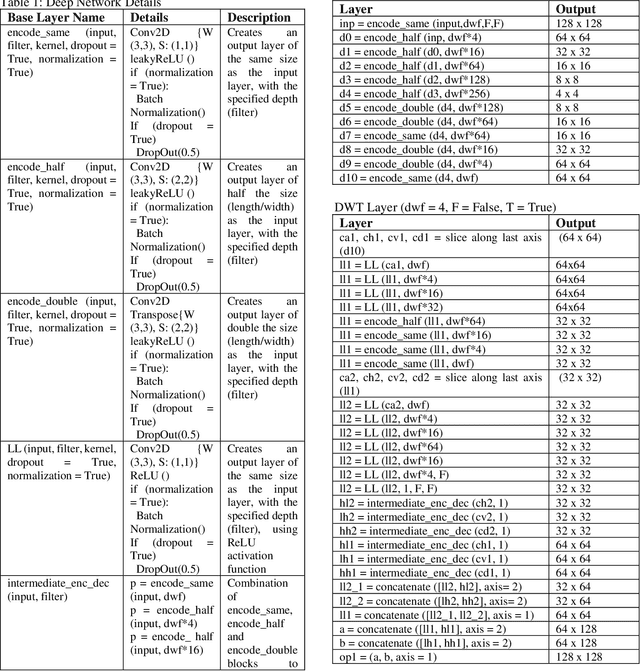
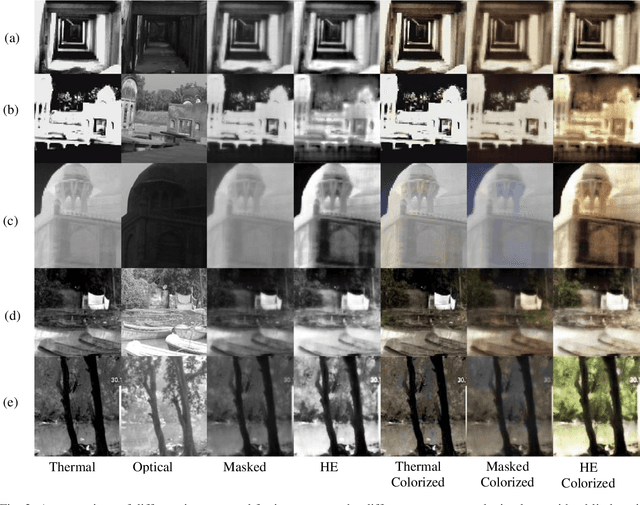


Abstract:Thermal Images profile the passive radiation of objects and capture them in grayscale images. Such images have a very different distribution of data compared to optical colored images. We present here a work that produces a grayscale thermo-optical fused mask given a thermal input. This is a deep learning based pioneering work since to the best of our knowledge, there exists no other work on thermal-optical grayscale fusion. Our method is also unique in the sense that the deep learning method we are proposing here works on the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) domain instead of the gray level domain. As a part of this work, we also present a new and unique database for obtaining the region of interest in thermal images based on an existing thermal visual paired database, containing the Region of Interest on 5 different classes of data. Finally, we are proposing a simple low cost overhead statistical measure for identifying the region of interest in the fused images, which we call as the Region of Fusion (RoF). Experiments on the database show encouraging results in identifying the region of interest in the fused images. We also show that they can be processed better in the mixed form rather than with only thermal images.
Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Optimization for IRS Based UAV-NOMA Downlink Networks
Jun 17, 2021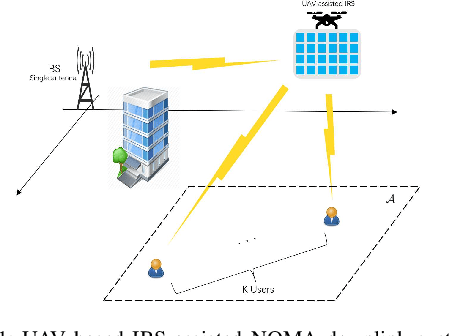
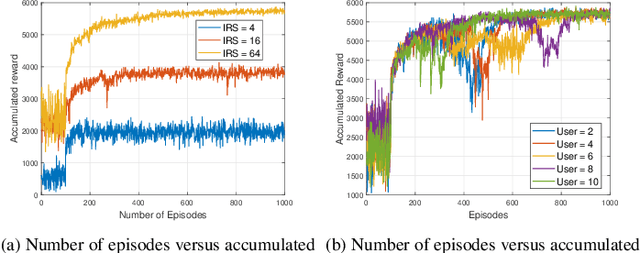
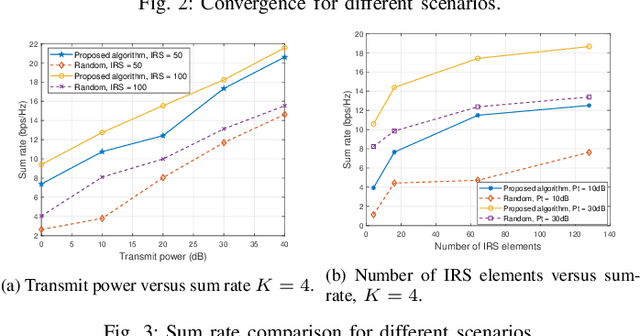
Abstract:This paper investigates the application of deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) to intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) based unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) assisted non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) downlink networks. The deployment of the UAV equipped with an IRS is important, as the UAV increases the flexibility of the IRS significantly, especially for the case of users who have no line of sight (LoS) path to the base station (BS). Therefore, the aim of this letter is to maximize the sum rate by jointly optimizing the power allocation of the BS, the phase shifting of the IRS and the horizontal position of the UAV. Because the formulated problem is not convex, the DDPG algorithm is utilized to solve it. The computer simulation results are provided to show the superior performance of the proposed DDPG based algorithm.
Deep Dual-resolution Networks for Real-time and Accurate Semantic Segmentation of Road Scenes
Jan 15, 2021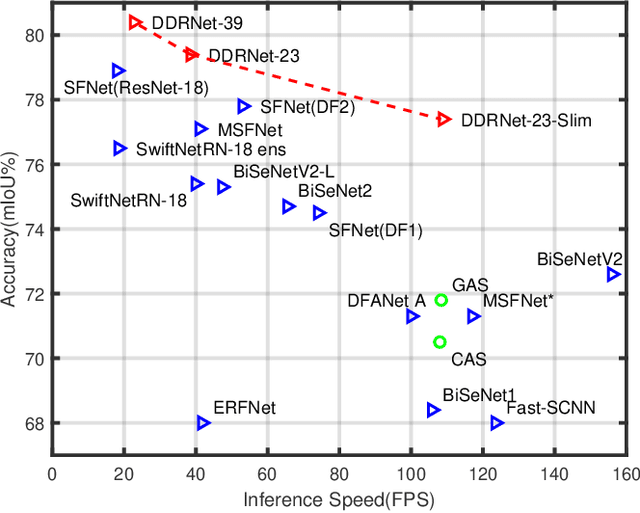
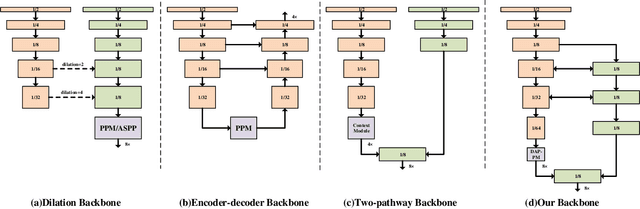
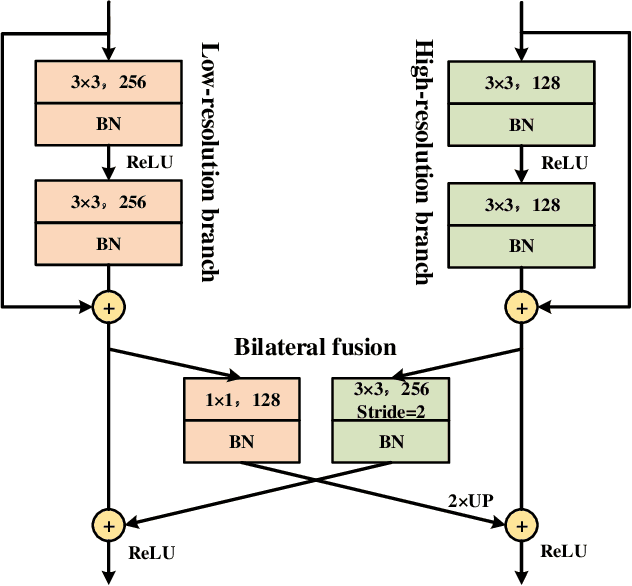
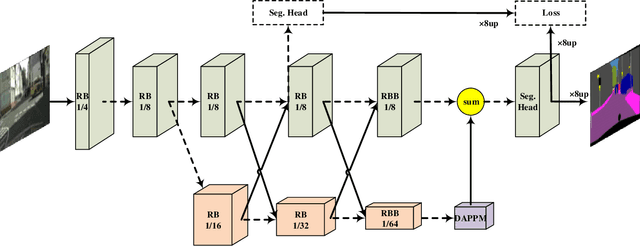
Abstract:Semantic segmentation is a critical technology for autonomous vehicles to understand surrounding scenes. For practical autonomous vehicles, it is undesirable to spend a considerable amount of inference time to achieve high-accuracy segmentation results. Using light-weight architectures (encoder-decoder or two-pathway) or reasoning on low-resolution images, recent methods realize very fast scene parsing which even run at more than 100 FPS on single 1080Ti GPU. However, there are still evident gaps in performance between these real-time methods and models based on dilation backbones. To tackle this problem, we propose novel deep dual-resolution networks (DDRNets) for real-time semantic segmentation of road scenes. Besides, we design a new contextual information extractor named Deep Aggregation Pyramid Pooling Module (DAPPM) to enlarge effective receptive fields and fuse multi-scale context. Our method achieves new state-of-the-art trade-off between accuracy and speed on both Cityscapes and CamVid dataset. Specially, on single 2080Ti GPU, DDRNet-23-slim yields 77.4% mIoU at 109 FPS on Cityscapes test set and 74.4% mIoU at 230 FPS on CamVid test set. Without utilizing attention mechanism, pre-training on larger semantic segmentation dataset or inference acceleration, DDRNet-39 attains 80.4% test mIoU at 23 FPS on Cityscapes. With widely used test augmentation, our method is still superior to most state-of-the-art models, requiring much less computation. Codes and trained models will be made publicly available.
Frame-wise Cross-modal Match for Video Moment Retrieval
Sep 22, 2020
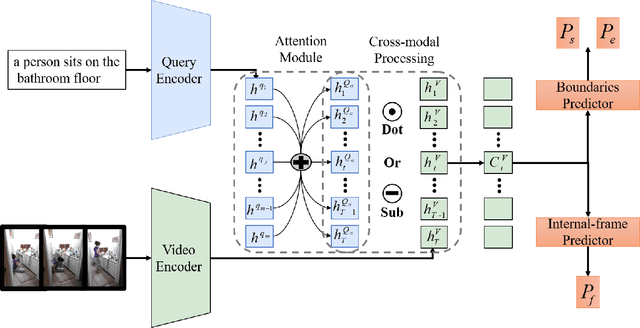
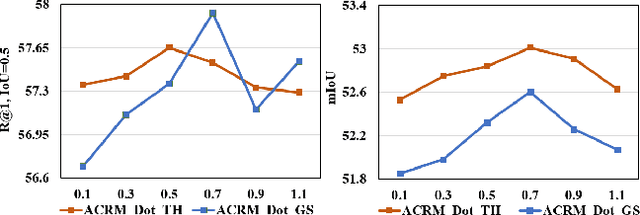

Abstract:Video moment retrieval targets at retrieving a golden moment in a video for a given natural language query. The main challenges of this task include 1) the requirement of accurately localizing (i.e., the start time and the end time of) the relevant moment in an untrimmed video stream, and 2) bridging the semantic gap between textual query and video contents. To tackle those problems, One mainstream approach is to generate a multimodal feature vector for the target query and video frames (e.g., concatenation) and then use a regression approach upon the multimodal feature vector for boundary detection. Although some progress has been achieved by this approach, we argue that those methods have not well captured the cross-modal interactions between the query and video frames. In this paper, we propose an Attentive Cross-modal Relevance Matching (ACRM) model which predicts the temporal bounders based on an interaction modeling between two modalities. In addition, an attention module is introduced to automatically assign higher weights to query words with richer semantic cues, which are considered to be more important for finding relevant video contents. Another contribution is that we propose an additional predictor to utilize the internal frames in the model training to improve the localization accuracy. Extensive experiments on two public datasetsdemonstrate the superiority of our method over several state-of-the-art methods.
Channel Estimation for RIS-Empowered Multi-User MISO Wireless Communications
Aug 04, 2020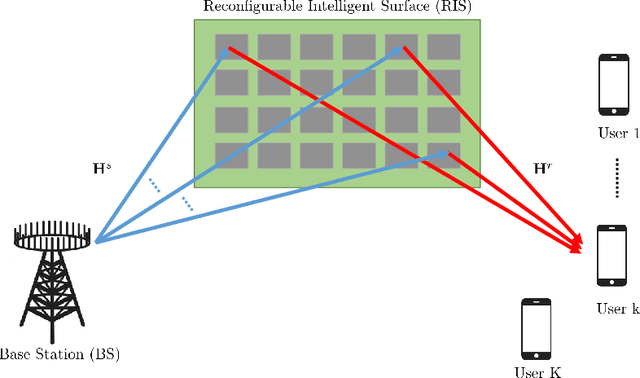
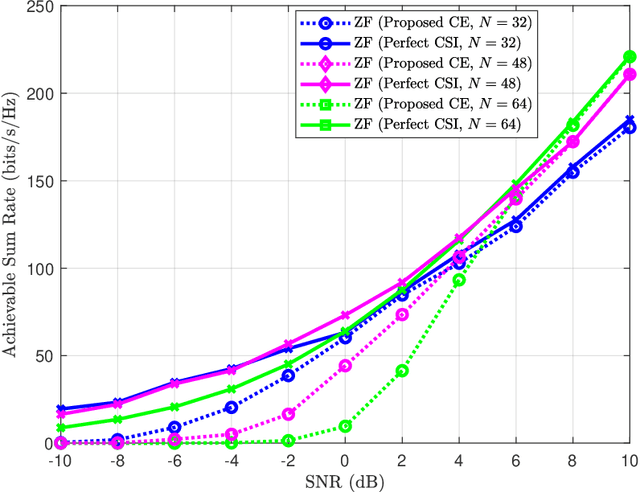
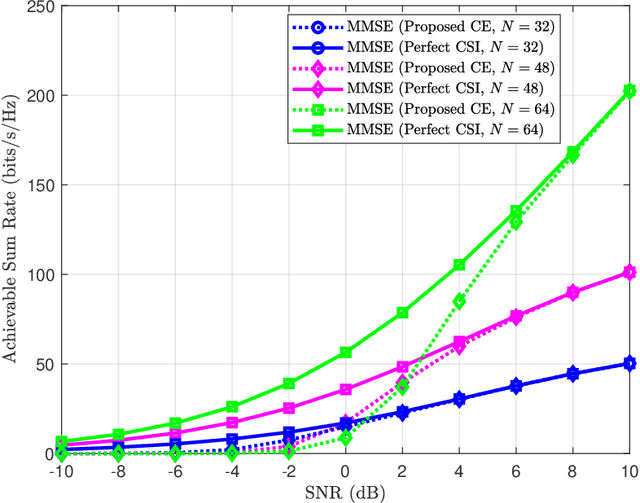
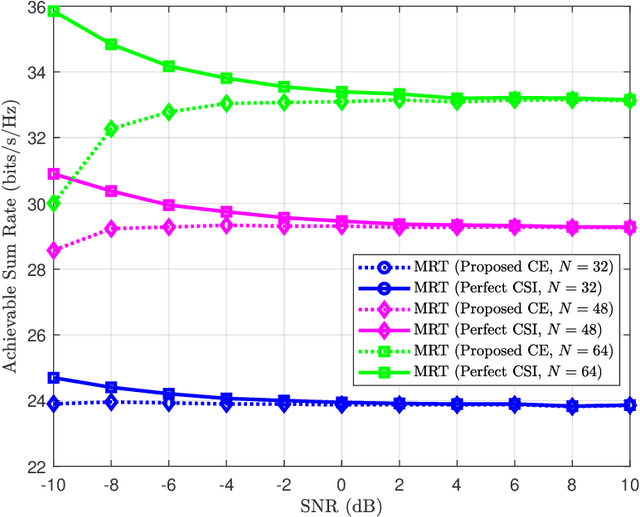
Abstract:Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs) have been recently considered as an energy-efficient solution for future wireless networks due to their fast and low-power configuration, which has increased potential in enabling massive connectivity and low-latency communications. Accurate and low-overhead channel estimation in RIS-based systems is one of the most critical challenges due to the usually large number of RIS unit elements and their distinctive hardware constraints. In this paper, we focus on the downlink of a RIS-empowered multi-user Multiple Input Single Output (MISO) downlink communication systems and propose a channel estimation framework based on the PARAllel FACtor (PARAFAC) decomposition to unfold the resulting cascaded channel model. We present two iterative estimation algorithms for the channels between the base station and RIS, as well as the channels between RIS and users. One is based on alternating least squares (ALS), while the other uses vector approximate message passing to iteratively reconstruct two unknown channels from the estimated vectors. To theoretically assess the performance of the ALS-based algorithm, we derived its estimation Cram\'er-Rao Bound (CRB). We also discuss the achievable sum-rate computation with estimated channels and different precoding schemes for the base station. Our extensive simulation results show that our algorithms outperform benchmark schemes and that the ALS technique achieve the CRB. It is also demonstrated that the sum rate using the estimated channels reached that of perfect channel estimation under various settings, thus, verifying the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed estimation algorithms.
Learning Person Re-identification Models from Videos with Weak Supervision
Jul 21, 2020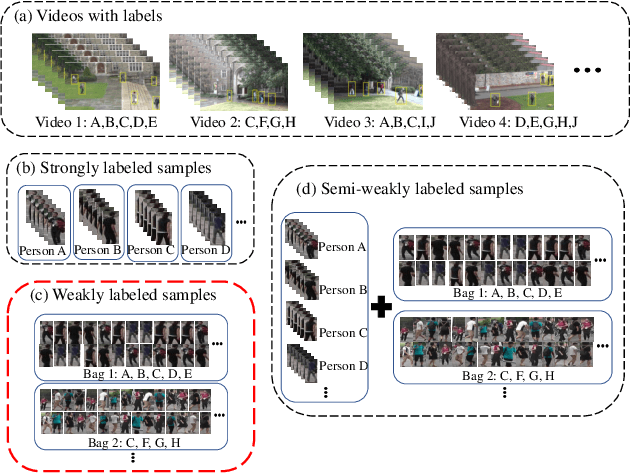
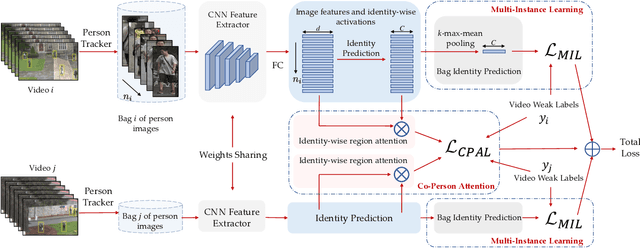
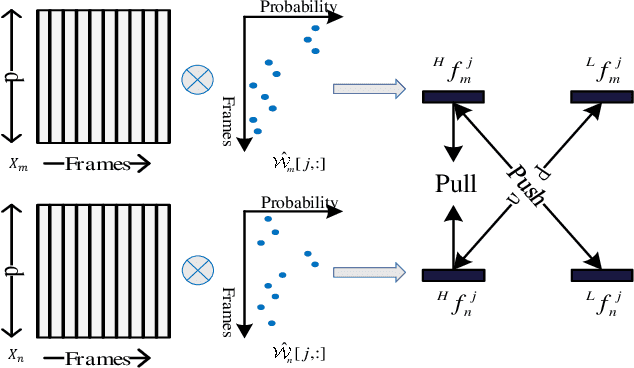
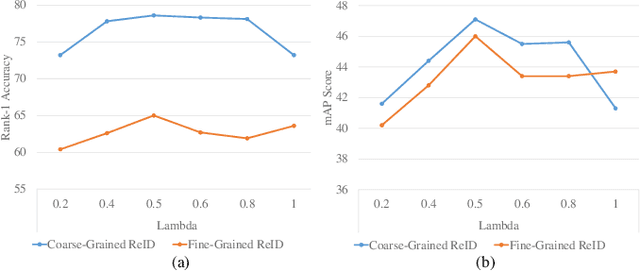
Abstract:Most person re-identification methods, being supervised techniques, suffer from the burden of massive annotation requirement. Unsupervised methods overcome this need for labeled data, but perform poorly compared to the supervised alternatives. In order to cope with this issue, we introduce the problem of learning person re-identification models from videos with weak supervision. The weak nature of the supervision arises from the requirement of video-level labels, i.e. person identities who appear in the video, in contrast to the more precise framelevel annotations. Towards this goal, we propose a multiple instance attention learning framework for person re-identification using such video-level labels. Specifically, we first cast the video person re-identification task into a multiple instance learning setting, in which person images in a video are collected into a bag. The relations between videos with similar labels can be utilized to identify persons, on top of that, we introduce a co-person attention mechanism which mines the similarity correlations between videos with person identities in common. The attention weights are obtained based on all person images instead of person tracklets in a video, making our learned model less affected by noisy annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over the related methods on two weakly labeled person re-identification datasets.
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted Multiuser MISO Systems Exploiting Deep Reinforcement Learning
Feb 24, 2020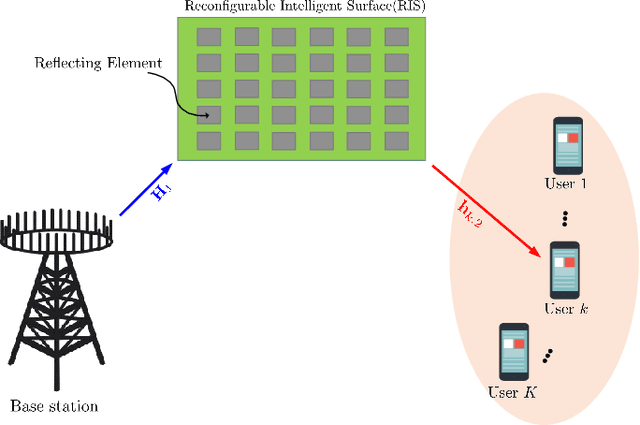
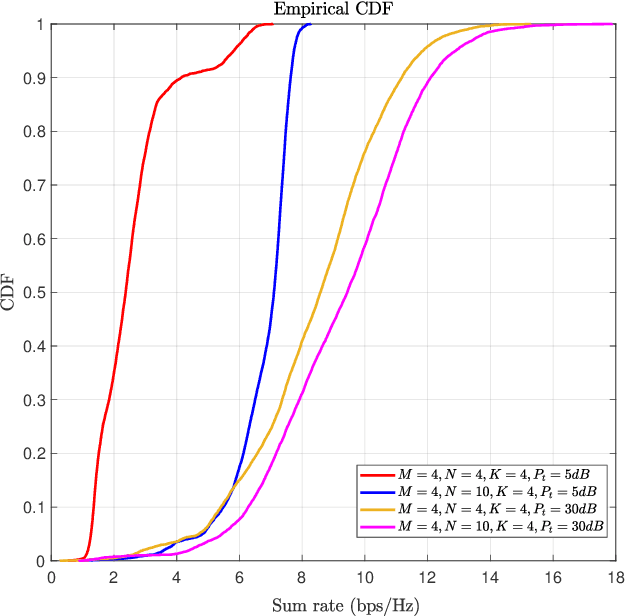
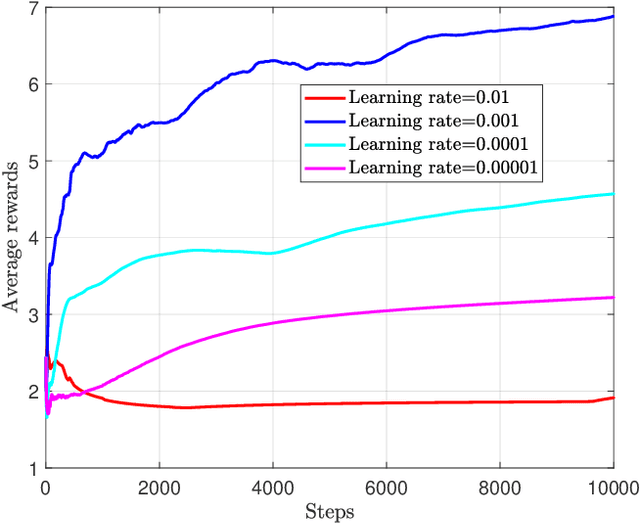
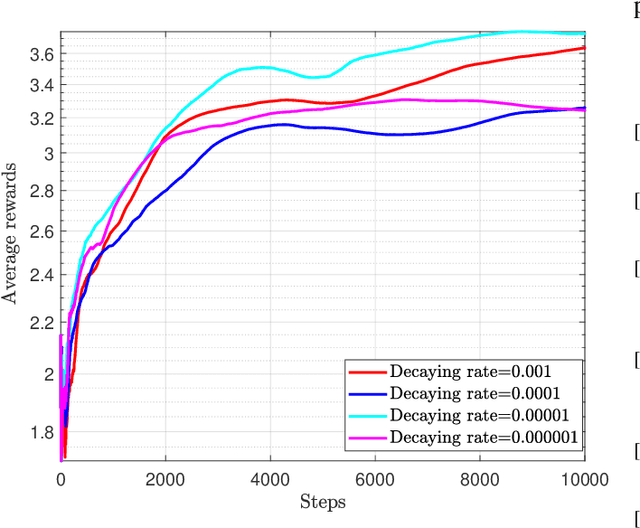
Abstract:Recently, the reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS), benefited from the breakthrough on the fabrication of programmable meta-material, has been speculated as one of the key enabling technologies for the future six generation (6G) wireless communication systems scaled up beyond massive multiple input multiple output (Massive-MIMO) technology to achieve smart radio environments. Employed as reflecting arrays, RIS is able to assist MIMO transmissions without the need of radio frequency chains resulting in considerable reduction in power consumption. In this paper, we investigate the joint design of transmit beamforming matrix at the base station and the phase shift matrix at the RIS, by leveraging recent advances in deep reinforcement learning (DRL). We first develop a DRL based algorithm, in which the joint design is obtained through trial-and-error interactions with the environment by observing predefined rewards, in the context of continuous state and action. Unlike the most reported works utilizing the alternating optimization techniques to alternatively obtain the transmit beamforming and phase shifts, the proposed DRL based algorithm obtains the joint design simultaneously as the output of the DRL neural network. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm is not only able to learn from the environment and gradually improve its behavior, but also obtains the comparable performance compared with two state-of-the-art benchmarks. It is also observed that, appropriate neural network parameter settings will improve significantly the performance and convergence rate of the proposed algorithm.
Broad Learning System Based on Maximum Correntropy Criterion
Dec 24, 2019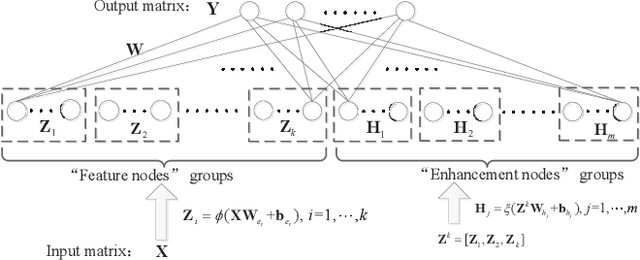
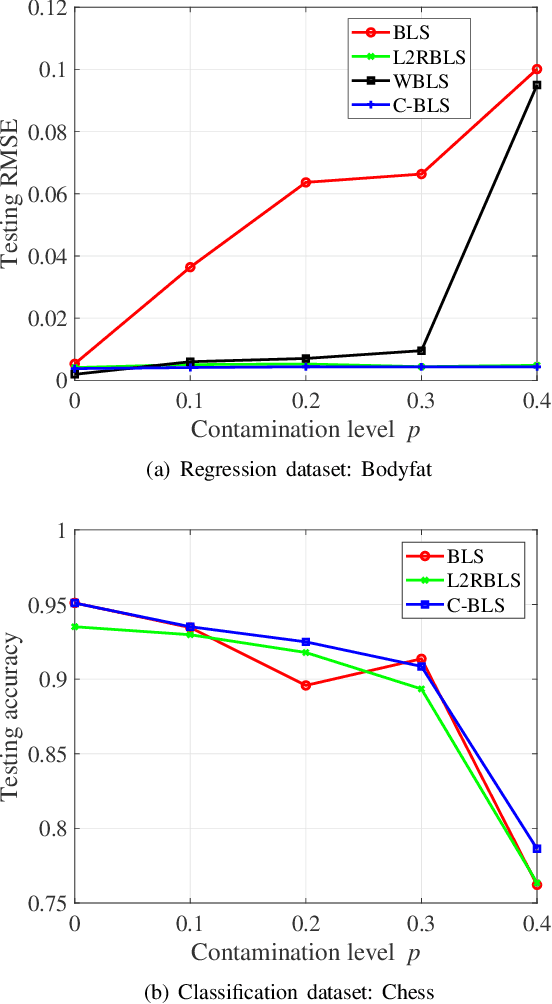
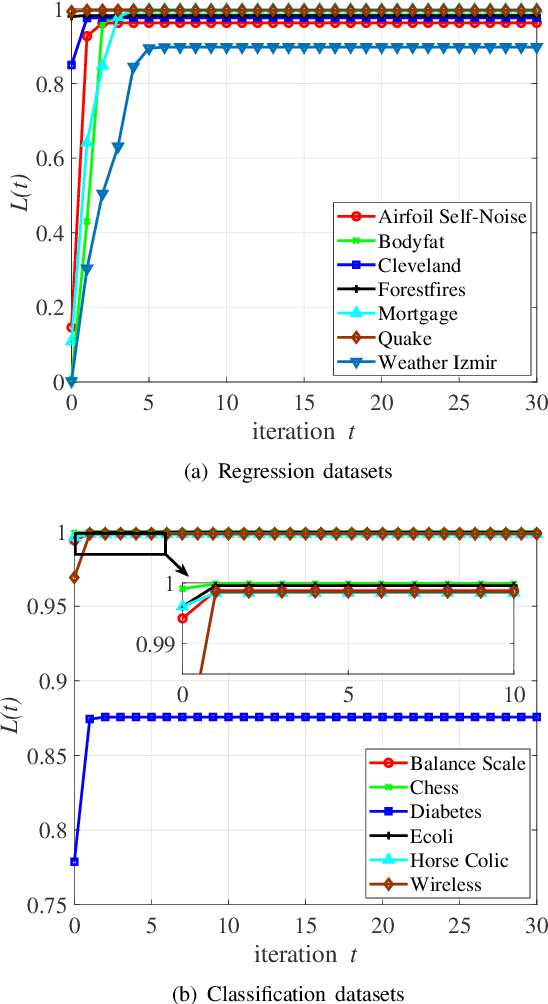
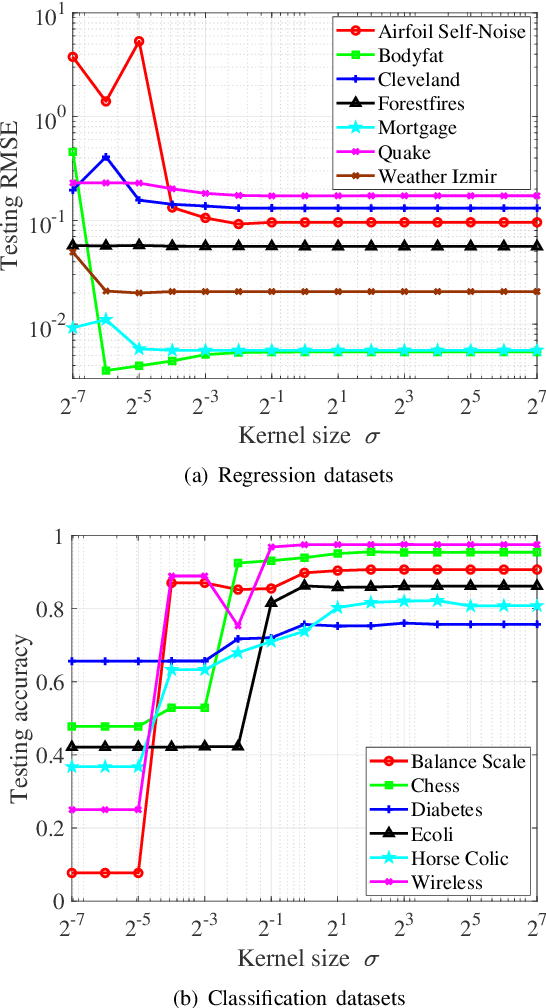
Abstract:As an effective and efficient discriminative learning method, Broad Learning System (BLS) has received increasing attention due to its outstanding performance in various regression and classification problems. However, the standard BLS is derived under the minimum mean square error (MMSE) criterion, which is, of course, not always a good choice due to its sensitivity to outliers. To enhance the robustness of BLS, we propose in this work to adopt the maximum correntropy criterion (MCC) to train the output weights, obtaining a correntropy based broad learning system (C-BLS). Thanks to the inherent superiorities of MCC, the proposed C-BLS is expected to achieve excellent robustness to outliers while maintaining the original performance of the standard BLS in Gaussian or noise-free environment. In addition, three alternative incremental learning algorithms, derived from a weighted regularized least-squares solution rather than pseudoinverse formula, for C-BLS are developed.With the incremental learning algorithms, the system can be updated quickly without the entire retraining process from the beginning, when some new samples arrive or the network deems to be expanded. Experiments on various regression and classification datasets are reported to demonstrate the desirable performance of the new methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge