Hongye Zeng
Multi-Class Segmentation of Aortic Branches and Zones in Computed Tomography Angiography: The AortaSeg24 Challenge
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:Multi-class segmentation of the aorta in computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans is essential for diagnosing and planning complex endovascular treatments for patients with aortic dissections. However, existing methods reduce aortic segmentation to a binary problem, limiting their ability to measure diameters across different branches and zones. Furthermore, no open-source dataset is currently available to support the development of multi-class aortic segmentation methods. To address this gap, we organized the AortaSeg24 MICCAI Challenge, introducing the first dataset of 100 CTA volumes annotated for 23 clinically relevant aortic branches and zones. This dataset was designed to facilitate both model development and validation. The challenge attracted 121 teams worldwide, with participants leveraging state-of-the-art frameworks such as nnU-Net and exploring novel techniques, including cascaded models, data augmentation strategies, and custom loss functions. We evaluated the submitted algorithms using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Normalized Surface Distance (NSD), highlighting the approaches adopted by the top five performing teams. This paper presents the challenge design, dataset details, evaluation metrics, and an in-depth analysis of the top-performing algorithms. The annotated dataset, evaluation code, and implementations of the leading methods are publicly available to support further research. All resources can be accessed at https://aortaseg24.grand-challenge.org.
Reliable Source Approximation: Source-Free Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Vestibular Schwannoma MRI Segmentation
May 25, 2024



Abstract:Source-Free Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (SFUDA) has recently become a focus in the medical image domain adaptation, as it only utilizes the source model and does not require annotated target data. However, current SFUDA approaches cannot tackle the complex segmentation task across different MRI sequences, such as the vestibular schwannoma segmentation. To address this problem, we proposed Reliable Source Approximation (RSA), which can generate source-like and structure-preserved images from the target domain for updating model parameters and adapting domain shifts. Specifically, RSA deploys a conditional diffusion model to generate multiple source-like images under the guidance of varying edges of one target image. An uncertainty estimation module is then introduced to predict and refine reliable pseudo labels of generated images, and the prediction consistency is developed to select the most reliable generations. Subsequently, all reliable generated images and their pseudo labels are utilized to update the model. Our RSA is validated on vestibular schwannoma segmentation across multi-modality MRI. The experimental results demonstrate that RSA consistently improves domain adaptation performance over other state-of-the-art SFUDA methods. Code is available at https://github.com/zenghy96/Reliable-Source-Approximation.
Training-free image style alignment for self-adapting domain shift on handheld ultrasound devices
Feb 17, 2024



Abstract:Handheld ultrasound devices face usage limitations due to user inexperience and cannot benefit from supervised deep learning without extensive expert annotations. Moreover, the models trained on standard ultrasound device data are constrained by training data distribution and perform poorly when directly applied to handheld device data. In this study, we propose the Training-free Image Style Alignment (TISA) framework to align the style of handheld device data to those of standard devices. The proposed TISA can directly infer handheld device images without extra training and is suited for clinical applications. We show that TISA performs better and more stably in medical detection and segmentation tasks for handheld device data. We further validate TISA as the clinical model for automatic measurements of spinal curvature and carotid intima-media thickness. The automatic measurements agree well with manual measurements made by human experts and the measurement errors remain within clinically acceptable ranges. We demonstrate the potential for TISA to facilitate automatic diagnosis on handheld ultrasound devices and expedite their eventual widespread use.
VertMatch: A Semi-supervised Framework for Vertebral Structure Detection in 3D Ultrasound Volume
Dec 28, 2022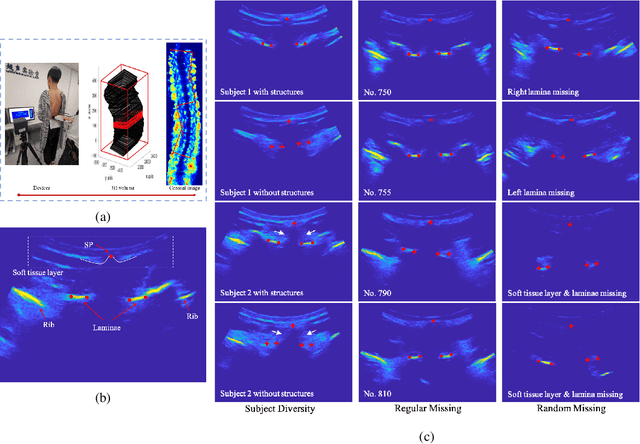
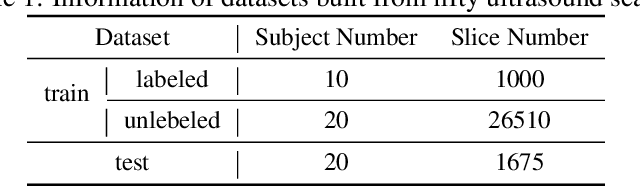
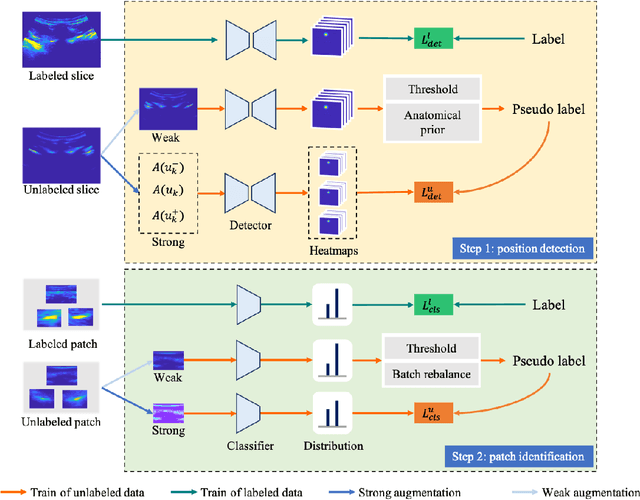
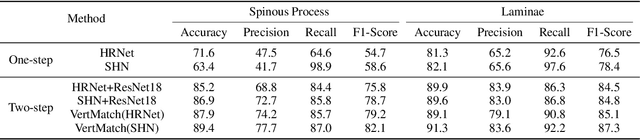
Abstract:Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound imaging technique has been applied for scoliosis assessment, but current assessment method only uses coronal projection image and cannot illustrate the 3D deformity and vertebra rotation. The vertebra detection is essential to reveal 3D spine information, but the detection task is challenging due to complex data and limited annotations. We propose VertMatch, a two-step framework to detect vertebral structures in 3D ultrasound volume by utilizing unlabeled data in semi-supervised manner. The first step is to detect the possible positions of structures on transverse slice globally, and then the local patches are cropped based on detected positions. The second step is to distinguish whether the patches contain real vertebral structures and screen the predicted positions from the first step. VertMatch develops three novel components for semi-supervised learning: for position detection in the first step, (1) anatomical prior is used to screen pseudo labels generated from confidence threshold method; (2) multi-slice consistency is used to utilize more unlabeled data by inputting multiple adjacent slices; (3) for patch identification in the second step, the categories are rebalanced in each batch to solve imbalance problem. Experimental results demonstrate that VertMatch can detect vertebra accurately in ultrasound volume and outperforms state-of-the-art methods. VertMatch is also validated in clinical application on forty ultrasound scans, and it can be a promising approach for 3D assessment of scoliosis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge