Hanwen Zhang
XEmoGPT: An Explainable Multimodal Emotion Recognition Framework with Cue-Level Perception and Reasoning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Explainable Multimodal Emotion Recognition plays a crucial role in applications such as human-computer interaction and social media analytics. However, current approaches struggle with cue-level perception and reasoning due to two main challenges: 1) general-purpose modality encoders are pretrained to capture global structures and general semantics rather than fine-grained emotional cues, resulting in limited sensitivity to emotional signals; and 2) available datasets usually involve a trade-off between annotation quality and scale, which leads to insufficient supervision for emotional cues and ultimately limits cue-level reasoning. Moreover, existing evaluation metrics are inadequate for assessing cue-level reasoning performance. To address these challenges, we propose eXplainable Emotion GPT (XEmoGPT), a novel EMER framework capable of both perceiving and reasoning over emotional cues. It incorporates two specialized modules: the Video Emotional Cue Bridge (VECB) and the Audio Emotional Cue Bridge (AECB), which enhance the video and audio encoders through carefully designed tasks for fine-grained emotional cue perception. To further support cue-level reasoning, we construct a large-scale dataset, EmoCue, designed to teach XEmoGPT how to reason over multimodal emotional cues. In addition, we introduce EmoCue-360, an automated metric that extracts and matches emotional cues using semantic similarity, and release EmoCue-Eval, a benchmark of 400 expert-annotated samples covering diverse emotional scenarios. Experimental results show that XEmoGPT achieves strong performance in both emotional cue perception and reasoning.
DSFedMed: Dual-Scale Federated Medical Image Segmentation via Mutual Distillation Between Foundation and Lightweight Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Foundation Models (FMs) have demonstrated strong generalization across diverse vision tasks. However, their deployment in federated settings is hindered by high computational demands, substantial communication overhead, and significant inference costs. We propose DSFedMed, a dual-scale federated framework that enables mutual knowledge distillation between a centralized foundation model and lightweight client models for medical image segmentation. To support knowledge distillation, a set of high-quality medical images is generated to replace real public datasets, and a learnability-guided sample selection strategy is proposed to enhance efficiency and effectiveness in dual-scale distillation. This mutual distillation enables the foundation model to transfer general knowledge to lightweight clients, while also incorporating client-specific insights to refine the foundation model. Evaluations on five medical imaging segmentation datasets show that DSFedMed achieves an average 2 percent improvement in Dice score while reducing communication costs and inference time by nearly 90 percent compared to existing federated foundation model baselines. These results demonstrate significant efficiency gains and scalability for resource-limited federated deployments.
Feature-Aware One-Shot Federated Learning via Hierarchical Token Sequences
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:One-shot federated learning (OSFL) reduces the communication cost and privacy risks of iterative federated learning by constructing a global model with a single round of communication. However, most existing methods struggle to achieve robust performance on real-world domains such as medical imaging, or are inefficient when handling non-IID (Independent and Identically Distributed) data. To address these limitations, we introduce FALCON, a framework that enhances the effectiveness of OSFL over non-IID image data. The core idea of FALCON is to leverage the feature-aware hierarchical token sequences generation and knowledge distillation into OSFL. First, each client leverages a pretrained visual encoder with hierarchical scale encoding to compress images into hierarchical token sequences, which capture multi-scale semantics. Second, a multi-scale autoregressive transformer generator is used to model the distribution of these token sequences and generate the synthetic sequences. Third, clients upload the synthetic sequences along with the local classifier trained on the real token sequences to the server. Finally, the server incorporates knowledge distillation into global training to reduce reliance on precise distribution modeling. Experiments on medical and natural image datasets validate the effectiveness of FALCON in diverse non-IID scenarios, outperforming the best OSFL baselines by 9.58% in average accuracy.
Ouroboros: Single-step Diffusion Models for Cycle-consistent Forward and Inverse Rendering
Aug 20, 2025



Abstract:While multi-step diffusion models have advanced both forward and inverse rendering, existing approaches often treat these problems independently, leading to cycle inconsistency and slow inference speed. In this work, we present Ouroboros, a framework composed of two single-step diffusion models that handle forward and inverse rendering with mutual reinforcement. Our approach extends intrinsic decomposition to both indoor and outdoor scenes and introduces a cycle consistency mechanism that ensures coherence between forward and inverse rendering outputs. Experimental results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across diverse scenes while achieving substantially faster inference speed compared to other diffusion-based methods. We also demonstrate that Ouroboros can transfer to video decomposition in a training-free manner, reducing temporal inconsistency in video sequences while maintaining high-quality per-frame inverse rendering.
URPlanner: A Universal Paradigm For Collision-Free Robotic Motion Planning Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Collision-free motion planning for redundant robot manipulators in complex environments is yet to be explored. Although recent advancements at the intersection of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and robotics have highlighted its potential to handle versatile robotic tasks, current DRL-based collision-free motion planners for manipulators are highly costly, hindering their deployment and application. This is due to an overreliance on the minimum distance between the manipulator and obstacles, inadequate exploration and decision-making by DRL, and inefficient data acquisition and utilization. In this article, we propose URPlanner, a universal paradigm for collision-free robotic motion planning based on DRL. URPlanner offers several advantages over existing approaches: it is platform-agnostic, cost-effective in both training and deployment, and applicable to arbitrary manipulators without solving inverse kinematics. To achieve this, we first develop a parameterized task space and a universal obstacle avoidance reward that is independent of minimum distance. Second, we introduce an augmented policy exploration and evaluation algorithm that can be applied to various DRL algorithms to enhance their performance. Third, we propose an expert data diffusion strategy for efficient policy learning, which can produce a large-scale trajectory dataset from only a few expert demonstrations. Finally, the superiority of the proposed methods is comprehensively verified through experiments.
Challenges and Trends in Egocentric Vision: A Survey
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technologies and wearable devices, egocentric vision understanding has emerged as a new and challenging research direction, gradually attracting widespread attention from both academia and industry. Egocentric vision captures visual and multimodal data through cameras or sensors worn on the human body, offering a unique perspective that simulates human visual experiences. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of the research on egocentric vision understanding, systematically analyzing the components of egocentric scenes and categorizing the tasks into four main areas: subject understanding, object understanding, environment understanding, and hybrid understanding. We explore in detail the sub-tasks within each category. We also summarize the main challenges and trends currently existing in the field. Furthermore, this paper presents an overview of high-quality egocentric vision datasets, offering valuable resources for future research. By summarizing the latest advancements, we anticipate the broad applications of egocentric vision technologies in fields such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and embodied intelligence, and propose future research directions based on the latest developments in the field.
Advancing Generative Artificial Intelligence and Large Language Models for Demand Side Management with Electric Vehicles
Jan 26, 2025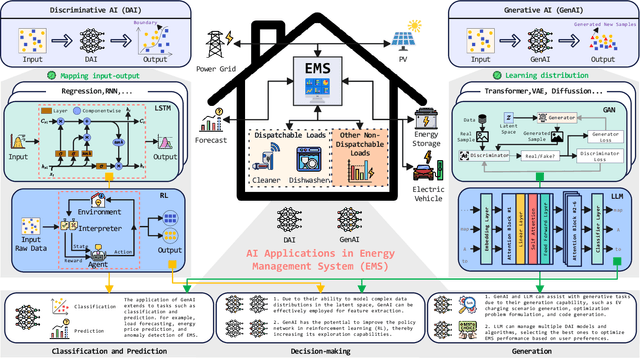
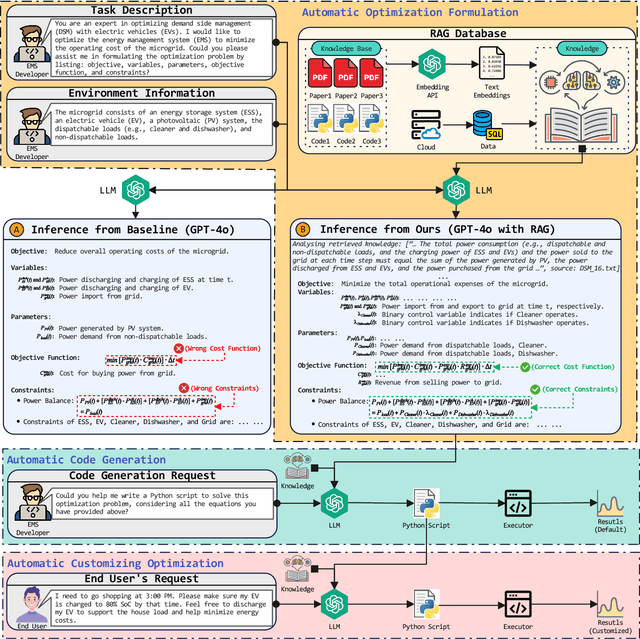
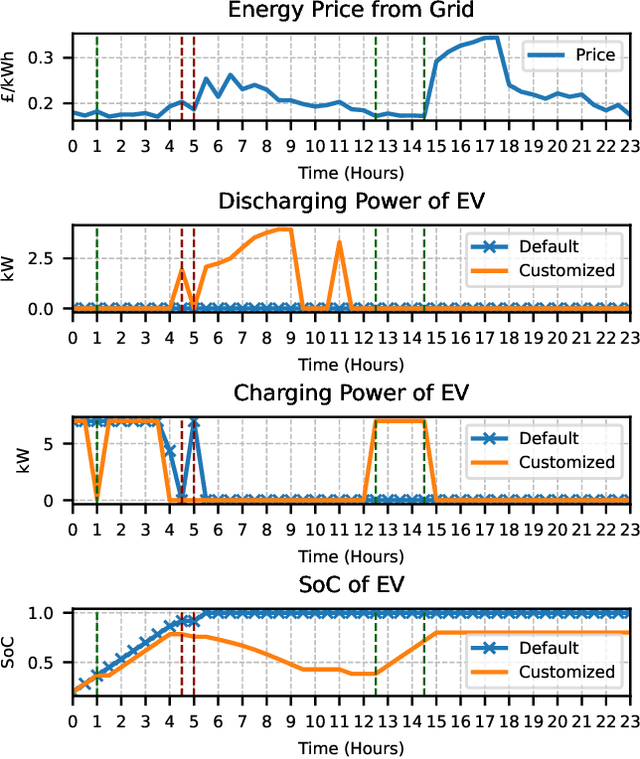
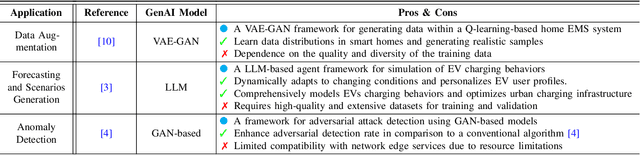
Abstract:Generative artificial intelligence, particularly through large language models (LLMs), is poised to transform energy optimization and demand side management (DSM) within microgrids. This paper explores the integration of LLMs into energy management, emphasizing their roles in automating the optimization of DSM strategies with electric vehicles. We investigate challenges and solutions associated with DSM and explore the new opportunities presented by leveraging LLMs. Then, We propose an innovative solution that enhances LLMs with retrieval-augmented generation for automatic problem formulation, code generation, and customizing optimization. We present a case study to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed solution in charging scheduling and optimization for electric vehicles, highlighting our solution's significant advancements in energy efficiency and user adaptability. This work underscores the potential of LLMs for energy optimization and fosters a new era of intelligent DSM solutions.
Optimal Bounds for Private Minimum Spanning Trees via Input Perturbation
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:We study the problem of privately releasing an approximate minimum spanning tree (MST). Given a graph $G = (V, E, \vec{W})$ where $V$ is a set of $n$ vertices, $E$ is a set of $m$ undirected edges, and $ \vec{W} \in \mathbb{R}^{|E|} $ is an edge-weight vector, our goal is to publish an approximate MST under edge-weight differential privacy, as introduced by Sealfon in PODS 2016, where $V$ and $E$ are considered public and the weight vector is private. Our neighboring relation is $\ell_\infty$-distance on weights: for a sensitivity parameter $\Delta_\infty$, graphs $ G = (V, E, \vec{W}) $ and $ G' = (V, E, \vec{W}') $ are neighboring if $\|\vec{W}-\vec{W}'\|_\infty \leq \Delta_\infty$. Existing private MST algorithms face a trade-off, sacrificing either computational efficiency or accuracy. We show that it is possible to get the best of both worlds: With a suitable random perturbation of the input that does not suffice to make the weight vector private, the result of any non-private MST algorithm will be private and achieves a state-of-the-art error guarantee. Furthermore, by establishing a connection to Private Top-k Selection [Steinke and Ullman, FOCS '17], we give the first privacy-utility trade-off lower bound for MST under approximate differential privacy, demonstrating that the error magnitude, $\tilde{O}(n^{3/2})$, is optimal up to logarithmic factors. That is, our approach matches the time complexity of any non-private MST algorithm and at the same time achieves optimal error. We complement our theoretical treatment with experiments that confirm the practicality of our approach.
CoMA: Compositional Human Motion Generation with Multi-modal Agents
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:3D human motion generation has seen substantial advancement in recent years. While state-of-the-art approaches have improved performance significantly, they still struggle with complex and detailed motions unseen in training data, largely due to the scarcity of motion datasets and the prohibitive cost of generating new training examples. To address these challenges, we introduce CoMA, an agent-based solution for complex human motion generation, editing, and comprehension. CoMA leverages multiple collaborative agents powered by large language and vision models, alongside a mask transformer-based motion generator featuring body part-specific encoders and codebooks for fine-grained control. Our framework enables generation of both short and long motion sequences with detailed instructions, text-guided motion editing, and self-correction for improved quality. Evaluations on the HumanML3D dataset demonstrate competitive performance against state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, we create a set of context-rich, compositional, and long text prompts, where user studies show our method significantly outperforms existing approaches.
Model-based Deep Learning for Rate Split Multiple Access in Vehicular Communications
May 02, 2024



Abstract:Rate split multiple access (RSMA) has been proven as an effective communication scheme for 5G and beyond, especially in vehicular scenarios. However, RSMA requires complicated iterative algorithms for proper resource allocation, which cannot fulfill the stringent latency requirement in resource constrained vehicles. Although data driven approaches can alleviate this issue, they suffer from poor generalizability and scarce training data. In this paper, we propose a fractional programming (FP) based deep unfolding (DU) approach to address resource allocation problem for a weighted sum rate optimization in RSMA. By carefully designing the penalty function, we couple the variable update with projected gradient descent algorithm (PGD). Following the structure of PGD, we embed few learnable parameters in each layer of the DU network. Through extensive simulation, we have shown that the proposed model-based neural networks has similar performance as optimal results given by traditional algorithm but with much lower computational complexity, less training data, and higher resilience to test set data and out-of-distribution (OOD) data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge