Shiyu Jiao
Energy-Efficiency Maximization for a WPT-D2D Pair in a MISO-NOMA Downlink Network
Oct 08, 2022



Abstract:The combination of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and wireless power transfer (WPT) is a promising solution to enhance the energy efficiency of Device-to-Device (D2D) enabled wireless communication networks. In this paper, we focus on maximizing the energy efficiency of a WPT-D2D pair in a multiple-input single-output (MISO)-NOMA downlink network, by alternatively optimizing the beamforming vectors of the base station (BS) and the time switching coefficient of the WPT assisted D2D transmitter. The formulated energy efficiency maximization problem is non-convex due to the highly coupled variables. To efficiently address the non-convex problem, we first divide it into two subproblems. Afterwards, an alternating algorithm based on the Dinkelbach method and quadratic transform is proposed to solve the two subproblems iteratively. To verify the proposed alternating algorithm's accuracy, partial exhaustive search algorithm is proposed as a benchmark. We also utilize a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) method to solve the non-convex problem and compare it with the proposed algorithm. To demonstrate the respective superiority of the proposed algorithm and DRL-based method, simulations are performed for two scenarios of perfect and imperfect channel state information (CSI). Simulation results are provided to compare NOMA and orthogonal multiple access (OMA), which demonstrate the superior performance of energy efficiency of the NOMA scheme.
Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Optimization for IRS Based UAV-NOMA Downlink Networks
Jun 17, 2021
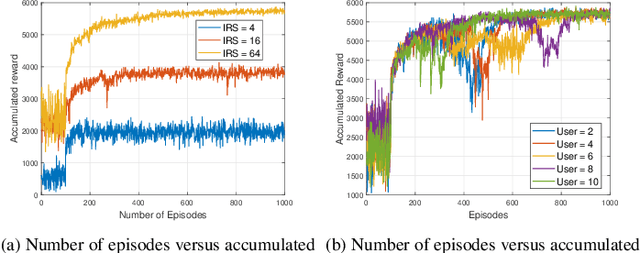
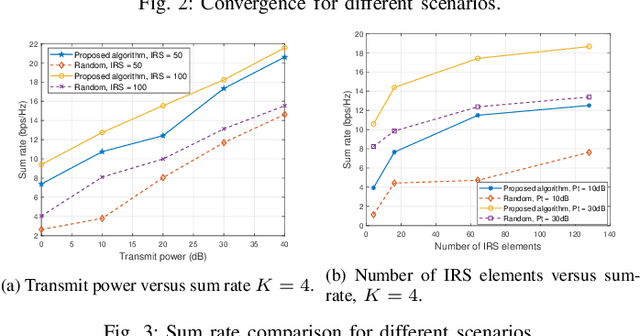
Abstract:This paper investigates the application of deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) to intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) based unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) assisted non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) downlink networks. The deployment of the UAV equipped with an IRS is important, as the UAV increases the flexibility of the IRS significantly, especially for the case of users who have no line of sight (LoS) path to the base station (BS). Therefore, the aim of this letter is to maximize the sum rate by jointly optimizing the power allocation of the BS, the phase shifting of the IRS and the horizontal position of the UAV. Because the formulated problem is not convex, the DDPG algorithm is utilized to solve it. The computer simulation results are provided to show the superior performance of the proposed DDPG based algorithm.
A Reinforcement Learning Approach for an IRS-assisted NOMA Network
Jun 17, 2021

Abstract:This letter investigates a sum rate maximizationproblem in an intelligent reflective surface (IRS) assisted non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) downlink network. Specif-ically, the sum rate of all the users is maximized by jointlyoptimizing the beams at the base station and the phase shiftat the IRS. The deep reinforcement learning (DRL), which hasachieved massive successes, is applied to solve this sum ratemaximization problem. In particular, an algorithm based on thedeep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) is proposed. Both therandom channel case and the fixed channel case are studied inthis letter. The simulation result illustrates that the DDPG basedalgorithm has the competitive performance on both case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge