Giovanni Da San Martino
Qatar Computing Research Institute, HBKU, Qatar
MemeLens: Multilingual Multitask VLMs for Memes
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Memes are a dominant medium for online communication and manipulation because meaning emerges from interactions between embedded text, imagery, and cultural context. Existing meme research is distributed across tasks (hate, misogyny, propaganda, sentiment, humour) and languages, which limits cross-domain generalization. To address this gap we propose MemeLens, a unified multilingual and multitask explanation-enhanced Vision Language Model (VLM) for meme understanding. We consolidate 38 public meme datasets, filter and map dataset-specific labels into a shared taxonomy of $20$ tasks spanning harm, targets, figurative/pragmatic intent, and affect. We present a comprehensive empirical analysis across modeling paradigms, task categories, and datasets. Our findings suggest that robust meme understanding requires multimodal training, exhibits substantial variation across semantic categories, and remains sensitive to over-specialization when models are fine-tuned on individual datasets rather than trained in a unified setting. We will make the experimental resources and datasets publicly available for the community.
Detecting Winning Arguments with Large Language Models and Persuasion Strategies
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Detecting persuasion in argumentative text is a challenging task with important implications for understanding human communication. This work investigates the role of persuasion strategies - such as Attack on reputation, Distraction, and Manipulative wording - in determining the persuasiveness of a text. We conduct experiments on three annotated argument datasets: Winning Arguments (built from the Change My View subreddit), Anthropic/Persuasion, and Persuasion for Good. Our approach leverages large language models (LLMs) with a Multi-Strategy Persuasion Scoring approach that guides reasoning over six persuasion strategies. Results show that strategy-guided reasoning improves the prediction of persuasiveness. To better understand the influence of content, we organize the Winning Argument dataset into broad discussion topics and analyze performance across them. We publicly release this topic-annotated version of the dataset to facilitate future research. Overall, our methodology demonstrates the value of structured, strategy-aware prompting for enhancing interpretability and robustness in argument quality assessment.
Can AI-Generated Persuasion Be Detected? Persuaficial Benchmark and AI vs. Human Linguistic Differences
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate highly persuasive text, raising concerns about their misuse for propaganda, manipulation, and other harmful purposes. This leads us to our central question: Is LLM-generated persuasion more difficult to automatically detect than human-written persuasion? To address this, we categorize controllable generation approaches for producing persuasive content with LLMs and introduce Persuaficial, a high-quality multilingual benchmark covering six languages: English, German, Polish, Italian, French and Russian. Using this benchmark, we conduct extensive empirical evaluations comparing human-authored and LLM-generated persuasive texts. We find that although overtly persuasive LLM-generated texts can be easier to detect than human-written ones, subtle LLM-generated persuasion consistently degrades automatic detection performance. Beyond detection performance, we provide the first comprehensive linguistic analysis contrasting human and LLM-generated persuasive texts, offering insights that may guide the development of more interpretable and robust detection tools.
FRaN-X: FRaming and Narratives-eXplorer
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:We present FRaN-X, a Framing and Narratives Explorer that automatically detects entity mentions and classifies their narrative roles directly from raw text. FRaN-X comprises a two-stage system that combines sequence labeling with fine-grained role classification to reveal how entities are portrayed as protagonists, antagonists, or innocents, using a unique taxonomy of 22 fine-grained roles nested under these three main categories. The system supports five languages (Bulgarian, English, Hindi, Russian, and Portuguese) and two domains (the Russia-Ukraine Conflict and Climate Change). It provides an interactive web interface for media analysts to explore and compare framing across different sources, tackling the challenge of automatically detecting and labeling how entities are framed. Our system allows end users to focus on a single article as well as analyze up to four articles simultaneously. We provide aggregate level analysis including an intuitive graph visualization that highlights the narrative a group of articles are pushing. Our system includes a search feature for users to look up entities of interest, along with a timeline view that allows analysts to track an entity's role transitions across different contexts within the article. The FRaN-X system and the trained models are licensed under an MIT License. FRaN-X is publicly accessible at https://fran-x.streamlit.app/ and a video demonstration is available at https://youtu.be/VZVi-1B6yYk.
PCoT: Persuasion-Augmented Chain of Thought for Detecting Fake News and Social Media Disinformation
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Disinformation detection is a key aspect of media literacy. Psychological studies have shown that knowledge of persuasive fallacies helps individuals detect disinformation. Inspired by these findings, we experimented with large language models (LLMs) to test whether infusing persuasion knowledge enhances disinformation detection. As a result, we introduce the Persuasion-Augmented Chain of Thought (PCoT), a novel approach that leverages persuasion to improve disinformation detection in zero-shot classification. We extensively evaluate PCoT on online news and social media posts. Moreover, we publish two novel, up-to-date disinformation datasets: EUDisinfo and MultiDis. These datasets enable the evaluation of PCoT on content entirely unseen by the LLMs used in our experiments, as the content was published after the models' knowledge cutoffs. We show that, on average, PCoT outperforms competitive methods by 15% across five LLMs and five datasets. These findings highlight the value of persuasion in strengthening zero-shot disinformation detection.
Reasoning About Persuasion: Can LLMs Enable Explainable Propaganda Detection?
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:There has been significant research on propagandistic content detection across different modalities and languages. However, most studies have primarily focused on detection, with little attention given to explanations justifying the predicted label. This is largely due to the lack of resources that provide explanations alongside annotated labels. To address this issue, we propose a multilingual (i.e., Arabic and English) explanation-enhanced dataset, the first of its kind. Additionally, we introduce an explanation-enhanced LLM for both label detection and rationale-based explanation generation. Our findings indicate that the model performs comparably while also generating explanations. We will make the dataset and experimental resources publicly available for the research community.
Entity Framing and Role Portrayal in the News
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:We introduce a novel multilingual hierarchical corpus annotated for entity framing and role portrayal in news articles. The dataset uses a unique taxonomy inspired by storytelling elements, comprising 22 fine-grained roles, or archetypes, nested within three main categories: protagonist, antagonist, and innocent. Each archetype is carefully defined, capturing nuanced portrayals of entities such as guardian, martyr, and underdog for protagonists; tyrant, deceiver, and bigot for antagonists; and victim, scapegoat, and exploited for innocents. The dataset includes 1,378 recent news articles in five languages (Bulgarian, English, Hindi, European Portuguese, and Russian) focusing on two critical domains of global significance: the Ukraine-Russia War and Climate Change. Over 5,800 entity mentions have been annotated with role labels. This dataset serves as a valuable resource for research into role portrayal and has broader implications for news analysis. We describe the characteristics of the dataset and the annotation process, and we report evaluation results on fine-tuned state-of-the-art multilingual transformers and hierarchical zero-shot learning using LLMs at the level of a document, a paragraph, and a sentence.
ArAIEval Shared Task: Persuasion Techniques and Disinformation Detection in Arabic Text
Nov 06, 2023



Abstract:We present an overview of the ArAIEval shared task, organized as part of the first ArabicNLP 2023 conference co-located with EMNLP 2023. ArAIEval offers two tasks over Arabic text: (i) persuasion technique detection, focusing on identifying persuasion techniques in tweets and news articles, and (ii) disinformation detection in binary and multiclass setups over tweets. A total of 20 teams participated in the final evaluation phase, with 14 and 16 teams participating in Tasks 1 and 2, respectively. Across both tasks, we observed that fine-tuning transformer models such as AraBERT was at the core of the majority of the participating systems. We provide a description of the task setup, including a description of the dataset construction and the evaluation setup. We further give a brief overview of the participating systems. All datasets and evaluation scripts from the shared task are released to the research community. (https://araieval.gitlab.io/) We hope this will enable further research on these important tasks in Arabic.
Temporal Dynamics of Coordinated Online Behavior: Stability, Archetypes, and Influence
Jan 17, 2023
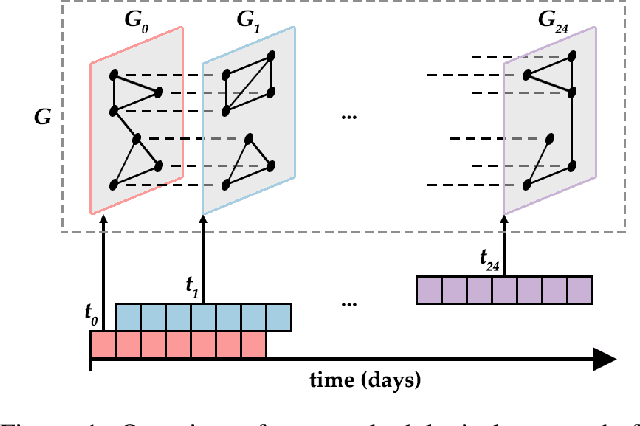
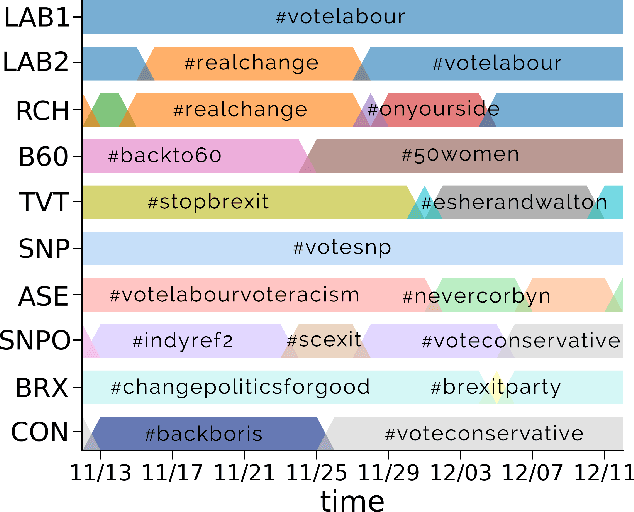

Abstract:Large-scale online campaigns, malicious or otherwise, require a significant degree of coordination among participants, which sparked interest in the study of coordinated online behavior. State-of-the-art methods for detecting coordinated behavior perform static analyses, disregarding the temporal dynamics of coordination. Here, we carry out the first dynamic analysis of coordinated behavior. To reach our goal we build a multiplex temporal network and we perform dynamic community detection to identify groups of users that exhibited coordinated behaviors in time. Thanks to our novel approach we find that: (i) coordinated communities feature variable degrees of temporal instability; (ii) dynamic analyses are needed to account for such instability, and results of static analyses can be unreliable and scarcely representative of unstable communities; (iii) some users exhibit distinct archetypal behaviors that have important practical implications; (iv) content and network characteristics contribute to explaining why users leave and join coordinated communities. Our results demonstrate the advantages of dynamic analyses and open up new directions of research on the unfolding of online debates, on the strategies of coordinated communities, and on the patterns of online influence.
Overview of the WANLP 2022 Shared Task on Propaganda Detection in Arabic
Nov 18, 2022



Abstract:Propaganda is the expression of an opinion or an action by an individual or a group deliberately designed to influence the opinions or the actions of other individuals or groups with reference to predetermined ends, which is achieved by means of well-defined rhetorical and psychological devices. Propaganda techniques are commonly used in social media to manipulate or to mislead users. Thus, there has been a lot of recent research on automatic detection of propaganda techniques in text as well as in memes. However, so far the focus has been primarily on English. With the aim to bridge this language gap, we ran a shared task on detecting propaganda techniques in Arabic tweets as part of the WANLP 2022 workshop, which included two subtasks. Subtask~1 asks to identify the set of propaganda techniques used in a tweet, which is a multilabel classification problem, while Subtask~2 asks to detect the propaganda techniques used in a tweet together with the exact span(s) of text in which each propaganda technique appears. The task attracted 63 team registrations, and eventually 14 and 3 teams made submissions for subtask 1 and 2, respectively. Finally, 11 teams submitted system description papers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge