Sujoy Paul
Test-Time Adaptation for Video Highlight Detection Using Meta-Auxiliary Learning and Cross-Modality Hallucinations
Aug 06, 2025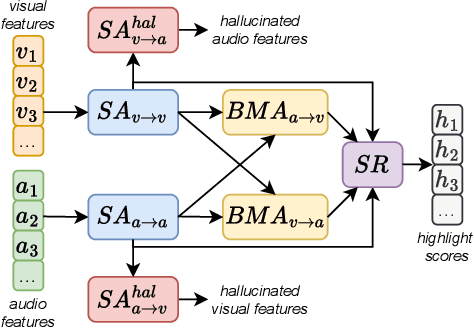
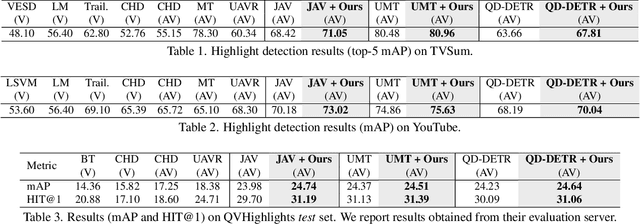
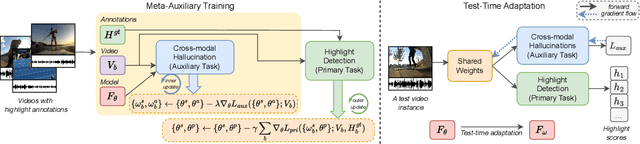
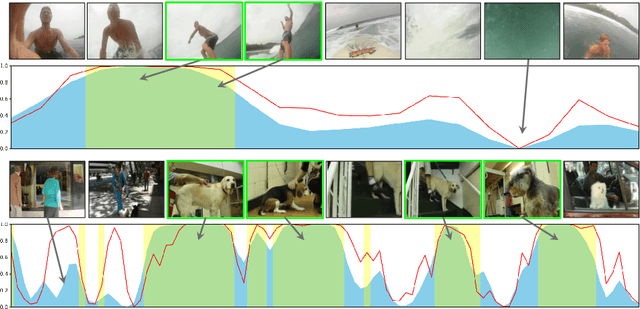
Abstract:Existing video highlight detection methods, although advanced, struggle to generalize well to all test videos. These methods typically employ a generic highlight detection model for each test video, which is suboptimal as it fails to account for the unique characteristics and variations of individual test videos. Such fixed models do not adapt to the diverse content, styles, or audio and visual qualities present in new, unseen test videos, leading to reduced highlight detection performance. In this paper, we propose Highlight-TTA, a test-time adaptation framework for video highlight detection that addresses this limitation by dynamically adapting the model during testing to better align with the specific characteristics of each test video, thereby improving generalization and highlight detection performance. Highlight-TTA is jointly optimized with an auxiliary task, cross-modality hallucinations, alongside the primary highlight detection task. We utilize a meta-auxiliary training scheme to enable effective adaptation through the auxiliary task while enhancing the primary task. During testing, we adapt the trained model using the auxiliary task on the test video to further enhance its highlight detection performance. Extensive experiments with three state-of-the-art highlight detection models and three benchmark datasets show that the introduction of Highlight-TTA to these models improves their performance, yielding superior results.
Mixture of Nested Experts: Adaptive Processing of Visual Tokens
Jul 29, 2024

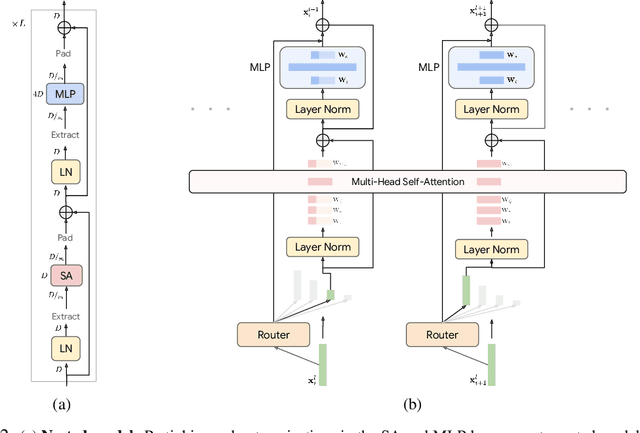
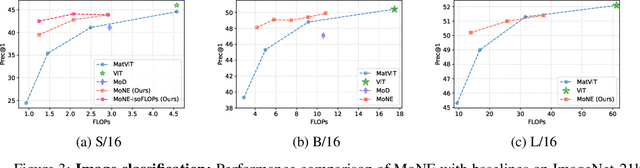
Abstract:The visual medium (images and videos) naturally contains a large amount of information redundancy, thereby providing a great opportunity for leveraging efficiency in processing. While Vision Transformer (ViT) based models scale effectively to large data regimes, they fail to capitalize on this inherent redundancy, leading to higher computational costs. Mixture of Experts (MoE) networks demonstrate scalability while maintaining same inference-time costs, but they come with a larger parameter footprint. We present Mixture of Nested Experts (MoNE), which utilizes a nested structure for experts, wherein individual experts fall on an increasing compute-accuracy curve. Given a compute budget, MoNE learns to dynamically choose tokens in a priority order, and thus redundant tokens are processed through cheaper nested experts. Using this framework, we achieve equivalent performance as the baseline models, while reducing inference time compute by over two-fold. We validate our approach on standard image and video datasets - ImageNet-21K, Kinetics400, and Something-Something-v2. We further highlight MoNE$'$s adaptability by showcasing its ability to maintain strong performance across different inference-time compute budgets on videos, using only a single trained model.
Unsupervised Video Highlight Detection by Learning from Audio and Visual Recurrence
Jul 18, 2024
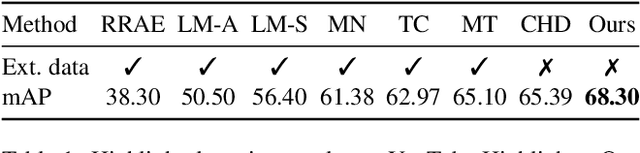
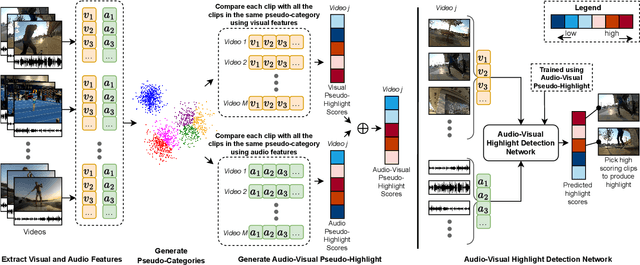
Abstract:With the exponential growth of video content, the need for automated video highlight detection to extract key moments or highlights from lengthy videos has become increasingly pressing. This technology has the potential to significantly enhance user experiences by allowing quick access to relevant content across diverse domains. Existing methods typically rely either on expensive manually labeled frame-level annotations, or on a large external dataset of videos for weak supervision through category information. To overcome this, we focus on unsupervised video highlight detection, eliminating the need for manual annotations. We propose an innovative unsupervised approach which capitalizes on the premise that significant moments tend to recur across multiple videos of the similar category in both audio and visual modalities. Surprisingly, audio remains under-explored, especially in unsupervised algorithms, despite its potential to detect key moments. Through a clustering technique, we identify pseudo-categories of videos and compute audio pseudo-highlight scores for each video by measuring the similarities of audio features among audio clips of all the videos within each pseudo-category. Similarly, we also compute visual pseudo-highlight scores for each video using visual features. Subsequently, we combine audio and visual pseudo-highlights to create the audio-visual pseudo ground-truth highlight of each video for training an audio-visual highlight detection network. Extensive experiments and ablation studies on three highlight detection benchmarks showcase the superior performance of our method over prior work.
LookupViT: Compressing visual information to a limited number of tokens
Jul 17, 2024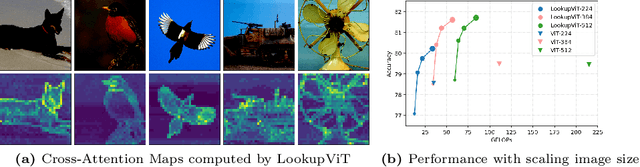
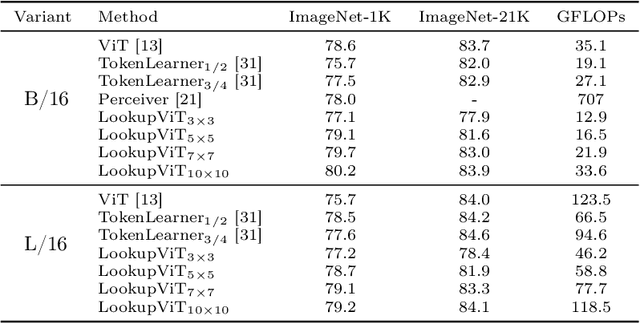
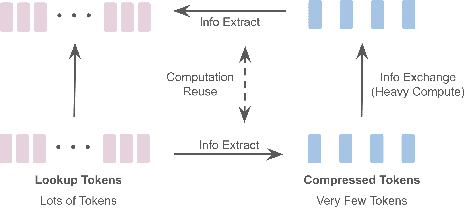
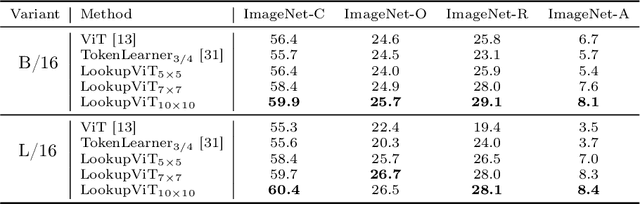
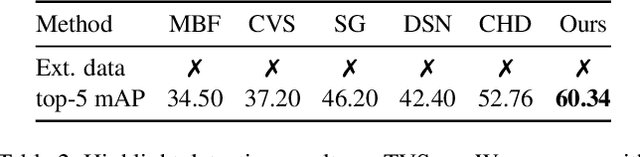
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViT) have emerged as the de-facto choice for numerous industry grade vision solutions. But their inference cost can be prohibitive for many settings, as they compute self-attention in each layer which suffers from quadratic computational complexity in the number of tokens. On the other hand, spatial information in images and spatio-temporal information in videos is usually sparse and redundant. In this work, we introduce LookupViT, that aims to exploit this information sparsity to reduce ViT inference cost. LookupViT provides a novel general purpose vision transformer block that operates by compressing information from higher resolution tokens to a fixed number of tokens. These few compressed tokens undergo meticulous processing, while the higher-resolution tokens are passed through computationally cheaper layers. Information sharing between these two token sets is enabled through a bidirectional cross-attention mechanism. The approach offers multiple advantages - (a) easy to implement on standard ML accelerators (GPUs/TPUs) via standard high-level operators, (b) applicable to standard ViT and its variants, thus generalizes to various tasks, (c) can handle different tokenization and attention approaches. LookupViT also offers flexibility for the compressed tokens, enabling performance-computation trade-offs in a single trained model. We show LookupViT's effectiveness on multiple domains - (a) for image-classification (ImageNet-1K and ImageNet-21K), (b) video classification (Kinetics400 and Something-Something V2), (c) image captioning (COCO-Captions) with a frozen encoder. LookupViT provides $2\times$ reduction in FLOPs while upholding or improving accuracy across these domains. In addition, LookupViT also demonstrates out-of-the-box robustness and generalization on image classification (ImageNet-C,R,A,O), improving by up to $4\%$ over ViT.
Analyzing the Efficacy of an LLM-Only Approach for Image-based Document Question Answering
Sep 25, 2023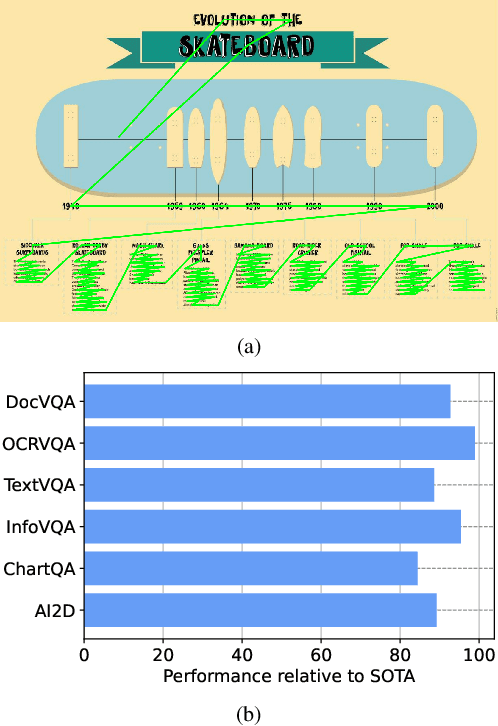
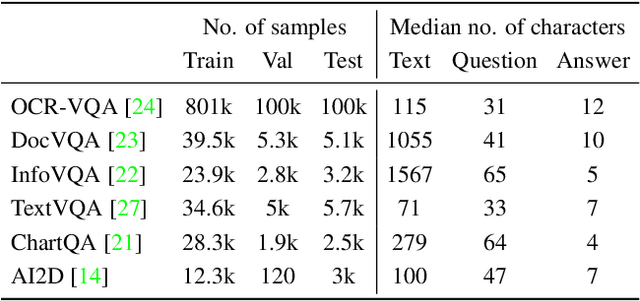
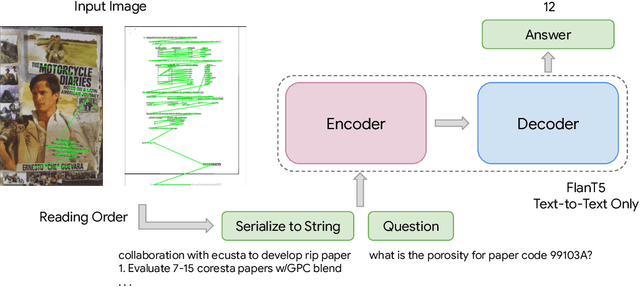
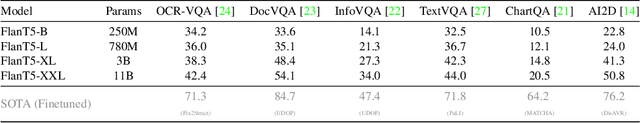
Abstract:Recent document question answering models consist of two key components: the vision encoder, which captures layout and visual elements in images, and a Large Language Model (LLM) that helps contextualize questions to the image and supplements them with external world knowledge to generate accurate answers. However, the relative contributions of the vision encoder and the language model in these tasks remain unclear. This is especially interesting given the effectiveness of instruction-tuned LLMs, which exhibit remarkable adaptability to new tasks. To this end, we explore the following aspects in this work: (1) The efficacy of an LLM-only approach on document question answering tasks (2) strategies for serializing textual information within document images and feeding it directly to an instruction-tuned LLM, thus bypassing the need for an explicit vision encoder (3) thorough quantitative analysis on the feasibility of such an approach. Our comprehensive analysis encompasses six diverse benchmark datasets, utilizing LLMs of varying scales. Our findings reveal that a strategy exclusively reliant on the LLM yields results that are on par with or closely approach state-of-the-art performance across a range of datasets. We posit that this evaluation framework will serve as a guiding resource for selecting appropriate datasets for future research endeavors that emphasize the fundamental importance of layout and image content information.
Is it an i or an l: Test-time Adaptation of Text Line Recognition Models
Aug 29, 2023



Abstract:Recognizing text lines from images is a challenging problem, especially for handwritten documents due to large variations in writing styles. While text line recognition models are generally trained on large corpora of real and synthetic data, such models can still make frequent mistakes if the handwriting is inscrutable or the image acquisition process adds corruptions, such as noise, blur, compression, etc. Writing style is generally quite consistent for an individual, which can be leveraged to correct mistakes made by such models. Motivated by this, we introduce the problem of adapting text line recognition models during test time. We focus on a challenging and realistic setting where, given only a single test image consisting of multiple text lines, the task is to adapt the model such that it performs better on the image, without any labels. We propose an iterative self-training approach that uses feedback from the language model to update the optical model, with confident self-labels in each iteration. The confidence measure is based on an augmentation mechanism that evaluates the divergence of the prediction of the model in a local region. We perform rigorous evaluation of our method on several benchmark datasets as well as their corrupted versions. Experimental results on multiple datasets spanning multiple scripts show that the proposed adaptation method offers an absolute improvement of up to 8% in character error rate with just a few iterations of self-training at test time.
Weakly supervised information extraction from inscrutable handwritten document images
Jun 12, 2023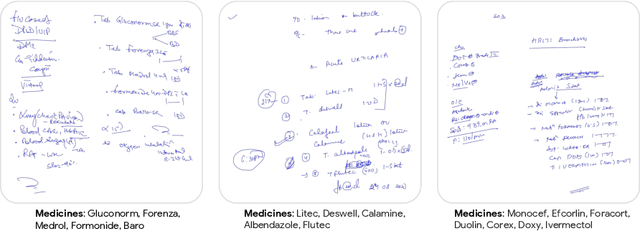

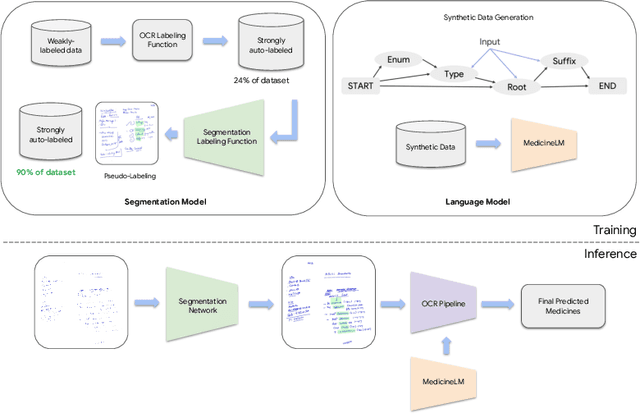
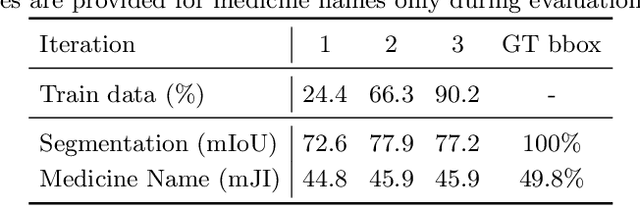
Abstract:State-of-the-art information extraction methods are limited by OCR errors. They work well for printed text in form-like documents, but unstructured, handwritten documents still remain a challenge. Adapting existing models to domain-specific training data is quite expensive, because of two factors, 1) limited availability of the domain-specific documents (such as handwritten prescriptions, lab notes, etc.), and 2) annotations become even more challenging as one needs domain-specific knowledge to decode inscrutable handwritten document images. In this work, we focus on the complex problem of extracting medicine names from handwritten prescriptions using only weakly labeled data. The data consists of images along with the list of medicine names in it, but not their location in the image. We solve the problem by first identifying the regions of interest, i.e., medicine lines from just weak labels and then injecting a domain-specific medicine language model learned using only synthetically generated data. Compared to off-the-shelf state-of-the-art methods, our approach performs >2.5x better in medicine names extraction from prescriptions.
Novel Class Discovery without Forgetting
Jul 21, 2022
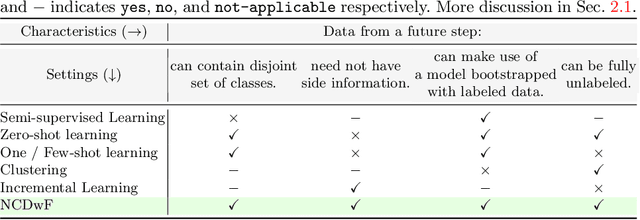
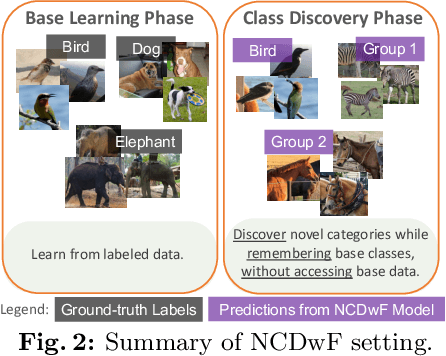
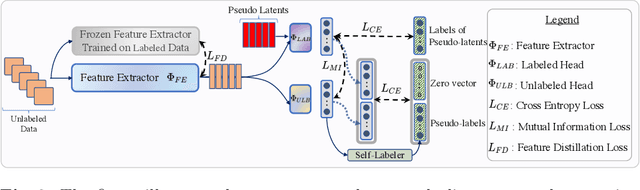
Abstract:Humans possess an innate ability to identify and differentiate instances that they are not familiar with, by leveraging and adapting the knowledge that they have acquired so far. Importantly, they achieve this without deteriorating the performance on their earlier learning. Inspired by this, we identify and formulate a new, pragmatic problem setting of NCDwF: Novel Class Discovery without Forgetting, which tasks a machine learning model to incrementally discover novel categories of instances from unlabeled data, while maintaining its performance on the previously seen categories. We propose 1) a method to generate pseudo-latent representations which act as a proxy for (no longer available) labeled data, thereby alleviating forgetting, 2) a mutual-information based regularizer which enhances unsupervised discovery of novel classes, and 3) a simple Known Class Identifier which aids generalized inference when the testing data contains instances form both seen and unseen categories. We introduce experimental protocols based on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100 and ImageNet-1000 to measure the trade-off between knowledge retention and novel class discovery. Our extensive evaluations reveal that existing models catastrophically forget previously seen categories while identifying novel categories, while our method is able to effectively balance between the competing objectives. We hope our work will attract further research into this newly identified pragmatic problem setting.
Spacing Loss for Discovering Novel Categories
Apr 22, 2022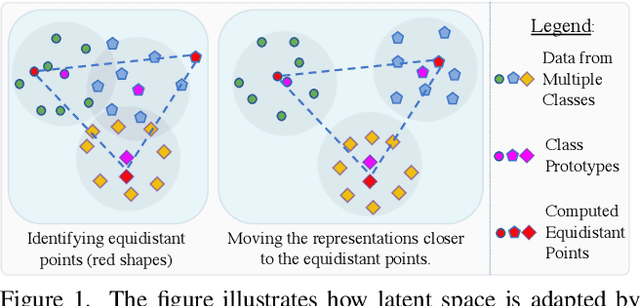
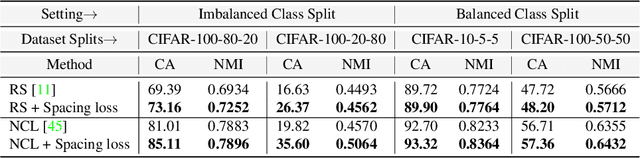
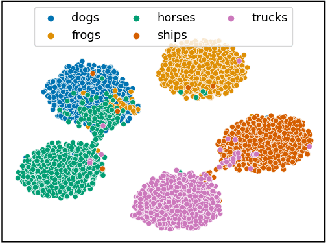
Abstract:Novel Class Discovery (NCD) is a learning paradigm, where a machine learning model is tasked to semantically group instances from unlabeled data, by utilizing labeled instances from a disjoint set of classes. In this work, we first characterize existing NCD approaches into single-stage and two-stage methods based on whether they require access to labeled and unlabeled data together while discovering new classes. Next, we devise a simple yet powerful loss function that enforces separability in the latent space using cues from multi-dimensional scaling, which we refer to as Spacing Loss. Our proposed formulation can either operate as a standalone method or can be plugged into existing methods to enhance them. We validate the efficacy of Spacing Loss with thorough experimental evaluation across multiple settings on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets.
SITA: Single Image Test-time Adaptation
Dec 08, 2021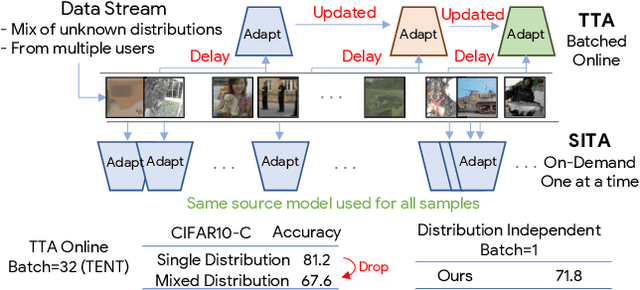
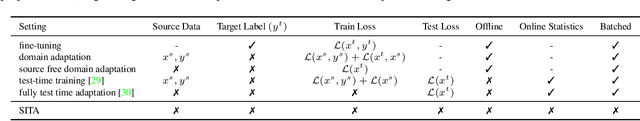
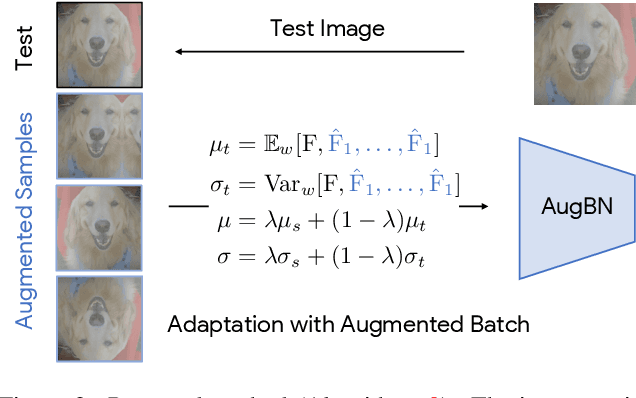
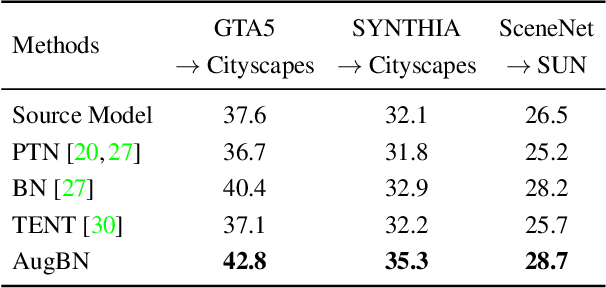
Abstract:In Test-time Adaptation (TTA), given a model trained on some source data, the goal is to adapt it to make better predictions for test instances from a different distribution. Crucially, TTA assumes no access to the source data or even any additional labeled/unlabeled samples from the target distribution to finetune the source model. In this work, we consider TTA in a more pragmatic setting which we refer to as SITA (Single Image Test-time Adaptation). Here, when making each prediction, the model has access only to the given single test instance, rather than a batch of instances, as has typically been considered in the literature. This is motivated by the realistic scenarios where inference is needed in an on-demand fashion that may not be delayed to "batch-ify" incoming requests or the inference is happening on an edge device (like mobile phone) where there is no scope for batching. The entire adaptation process in SITA should be extremely fast as it happens at inference time. To address this, we propose a novel approach AugBN for the SITA setting that requires only forward propagation. The approach can adapt any off-the-shelf trained model to individual test instances for both classification and segmentation tasks. AugBN estimates normalisation statistics of the unseen test distribution from the given test image using only one forward pass with label-preserving transformations. Since AugBN does not involve any back-propagation, it is significantly faster compared to other recent methods. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that addresses this hard adaptation problem using only a single test image. Despite being very simple, our framework is able to achieve significant performance gains compared to directly applying the source model on the target instances, as reflected in our extensive experiments and ablation studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge