Watheq Mansour
Revisiting Human-vs-LLM judgments using the TREC Podcast Track
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Using large language models (LLMs) to annotate relevance is an increasingly important technique in the information retrieval community. While some studies demonstrate that LLMs can achieve high user agreement with ground truth (human) judgments, other studies have argued for the opposite conclusion. To the best of our knowledge, these studies have primarily focused on classic ad-hoc text search scenarios. In this paper, we conduct an analysis on user agreement between LLM and human experts, and explore the impact disagreement has on system rankings. In contrast to prior studies, we focus on a collection composed of audio files that are transcribed into two-minute segments -- the TREC 2020 and 2021 podcast track. We employ five different LLM models to re-assess all of the query-segment pairs, which were originally annotated by TREC assessors. Furthermore, we re-assess a small subset of pairs where LLM and TREC assessors have the highest disagreement, and found that the human experts tend to agree with LLMs more than with the TREC assessors. Our results reinforce the previous insights of Sormunen in 2002 -- that relying on a single assessor leads to lower user agreement.
Can Large Language Models Automatically Score Proficiency of Written Essays?
Mar 10, 2024



Abstract:Although several methods were proposed to address the problem of automated essay scoring (AES) in the last 50 years, there is still much to desire in terms of effectiveness. Large Language Models (LLMs) are transformer-based models that demonstrate extraordinary capabilities on various tasks. In this paper, we test the ability of LLMs, given their powerful linguistic knowledge, to analyze and effectively score written essays. We experimented with two popular LLMs, namely ChatGPT and Llama. We aim to check if these models can do this task and, if so, how their performance is positioned among the state-of-the-art (SOTA) models across two levels, holistically and per individual writing trait. We utilized prompt-engineering tactics in designing four different prompts to bring their maximum potential to this task. Our experiments conducted on the ASAP dataset revealed several interesting observations. First, choosing the right prompt depends highly on the model and nature of the task. Second, the two LLMs exhibited comparable average performance in AES, with a slight advantage for ChatGPT. Finally, despite the performance gap between the two LLMs and SOTA models in terms of predictions, they provide feedback to enhance the quality of the essays, which can potentially help both teachers and students.
Overview of the CLEF--2021 CheckThat! Lab on Detecting Check-Worthy Claims, Previously Fact-Checked Claims, and Fake News
Sep 23, 2021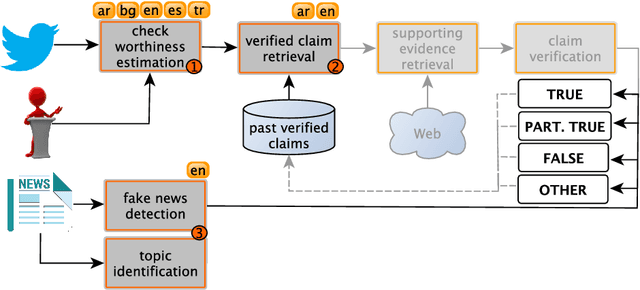
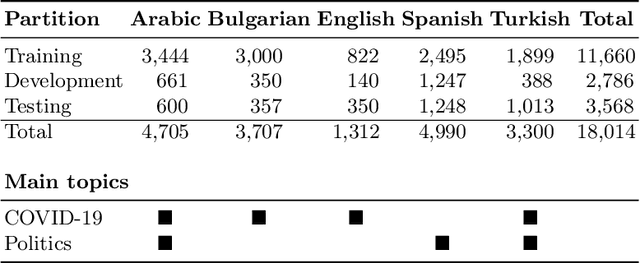
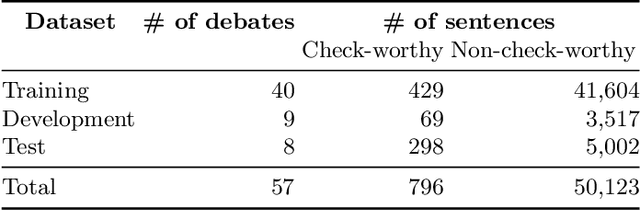
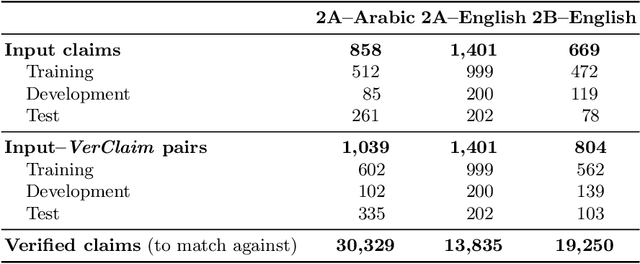
Abstract:We describe the fourth edition of the CheckThat! Lab, part of the 2021 Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF). The lab evaluates technology supporting tasks related to factuality, and covers Arabic, Bulgarian, English, Spanish, and Turkish. Task 1 asks to predict which posts in a Twitter stream are worth fact-checking, focusing on COVID-19 and politics (in all five languages). Task 2 asks to determine whether a claim in a tweet can be verified using a set of previously fact-checked claims (in Arabic and English). Task 3 asks to predict the veracity of a news article and its topical domain (in English). The evaluation is based on mean average precision or precision at rank k for the ranking tasks, and macro-F1 for the classification tasks. This was the most popular CLEF-2021 lab in terms of team registrations: 132 teams. Nearly one-third of them participated: 15, 5, and 25 teams submitted official runs for tasks 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
* Check-Worthiness Estimation, Fact-Checking, Veracity, Evidence-based Verification, Detecting Previously Fact-Checked Claims, Social Media Verification, Computational Journalism, COVID-19
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge