Akankshya Mishra
Is the Top Still Spinning? Evaluating Subjectivity in Narrative Understanding
Apr 01, 2025
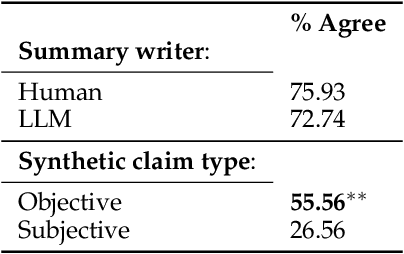
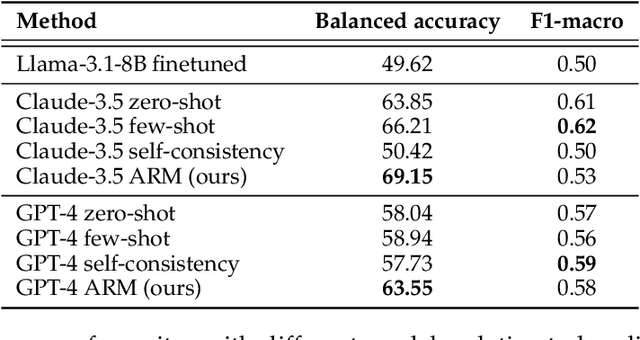
Abstract:Determining faithfulness of a claim to a source document is an important problem across many domains. This task is generally treated as a binary judgment of whether the claim is supported or unsupported in relation to the source. In many cases, though, whether a claim is supported can be ambiguous. For instance, it may depend on making inferences from given evidence, and different people can reasonably interpret the claim as either supported or unsupported based on their agreement with those inferences. Forcing binary labels upon such claims lowers the reliability of evaluation. In this work, we reframe the task to manage the subjectivity involved with factuality judgments of ambiguous claims. We introduce LLM-generated edits of summaries as a method of providing a nuanced evaluation of claims: how much does a summary need to be edited to be unambiguous? Whether a claim gets rewritten and how much it changes can be used as an automatic evaluation metric, the Ambiguity Rewrite Metric (ARM), with a much richer feedback signal than a binary judgment of faithfulness. We focus on the area of narrative summarization as it is particularly rife with ambiguity and subjective interpretation. We show that ARM produces a 21% absolute improvement in annotator agreement on claim faithfulness, indicating that subjectivity is reduced.
STORYSUMM: Evaluating Faithfulness in Story Summarization
Jul 09, 2024
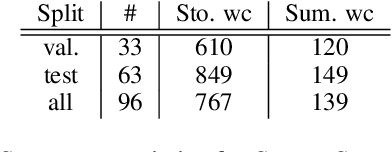
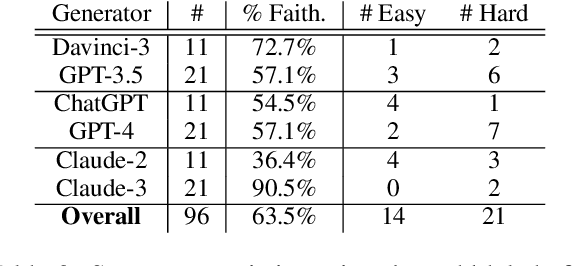
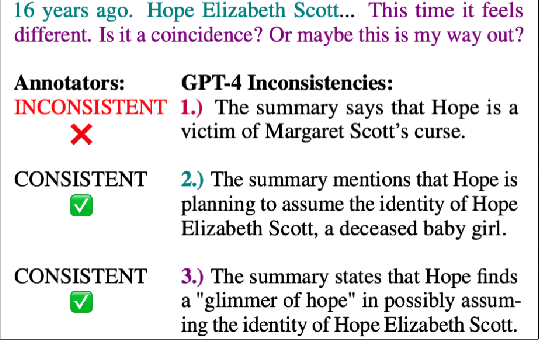
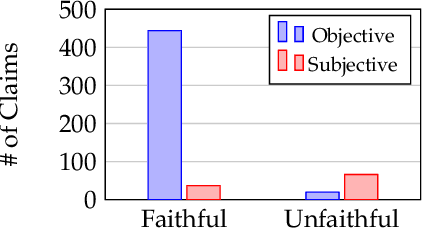
Abstract:Human evaluation has been the gold standard for checking faithfulness in abstractive summarization. However, with a challenging source domain like narrative, multiple annotators can agree a summary is faithful, while missing details that are obvious errors only once pointed out. We therefore introduce a new dataset, STORYSUMM, comprising LLM summaries of short stories with localized faithfulness labels and error explanations. This benchmark is for evaluation methods, testing whether a given method can detect challenging inconsistencies. Using this dataset, we first show that any one human annotation protocol is likely to miss inconsistencies, and we advocate for pursuing a range of methods when establishing ground truth for a summarization dataset. We finally test recent automatic metrics and find that none of them achieve more than 70% balanced accuracy on this task, demonstrating that it is a challenging benchmark for future work in faithfulness evaluation.
Weakly supervised information extraction from inscrutable handwritten document images
Jun 12, 2023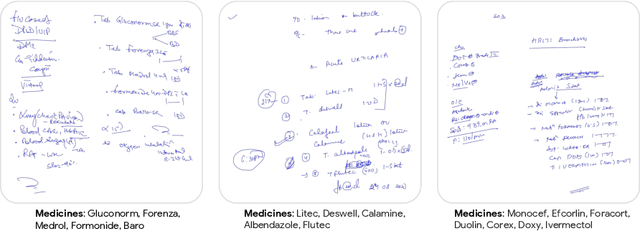

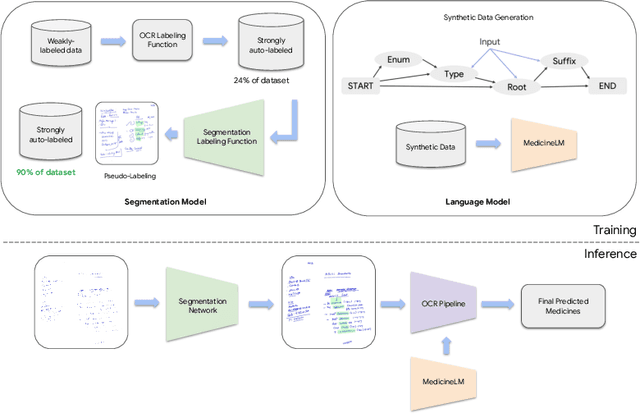
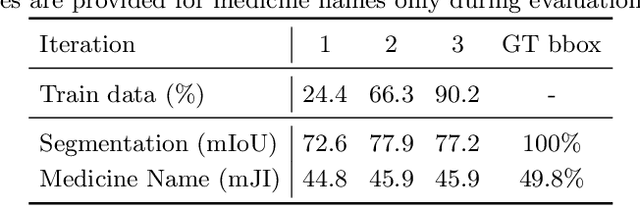
Abstract:State-of-the-art information extraction methods are limited by OCR errors. They work well for printed text in form-like documents, but unstructured, handwritten documents still remain a challenge. Adapting existing models to domain-specific training data is quite expensive, because of two factors, 1) limited availability of the domain-specific documents (such as handwritten prescriptions, lab notes, etc.), and 2) annotations become even more challenging as one needs domain-specific knowledge to decode inscrutable handwritten document images. In this work, we focus on the complex problem of extracting medicine names from handwritten prescriptions using only weakly labeled data. The data consists of images along with the list of medicine names in it, but not their location in the image. We solve the problem by first identifying the regions of interest, i.e., medicine lines from just weak labels and then injecting a domain-specific medicine language model learned using only synthetically generated data. Compared to off-the-shelf state-of-the-art methods, our approach performs >2.5x better in medicine names extraction from prescriptions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge