Rubén Míguez
MultiClaimNet: A Massively Multilingual Dataset of Fact-Checked Claim Clusters
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:In the context of fact-checking, claims are often repeated across various platforms and in different languages, which can benefit from a process that reduces this redundancy. While retrieving previously fact-checked claims has been investigated as a solution, the growing number of unverified claims and expanding size of fact-checked databases calls for alternative, more efficient solutions. A promising solution is to group claims that discuss the same underlying facts into clusters to improve claim retrieval and validation. However, research on claim clustering is hindered by the lack of suitable datasets. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textit{MultiClaimNet}, a collection of three multilingual claim cluster datasets containing claims in 86 languages across diverse topics. Claim clusters are formed automatically from claim-matching pairs with limited manual intervention. We leverage two existing claim-matching datasets to form the smaller datasets within \textit{MultiClaimNet}. To build the larger dataset, we propose and validate an approach involving retrieval of approximate nearest neighbors to form candidate claim pairs and an automated annotation of claim similarity using large language models. This larger dataset contains 85.3K fact-checked claims written in 78 languages. We further conduct extensive experiments using various clustering techniques and sentence embedding models to establish baseline performance. Our datasets and findings provide a strong foundation for scalable claim clustering, contributing to efficient fact-checking pipelines.
Overview of the CLEF--2021 CheckThat! Lab on Detecting Check-Worthy Claims, Previously Fact-Checked Claims, and Fake News
Sep 23, 2021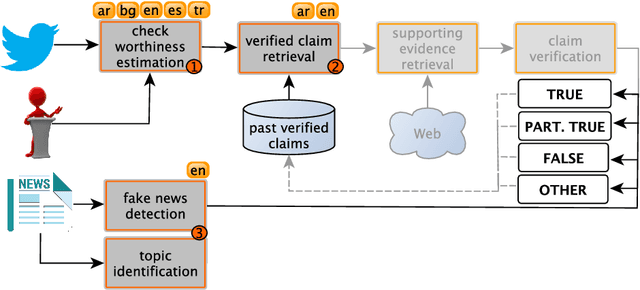
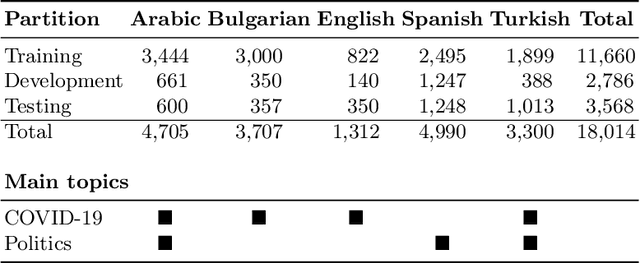
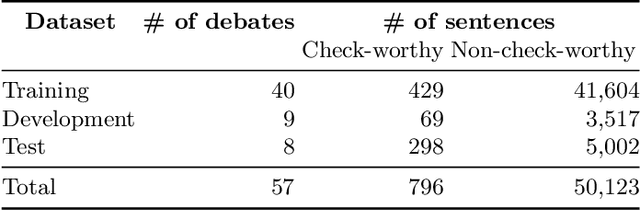
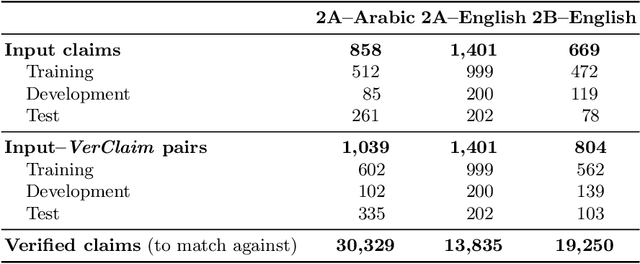
Abstract:We describe the fourth edition of the CheckThat! Lab, part of the 2021 Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF). The lab evaluates technology supporting tasks related to factuality, and covers Arabic, Bulgarian, English, Spanish, and Turkish. Task 1 asks to predict which posts in a Twitter stream are worth fact-checking, focusing on COVID-19 and politics (in all five languages). Task 2 asks to determine whether a claim in a tweet can be verified using a set of previously fact-checked claims (in Arabic and English). Task 3 asks to predict the veracity of a news article and its topical domain (in English). The evaluation is based on mean average precision or precision at rank k for the ranking tasks, and macro-F1 for the classification tasks. This was the most popular CLEF-2021 lab in terms of team registrations: 132 teams. Nearly one-third of them participated: 15, 5, and 25 teams submitted official runs for tasks 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
* Check-Worthiness Estimation, Fact-Checking, Veracity, Evidence-based Verification, Detecting Previously Fact-Checked Claims, Social Media Verification, Computational Journalism, COVID-19
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge