Gregory S. Fischer
A Hybrid Model and Learning-Based Force Estimation Framework for Surgical Robots
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Haptic feedback to the surgeon during robotic surgery would enable safer and more immersive surgeries but estimating tissue interaction forces at the tips of robotically controlled surgical instruments has proven challenging. Few existing surgical robots can measure interaction forces directly and the additional sensor may limit the life of instruments. We present a hybrid model and learning-based framework for force estimation for the Patient Side Manipulators (PSM) of a da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK). The model-based component identifies the dynamic parameters of the robot and estimates free-space joint torque, while the learning-based component compensates for environmental factors, such as the additional torque caused by trocar interaction between the PSM instrument and the patient's body wall. We evaluate our method in an abdominal phantom and achieve an error in force estimation of under 10% normalized root-mean-squared error. We show that by using a model-based method to perform dynamics identification, we reduce reliance on the training data covering the entire workspace. Although originally developed for the dVRK, the proposed method is a generalizable framework for other compliant surgical robots. The code is available at https://github.com/vu-maple-lab/dvrk_force_estimation.
Loss Distillation via Gradient Matching for Point Cloud Completion with Weighted Chamfer Distance
Sep 10, 2024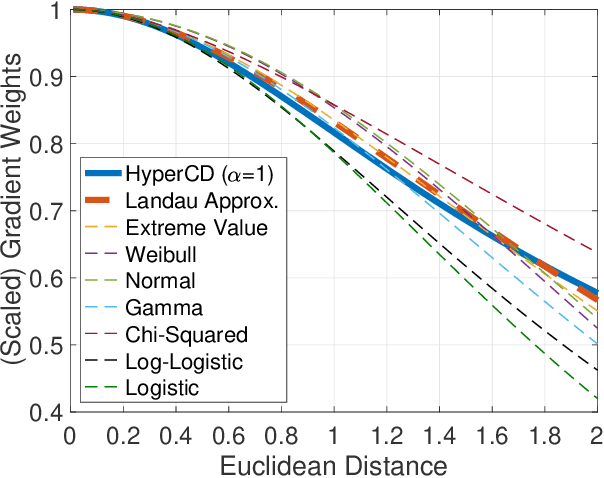
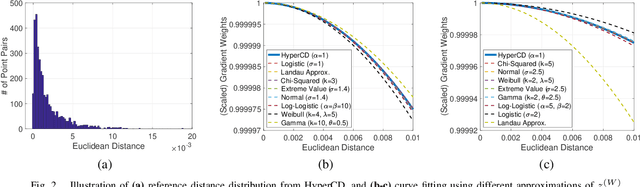
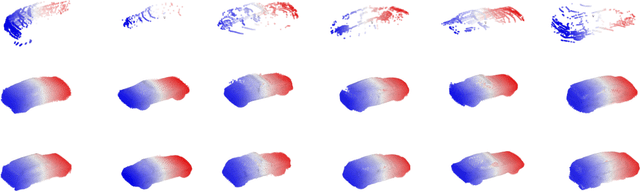
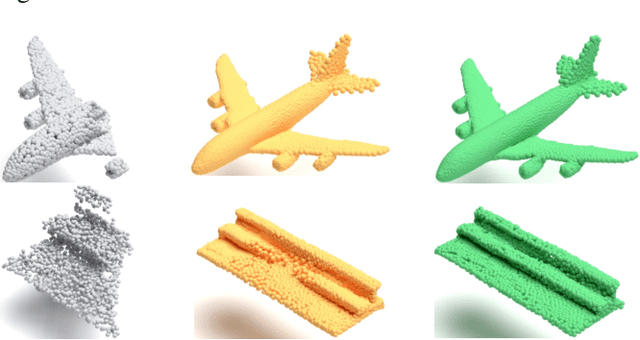
Abstract:3D point clouds enhanced the robot's ability to perceive the geometrical information of the environments, making it possible for many downstream tasks such as grasp pose detection and scene understanding. The performance of these tasks, though, heavily relies on the quality of data input, as incomplete can lead to poor results and failure cases. Recent training loss functions designed for deep learning-based point cloud completion, such as Chamfer distance (CD) and its variants (\eg HyperCD ), imply a good gradient weighting scheme can significantly boost performance. However, these CD-based loss functions usually require data-related parameter tuning, which can be time-consuming for data-extensive tasks. To address this issue, we aim to find a family of weighted training losses ({\em weighted CD}) that requires no parameter tuning. To this end, we propose a search scheme, {\em Loss Distillation via Gradient Matching}, to find good candidate loss functions by mimicking the learning behavior in backpropagation between HyperCD and weighted CD. Once this is done, we propose a novel bilevel optimization formula to train the backbone network based on the weighted CD loss. We observe that: (1) with proper weighted functions, the weighted CD can always achieve similar performance to HyperCD, and (2) the Landau weighted CD, namely {\em Landau CD}, can outperform HyperCD for point cloud completion and lead to new state-of-the-art results on several benchmark datasets. {\it Our demo code is available at \url{https://github.com/Zhang-VISLab/IROS2024-LossDistillationWeightedCD}.}
Deep Brain Ultrasound Ablation Thermal Dose Modeling with in Vivo Experimental Validation
Sep 04, 2024



Abstract:Intracorporeal needle-based therapeutic ultrasound (NBTU) is a minimally invasive option for intervening in malignant brain tumors, commonly used in thermal ablation procedures. This technique is suitable for both primary and metastatic cancers, utilizing a high-frequency alternating electric field (up to 10 MHz) to excite a piezoelectric transducer. The resulting rapid deformation of the transducer produces an acoustic wave that propagates through tissue, leading to localized high-temperature heating at the target tumor site and inducing rapid cell death. To optimize the design of NBTU transducers for thermal dose delivery during treatment, numerical modeling of the acoustic pressure field generated by the deforming piezoelectric transducer is frequently employed. The bioheat transfer process generated by the input pressure field is used to track the thermal propagation of the applicator over time. Magnetic resonance thermal imaging (MRTI) can be used to experimentally validate these models. Validation results using MRTI demonstrated the feasibility of this model, showing a consistent thermal propagation pattern. However, a thermal damage isodose map is more advantageous for evaluating therapeutic efficacy. To achieve a more accurate simulation based on the actual brain tissue environment, a new finite element method (FEM) simulation with enhanced damage evaluation capabilities was conducted. The results showed that the highest temperature and ablated volume differed between experimental and simulation results by 2.1884{\deg}C (3.71%) and 0.0631 cm$^3$ (5.74%), respectively. The lowest Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) for peak temperature was 0.7117, and the lowest Dice coefficient for the ablated area was 0.7021, indicating a good agreement in accuracy between simulation and experiment.
Study of MRI-compatible Notched Plastic Ultrasonic Stator with FEM Simulation and Holography Validation
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:Intra-operative image guidance using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can significantly enhance the precision of surgical procedures, such as deep brain tumor ablation. However, the powerful magnetic fields and limited space within an MRI scanner require the use of robotic devices to aid surgeons. Piezoelectric motors are commonly utilized to drive these robots, with piezoelectric ultrasonic motors being particularly notable. These motors consist of a piezoelectric ring stator that is bonded to a rotor through frictional coupling. When the stator is excited at specific frequencies, it generates distinctive mode shapes with surface waves that exhibit both in-plane and out-of-plane displacement, leading to the rotation of the rotor. In this study, we continue our previous work and refine the motor design and performance, we combine finite element modeling (FEM) with stroboscopic and time-averaged digital holography to validate a further plastic-based ultrasonic motor with better rotary performance.
Suturing Tasks Automation Based on Skills Learned From Demonstrations: A Simulation Study
Mar 01, 2024Abstract:In this work, we develop an open-source surgical simulation environment that includes a realistic model obtained by MRI-scanning a physical phantom, for the purpose of training and evaluating a Learning from Demonstration (LfD) algorithm for autonomous suturing. The LfD algorithm utilizes Dynamic Movement Primitives (DMP) and Locally Weighted Regression (LWR), but focuses on the needle trajectory, rather than the instruments, to obtain better generality with respect to needle grasps. We conduct a user study to collect multiple suturing demonstrations and perform a comprehensive analysis of the ability of the LfD algorithm to generalize from a demonstration at one location in one phantom to different locations in the same phantom and to a different phantom. Our results indicate good generalization, on the order of 91.5%, when learning from more experienced subjects, indicating the need to integrate skill assessment in the future.
Human-Robot Shared Control for Surgical Robot Based on Context-Aware Sim-to-Real Adaptation
Apr 23, 2022



Abstract:Human-robot shared control, which integrates the advantages of both humans and robots, is an effective approach to facilitate efficient surgical operation. Learning from demonstration (LfD) techniques can be used to automate some of the surgical subtasks for the construction of the shared control mechanism. However, a sufficient amount of data is required for the robot to learn the manoeuvres. Using a surgical simulator to collect data is a less resource-demanding approach. With sim-to-real adaptation, the manoeuvres learned from a simulator can be transferred to a physical robot. To this end, we propose a sim-to-real adaptation method to construct a human-robot shared control framework for robotic surgery. In this paper, a desired trajectory is generated from a simulator using LfD method, while dynamic motion primitives (DMP) is used to transfer the desired trajectory from the simulator to the physical robotic platform. Moreover, a role adaptation mechanism is developed such that the robot can adjust its role according to the surgical operation contexts predicted by a neural network model. The effectiveness of the proposed framework is validated on the da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK). Results of the user studies indicated that with the adaptive human-robot shared control framework, the path length of the remote controller, the total clutching number and the task completion time can be reduced significantly. The proposed method outperformed the traditional manual control via teleoperation.
Accelerating Surgical Robotics Research: Reviewing 10 Years of Research with the dVRK
May 13, 2021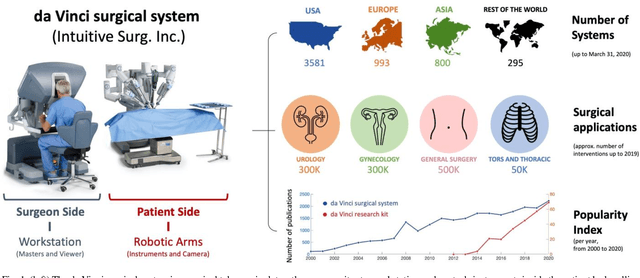
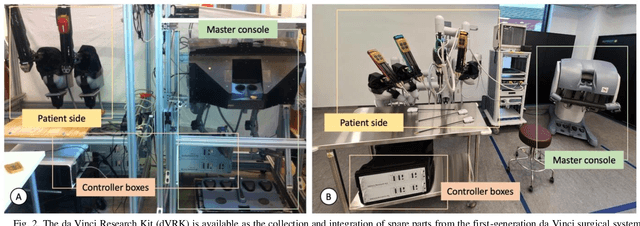
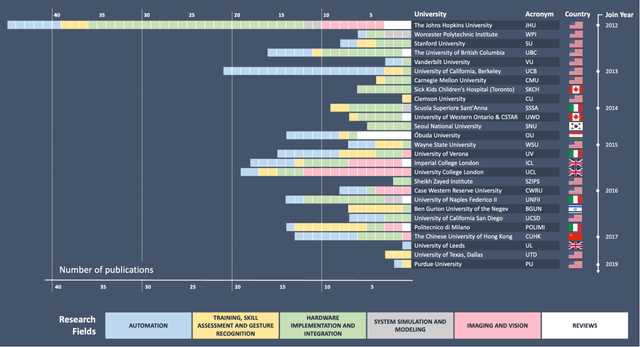
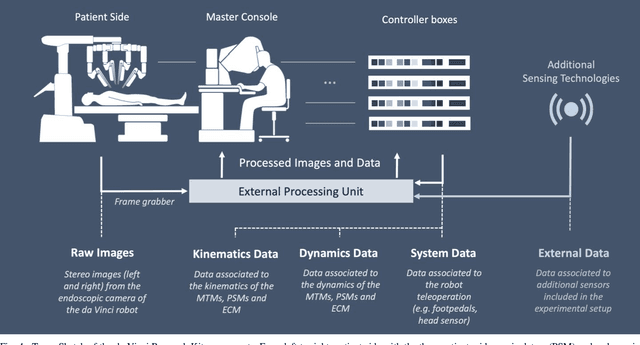
Abstract:Robotic-assisted surgery is now well-established in clinical practice and has become the gold standard clinical treatment option for several clinical indications. The field of robotic-assisted surgery is expected to grow substantially in the next decade with a range of new robotic devices emerging to address unmet clinical needs across different specialities. A vibrant surgical robotics research community is pivotal for conceptualizing such new systems as well as for developing and training the engineers and scientists to translate them into practice. The da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK), an academic and industry collaborative effort to re-purpose decommissioned da Vinci surgical systems (Intuitive Surgical Inc, CA, USA) as a research platform for surgical robotics research, has been a key initiative for addressing a barrier to entry for new research groups in surgical robotics. In this paper, we present an extensive review of the publications that have been facilitated by the dVRK over the past decade. We classify research efforts into different categories and outline some of the major challenges and needs for the robotics community to maintain this initiative and build upon it.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge