Satish Kumar Singh
Non-Uniform Illumination Attack for Fooling Convolutional Neural Networks
Sep 05, 2024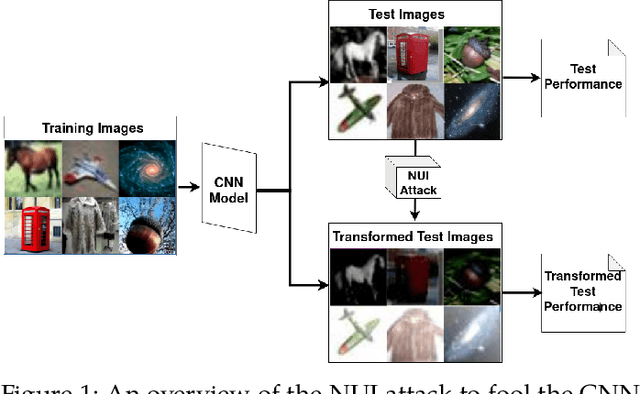
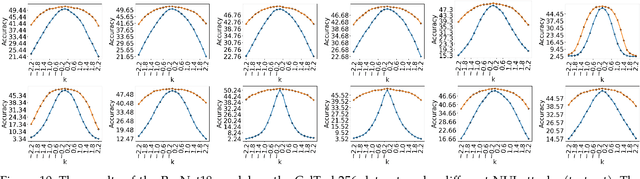
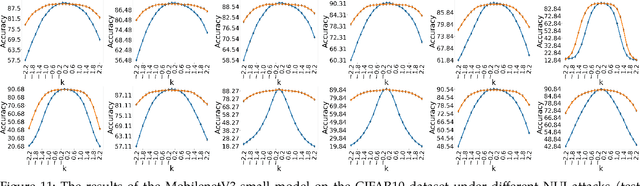
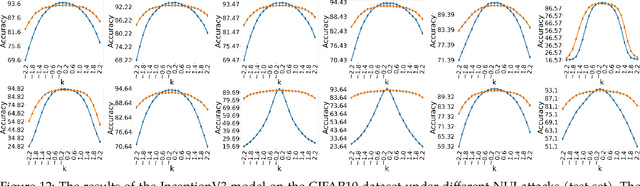
Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have made remarkable strides; however, they remain susceptible to vulnerabilities, particularly in the face of minor image perturbations that humans can easily recognize. This weakness, often termed as 'attacks', underscores the limited robustness of CNNs and the need for research into fortifying their resistance against such manipulations. This study introduces a novel Non-Uniform Illumination (NUI) attack technique, where images are subtly altered using varying NUI masks. Extensive experiments are conducted on widely-accepted datasets including CIFAR10, TinyImageNet, and CalTech256, focusing on image classification with 12 different NUI attack models. The resilience of VGG, ResNet, MobilenetV3-small and InceptionV3 models against NUI attacks are evaluated. Our results show a substantial decline in the CNN models' classification accuracy when subjected to NUI attacks, indicating their vulnerability under non-uniform illumination. To mitigate this, a defense strategy is proposed, including NUI-attacked images, generated through the new NUI transformation, into the training set. The results demonstrate a significant enhancement in CNN model performance when confronted with perturbed images affected by NUI attacks. This strategy seeks to bolster CNN models' resilience against NUI attacks.
3D-Convolution Guided Spectral-Spatial Transformer for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Apr 20, 2024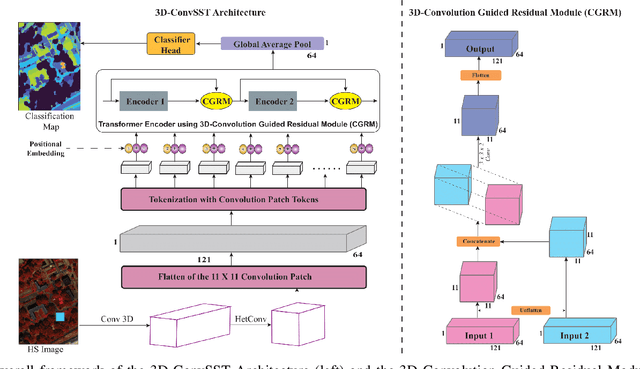
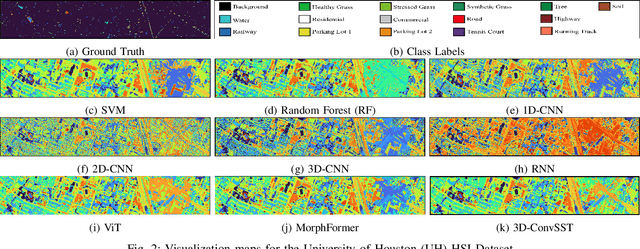
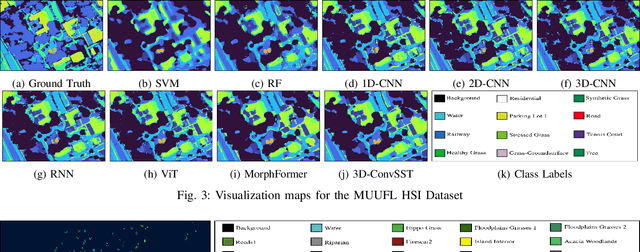
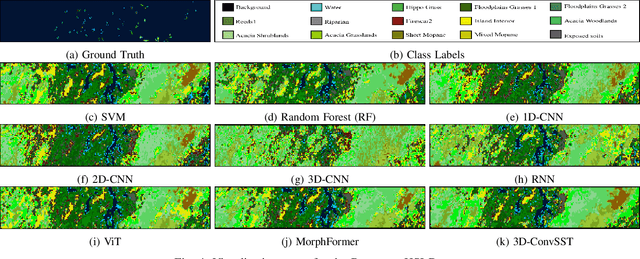
Abstract:In recent years, Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown promising classification performance over Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) due to their self-attention mechanism. Many researchers have incorporated ViTs for Hyperspectral Image (HSI) classification. HSIs are characterised by narrow contiguous spectral bands, providing rich spectral data. Although ViTs excel with sequential data, they cannot extract spectral-spatial information like CNNs. Furthermore, to have high classification performance, there should be a strong interaction between the HSI token and the class (CLS) token. To solve these issues, we propose a 3D-Convolution guided Spectral-Spatial Transformer (3D-ConvSST) for HSI classification that utilizes a 3D-Convolution Guided Residual Module (CGRM) in-between encoders to "fuse" the local spatial and spectral information and to enhance the feature propagation. Furthermore, we forego the class token and instead apply Global Average Pooling, which effectively encodes more discriminative and pertinent high-level features for classification. Extensive experiments have been conducted on three public HSI datasets to show the superiority of the proposed model over state-of-the-art traditional, convolutional, and Transformer models. The code is available at https://github.com/ShyamVarahagiri/3D-ConvSST.
Transformer-based Clipped Contrastive Quantization Learning for Unsupervised Image Retrieval
Jan 27, 2024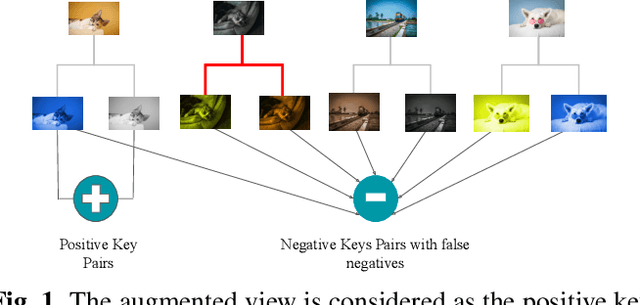
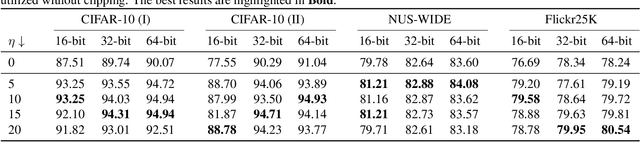
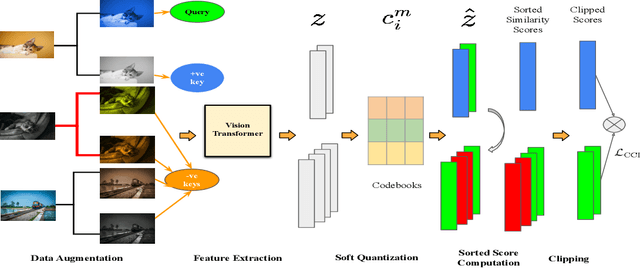
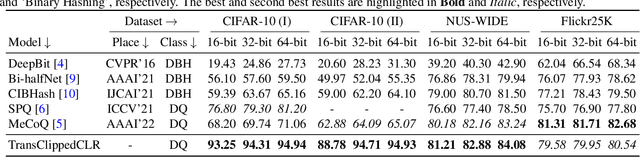
Abstract:Unsupervised image retrieval aims to learn the important visual characteristics without any given level to retrieve the similar images for a given query image. The Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based approaches have been extensively exploited with self-supervised contrastive learning for image hashing. However, the existing approaches suffer due to lack of effective utilization of global features by CNNs and biased-ness created by false negative pairs in the contrastive learning. In this paper, we propose a TransClippedCLR model by encoding the global context of an image using Transformer having local context through patch based processing, by generating the hash codes through product quantization and by avoiding the potential false negative pairs through clipped contrastive learning. The proposed model is tested with superior performance for unsupervised image retrieval on benchmark datasets, including CIFAR10, NUS-Wide and Flickr25K, as compared to the recent state-of-the-art deep models. The results using the proposed clipped contrastive learning are greatly improved on all datasets as compared to same backbone network with vanilla contrastive learning.
Face to Cartoon Incremental Super-Resolution using Knowledge Distillation
Jan 27, 2024



Abstract:Facial super-resolution/hallucination is an important area of research that seeks to enhance low-resolution facial images for a variety of applications. While Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have shown promise in this area, their ability to adapt to new, unseen data remains a challenge. This paper addresses this problem by proposing an incremental super-resolution using GANs with knowledge distillation (ISR-KD) for face to cartoon. Previous research in this area has not investigated incremental learning, which is critical for real-world applications where new data is continually being generated. The proposed ISR-KD aims to develop a novel unified framework for facial super-resolution that can handle different settings, including different types of faces such as cartoon face and various levels of detail. To achieve this, a GAN-based super-resolution network was pre-trained on the CelebA dataset and then incrementally trained on the iCartoonFace dataset, using knowledge distillation to retain performance on the CelebA test set while improving the performance on iCartoonFace test set. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of knowledge distillation in incrementally adding capability to the model for cartoon face super-resolution while retaining the learned knowledge for facial hallucination tasks in GANs.
SRTransGAN: Image Super-Resolution using Transformer based Generative Adversarial Network
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:Image super-resolution aims to synthesize high-resolution image from a low-resolution image. It is an active area to overcome the resolution limitations in several applications like low-resolution object-recognition, medical image enhancement, etc. The generative adversarial network (GAN) based methods have been the state-of-the-art for image super-resolution by utilizing the convolutional neural networks (CNNs) based generator and discriminator networks. However, the CNNs are not able to exploit the global information very effectively in contrast to the transformers, which are the recent breakthrough in deep learning by exploiting the self-attention mechanism. Motivated from the success of transformers in language and vision applications, we propose a SRTransGAN for image super-resolution using transformer based GAN. Specifically, we propose a novel transformer-based encoder-decoder network as a generator to generate 2x images and 4x images. We design the discriminator network using vision transformer which uses the image as sequence of patches and hence useful for binary classification between synthesized and real high-resolution images. The proposed SRTransGAN outperforms the existing methods by 4.38 % on an average of PSNR and SSIM scores. We also analyze the saliency map to understand the learning ability of the proposed method.
PTSR: Patch Translator for Image Super-Resolution
Oct 20, 2023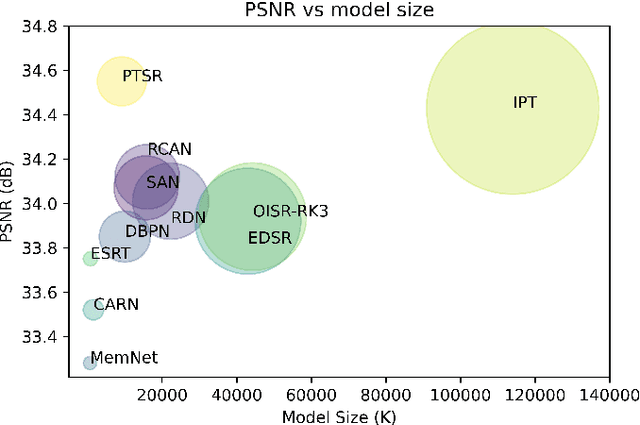
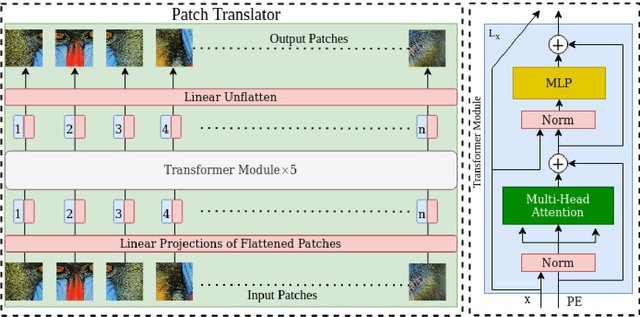
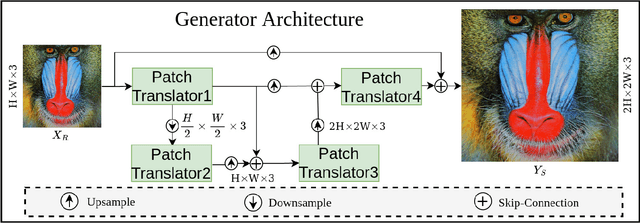
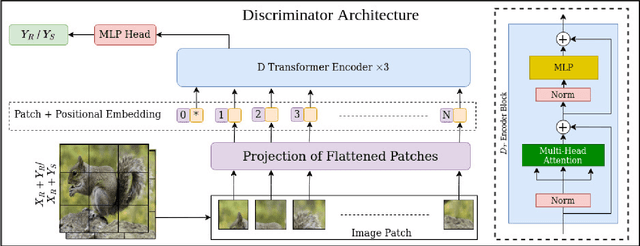
Abstract:Image super-resolution generation aims to generate a high-resolution image from its low-resolution image. However, more complex neural networks bring high computational costs and memory storage. It is still an active area for offering the promise of overcoming resolution limitations in many applications. In recent years, transformers have made significant progress in computer vision tasks as their robust self-attention mechanism. However, recent works on the transformer for image super-resolution also contain convolution operations. We propose a patch translator for image super-resolution (PTSR) to address this problem. The proposed PTSR is a transformer-based GAN network with no convolution operation. We introduce a novel patch translator module for regenerating the improved patches utilising multi-head attention, which is further utilised by the generator to generate the 2x and 4x super-resolution images. The experiments are performed using benchmark datasets, including DIV2K, Set5, Set14, and BSD100. The results of the proposed model is improved on an average for $4\times$ super-resolution by 21.66% in PNSR score and 11.59% in SSIM score, as compared to the best competitive models. We also analyse the proposed loss and saliency map to show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Transformer-based Generative Adversarial Networks in Computer Vision: A Comprehensive Survey
Feb 17, 2023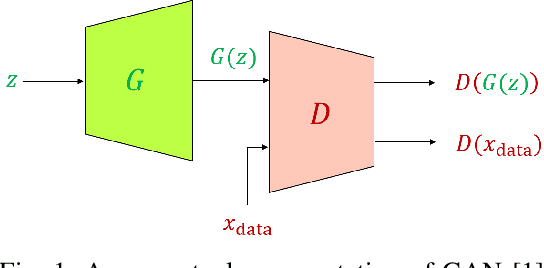
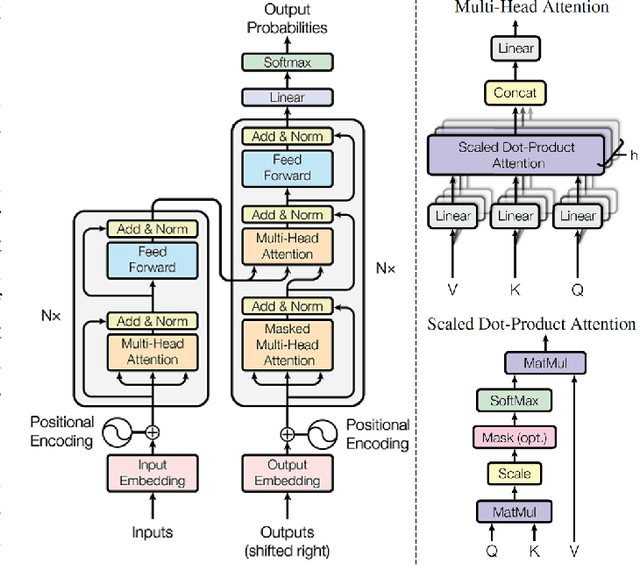
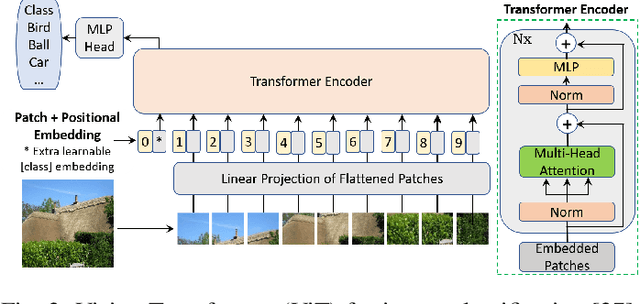
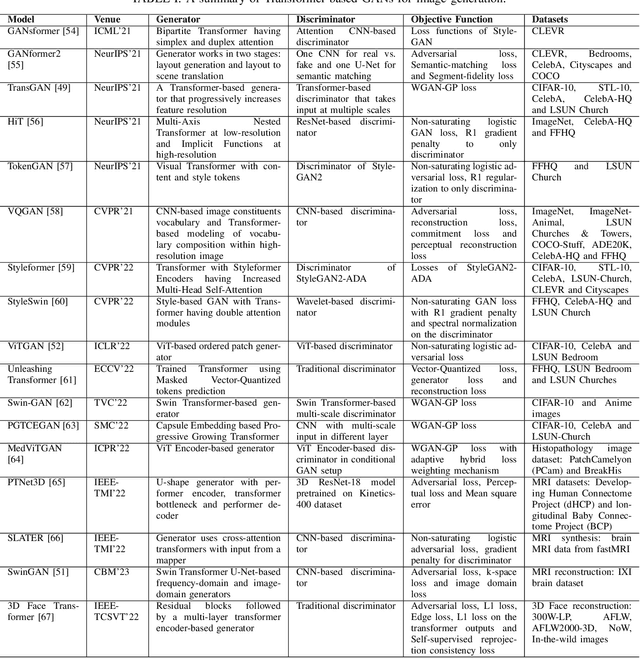
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have been very successful for synthesizing the images in a given dataset. The artificially generated images by GANs are very realistic. The GANs have shown potential usability in several computer vision applications, including image generation, image-to-image translation, video synthesis, and others. Conventionally, the generator network is the backbone of GANs, which generates the samples and the discriminator network is used to facilitate the training of the generator network. The discriminator network is usually a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). Whereas, the generator network is usually either an Up-CNN for image generation or an Encoder-Decoder network for image-to-image translation. The convolution-based networks exploit the local relationship in a layer, which requires the deep networks to extract the abstract features. Hence, CNNs suffer to exploit the global relationship in the feature space. However, recently developed Transformer networks are able to exploit the global relationship at every layer. The Transformer networks have shown tremendous performance improvement for several problems in computer vision. Motivated from the success of Transformer networks and GANs, recent works have tried to exploit the Transformers in GAN framework for the image/video synthesis. This paper presents a comprehensive survey on the developments and advancements in GANs utilizing the Transformer networks for computer vision applications. The performance comparison for several applications on benchmark datasets is also performed and analyzed. The conducted survey will be very useful to deep learning and computer vision community to understand the research trends \& gaps related with Transformer-based GANs and to develop the advanced GAN architectures by exploiting the global and local relationships for different applications.
AdaNorm: Adaptive Gradient Norm Correction based Optimizer for CNNs
Oct 12, 2022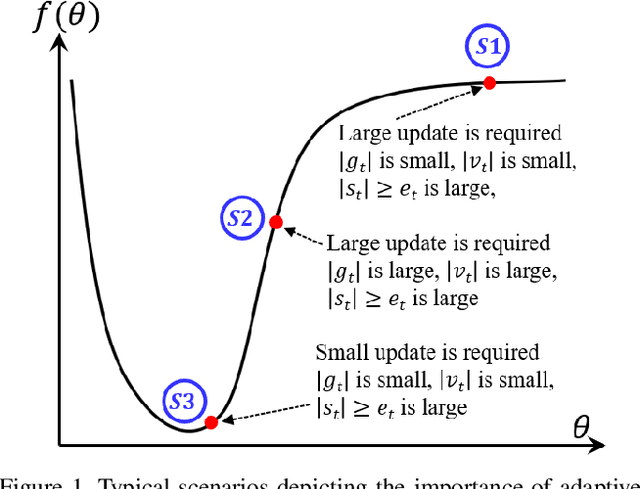
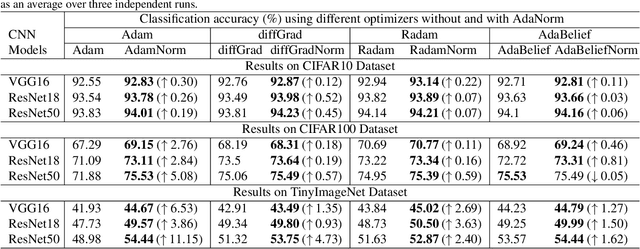
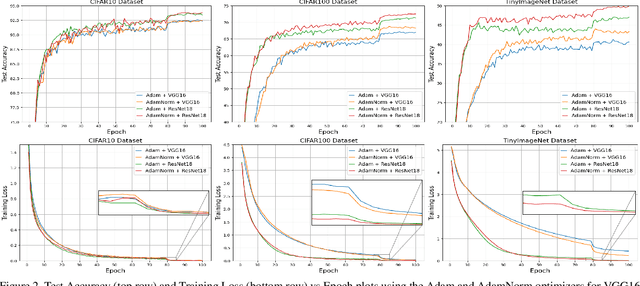
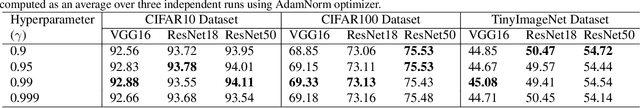
Abstract:The stochastic gradient descent (SGD) optimizers are generally used to train the convolutional neural networks (CNNs). In recent years, several adaptive momentum based SGD optimizers have been introduced, such as Adam, diffGrad, Radam and AdaBelief. However, the existing SGD optimizers do not exploit the gradient norm of past iterations and lead to poor convergence and performance. In this paper, we propose a novel AdaNorm based SGD optimizers by correcting the norm of gradient in each iteration based on the adaptive training history of gradient norm. By doing so, the proposed optimizers are able to maintain high and representive gradient throughout the training and solves the low and atypical gradient problems. The proposed concept is generic and can be used with any existing SGD optimizer. We show the efficacy of the proposed AdaNorm with four state-of-the-art optimizers, including Adam, diffGrad, Radam and AdaBelief. We depict the performance improvement due to the proposed optimizers using three CNN models, including VGG16, ResNet18 and ResNet50, on three benchmark object recognition datasets, including CIFAR10, CIFAR100 and TinyImageNet. Code: \url{https://github.com/shivram1987/AdaNorm}.
Bag of Visual Words with Deep Features -- Patch Classification Model for Limited Dataset of Breast Tumours
Feb 22, 2022
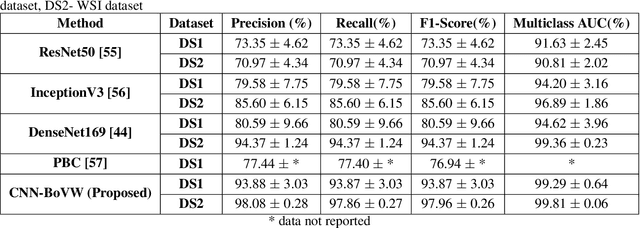
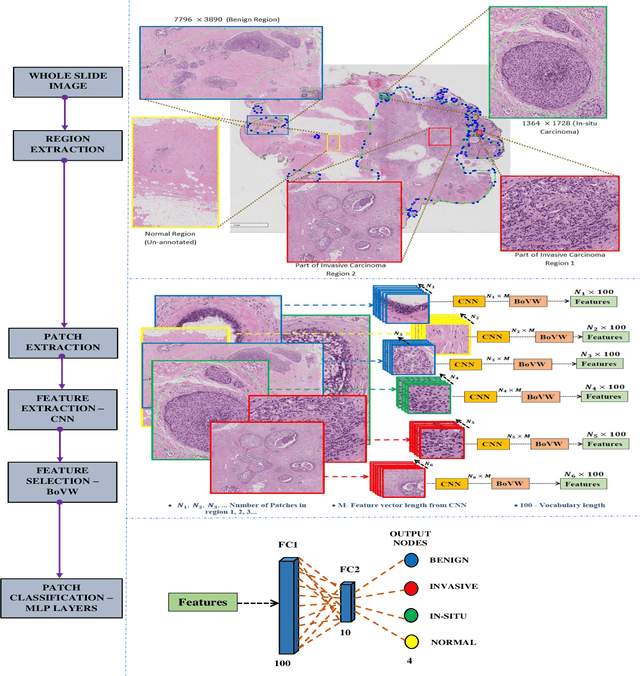
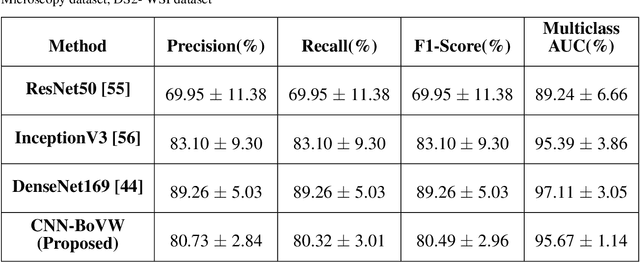
Abstract:Currently, the computational complexity limits the training of high resolution gigapixel images using Convolutional Neural Networks. Therefore, such images are divided into patches or tiles. Since, these high resolution patches are encoded with discriminative information therefore; CNNs are trained on these patches to perform patch-level predictions. However, the problem with patch-level prediction is that pathologist generally annotates at image-level and not at patch level. Due to this limitation most of the patches may not contain enough class-relevant features. Through this work, we tried to incorporate patch descriptive capability within the deep framework by using Bag of Visual Words (BoVW) as a kind of regularisation to improve generalizability. Using this hypothesis, we aim to build a patch based classifier to discriminate between four classes of breast biopsy image patches (normal, benign, \textit{In situ} carcinoma, invasive carcinoma). The task is to incorporate quality deep features using CNN to describe relevant information in the images while simultaneously discarding irrelevant information using Bag of Visual Words (BoVW). The proposed method passes patches obtained from WSI and microscopy images through pre-trained CNN to extract features. BoVW is used as a feature selector to select most discriminative features among the CNN features. Finally, the selected feature sets are classified as one of the four classes. The hybrid model provides flexibility in terms of choice of pre-trained models for feature extraction. The pipeline is end-to-end since it does not require post processing of patch predictions to select discriminative patches. We compared our observations with state-of-the-art methods like ResNet50, DenseNet169, and InceptionV3 on the BACH-2018 challenge dataset. Our proposed method shows better performance than all the three methods.
Ensembling Handcrafted Features with Deep Features: An Analytical Study for Classification of Routine Colon Cancer Histopathological Nuclei Images
Feb 22, 2022

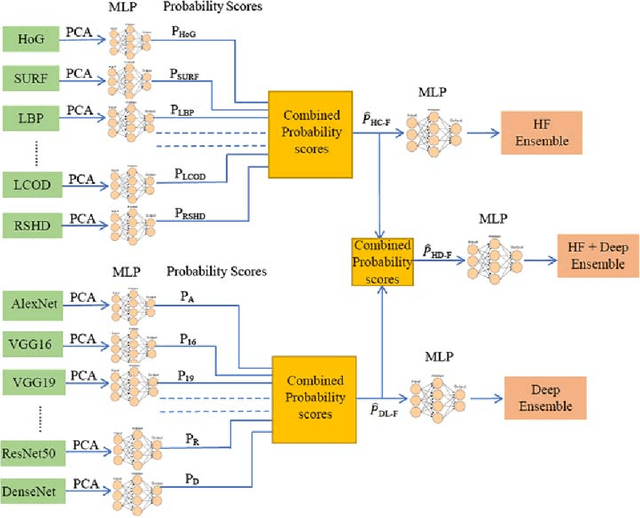

Abstract:The use of Deep Learning (DL) based methods in medical histopathology images have been one of the most sought after solutions to classify, segment, and detect diseased biopsy samples. However, given the complex nature of medical datasets due to the presence of intra-class variability and heterogeneity, the use of complex DL models might not give the optimal performance up to the level which is suitable for assisting pathologists. Therefore, ensemble DL methods with the scope of including domain agnostic handcrafted Features (HC-F) inspired this work. We have, through experiments, tried to highlight that a single DL network (domain-specific or state of the art pre-trained models) cannot be directly used as the base model without proper analysis with the relevant dataset. We have used F1-measure, Precision, Recall, AUC, and Cross-Entropy Loss to analyse the performance of our approaches. We observed from the results that the DL features ensemble bring a marked improvement in the overall performance of the model, whereas, domain agnostic HC-F remains dormant on the performance of the DL models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge