Fuwei Zhang
Multi-Aspect Cross-modal Quantization for Generative Recommendation
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Generative Recommendation (GR) has emerged as a new paradigm in recommender systems. This approach relies on quantized representations to discretize item features, modeling users' historical interactions as sequences of discrete tokens. Based on these tokenized sequences, GR predicts the next item by employing next-token prediction methods. The challenges of GR lie in constructing high-quality semantic identifiers (IDs) that are hierarchically organized, minimally conflicting, and conducive to effective generative model training. However, current approaches remain limited in their ability to harness multimodal information and to capture the deep and intricate interactions among diverse modalities, both of which are essential for learning high-quality semantic IDs and for effectively training GR models. To address this, we propose Multi-Aspect Cross-modal quantization for generative Recommendation (MACRec), which introduces multimodal information and incorporates it into both semantic ID learning and generative model training from different aspects. Specifically, we first introduce cross-modal quantization during the ID learning process, which effectively reduces conflict rates and thus improves codebook usability through the complementary integration of multimodal information. In addition, to further enhance the generative ability of our GR model, we incorporate multi-aspect cross-modal alignments, including the implicit and explicit alignments. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on three well-known recommendation datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
TextAtlas5M: A Large-scale Dataset for Dense Text Image Generation
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Text-conditioned image generation has gained significant attention in recent years and are processing increasingly longer and comprehensive text prompt. In everyday life, dense and intricate text appears in contexts like advertisements, infographics, and signage, where the integration of both text and visuals is essential for conveying complex information. However, despite these advances, the generation of images containing long-form text remains a persistent challenge, largely due to the limitations of existing datasets, which often focus on shorter and simpler text. To address this gap, we introduce TextAtlas5M, a novel dataset specifically designed to evaluate long-text rendering in text-conditioned image generation. Our dataset consists of 5 million long-text generated and collected images across diverse data types, enabling comprehensive evaluation of large-scale generative models on long-text image generation. We further curate 3000 human-improved test set TextAtlasEval across 3 data domains, establishing one of the most extensive benchmarks for text-conditioned generation. Evaluations suggest that the TextAtlasEval benchmarks present significant challenges even for the most advanced proprietary models (e.g. GPT4o with DallE-3), while their open-source counterparts show an even larger performance gap. These evidences position TextAtlas5M as a valuable dataset for training and evaluating future-generation text-conditioned image generation models.
LD-DETR: Loop Decoder DEtection TRansformer for Video Moment Retrieval and Highlight Detection
Jan 18, 2025Abstract:Video Moment Retrieval and Highlight Detection aim to find corresponding content in the video based on a text query. Existing models usually first use contrastive learning methods to align video and text features, then fuse and extract multimodal information, and finally use a Transformer Decoder to decode multimodal information. However, existing methods face several issues: (1) Overlapping semantic information between different samples in the dataset hinders the model's multimodal aligning performance; (2) Existing models are not able to efficiently extract local features of the video; (3) The Transformer Decoder used by the existing model cannot adequately decode multimodal features. To address the above issues, we proposed the LD-DETR model for Video Moment Retrieval and Highlight Detection tasks. Specifically, we first distilled the similarity matrix into the identity matrix to mitigate the impact of overlapping semantic information. Then, we designed a method that enables convolutional layers to extract multimodal local features more efficiently. Finally, we fed the output of the Transformer Decoder back into itself to adequately decode multimodal information. We evaluated LD-DETR on four public benchmarks and conducted extensive experiments to demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of our approach. Our model outperforms the State-Of-The-Art models on QVHighlight, Charades-STA and TACoS datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/qingchen239/ld-detr.
QTG-VQA: Question-Type-Guided Architectural for VideoQA Systems
Sep 14, 2024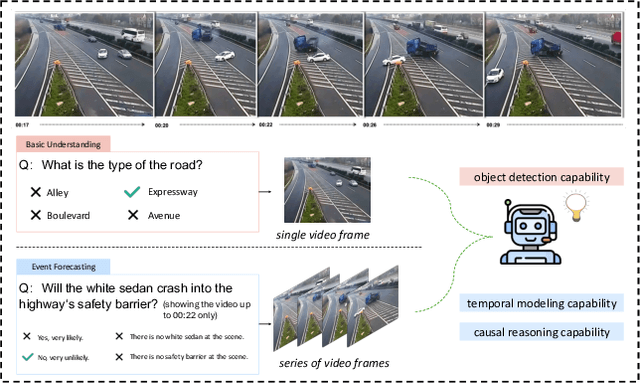
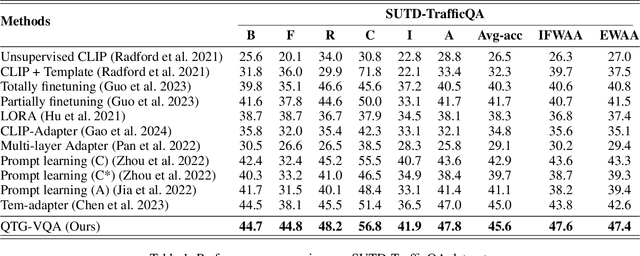
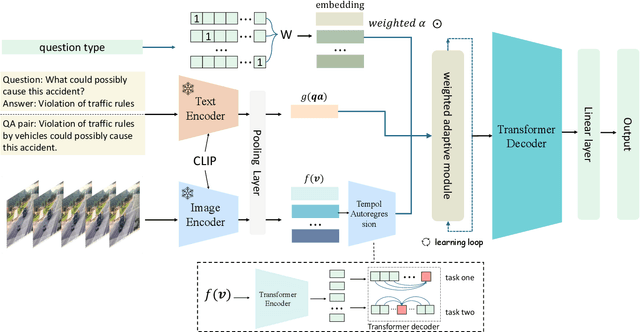
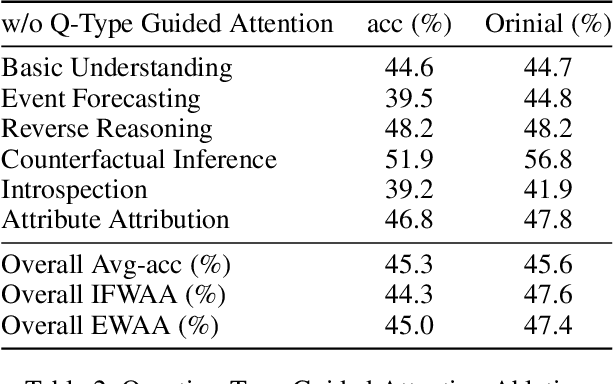
Abstract:In the domain of video question answering (VideoQA), the impact of question types on VQA systems, despite its critical importance, has been relatively under-explored to date. However, the richness of question types directly determines the range of concepts a model needs to learn, thereby affecting the upper limit of its learning capability. This paper focuses on exploring the significance of different question types for VQA systems and their impact on performance, revealing a series of issues such as insufficient learning and model degradation due to uneven distribution of question types. Particularly, considering the significant variation in dependency on temporal information across different question types, and given that the representation of such information coincidentally represents a principal challenge and difficulty for VideoQA as opposed to ImageQA. To address these challenges, we propose QTG-VQA, a novel architecture that incorporates question-type-guided attention and adaptive learning mechanism. Specifically, as to temporal-type questions, we design Masking Frame Modeling technique to enhance temporal modeling, aimed at encouraging the model to grasp richer visual-language relationships and manage more intricate temporal dependencies. Furthermore, a novel evaluation metric tailored to question types is introduced. Experimental results confirm the effectiveness of our approach.
Modeling Semantic Composition with Syntactic Hypergraph for Video Question Answering
May 13, 2022
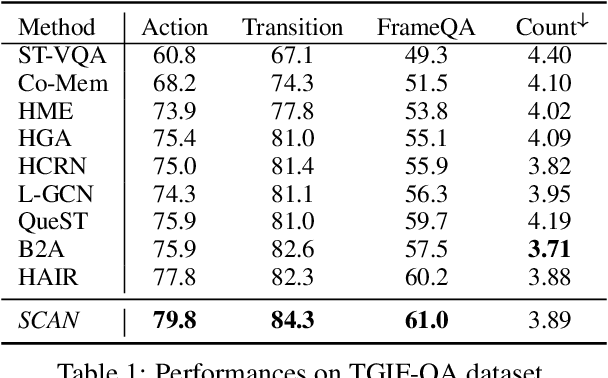
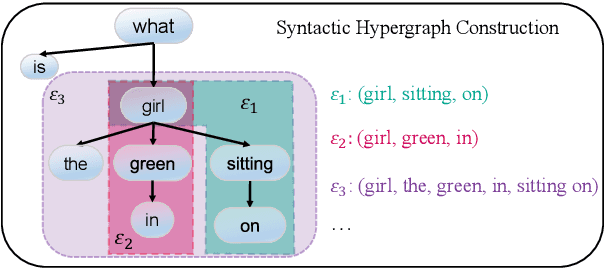
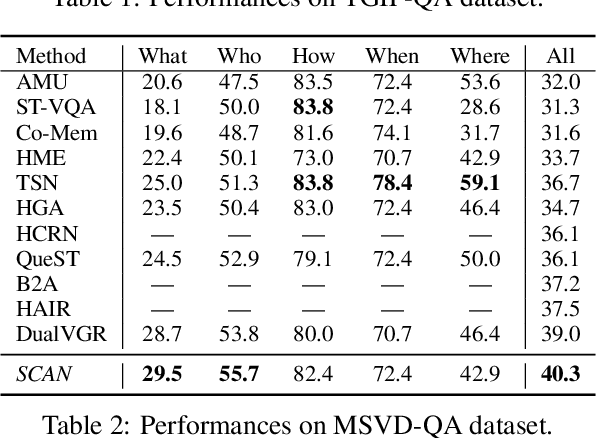
Abstract:A key challenge in video question answering is how to realize the cross-modal semantic alignment between textual concepts and corresponding visual objects. Existing methods mostly seek to align the word representations with the video regions. However, word representations are often not able to convey a complete description of textual concepts, which are in general described by the compositions of certain words. To address this issue, we propose to first build a syntactic dependency tree for each question with an off-the-shelf tool and use it to guide the extraction of meaningful word compositions. Based on the extracted compositions, a hypergraph is further built by viewing the words as nodes and the compositions as hyperedges. Hypergraph convolutional networks (HCN) are then employed to learn the initial representations of word compositions. Afterwards, an optimal transport based method is proposed to perform cross-modal semantic alignment for the textual and visual semantic space. To reflect the cross-modal influences, the cross-modal information is incorporated into the initial representations, leading to a model named cross-modality-aware syntactic HCN. Experimental results on three benchmarks show that our method outperforms all strong baselines. Further analyses demonstrate the effectiveness of each component, and show that our model is good at modeling different levels of semantic compositions and filtering out irrelevant information.
Mind the Gap: Cross-Lingual Information Retrieval with Hierarchical Knowledge Enhancement
Dec 27, 2021



Abstract:Cross-Lingual Information Retrieval (CLIR) aims to rank the documents written in a language different from the user's query. The intrinsic gap between different languages is an essential challenge for CLIR. In this paper, we introduce the multilingual knowledge graph (KG) to the CLIR task due to the sufficient information of entities in multiple languages. It is regarded as a "silver bullet" to simultaneously perform explicit alignment between queries and documents and also broaden the representations of queries. And we propose a model named CLIR with hierarchical knowledge enhancement (HIKE) for our task. The proposed model encodes the textual information in queries, documents and the KG with multilingual BERT, and incorporates the KG information in the query-document matching process with a hierarchical information fusion mechanism. Particularly, HIKE first integrates the entities and their neighborhood in KG into query representations with a knowledge-level fusion, then combines the knowledge from both source and target languages to further mitigate the linguistic gap with a language-level fusion. Finally, experimental results demonstrate that HIKE achieves substantial improvements over state-of-the-art competitors.
The Multi-Modal Video Reasoning and Analyzing Competition
Aug 18, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the Multi-Modal Video Reasoning and Analyzing Competition (MMVRAC) workshop in conjunction with ICCV 2021. This competition is composed of four different tracks, namely, video question answering, skeleton-based action recognition, fisheye video-based action recognition, and person re-identification, which are based on two datasets: SUTD-TrafficQA and UAV-Human. We summarize the top-performing methods submitted by the participants in this competition and show their results achieved in the competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge