He Xie
Multiview Point Cloud Registration Based on Minimum Potential Energy for Free-Form Blade Measurement
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Point cloud registration is an essential step for free-form blade reconstruction in industrial measurement. Nonetheless, measuring defects of the 3D acquisition system unavoidably result in noisy and incomplete point cloud data, which renders efficient and accurate registration challenging. In this paper, we propose a novel global registration method that is based on the minimum potential energy (MPE) method to address these problems. The basic strategy is that the objective function is defined as the minimum potential energy optimization function of the physical registration system. The function distributes more weight to the majority of inlier points and less weight to the noise and outliers, which essentially reduces the influence of perturbations in the mathematical formulation. We decompose the solution into a globally optimal approximation procedure and a fine registration process with the trimmed iterative closest point algorithm to boost convergence. The approximation procedure consists of two main steps. First, according to the construction of the force traction operator, we can simply compute the position of the potential energy minimum. Second, to find the MPE point, we propose a new theory that employs two flags to observe the status of the registration procedure. We demonstrate the performance of the proposed algorithm on four types of blades. The proposed method outperforms the other global methods in terms of both accuracy and noise resistance.
External Knowledge Enhanced 3D Scene Generation from Sketch
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:Generating realistic 3D scenes is challenging due to the complexity of room layouts and object geometries.We propose a sketch based knowledge enhanced diffusion architecture (SEK) for generating customized, diverse, and plausible 3D scenes. SEK conditions the denoising process with a hand-drawn sketch of the target scene and cues from an object relationship knowledge base. We first construct an external knowledge base containing object relationships and then leverage knowledge enhanced graph reasoning to assist our model in understanding hand-drawn sketches. A scene is represented as a combination of 3D objects and their relationships, and then incrementally diffused to reach a Gaussian distribution.We propose a 3D denoising scene transformer that learns to reverse the diffusion process, conditioned by a hand-drawn sketch along with knowledge cues, to regressively generate the scene including the 3D object instances as well as their layout. Experiments on the 3D-FRONT dataset show that our model improves FID, CKL by 17.41%, 37.18% in 3D scene generation and FID, KID by 19.12%, 20.06% in 3D scene completion compared to the nearest competitor DiffuScene.
Sketch and Text Guided Diffusion Model for Colored Point Cloud Generation
Aug 05, 2023Abstract:Diffusion probabilistic models have achieved remarkable success in text guided image generation. However, generating 3D shapes is still challenging due to the lack of sufficient data containing 3D models along with their descriptions. Moreover, text based descriptions of 3D shapes are inherently ambiguous and lack details. In this paper, we propose a sketch and text guided probabilistic diffusion model for colored point cloud generation that conditions the denoising process jointly with a hand drawn sketch of the object and its textual description. We incrementally diffuse the point coordinates and color values in a joint diffusion process to reach a Gaussian distribution. Colored point cloud generation thus amounts to learning the reverse diffusion process, conditioned by the sketch and text, to iteratively recover the desired shape and color. Specifically, to learn effective sketch-text embedding, our model adaptively aggregates the joint embedding of text prompt and the sketch based on a capsule attention network. Our model uses staged diffusion to generate the shape and then assign colors to different parts conditioned on the appearance prompt while preserving precise shapes from the first stage. This gives our model the flexibility to extend to multiple tasks, such as appearance re-editing and part segmentation. Experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms recent state-of-the-art in point cloud generation.
Measuring and Mitigating Local Instability in Deep Neural Networks
May 19, 2023



Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are becoming integral components of real world services relied upon by millions of users. Unfortunately, architects of these systems can find it difficult to ensure reliable performance as irrelevant details like random initialization can unexpectedly change the outputs of a trained system with potentially disastrous consequences. We formulate the model stability problem by studying how the predictions of a model change, even when it is retrained on the same data, as a consequence of stochasticity in the training process. For Natural Language Understanding (NLU) tasks, we find instability in predictions for a significant fraction of queries. We formulate principled metrics, like per-sample ``label entropy'' across training runs or within a single training run, to quantify this phenomenon. Intriguingly, we find that unstable predictions do not appear at random, but rather appear to be clustered in data-specific ways. We study data-agnostic regularization methods to improve stability and propose new data-centric methods that exploit our local stability estimates. We find that our localized data-specific mitigation strategy dramatically outperforms data-agnostic methods, and comes within 90% of the gold standard, achieved by ensembling, at a fraction of the computational cost
Towards Realistic Single-Task Continuous Learning Research for NER
Oct 27, 2021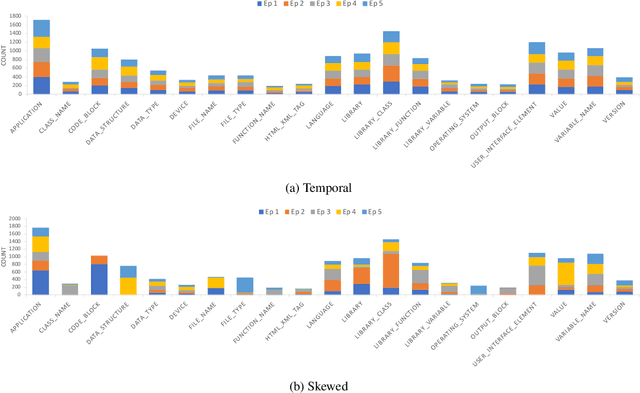
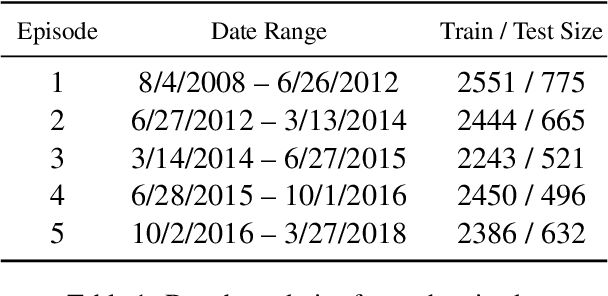
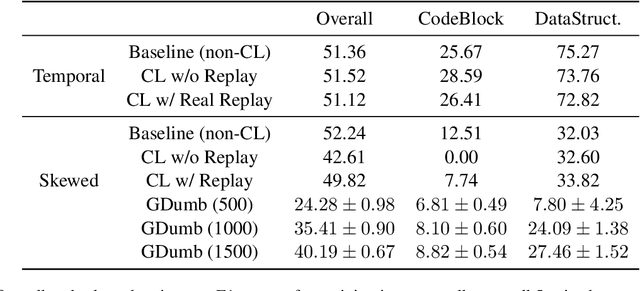
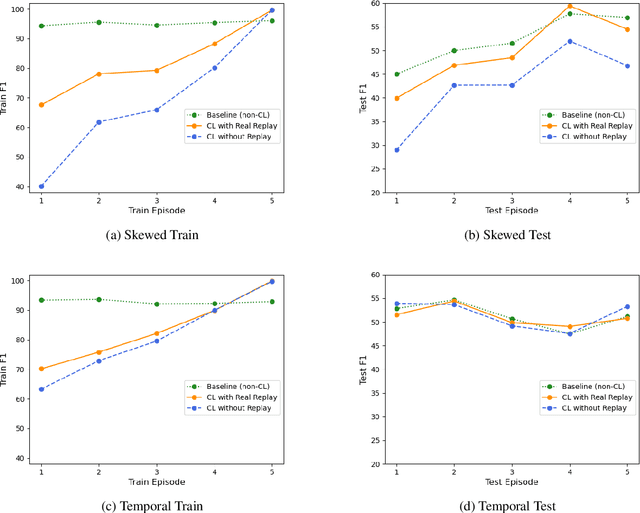
Abstract:There is an increasing interest in continuous learning (CL), as data privacy is becoming a priority for real-world machine learning applications. Meanwhile, there is still a lack of academic NLP benchmarks that are applicable for realistic CL settings, which is a major challenge for the advancement of the field. In this paper we discuss some of the unrealistic data characteristics of public datasets, study the challenges of realistic single-task continuous learning as well as the effectiveness of data rehearsal as a way to mitigate accuracy loss. We construct a CL NER dataset from an existing publicly available dataset and release it along with the code to the research community.
Industry Scale Semi-Supervised Learning for Natural Language Understanding
Mar 29, 2021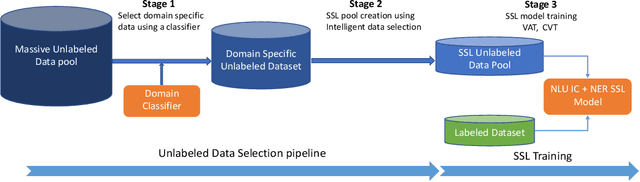
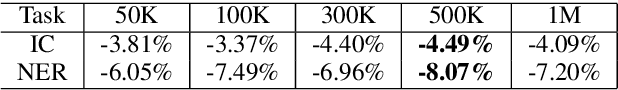
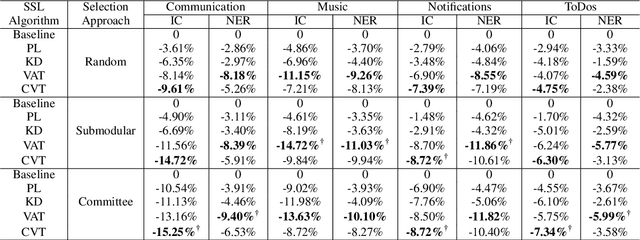
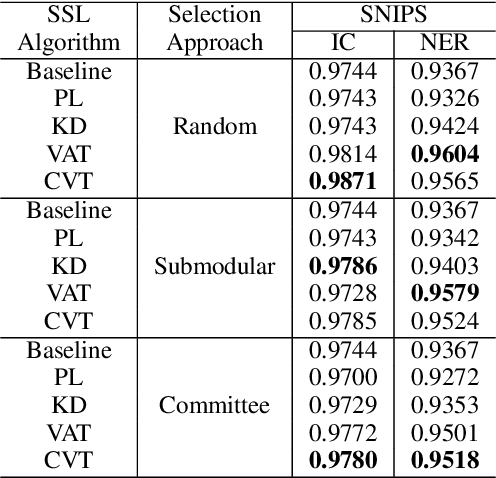
Abstract:This paper presents a production Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) pipeline based on the student-teacher framework, which leverages millions of unlabeled examples to improve Natural Language Understanding (NLU) tasks. We investigate two questions related to the use of unlabeled data in production SSL context: 1) how to select samples from a huge unlabeled data pool that are beneficial for SSL training, and 2) how do the selected data affect the performance of different state-of-the-art SSL techniques. We compare four widely used SSL techniques, Pseudo-Label (PL), Knowledge Distillation (KD), Virtual Adversarial Training (VAT) and Cross-View Training (CVT) in conjunction with two data selection methods including committee-based selection and submodular optimization based selection. We further examine the benefits and drawbacks of these techniques when applied to intent classification (IC) and named entity recognition (NER) tasks, and provide guidelines specifying when each of these methods might be beneficial to improve large scale NLU systems.
Efficient Semi-Supervised Learning for Natural Language Understanding by Optimizing Diversity
Oct 09, 2019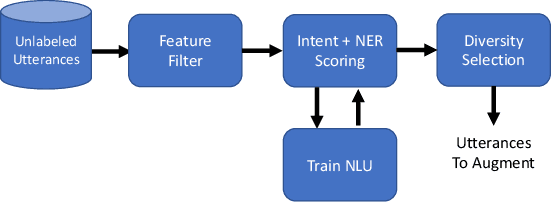
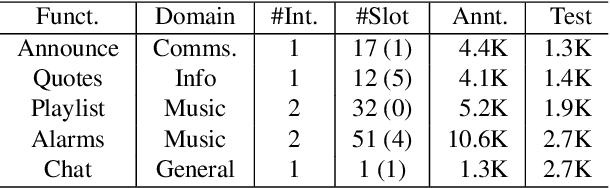
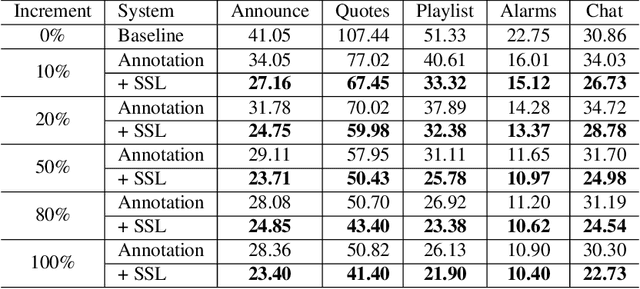
Abstract:Expanding new functionalities efficiently is an ongoing challenge for single-turn task-oriented dialogue systems. In this work, we explore functionality-specific semi-supervised learning via self-training. We consider methods that augment training data automatically from unlabeled data sets in a functionality-targeted manner. In addition, we examine multiple techniques for efficient selection of augmented utterances to reduce training time and increase diversity. First, we consider paraphrase detection methods that attempt to find utterance variants of labeled training data with good coverage. Second, we explore sub-modular optimization based on n-grams features for utterance selection. Experiments show that functionality-specific self-training is very effective for improving system performance. In addition, methods optimizing diversity can reduce training data in many cases to 50% with little impact on performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge