Greg Ver Steeg
ADNI
Generation Order and Parallel Decoding in Masked Diffusion Models: An Information-Theoretic Perspective
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Masked Diffusion Models (MDMs) significantly accelerate inference by trading off sequential determinism. However, the theoretical mechanisms governing generation order and the risks inherent in parallelization remain under-explored. In this work, we provide a unified information-theoretic framework to decouple and analyze two fundamental sources of failure: order sensitivity and parallelization bias. Our analysis yields three key insights: (1) The benefits of Easy-First decoding (prioritizing low-entropy tokens) are magnified as model error increases; (2) factorized parallel decoding introduces intrinsic sampling errors that can lead to arbitrary large Reverse KL divergence, capturing "incoherence" failures that standard Forward KL metrics overlook; and (3) while verification can eliminate sampling error, it incurs an exponential cost governed by the total correlation within a block. Conversely, heuristics like remasking, though computationally efficient, cannot guarantee distributional correctness. Experiments on a controlled Block-HMM and large-scale MDMs (LLaDA) for arithmetic reasoning validate our theoretical framework.
Thinking Out of Order: When Output Order Stops Reflecting Reasoning Order in Diffusion Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) language models enforce a fixed left-to-right generation order, creating a fundamental limitation when the required output structure conflicts with natural reasoning (e.g., producing answers before explanations due to presentation or schema constraints). In such cases, AR models must commit to answers before generating intermediate reasoning, and this rigid constraint forces premature commitment. Masked diffusion language models (MDLMs), which iteratively refine all tokens in parallel, offer a way to decouple computation order from output structure. We validate this capability on GSM8K, Math500, and ReasonOrderQA, a benchmark we introduce with controlled difficulty and order-level evaluation. When prompts request answers before reasoning, AR models exhibit large accuracy gaps compared to standard chain-of-thought ordering (up to 67% relative drop), while MDLMs remain stable ($\leq$14% relative drop), a property we term "order robustness". Using ReasonOrderQA, we present evidence that MDLMs achieve order robustness by stabilizing simpler tokens (e.g., reasoning steps) earlier in the diffusion process than complex ones (e.g., final answers), enabling reasoning tokens to stabilize before answer commitment. Finally, we identify failure conditions where this advantage weakens, outlining the limits required for order robustness.
Multi-modal Imputation for Alzheimer's Disease Classification
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Deep learning has been successful in predicting neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Combining multiple imaging modalities, such as T1-weighted (T1) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) scans, can increase diagnostic performance. However, complete multimodal datasets are not always available. We use a conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic model to impute missing DWI scans from T1 scans. We perform extensive experiments to evaluate whether such imputation improves the accuracy of uni-modal and bi-modal deep learning models for 3-way Alzheimer's disease classification-cognitively normal, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's disease. We observe improvements in several metrics, particularly those sensitive to minority classes, for several imputation configurations.
Measurement-aligned Flow for Inverse Problem
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models provide a powerful way to incorporate complex prior information for solving inverse problems. However, existing methods struggle to correctly incorporate guidance from conflicting signals in the prior and measurement, especially in the challenging setting of non-Gaussian or unknown noise. To bridge these gaps, we propose Measurement-Aligned Sampling (MAS), a novel framework for linear inverse problem solving that can more flexibly balance prior and measurement information. MAS unifies and extends existing approaches like DDNM and DAPS, and offers a new optimization perspective. MAS can generalize to handle known Gaussian noise, unknown or non-Gaussian noise types. Extensive experiments show that MAS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across a range of tasks.
AbFlowNet: Optimizing Antibody-Antigen Binding Energy via Diffusion-GFlowNet Fusion
May 18, 2025Abstract:Complementarity Determining Regions (CDRs) are critical segments of an antibody that facilitate binding to specific antigens. Current computational methods for CDR design utilize reconstruction losses and do not jointly optimize binding energy, a crucial metric for antibody efficacy. Rather, binding energy optimization is done through computationally expensive Online Reinforcement Learning (RL) pipelines rely heavily on unreliable binding energy estimators. In this paper, we propose AbFlowNet, a novel generative framework that integrates GFlowNet with Diffusion models. By framing each diffusion step as a state in the GFlowNet framework, AbFlowNet jointly optimizes standard diffusion losses and binding energy by directly incorporating energy signals into the training process, thereby unifying diffusion and reward optimization in a single procedure. Experimental results show that AbFlowNet outperforms the base diffusion model by 3.06% in amino acid recovery, 20.40% in geometric reconstruction (RMSD), and 3.60% in binding energy improvement ratio. ABFlowNet also decreases Top-1 total energy and binding energy errors by 24.8% and 38.1% without pseudo-labeling the test dataset or using computationally expensive online RL regimes.
Diffusion Bridge Models for 3D Medical Image Translation
Apr 21, 2025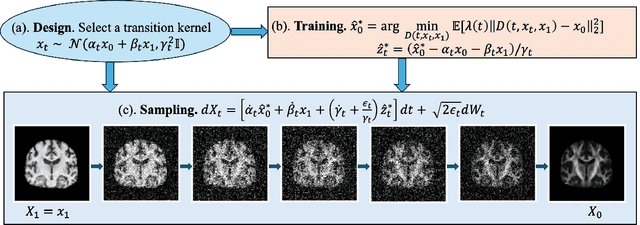
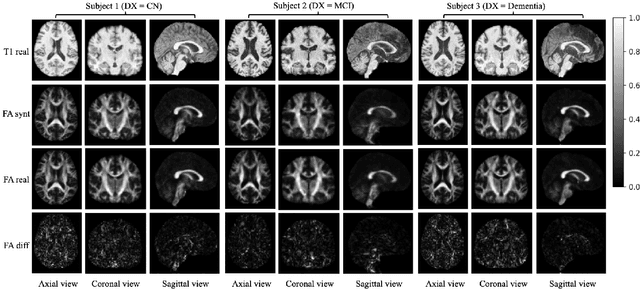
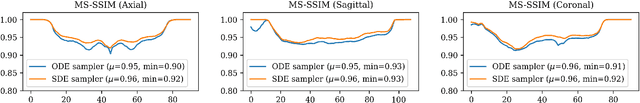
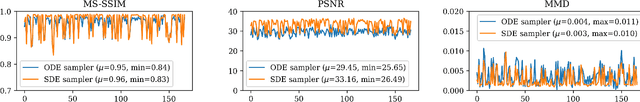
Abstract:Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) provides crucial insights into the microstructure of the human brain, but it can be time-consuming to acquire compared to more readily available T1-weighted (T1w) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). To address this challenge, we propose a diffusion bridge model for 3D brain image translation between T1w MRI and DTI modalities. Our model learns to generate high-quality DTI fractional anisotropy (FA) images from T1w images and vice versa, enabling cross-modality data augmentation and reducing the need for extensive DTI acquisition. We evaluate our approach using perceptual similarity, pixel-level agreement, and distributional consistency metrics, demonstrating strong performance in capturing anatomical structures and preserving information on white matter integrity. The practical utility of the synthetic data is validated through sex classification and Alzheimer's disease classification tasks, where the generated images achieve comparable performance to real data. Our diffusion bridge model offers a promising solution for improving neuroimaging datasets and supporting clinical decision-making, with the potential to significantly impact neuroimaging research and clinical practice.
KG-LLM-Bench: A Scalable Benchmark for Evaluating LLM Reasoning on Textualized Knowledge Graphs
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Knowledge graphs have emerged as a popular method for injecting up-to-date, factual knowledge into large language models (LLMs). This is typically achieved by converting the knowledge graph into text that the LLM can process in context. While multiple methods of encoding knowledge graphs have been proposed, the impact of this textualization process on LLM performance remains under-explored. We introduce KG-LLM-Bench, a comprehensive and extensible benchmark spanning five knowledge graph understanding tasks, and evaluate how different encoding strategies affect performance across various base models. Our extensive experiments with seven language models and five textualization strategies provide insights for optimizing LLM performance on KG reasoning tasks.
Making Sense Of Distributed Representations With Activation Spectroscopy
Jan 26, 2025Abstract:In the study of neural network interpretability, there is growing evidence to suggest that relevant features are encoded across many neurons in a distributed fashion. Making sense of these distributed representations without knowledge of the network's encoding strategy is a combinatorial task that is not guaranteed to be tractable. This work explores one feasible path to both detecting and tracing the joint influence of neurons in a distributed representation. We term this approach Activation Spectroscopy (ActSpec), owing to its analysis of the pseudo-Boolean Fourier spectrum defined over the activation patterns of a network layer. The sub-network defined between a given layer and an output logit is cast as a special class of pseudo-Boolean function. The contributions of each subset of neurons in the specified layer can be quantified through the function's Fourier coefficients. We propose a combinatorial optimization procedure to search for Fourier coefficients that are simultaneously high-valued, and non-redundant. This procedure can be viewed as an extension of the Goldreich-Levin algorithm which incorporates additional problem-specific constraints. The resulting coefficients specify a collection of subsets, which are used to test the degree to which a representation is distributed. We verify our approach in a number of synthetic settings and compare against existing interpretability benchmarks. We conclude with a number of experimental evaluations on an MNIST classifier, and a transformer-based network for sentiment analysis.
Learning Morphisms with Gauss-Newton Approximation for Growing Networks
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:A popular method for Neural Architecture Search (NAS) is based on growing networks via small local changes to the network's architecture called network morphisms. These methods start with a small seed network and progressively grow the network by adding new neurons in an automated way. However, it remains a challenge to efficiently determine which parts of the network are best to grow. Here we propose a NAS method for growing a network by using a Gauss-Newton approximation of the loss function to efficiently learn and evaluate candidate network morphisms. We compare our method with state of the art NAS methods for CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 classification tasks, and conclude our method learns similar quality or better architectures at a smaller computational cost.
Your Diffusion Model is Secretly a Noise Classifier and Benefits from Contrastive Training
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models learn to denoise data and the trained denoiser is then used to generate new samples from the data distribution. In this paper, we revisit the diffusion sampling process and identify a fundamental cause of sample quality degradation: the denoiser is poorly estimated in regions that are far Outside Of the training Distribution (OOD), and the sampling process inevitably evaluates in these OOD regions. This can become problematic for all sampling methods, especially when we move to parallel sampling which requires us to initialize and update the entire sample trajectory of dynamics in parallel, leading to many OOD evaluations. To address this problem, we introduce a new self-supervised training objective that differentiates the levels of noise added to a sample, leading to improved OOD denoising performance. The approach is based on our observation that diffusion models implicitly define a log-likelihood ratio that distinguishes distributions with different amounts of noise, and this expression depends on denoiser performance outside the standard training distribution. We show by diverse experiments that the proposed contrastive diffusion training is effective for both sequential and parallel settings, and it improves the performance and speed of parallel samplers significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge