Hongbo Chen
OMG-Bench: A New Challenging Benchmark for Skeleton-based Online Micro Hand Gesture Recognition
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Online micro gesture recognition from hand skeletons is critical for VR/AR interaction but faces challenges due to limited public datasets and task-specific algorithms. Micro gestures involve subtle motion patterns, which make constructing datasets with precise skeletons and frame-level annotations difficult. To this end, we develop a multi-view self-supervised pipeline to automatically generate skeleton data, complemented by heuristic rules and expert refinement for semi-automatic annotation. Based on this pipeline, we introduce OMG-Bench, the first large-scale public benchmark for skeleton-based online micro gesture recognition. It features 40 fine-grained gesture classes with 13,948 instances across 1,272 sequences, characterized by subtle motions, rapid dynamics, and continuous execution. To tackle these challenges, we propose Hierarchical Memory-Augmented Transformer (HMATr), an end-to-end framework that unifies gesture detection and classification by leveraging hierarchical memory banks which store frame-level details and window-level semantics to preserve historical context. In addition, it employs learnable position-aware queries initialized from the memory to implicitly encode gesture positions and semantics. Experiments show that HMATr outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 7.6\% in detection rate, establishing a strong baseline for online micro gesture recognition. Project page: https://omg-bench.github.io/
RAVES-Calib: Robust, Accurate and Versatile Extrinsic Self Calibration Using Optimal Geometric Features
Dec 09, 2025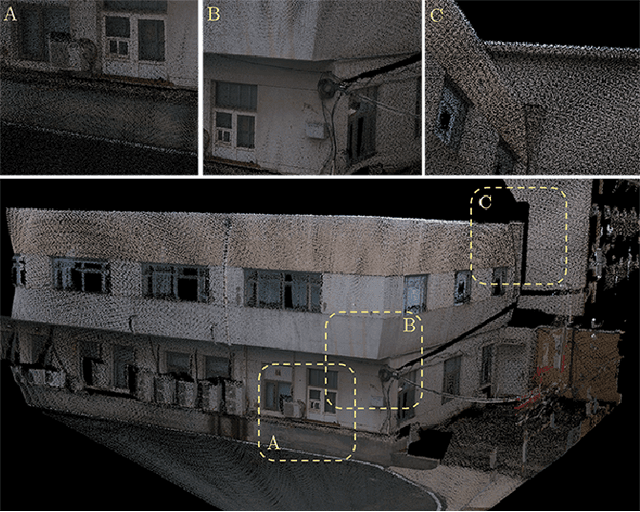
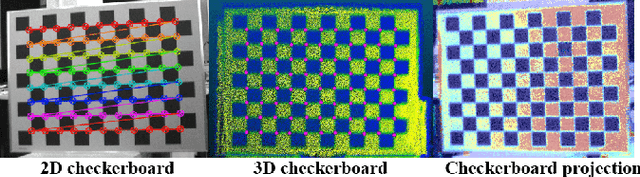
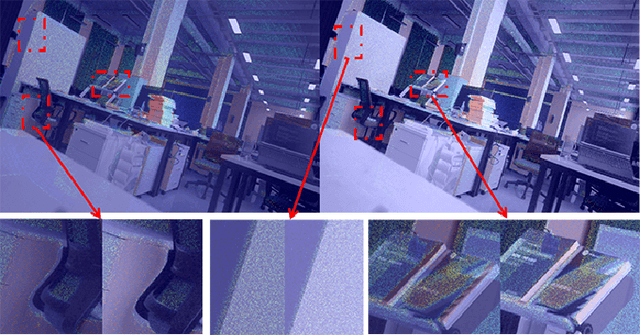
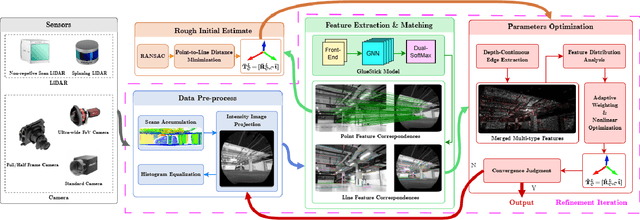
Abstract:In this paper, we present a user-friendly LiDAR-camera calibration toolkit that is compatible with various LiDAR and camera sensors and requires only a single pair of laser points and a camera image in targetless environments. Our approach eliminates the need for an initial transform and remains robust even with large positional and rotational LiDAR-camera extrinsic parameters. We employ the Gluestick pipeline to establish 2D-3D point and line feature correspondences for a robust and automatic initial guess. To enhance accuracy, we quantitatively analyze the impact of feature distribution on calibration results and adaptively weight the cost of each feature based on these metrics. As a result, extrinsic parameters are optimized by filtering out the adverse effects of inferior features. We validated our method through extensive experiments across various LiDAR-camera sensors in both indoor and outdoor settings. The results demonstrate that our method provides superior robustness and accuracy compared to SOTA techniques. Our code is open-sourced on GitHub to benefit the community.
MA-SLAM: Active SLAM in Large-Scale Unknown Environment using Map Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Active Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (Active SLAM) involves the strategic planning and precise control of a robotic system's movement in order to construct a highly accurate and comprehensive representation of its surrounding environment, which has garnered significant attention within the research community. While the current methods demonstrate efficacy in small and controlled settings, they face challenges when applied to large-scale and diverse environments, marked by extended periods of exploration and suboptimal paths of discovery. In this paper, we propose MA-SLAM, a Map-Aware Active SLAM system based on Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL), designed to address the challenge of efficient exploration in large-scale environments. In pursuit of this objective, we put forward a novel structured map representation. By discretizing the spatial data and integrating the boundary points and the historical trajectory, the structured map succinctly and effectively encapsulates the visited regions, thereby serving as input for the deep reinforcement learning based decision module. Instead of sequentially predicting the next action step within the decision module, we have implemented an advanced global planner to optimize the exploration path by leveraging long-range target points. We conducted experiments in three simulation environments and deployed in a real unmanned ground vehicle (UGV), the results demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces both the duration and distance of exploration compared with state-of-the-art methods.
PUL-SLAM: Path-Uncertainty Co-Optimization with Lightweight Stagnation Detection for Efficient Robotic Exploration
Nov 06, 2025
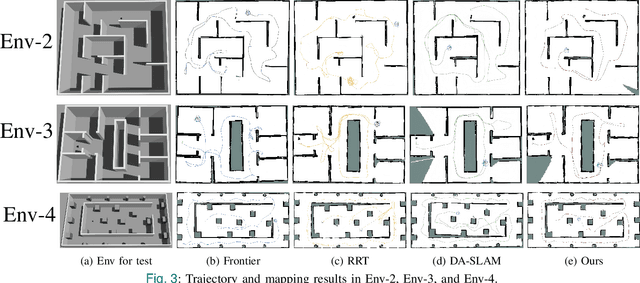
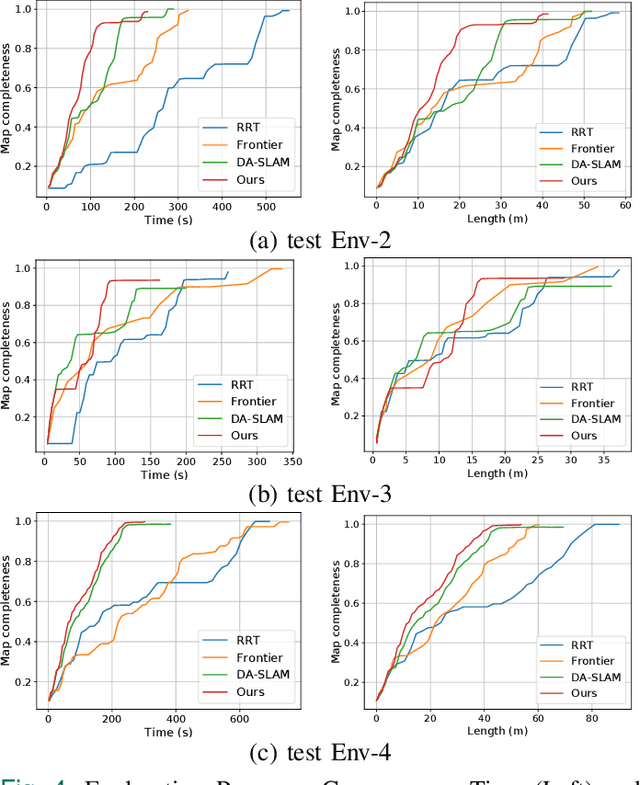
Abstract:Existing Active SLAM methodologies face issues such as slow exploration speed and suboptimal paths. To address these limitations, we propose a hybrid framework combining a Path-Uncertainty Co-Optimization Deep Reinforcement Learning framework and a Lightweight Stagnation Detection mechanism. The Path-Uncertainty Co-Optimization framework jointly optimizes travel distance and map uncertainty through a dual-objective reward function, balancing exploration and exploitation. The Lightweight Stagnation Detection reduces redundant exploration through Lidar Static Anomaly Detection and Map Update Stagnation Detection, terminating episodes on low expansion rates. Experimental results show that compared with the frontier-based method and RRT method, our approach shortens exploration time by up to 65% and reduces path distance by up to 42%, significantly improving exploration efficiency in complex environments while maintaining reliable map completeness. Ablation studies confirm that the collaborative mechanism accelerates training convergence. Empirical validation on a physical robotic platform demonstrates the algorithm's practical applicability and its successful transferability from simulation to real-world environments.
General and Estimable Learning Bound Unifying Covariate and Concept Shifts
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Generalization under distribution shift remains a core challenge in modern machine learning, yet existing learning bound theory is limited to narrow, idealized settings and is non-estimable from samples. In this paper, we bridge the gap between theory and practical applications. We first show that existing bounds become loose and non-estimable because their concept shift definition breaks when the source and target supports mismatch. Leveraging entropic optimal transport, we propose new support-agnostic definitions for covariate and concept shifts, and derive a novel unified error bound that applies to broad loss functions, label spaces, and stochastic labeling. We further develop estimators for these shifts with concentration guarantees, and the DataShifts algorithm, which can quantify distribution shifts and estimate the error bound in most applications -- a rigorous and general tool for analyzing learning error under distribution shift.
Reinforcing Video Reasoning with Focused Thinking
May 30, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in reinforcement learning, particularly through Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), have significantly improved multimodal large language models for complex reasoning tasks. However, two critical limitations persist: 1) they often produce unfocused, verbose reasoning chains that obscure salient spatiotemporal cues and 2) binary rewarding fails to account for partially correct answers, resulting in high reward variance and inefficient learning. In this paper, we propose TW-GRPO, a novel framework that enhances visual reasoning with focused thinking and dense reward granularity. Specifically, we employs a token weighting mechanism that prioritizes tokens with high informational density (estimated by intra-group variance), suppressing redundant tokens like generic reasoning prefixes. Furthermore, we reformulate RL training by shifting from single-choice to multi-choice QA tasks, where soft rewards enable finer-grained gradient estimation by distinguishing partial correctness. Additionally, we propose question-answer inversion, a data augmentation strategy to generate diverse multi-choice samples from existing benchmarks. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on several video reasoning and general understanding benchmarks. Notably, TW-GRPO achieves 50.4\% accuracy on CLEVRER (18.8\% improvement over Video-R1) and 65.8\% on MMVU. Our codes are available at \href{https://github.com/longmalongma/TW-GRPO}{https://github.com/longmalongma/TW-GRPO}.
ImplicitCell: Resolution Cell Modeling of Joint Implicit Volume Reconstruction and Pose Refinement in Freehand 3D Ultrasound
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Freehand 3D ultrasound enables volumetric imaging by tracking a conventional ultrasound probe during freehand scanning, offering enriched spatial information that improves clinical diagnosis. However, the quality of reconstructed volumes is often compromised by tracking system noise and irregular probe movements, leading to artifacts in the final reconstruction. To address these challenges, we propose ImplicitCell, a novel framework that integrates Implicit Neural Representation (INR) with an ultrasound resolution cell model for joint optimization of volume reconstruction and pose refinement. Three distinct datasets are used for comprehensive validation, including phantom, common carotid artery, and carotid atherosclerosis. Experimental results demonstrate that ImplicitCell significantly reduces reconstruction artifacts and improves volume quality compared to existing methods, particularly in challenging scenarios with noisy tracking data. These improvements enhance the clinical utility of freehand 3D ultrasound by providing more reliable and precise diagnostic information.
CaRtGS: Computational Alignment for Real-Time Gaussian Splatting SLAM
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is pivotal in robotics, with photorealistic scene reconstruction emerging as a key challenge. To address this, we introduce Computational Alignment for Real-Time Gaussian Splatting SLAM (CaRtGS), a novel method enhancing the efficiency and quality of photorealistic scene reconstruction in real-time environments. Leveraging 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), CaRtGS achieves superior rendering quality and processing speed, which is crucial for scene photorealistic reconstruction. Our approach tackles computational misalignment in Gaussian Splatting SLAM (GS-SLAM) through an adaptive strategy that optimizes training, addresses long-tail optimization, and refines densification. Experiments on Replica and TUM-RGBD datasets demonstrate CaRtGS's effectiveness in achieving high-fidelity rendering with fewer Gaussian primitives. This work propels SLAM towards real-time, photorealistic dense rendering, significantly advancing photorealistic scene representation. For the benefit of the research community, we release the code on our project website: https://dapengfeng.github.io/cartgs.
Heterogeneous LiDAR Dataset for Benchmarking Robust Localization in Diverse Degenerate Scenarios
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:The ability to estimate pose and generate maps using 3D LiDAR significantly enhances robotic system autonomy. However, existing open-source datasets lack representation of geometrically degenerate environments, limiting the development and benchmarking of robust LiDAR SLAM algorithms. To address this gap, we introduce GEODE, a comprehensive multi-LiDAR, multi-scenario dataset specifically designed to include real-world geometrically degenerate environments. GEODE comprises 64 trajectories spanning over 64 kilometers across seven diverse settings with varying degrees of degeneracy. The data was meticulously collected to promote the development of versatile algorithms by incorporating various LiDAR sensors, stereo cameras, IMUs, and diverse motion conditions. We evaluate state-of-the-art SLAM approaches using the GEODE dataset to highlight current limitations in LiDAR SLAM techniques. This extensive dataset will be publicly available at https://geode.github.io, supporting further advancements in LiDAR-based SLAM.
RoCoSDF: Row-Column Scanned Neural Signed Distance Fields for Freehand 3D Ultrasound Imaging Shape Reconstruction
Aug 14, 2024



Abstract:The reconstruction of high-quality shape geometry is crucial for developing freehand 3D ultrasound imaging. However, the shape reconstruction of multi-view ultrasound data remains challenging due to the elevation distortion caused by thick transducer probes. In this paper, we present a novel learning-based framework RoCoSDF, which can effectively generate an implicit surface through continuous shape representations derived from row-column scanned datasets. In RoCoSDF, we encode the datasets from different views into the corresponding neural signed distance function (SDF) and then operate all SDFs in a normalized 3D space to restore the actual surface contour. Without requiring pre-training on large-scale ground truth shapes, our approach can synthesize a smooth and continuous signed distance field from multi-view SDFs to implicitly represent the actual geometry. Furthermore, two regularizers are introduced to facilitate shape refinement by constraining the SDF near the surface. The experiments on twelve shapes data acquired by two ultrasound transducer probes validate that RoCoSDF can effectively reconstruct accurate geometric shapes from multi-view ultrasound data, which outperforms current reconstruction methods. Code is available at https://github.com/chenhbo/RoCoSDF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge