Serena Tardelli
The Big Ban Theory: A Pre- and Post-Intervention Dataset of Online Content Moderation Actions
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Online platforms rely on moderation interventions to curb harmful behavior such hate speech, toxicity, and the spread of mis- and disinformation. Yet research on the effects and possible biases of such interventions faces multiple limitations. For example, existing works frequently focus on single or a few interventions, due to the absence of comprehensive datasets. As a result, researchers must typically collect the necessary data for each new study, which limits opportunities for systematic comparisons. To overcome these challenges, we introduce The Big Ban Theory (TBBT), a large dataset of moderation interventions. TBBT covers 25 interventions of varying type, severity, and scope, comprising in total over 339K users and nearly 39M posted messages. For each intervention, we provide standardized metadata and pseudonymized user activity collected three months before and after its enforcement, enabling consistent and comparable analyses of intervention effects. In addition, we provide a descriptive exploratory analysis of the dataset, along with several use cases of how it can support research on content moderation. With this dataset, we aim to support researchers studying the effects of moderation interventions and to promote more systematic, reproducible, and comparable research. TBBT is publicly available at: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.18245670.
Mapping the Italian Telegram Ecosystem
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Telegram has become a major space for political discourse and alternative media. However, its lack of moderation allows misinformation, extremism, and toxicity to spread. While prior research focused on these particular phenomena or topics, these have mostly been examined separately, and a broader understanding of the Telegram ecosystem is still missing. In this work, we fill this gap by conducting a large-scale analysis of the Italian Telegram sphere, leveraging a dataset of 186 million messages from 13,151 chats collected in 2023. Using network analysis, Large Language Models, and toxicity detection tools, we examine how different thematic communities form, align ideologically, and engage in harmful discourse within the Italian cultural context. Results show strong thematic and ideological homophily. We also identify mixed ideological communities where far-left and far-right rhetoric coexist on particular geopolitical issues. Beyond political analysis, we find that toxicity, rather than being isolated in a few extreme chats, appears widely normalized within highly toxic communities. Moreover, we find that Italian discourse primarily targets Black people, Jews, and gay individuals independently of the topic. Finally, we uncover common trend of intra-national hostility, where Italians often attack other Italians, reflecting regional and intra-regional cultural conflicts that can be traced back to old historical divisions. This study provides the first large-scale mapping of the Italian Telegram ecosystem, offering insights into ideological interactions, toxicity, and identity-targets of hate and contributing to research on online toxicity across different cultural and linguistic contexts on Telegram.
The Anatomy of Conspirators: Unveiling Traits using a Comprehensive Twitter Dataset
Aug 29, 2023
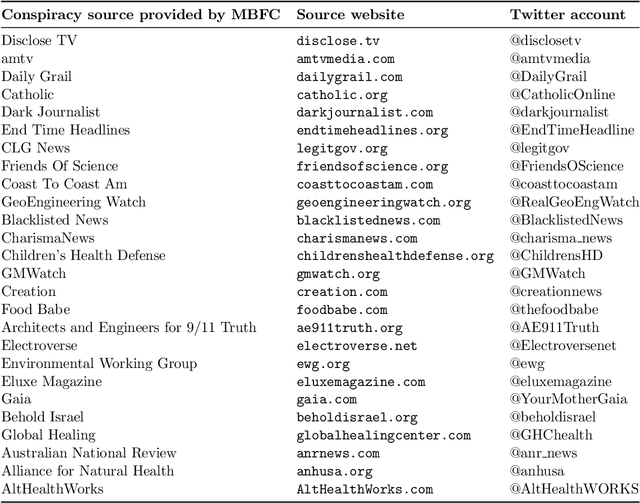
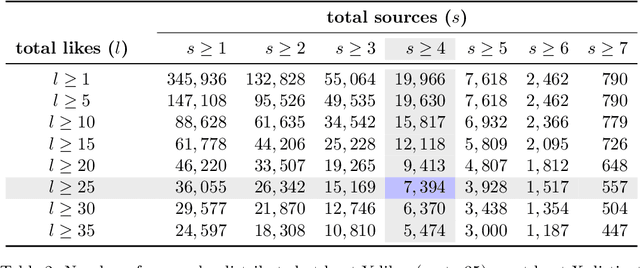
Abstract:The discourse around conspiracy theories is currently thriving amidst the rampant misinformation prevalent in online environments. Research in this field has been focused on detecting conspiracy theories on social media, often relying on limited datasets. In this study, we present a novel methodology for constructing a Twitter dataset that encompasses accounts engaged in conspiracy-related activities throughout the year 2022. Our approach centers on data collection that is independent of specific conspiracy theories and information operations. Additionally, our dataset includes a control group comprising randomly selected users who can be fairly compared to the individuals involved in conspiracy activities. This comprehensive collection effort yielded a total of 15K accounts and 37M tweets extracted from their timelines. We conduct a comparative analysis of the two groups across three dimensions: topics, profiles, and behavioral characteristics. The results indicate that conspiracy and control users exhibit similarity in terms of their profile metadata characteristics. However, they diverge significantly in terms of behavior and activity, particularly regarding the discussed topics, the terminology used, and their stance on trending subjects. Interestingly, there is no significant disparity in the presence of bot users between the two groups, suggesting that conspiracy and automation are orthogonal concepts. Finally, we develop a classifier to identify conspiracy users using 93 features, some of which are commonly employed in literature for troll identification. The results demonstrate a high accuracy level (with an average F1 score of 0.98%), enabling us to uncover the most discriminative features associated with conspiracy-related accounts.
Temporal Dynamics of Coordinated Online Behavior: Stability, Archetypes, and Influence
Jan 17, 2023
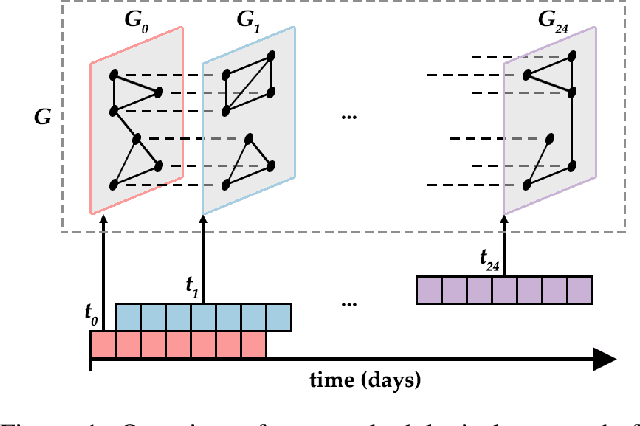
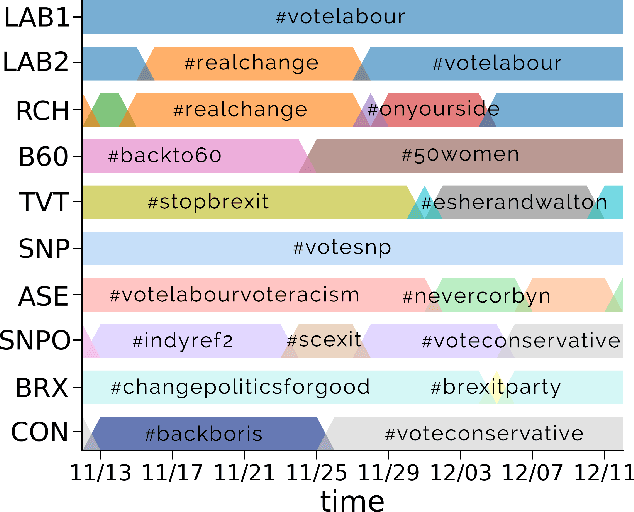

Abstract:Large-scale online campaigns, malicious or otherwise, require a significant degree of coordination among participants, which sparked interest in the study of coordinated online behavior. State-of-the-art methods for detecting coordinated behavior perform static analyses, disregarding the temporal dynamics of coordination. Here, we carry out the first dynamic analysis of coordinated behavior. To reach our goal we build a multiplex temporal network and we perform dynamic community detection to identify groups of users that exhibited coordinated behaviors in time. Thanks to our novel approach we find that: (i) coordinated communities feature variable degrees of temporal instability; (ii) dynamic analyses are needed to account for such instability, and results of static analyses can be unreliable and scarcely representative of unstable communities; (iii) some users exhibit distinct archetypal behaviors that have important practical implications; (iv) content and network characteristics contribute to explaining why users leave and join coordinated communities. Our results demonstrate the advantages of dynamic analyses and open up new directions of research on the unfolding of online debates, on the strategies of coordinated communities, and on the patterns of online influence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge