Dapeng Feng
MA-SLAM: Active SLAM in Large-Scale Unknown Environment using Map Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Active Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (Active SLAM) involves the strategic planning and precise control of a robotic system's movement in order to construct a highly accurate and comprehensive representation of its surrounding environment, which has garnered significant attention within the research community. While the current methods demonstrate efficacy in small and controlled settings, they face challenges when applied to large-scale and diverse environments, marked by extended periods of exploration and suboptimal paths of discovery. In this paper, we propose MA-SLAM, a Map-Aware Active SLAM system based on Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL), designed to address the challenge of efficient exploration in large-scale environments. In pursuit of this objective, we put forward a novel structured map representation. By discretizing the spatial data and integrating the boundary points and the historical trajectory, the structured map succinctly and effectively encapsulates the visited regions, thereby serving as input for the deep reinforcement learning based decision module. Instead of sequentially predicting the next action step within the decision module, we have implemented an advanced global planner to optimize the exploration path by leveraging long-range target points. We conducted experiments in three simulation environments and deployed in a real unmanned ground vehicle (UGV), the results demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces both the duration and distance of exploration compared with state-of-the-art methods.
PUL-SLAM: Path-Uncertainty Co-Optimization with Lightweight Stagnation Detection for Efficient Robotic Exploration
Nov 06, 2025
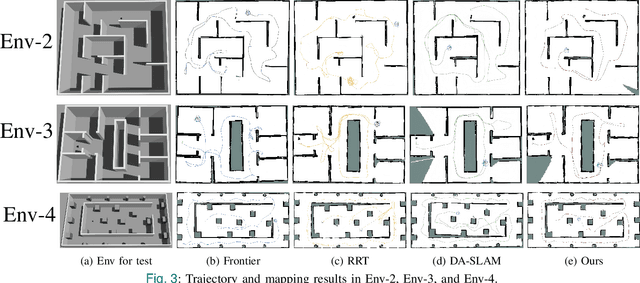
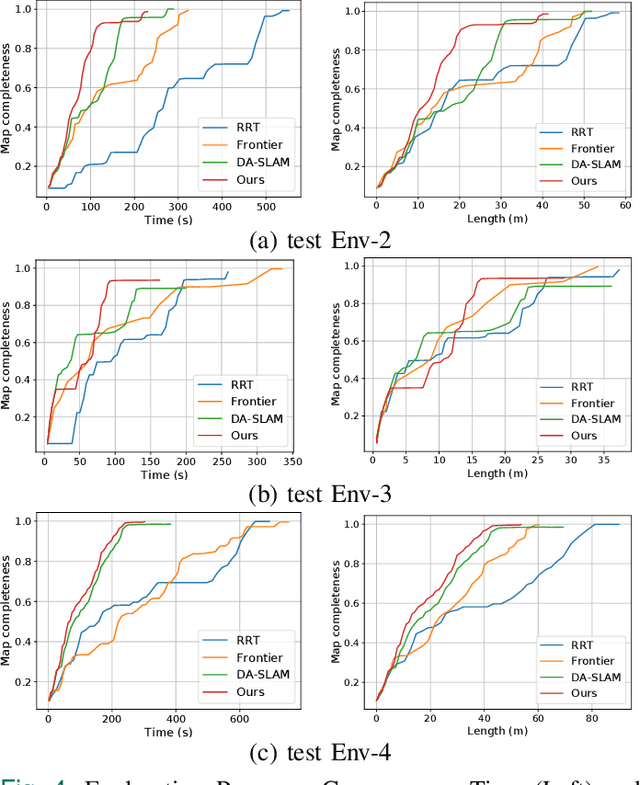
Abstract:Existing Active SLAM methodologies face issues such as slow exploration speed and suboptimal paths. To address these limitations, we propose a hybrid framework combining a Path-Uncertainty Co-Optimization Deep Reinforcement Learning framework and a Lightweight Stagnation Detection mechanism. The Path-Uncertainty Co-Optimization framework jointly optimizes travel distance and map uncertainty through a dual-objective reward function, balancing exploration and exploitation. The Lightweight Stagnation Detection reduces redundant exploration through Lidar Static Anomaly Detection and Map Update Stagnation Detection, terminating episodes on low expansion rates. Experimental results show that compared with the frontier-based method and RRT method, our approach shortens exploration time by up to 65% and reduces path distance by up to 42%, significantly improving exploration efficiency in complex environments while maintaining reliable map completeness. Ablation studies confirm that the collaborative mechanism accelerates training convergence. Empirical validation on a physical robotic platform demonstrates the algorithm's practical applicability and its successful transferability from simulation to real-world environments.
CaRtGS: Computational Alignment for Real-Time Gaussian Splatting SLAM
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is pivotal in robotics, with photorealistic scene reconstruction emerging as a key challenge. To address this, we introduce Computational Alignment for Real-Time Gaussian Splatting SLAM (CaRtGS), a novel method enhancing the efficiency and quality of photorealistic scene reconstruction in real-time environments. Leveraging 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), CaRtGS achieves superior rendering quality and processing speed, which is crucial for scene photorealistic reconstruction. Our approach tackles computational misalignment in Gaussian Splatting SLAM (GS-SLAM) through an adaptive strategy that optimizes training, addresses long-tail optimization, and refines densification. Experiments on Replica and TUM-RGBD datasets demonstrate CaRtGS's effectiveness in achieving high-fidelity rendering with fewer Gaussian primitives. This work propels SLAM towards real-time, photorealistic dense rendering, significantly advancing photorealistic scene representation. For the benefit of the research community, we release the code on our project website: https://dapengfeng.github.io/cartgs.
Heterogeneous LiDAR Dataset for Benchmarking Robust Localization in Diverse Degenerate Scenarios
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:The ability to estimate pose and generate maps using 3D LiDAR significantly enhances robotic system autonomy. However, existing open-source datasets lack representation of geometrically degenerate environments, limiting the development and benchmarking of robust LiDAR SLAM algorithms. To address this gap, we introduce GEODE, a comprehensive multi-LiDAR, multi-scenario dataset specifically designed to include real-world geometrically degenerate environments. GEODE comprises 64 trajectories spanning over 64 kilometers across seven diverse settings with varying degrees of degeneracy. The data was meticulously collected to promote the development of versatile algorithms by incorporating various LiDAR sensors, stereo cameras, IMUs, and diverse motion conditions. We evaluate state-of-the-art SLAM approaches using the GEODE dataset to highlight current limitations in LiDAR SLAM techniques. This extensive dataset will be publicly available at https://geode.github.io, supporting further advancements in LiDAR-based SLAM.
RELEAD: Resilient Localization with Enhanced LiDAR Odometry in Adverse Environments
Mar 15, 2024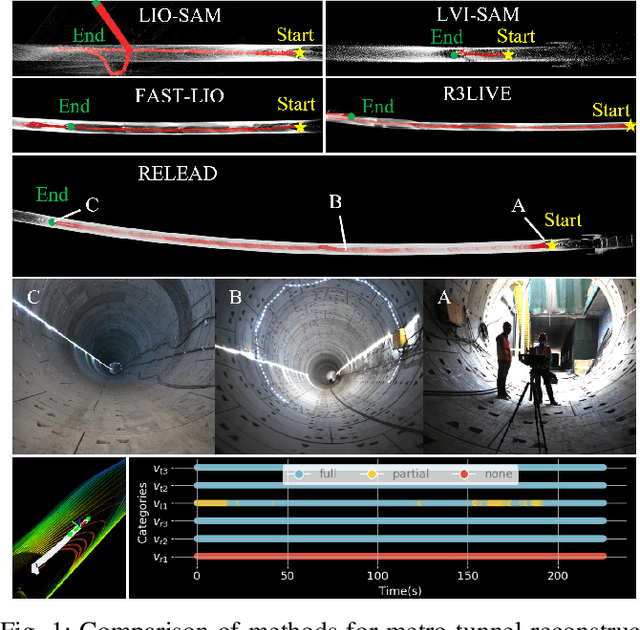
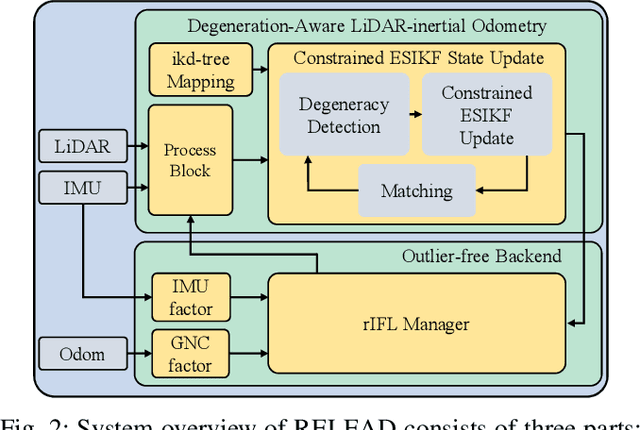
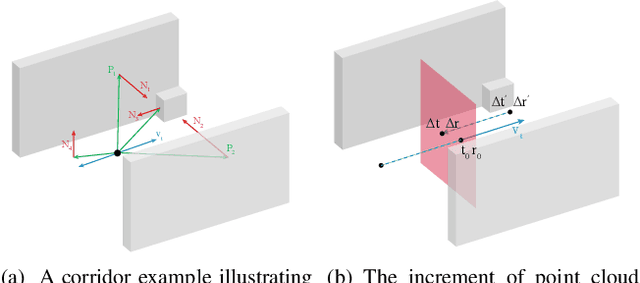
Abstract:LiDAR-based localization is valuable for applications like mining surveys and underground facility maintenance. However, existing methods can struggle when dealing with uninformative geometric structures in challenging scenarios. This paper presents RELEAD, a LiDAR-centric solution designed to address scan-matching degradation. Our method enables degeneracy-free point cloud registration by solving constrained ESIKF updates in the front end and incorporates multisensor constraints, even when dealing with outlier measurements, through graph optimization based on Graduated Non-Convexity (GNC). Additionally, we propose a robust Incremental Fixed Lag Smoother (rIFL) for efficient GNC-based optimization. RELEAD has undergone extensive evaluation in degenerate scenarios and has outperformed existing state-of-the-art LiDAR-Inertial odometry and LiDAR-Visual-Inertial odometry methods.
CoLRIO: LiDAR-Ranging-Inertial Centralized State Estimation for Robotic Swarms
Feb 23, 2024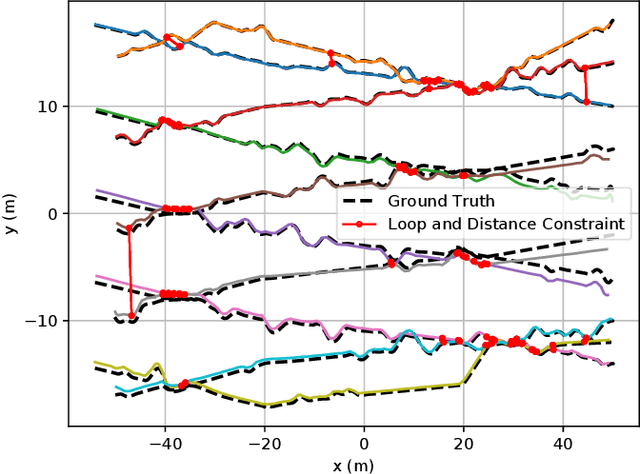
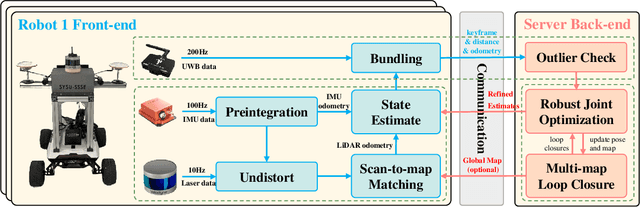
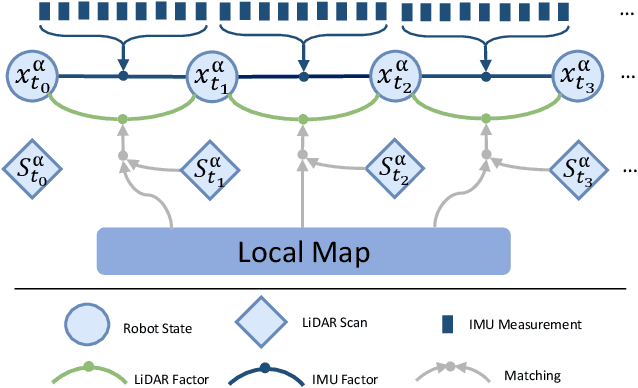
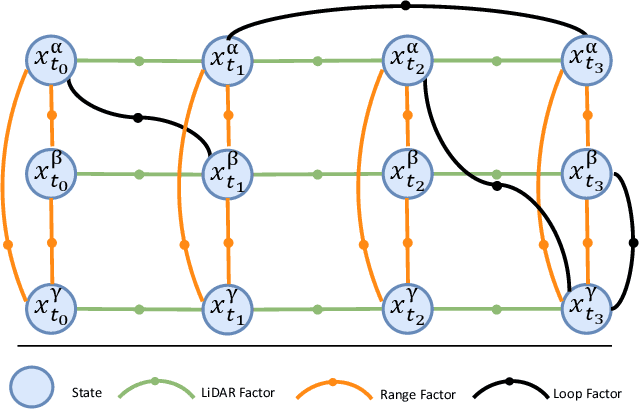
Abstract:Collaborative state estimation using different heterogeneous sensors is a fundamental prerequisite for robotic swarms operating in GPS-denied environments, posing a significant research challenge. In this paper, we introduce a centralized system to facilitate collaborative LiDAR-ranging-inertial state estimation, enabling robotic swarms to operate without the need for anchor deployment. The system efficiently distributes computationally intensive tasks to a central server, thereby reducing the computational burden on individual robots for local odometry calculations. The server back-end establishes a global reference by leveraging shared data and refining joint pose graph optimization through place recognition, global optimization techniques, and removal of outlier data to ensure precise and robust collaborative state estimation. Extensive evaluations of our system, utilizing both publicly available datasets and our custom datasets, demonstrate significant enhancements in the accuracy of collaborative SLAM estimates. Moreover, our system exhibits remarkable proficiency in large-scale missions, seamlessly enabling ten robots to collaborate effectively in performing SLAM tasks. In order to contribute to the research community, we will make our code open-source and accessible at \url{https://github.com/PengYu-team/Co-LRIO}.
Differentiable modeling to unify machine learning and physical models and advance Geosciences
Jan 10, 2023



Abstract:Process-Based Modeling (PBM) and Machine Learning (ML) are often perceived as distinct paradigms in the geosciences. Here we present differentiable geoscientific modeling as a powerful pathway toward dissolving the perceived barrier between them and ushering in a paradigm shift. For decades, PBM offered benefits in interpretability and physical consistency but struggled to efficiently leverage large datasets. ML methods, especially deep networks, presented strong predictive skills yet lacked the ability to answer specific scientific questions. While various methods have been proposed for ML-physics integration, an important underlying theme -- differentiable modeling -- is not sufficiently recognized. Here we outline the concepts, applicability, and significance of differentiable geoscientific modeling (DG). "Differentiable" refers to accurately and efficiently calculating gradients with respect to model variables, critically enabling the learning of high-dimensional unknown relationships. DG refers to a range of methods connecting varying amounts of prior knowledge to neural networks and training them together, capturing a different scope than physics-guided machine learning and emphasizing first principles. Preliminary evidence suggests DG offers better interpretability and causality than ML, improved generalizability and extrapolation capability, and strong potential for knowledge discovery, while approaching the performance of purely data-driven ML. DG models require less training data while scaling favorably in performance and efficiency with increasing amounts of data. With DG, geoscientists may be better able to frame and investigate questions, test hypotheses, and discover unrecognized linkages.
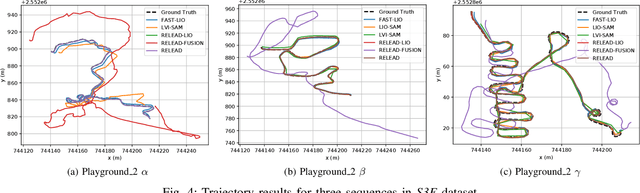
S3E: A Large-scale Multimodal Dataset for Collaborative SLAM
Oct 25, 2022



Abstract:With the advanced request to employ a team of robots to perform a task collaboratively, the research community has become increasingly interested in collaborative simultaneous localization and mapping. Unfortunately, existing datasets are limited in the scale and variation of the collaborative trajectories they capture, even though generalization between inter-trajectories among different agents is crucial to the overall viability of collaborative tasks. To help align the research community's contributions with real-world multiagent ordinated SLAM problems, we introduce S3E, a novel large-scale multimodal dataset captured by a fleet of unmanned ground vehicles along four designed collaborative trajectory paradigms. S3E consists of 7 outdoor and 5 indoor scenes that each exceed 200 seconds, consisting of well synchronized and calibrated high-quality stereo camera, LiDAR, and high-frequency IMU data. Crucially, our effort exceeds previous attempts regarding dataset size, scene variability, and complexity. It has 4x as much average recording time as the pioneering EuRoC dataset. We also provide careful dataset analysis as well as baselines for collaborative SLAM and single counterparts. Find data, code, and more up-to-date information at https://github.com/PengYu-Team/S3E.
Differentiable, learnable, regionalized process-based models with physical outputs can approach state-of-the-art hydrologic prediction accuracy
Mar 28, 2022



Abstract:Predictions of hydrologic variables across the entire water cycle have significant value for water resource management as well as downstream applications such as ecosystem and water quality modeling. Recently, purely data-driven deep learning models like long short-term memory (LSTM) showed seemingly-insurmountable performance in modeling rainfall-runoff and other geoscientific variables, yet they cannot predict unobserved physical variables and remain challenging to interpret. Here we show that differentiable, learnable, process-based models (called {\delta} models here) can approach the performance level of LSTM for the intensively-observed variable (streamflow) with regionalized parameterization. We use a simple hydrologic model HBV as the backbone and use embedded neural networks, which can only be trained in a differentiable programming framework, to parameterize, replace, or enhance the process-based model modules. Without using an ensemble or post-processor, {\delta} models can obtain a median Nash Sutcliffe efficiency of 0.715 for 671 basins across the USA for a particular forcing data, compared to 0.72 from a state-of-the-art LSTM model with the same setup. Meanwhile, the resulting learnable process-based models can be evaluated (and later, to be trained) by multiple sources of observations, e.g., groundwater storage, evapotranspiration, surface runoff, and baseflow. Both simulated evapotranspiration and fraction of discharge from baseflow agreed decently with alternative estimates. The general framework can work with models with various process complexity and opens up the path for learning physics from big data.
Continental-scale streamflow modeling of basins with reservoirs: a demonstration of effectiveness and a delineation of challenges
Jan 12, 2021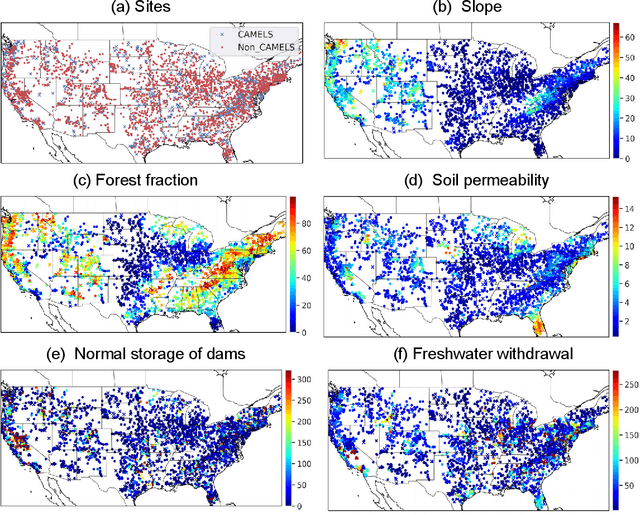


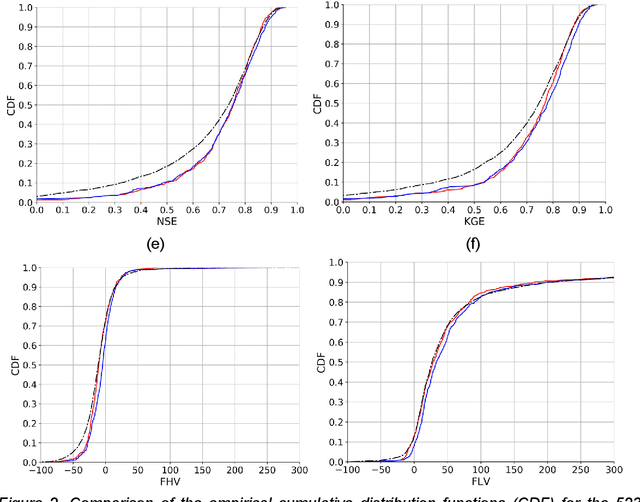
Abstract:A large fraction of major waterways have dams influencing streamflow, which must be accounted for in large-scale hydrologic modeling. However, daily streamflow prediction for basins with dams is challenging for various modeling approaches, especially at large scales. Here we took a divide-and-conquer approach to examine which types of basins could be well represented by a long short-term memory (LSTM) deep learning model using only readily-available information. We analyzed data from 3557 basins (83% dammed) over the contiguous United States and noted strong impacts of reservoir purposes, capacity-to-runoff ratio (dor), and diversion on streamflow on streamflow modeling. Surprisingly, while the LSTM model trained on a widely-used reference-basin dataset performed poorly for more non-reference basins, the model trained on the whole dataset presented a median test Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE) of 0.74, reaching benchmark-level performance. The zero-dor, small-dor, and large-dor basins were found to have distinct behaviors, so migrating models between categories yielded catastrophic results. However, training with pooled data from different sets yielded optimal median NSEs of 0.73, 0.78, and 0.71 for these groups, respectively, showing noticeable advantages over existing models. These results support a coherent, mixed modeling strategy where smaller dams are modeled as part of rainfall-runoff processes, but dammed basins must not be treated as reference ones and must be included in the training set; then, large-dor reservoirs can be represented explicitly and future work should examine modeling reservoirs for fire protection and irrigation, followed by those for hydroelectric power generation, and flood control, etc.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge