Yaonan Wang
TRACER: Texture-Robust Affordance Chain-of-Thought for Deformable-Object Refinement
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The central challenge in robotic manipulation of deformable objects lies in aligning high-level semantic instructions with physical interaction points under complex appearance and texture variations. Due to near-infinite degrees of freedom, complex dynamics, and heterogeneous patterns, existing vision-based affordance prediction methods often suffer from boundary overflow and fragmented functional regions. To address these issues, we propose TRACER, a Texture-Robust Affordance Chain-of-thought with dEformable-object Refinement framework, which establishes a cross-hierarchical mapping from hierarchical semantic reasoning to appearance-robust and physically consistent functional region refinement. Specifically, a Tree-structured Affordance Chain-of-Thought (TA-CoT) is formulated to decompose high-level task intentions into hierarchical sub-task semantics, providing consistent guidance across various execution stages. To ensure spatial integrity, a Spatial-Constrained Boundary Refinement (SCBR) mechanism is introduced to suppress prediction spillover, guiding the perceptual response to converge toward authentic interaction manifolds. Furthermore, an Interactive Convergence Refinement Flow (ICRF) is developed to aggregate discrete pixels corrupted by appearance noise, significantly enhancing the spatial continuity and physical plausibility of the identified functional regions. Extensive experiments conducted on the Fine-AGDDO15 dataset and a real-world robotic platform demonstrate that TRACER significantly improves affordance grounding precision across diverse textures and patterns inherent to deformable objects. More importantly, it enhances the success rate of long-horizon tasks, effectively bridging the gap between high-level semantic reasoning and low-level physical execution. The source code and dataset will be made publicly available at https://github.com/Dikay1/TRACER.
Reg-TTR, Test-Time Refinement for Fast, Robust and Accurate Image Registration
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Traditional image registration methods are robust but slow due to their iterative nature. While deep learning has accelerated inference, it often struggles with domain shifts. Emerging registration foundation models offer a balance of speed and robustness, yet typically cannot match the peak accuracy of specialized models trained on specific datasets. To mitigate this limitation, we propose Reg-TTR, a test-time refinement framework that synergizes the complementary strengths of both deep learning and conventional registration techniques. By refining the predictions of pre-trained models at inference, our method delivers significantly improved registration accuracy at a modest computational cost, requiring only 21% additional inference time (0.56s). We evaluate Reg-TTR on two distinct tasks and show that it achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance while maintaining inference speeds close to previous deep learning methods. As foundation models continue to emerge, our framework offers an efficient strategy to narrow the performance gap between registration foundation models and SOTA methods trained on specialized datasets. The source code will be publicly available following the acceptance of this work.
A Step to Decouple Optimization in 3DGS
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful technique for real-time novel view synthesis. As an explicit representation optimized through gradient propagation among primitives, optimization widely accepted in deep neural networks (DNNs) is actually adopted in 3DGS, such as synchronous weight updating and Adam with the adaptive gradient. However, considering the physical significance and specific design in 3DGS, there are two overlooked details in the optimization of 3DGS: (i) update step coupling, which induces optimizer state rescaling and costly attribute updates outside the viewpoints, and (ii) gradient coupling in the moment, which may lead to under- or over-effective regularization. Nevertheless, such a complex coupling is under-explored. After revisiting the optimization of 3DGS, we take a step to decouple it and recompose the process into: Sparse Adam, Re-State Regularization and Decoupled Attribute Regularization. Taking a large number of experiments under the 3DGS and 3DGS-MCMC frameworks, our work provides a deeper understanding of these components. Finally, based on the empirical analysis, we re-design the optimization and propose AdamW-GS by re-coupling the beneficial components, under which better optimization efficiency and representation effectiveness are achieved simultaneously.
FMIR, a foundation model-based Image Registration Framework for Robust Image Registration
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Deep learning has revolutionized medical image registration by achieving unprecedented speeds, yet its clinical application is hindered by a limited ability to generalize beyond the training domain, a critical weakness given the typically small scale of medical datasets. In this paper, we introduce FMIR, a foundation model-based registration framework that overcomes this limitation.Combining a foundation model-based feature encoder for extracting anatomical structures with a general registration head, and trained with a channel regularization strategy on just a single dataset, FMIR achieves state-of-the-art(SOTA) in-domain performance while maintaining robust registration on out-of-domain images.Our approach demonstrates a viable path toward building generalizable medical imaging foundation models with limited resources. The code is available at https://github.com/Monday0328/FMIR.git.
MIRNet: Integrating Constrained Graph-Based Reasoning with Pre-training for Diagnostic Medical Imaging
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Automated interpretation of medical images demands robust modeling of complex visual-semantic relationships while addressing annotation scarcity, label imbalance, and clinical plausibility constraints. We introduce MIRNet (Medical Image Reasoner Network), a novel framework that integrates self-supervised pre-training with constrained graph-based reasoning. Tongue image diagnosis is a particularly challenging domain that requires fine-grained visual and semantic understanding. Our approach leverages self-supervised masked autoencoder (MAE) to learn transferable visual representations from unlabeled data; employs graph attention networks (GAT) to model label correlations through expert-defined structured graphs; enforces clinical priors via constraint-aware optimization using KL divergence and regularization losses; and mitigates imbalance using asymmetric loss (ASL) and boosting ensembles. To address annotation scarcity, we also introduce TongueAtlas-4K, a comprehensive expert-curated benchmark comprising 4,000 images annotated with 22 diagnostic labels--representing the largest public dataset in tongue analysis. Validation shows our method achieves state-of-the-art performance. While optimized for tongue diagnosis, the framework readily generalizes to broader diagnostic medical imaging tasks.
Mono3DVG-EnSD: Enhanced Spatial-aware and Dimension-decoupled Text Encoding for Monocular 3D Visual Grounding
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Monocular 3D Visual Grounding (Mono3DVG) is an emerging task that locates 3D objects in RGB images using text descriptions with geometric cues. However, existing methods face two key limitations. Firstly, they often over-rely on high-certainty keywords that explicitly identify the target object while neglecting critical spatial descriptions. Secondly, generalized textual features contain both 2D and 3D descriptive information, thereby capturing an additional dimension of details compared to singular 2D or 3D visual features. This characteristic leads to cross-dimensional interference when refining visual features under text guidance. To overcome these challenges, we propose Mono3DVG-EnSD, a novel framework that integrates two key components: the CLIP-Guided Lexical Certainty Adapter (CLIP-LCA) and the Dimension-Decoupled Module (D2M). The CLIP-LCA dynamically masks high-certainty keywords while retaining low-certainty implicit spatial descriptions, thereby forcing the model to develop a deeper understanding of spatial relationships in captions for object localization. Meanwhile, the D2M decouples dimension-specific (2D/3D) textual features from generalized textual features to guide corresponding visual features at same dimension, which mitigates cross-dimensional interference by ensuring dimensionally-consistent cross-modal interactions. Through comprehensive comparisons and ablation studies on the Mono3DRefer dataset, our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across all metrics. Notably, it improves the challenging Far(Acc@0.5) scenario by a significant +13.54%.
A Dual-stage Prompt-driven Privacy-preserving Paradigm for Person Re-Identification
Nov 07, 2025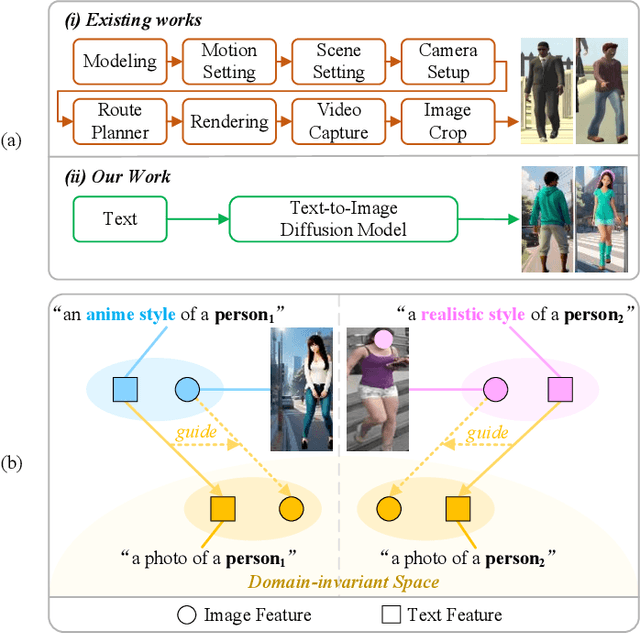
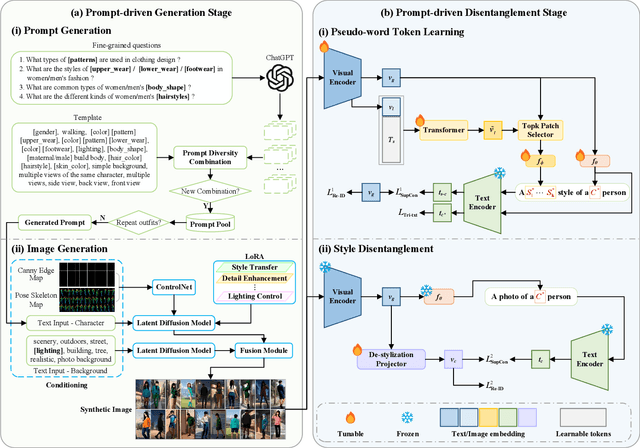
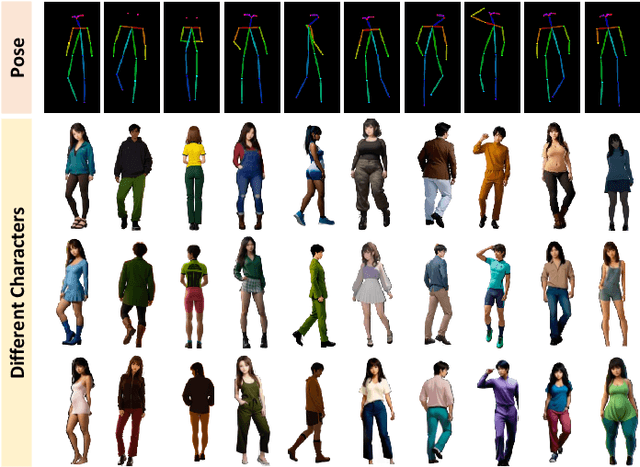

Abstract:With growing concerns over data privacy, researchers have started using virtual data as an alternative to sensitive real-world images for training person re-identification (Re-ID) models. However, existing virtual datasets produced by game engines still face challenges such as complex construction and poor domain generalization, making them difficult to apply in real scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose a Dual-stage Prompt-driven Privacy-preserving Paradigm (DPPP). In the first stage, we generate rich prompts incorporating multi-dimensional attributes such as pedestrian appearance, illumination, and viewpoint that drive the diffusion model to synthesize diverse data end-to-end, building a large-scale virtual dataset named GenePerson with 130,519 images of 6,641 identities. In the second stage, we propose a Prompt-driven Disentanglement Mechanism (PDM) to learn domain-invariant generalization features. With the aid of contrastive learning, we employ two textual inversion networks to map images into pseudo-words representing style and content, respectively, thereby constructing style-disentangled content prompts to guide the model in learning domain-invariant content features at the image level. Experiments demonstrate that models trained on GenePerson with PDM achieve state-of-the-art generalization performance, surpassing those on popular real and virtual Re-ID datasets.
Ideal Registration? Segmentation is All You Need
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Deep learning has revolutionized image registration by its ability to handle diverse tasks while achieving significant speed advantages over conventional approaches. Current approaches, however, often employ globally uniform smoothness constraints that fail to accommodate the complex, regionally varying deformations characteristic of anatomical motion. To address this limitation, we propose SegReg, a Segmentation-driven Registration framework that implements anatomically adaptive regularization by exploiting region-specific deformation patterns. Our SegReg first decomposes input moving and fixed images into anatomically coherent subregions through segmentation. These localized domains are then processed by the same registration backbone to compute optimized partial deformation fields, which are subsequently integrated into a global deformation field. SegReg achieves near-perfect structural alignment (98.23% Dice on critical anatomies) using ground-truth segmentation, and outperforms existing methods by 2-12% across three clinical registration scenarios (cardiac, abdominal, and lung images) even with automatic segmentation. Our SegReg demonstrates a near-linear dependence of registration accuracy on segmentation quality, transforming the registration challenge into a segmentation problem. The source code will be released upon manuscript acceptance.
Dual Enhancement on 3D Vision-Language Perception for Monocular 3D Visual Grounding
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Monocular 3D visual grounding is a novel task that aims to locate 3D objects in RGB images using text descriptions with explicit geometry information. Despite the inclusion of geometry details in the text, we observe that the text embeddings are sensitive to the magnitude of numerical values but largely ignore the associated measurement units. For example, simply equidistant mapping the length with unit "meter" to "decimeters" or "centimeters" leads to severe performance degradation, even though the physical length remains equivalent. This observation signifies the weak 3D comprehension of pre-trained language model, which generates misguiding text features to hinder 3D perception. Therefore, we propose to enhance the 3D perception of model on text embeddings and geometry features with two simple and effective methods. Firstly, we introduce a pre-processing method named 3D-text Enhancement (3DTE), which enhances the comprehension of mapping relationships between different units by augmenting the diversity of distance descriptors in text queries. Next, we propose a Text-Guided Geometry Enhancement (TGE) module to further enhance the 3D-text information by projecting the basic text features into geometrically consistent space. These 3D-enhanced text features are then leveraged to precisely guide the attention of geometry features. We evaluate the proposed method through extensive comparisons and ablation studies on the Mono3DRefer dataset. Experimental results demonstrate substantial improvements over previous methods, achieving new state-of-the-art results with a notable accuracy gain of 11.94\% in the "Far" scenario. Our code will be made publicly available.
ImprovDML: Improved Trade-off in Private Byzantine-Resilient Distributed Machine Learning
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Jointly addressing Byzantine attacks and privacy leakage in distributed machine learning (DML) has become an important issue. A common strategy involves integrating Byzantine-resilient aggregation rules with differential privacy mechanisms. However, the incorporation of these techniques often results in a significant degradation in model accuracy. To address this issue, we propose a decentralized DML framework, named ImprovDML, that achieves high model accuracy while simultaneously ensuring privacy preservation and resilience to Byzantine attacks. The framework leverages a kind of resilient vector consensus algorithms that can compute a point within the normal (non-Byzantine) agents' convex hull for resilient aggregation at each iteration. Then, multivariate Gaussian noises are introduced to the gradients for privacy preservation. We provide convergence guarantees and derive asymptotic learning error bounds under non-convex settings, which are tighter than those reported in existing works. For the privacy analysis, we adopt the notion of concentrated geo-privacy, which quantifies privacy preservation based on the Euclidean distance between inputs. We demonstrate that it enables an improved trade-off between privacy preservation and model accuracy compared to differential privacy. Finally, numerical simulations validate our theoretical results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge