Alex Nikolov
Findings of the NLP4IF-2021 Shared Tasks on Fighting the COVID-19 Infodemic and Censorship Detection
Sep 23, 2021



Abstract:We present the results and the main findings of the NLP4IF-2021 shared tasks. Task 1 focused on fighting the COVID-19 infodemic in social media, and it was offered in Arabic, Bulgarian, and English. Given a tweet, it asked to predict whether that tweet contains a verifiable claim, and if so, whether it is likely to be false, is of general interest, is likely to be harmful, and is worthy of manual fact-checking; also, whether it is harmful to society, and whether it requires the attention of policy makers. Task~2 focused on censorship detection, and was offered in Chinese. A total of ten teams submitted systems for task 1, and one team participated in task 2; nine teams also submitted a system description paper. Here, we present the tasks, analyze the results, and discuss the system submissions and the methods they used. Most submissions achieved sizable improvements over several baselines, and the best systems used pre-trained Transformers and ensembles. The data, the scorers and the leaderboards for the tasks are available at http://gitlab.com/NLP4IF/nlp4if-2021.
* COVID-19, infodemic, harmfulness, check-worthiness, censorship, social media, tweets, Arabic, Bulgarian, English, Chinese
Overview of the CLEF--2021 CheckThat! Lab on Detecting Check-Worthy Claims, Previously Fact-Checked Claims, and Fake News
Sep 23, 2021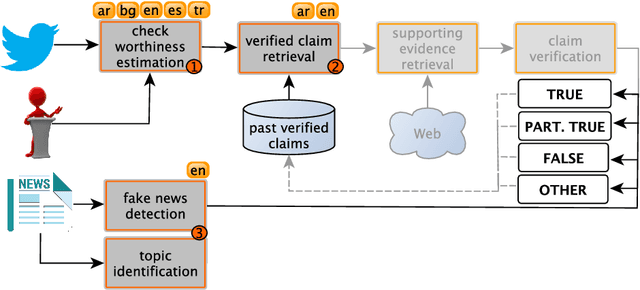
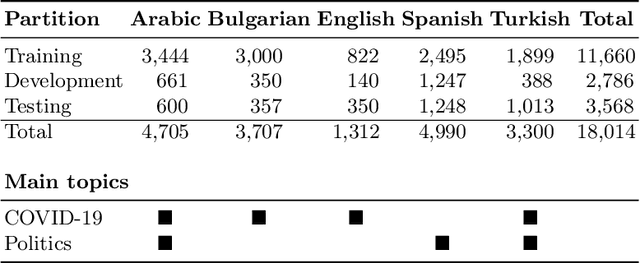
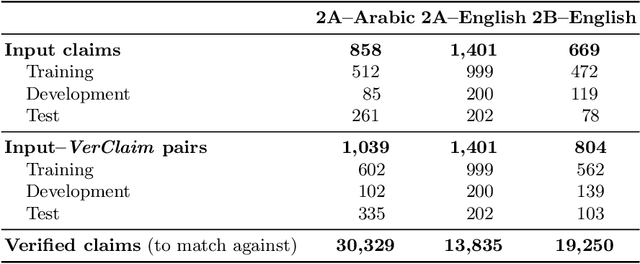
Abstract:We describe the fourth edition of the CheckThat! Lab, part of the 2021 Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF). The lab evaluates technology supporting tasks related to factuality, and covers Arabic, Bulgarian, English, Spanish, and Turkish. Task 1 asks to predict which posts in a Twitter stream are worth fact-checking, focusing on COVID-19 and politics (in all five languages). Task 2 asks to determine whether a claim in a tweet can be verified using a set of previously fact-checked claims (in Arabic and English). Task 3 asks to predict the veracity of a news article and its topical domain (in English). The evaluation is based on mean average precision or precision at rank k for the ranking tasks, and macro-F1 for the classification tasks. This was the most popular CLEF-2021 lab in terms of team registrations: 132 teams. Nearly one-third of them participated: 15, 5, and 25 teams submitted official runs for tasks 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
* Check-Worthiness Estimation, Fact-Checking, Veracity, Evidence-based Verification, Detecting Previously Fact-Checked Claims, Social Media Verification, Computational Journalism, COVID-19
Team Alex at CLEF CheckThat! 2020: Identifying Check-Worthy Tweets With Transformer Models
Sep 07, 2020



Abstract:While misinformation and disinformation have been thriving in social media for years, with the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, the political and the health misinformation merged, thus elevating the problem to a whole new level and giving rise to the first global infodemic. The fight against this infodemic has many aspects, with fact-checking and debunking false and misleading claims being among the most important ones. Unfortunately, manual fact-checking is time-consuming and automatic fact-checking is resource-intense, which means that we need to pre-filter the input social media posts and to throw out those that do not appear to be check-worthy. With this in mind, here we propose a model for detecting check-worthy tweets about COVID-19, which combines deep contextualized text representations with modeling the social context of the tweet. We further describe a number of additional experiments and comparisons, which we believe should be useful for future research as they provide some indication about what techniques are effective for the task. Our official submission to the English version of CLEF-2020 CheckThat! Task 1, system Team_Alex, was ranked second with a MAP score of 0.8034, which is almost tied with the wining system, lagging behind by just 0.003 MAP points absolute.
* Check-worthiness; Fact-Checking; Veracity
Overview of CheckThat! 2020: Automatic Identification and Verification of Claims in Social Media
Jul 15, 2020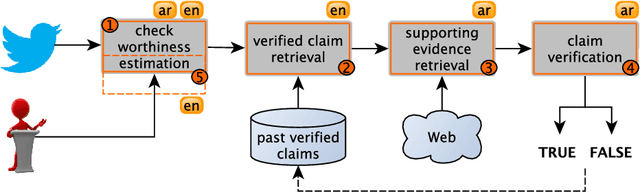
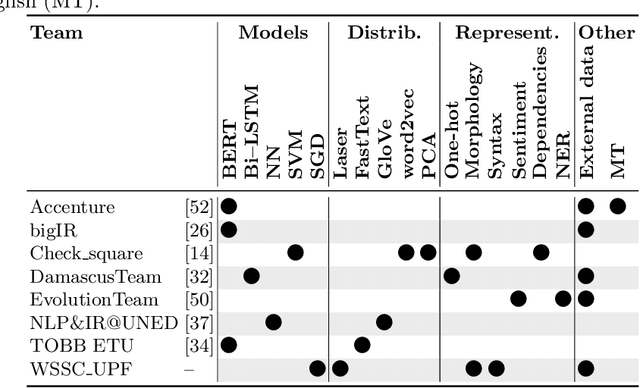
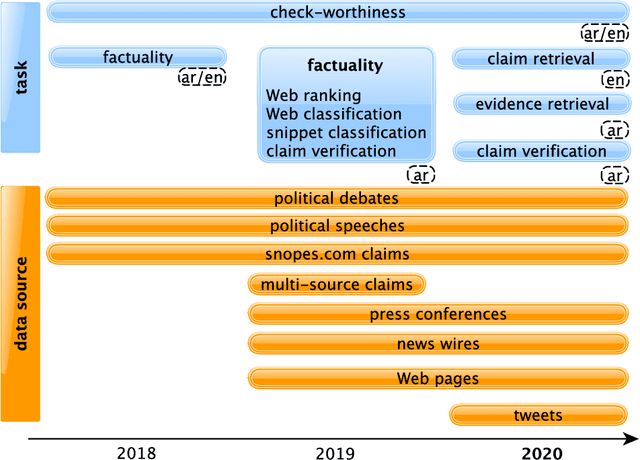
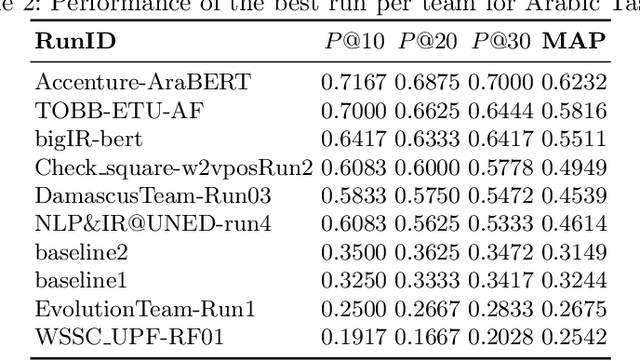
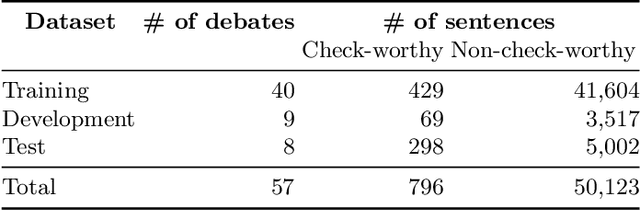
Abstract:We present an overview of the third edition of the CheckThat! Lab at CLEF 2020. The lab featured five tasks in two different languages: English and Arabic. The first four tasks compose the full pipeline of claim verification in social media: Task 1 on check-worthiness estimation, Task 2 on retrieving previously fact-checked claims, Task 3 on evidence retrieval, and Task 4 on claim verification. The lab is completed with Task 5 on check-worthiness estimation in political debates and speeches. A total of 67 teams registered to participate in the lab (up from 47 at CLEF 2019), and 23 of them actually submitted runs (compared to 14 at CLEF 2019). Most teams used deep neural networks based on BERT, LSTMs, or CNNs, and achieved sizable improvements over the baselines on all tasks. Here we describe the tasks setup, the evaluation results, and a summary of the approaches used by the participants, and we discuss some lessons learned. Last but not least, we release to the research community all datasets from the lab as well as the evaluation scripts, which should enable further research in the important tasks of check-worthiness estimation and automatic claim verification.
* Check-Worthiness Estimation, Fact-Checking, Veracity, Evidence-based Verification, Detecting Previously Fact-Checked Claims, Social Media Verification, Computational Journalism, COVID-19
Fighting the COVID-19 Infodemic in Social Media: A Holistic Perspective and a Call to Arms
Jul 15, 2020



Abstract:With the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, people turned to social media to read and to share timely information including statistics, warnings, advice, and inspirational stories. Unfortunately, alongside all this useful information, there was also a new blending of medical and political misinformation and disinformation, which gave rise to the first global infodemic. While fighting this infodemic is typically thought of in terms of factuality, the problem is much broader as malicious content includes not only fake news, rumors, and conspiracy theories, but also promotion of fake cures, panic, racism, xenophobia, and mistrust in the authorities, among others. This is a complex problem that needs a holistic approach combining the perspectives of journalists, fact-checkers, policymakers, government entities, social media platforms, and society as a whole. Taking them into account we define an annotation schema and detailed annotation instructions, which reflect these perspectives. We performed initial annotations using this schema, and our initial experiments demonstrated sizable improvements over the baselines. Now, we issue a call to arms to the research community and beyond to join the fight by supporting our crowdsourcing annotation efforts.
Fighting the COVID-19 Infodemic: Modeling the Perspective of Journalists, Fact-Checkers, Social Media Platforms, Policy Makers, and the Society
Apr 30, 2020



Abstract:Disinformation, i.e., information that is both false and means harm, thrives in social media. Most often, it is used for political purposes, e.g., to influence elections or simply to cause distrust in society. It can also target medical issues, most notably the use of vaccines. With the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, the political and the medical aspects merged as disinformation got elevated to a whole new level to become the first global infodemic. Fighting this infodemic is now ranked second on the list of the most important focus areas of the World Health Organization, with dangers ranging from promoting fake cures, rumors, and conspiracy theories to spreading xenophobia and panic. The fight requires solving a number of problems such as identifying tweets containing claims, determining their check-worthiness and factuality, and their potential to do harm as well as the nature of that harm, to mention just a few. These are challenging problems, and some of them have been studied previously, but typically in isolation. Here, we design, annotate, and release to the research community a new dataset for fine-grained disinformation analysis that (i) focuses on COVID-19, (ii) combines the perspectives and the interests of journalists, fact-checkers, social media platforms, policy makers, and society as a whole, and (iii) covers both English and Arabic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge