Degen Huang
How to Leverage Personal Textual Knowledge for Personalized Conversational Information Retrieval
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:Personalized conversational information retrieval (CIR) combines conversational and personalizable elements to satisfy various users' complex information needs through multi-turn interaction based on their backgrounds. The key promise is that the personal textual knowledge base (PTKB) can improve the CIR effectiveness because the retrieval results can be more related to the user's background. However, PTKB is noisy: not every piece of knowledge in PTKB is relevant to the specific query at hand. In this paper, we explore and test several ways to select knowledge from PTKB and use it for query reformulation by using a large language model (LLM). The experimental results show the PTKB might not always improve the search results when used alone, but LLM can help generate a more appropriate personalized query when high-quality guidance is provided.
Exploring Better Text Image Translation with Multimodal Codebook
Jun 02, 2023



Abstract:Text image translation (TIT) aims to translate the source texts embedded in the image to target translations, which has a wide range of applications and thus has important research value. However, current studies on TIT are confronted with two main bottlenecks: 1) this task lacks a publicly available TIT dataset, 2) dominant models are constructed in a cascaded manner, which tends to suffer from the error propagation of optical character recognition (OCR). In this work, we first annotate a Chinese-English TIT dataset named OCRMT30K, providing convenience for subsequent studies. Then, we propose a TIT model with a multimodal codebook, which is able to associate the image with relevant texts, providing useful supplementary information for translation. Moreover, we present a multi-stage training framework involving text machine translation, image-text alignment, and TIT tasks, which fully exploits additional bilingual texts, OCR dataset and our OCRMT30K dataset to train our model. Extensive experiments and in-depth analyses strongly demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model and training framework.
Towards Robust k-Nearest-Neighbor Machine Translation
Oct 17, 2022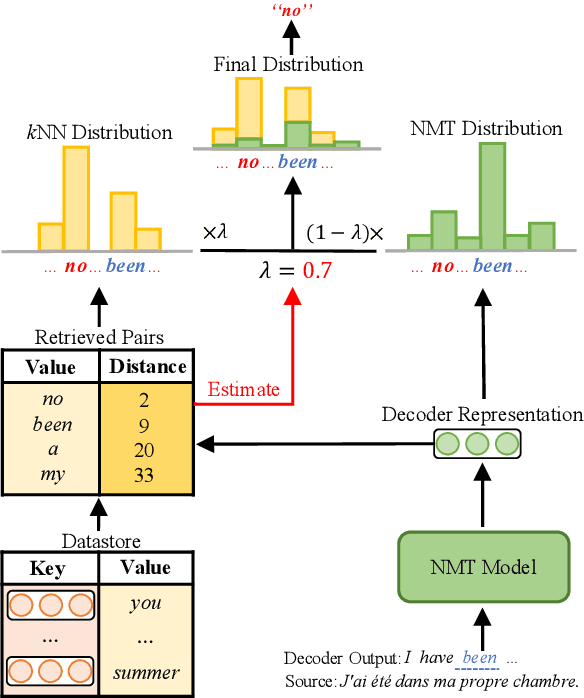
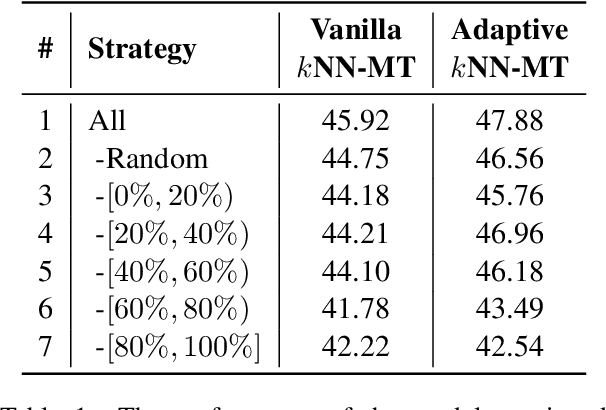
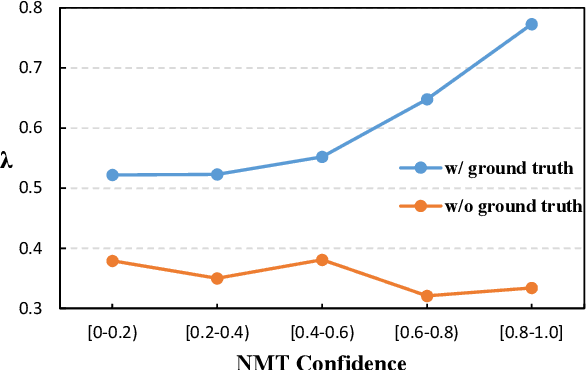
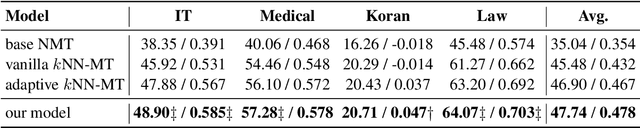
Abstract:k-Nearest-Neighbor Machine Translation (kNN-MT) becomes an important research direction of NMT in recent years. Its main idea is to retrieve useful key-value pairs from an additional datastore to modify translations without updating the NMT model. However, the underlying retrieved noisy pairs will dramatically deteriorate the model performance. In this paper, we conduct a preliminary study and find that this problem results from not fully exploiting the prediction of the NMT model. To alleviate the impact of noise, we propose a confidence-enhanced kNN-MT model with robust training. Concretely, we introduce the NMT confidence to refine the modeling of two important components of kNN-MT: kNN distribution and the interpolation weight. Meanwhile we inject two types of perturbations into the retrieved pairs for robust training. Experimental results on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that our model not only achieves significant improvements over current kNN-MT models, but also exhibits better robustness. Our code is available at https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/Robust-knn-mt.
Improving Graph-based Sentence Ordering with Iteratively Predicted Pairwise Orderings
Oct 13, 2021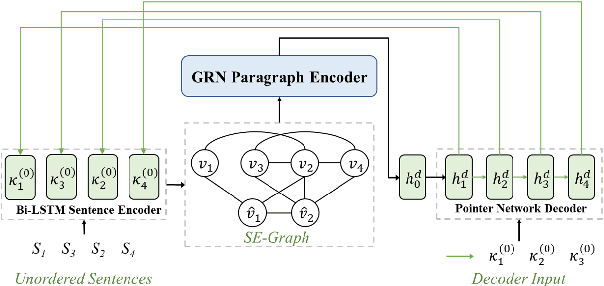
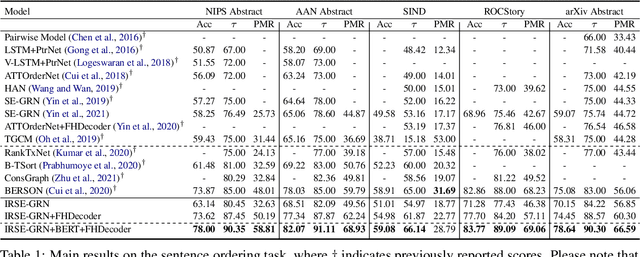
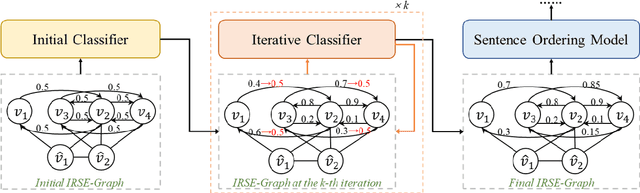

Abstract:Dominant sentence ordering models can be classified into pairwise ordering models and set-to-sequence models. However, there is little attempt to combine these two types of models, which inituitively possess complementary advantages. In this paper, we propose a novel sentence ordering framework which introduces two classifiers to make better use of pairwise orderings for graph-based sentence ordering. Specially, given an initial sentence-entity graph, we first introduce a graph-based classifier to predict pairwise orderings between linked sentences. Then, in an iterative manner, based on the graph updated by previously predicted high-confident pairwise orderings, another classifier is used to predict the remaining uncertain pairwise orderings. At last, we adapt a GRN-based sentence ordering model on the basis of final graph. Experiments on five commonly-used datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of our model. Particularly, when equipped with BERT and FHDecoder, our model achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Towards User-Driven Neural Machine Translation
Jun 11, 2021



Abstract:A good translation should not only translate the original content semantically, but also incarnate personal traits of the original text. For a real-world neural machine translation (NMT) system, these user traits (e.g., topic preference, stylistic characteristics and expression habits) can be preserved in user behavior (e.g., historical inputs). However, current NMT systems marginally consider the user behavior due to: 1) the difficulty of modeling user portraits in zero-shot scenarios, and 2) the lack of user-behavior annotated parallel dataset. To fill this gap, we introduce a novel framework called user-driven NMT. Specifically, a cache-based module and a user-driven contrastive learning method are proposed to offer NMT the ability to capture potential user traits from their historical inputs under a zero-shot learning fashion. Furthermore, we contribute the first Chinese-English parallel corpus annotated with user behavior called UDT-Corpus. Experimental results confirm that the proposed user-driven NMT can generate user-specific translations.
Exploring Dynamic Selection of Branch Expansion Orders for Code Generation
Jun 01, 2021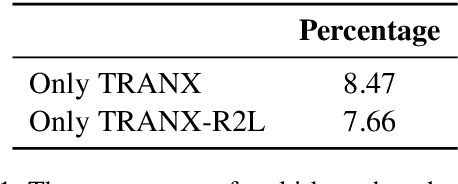
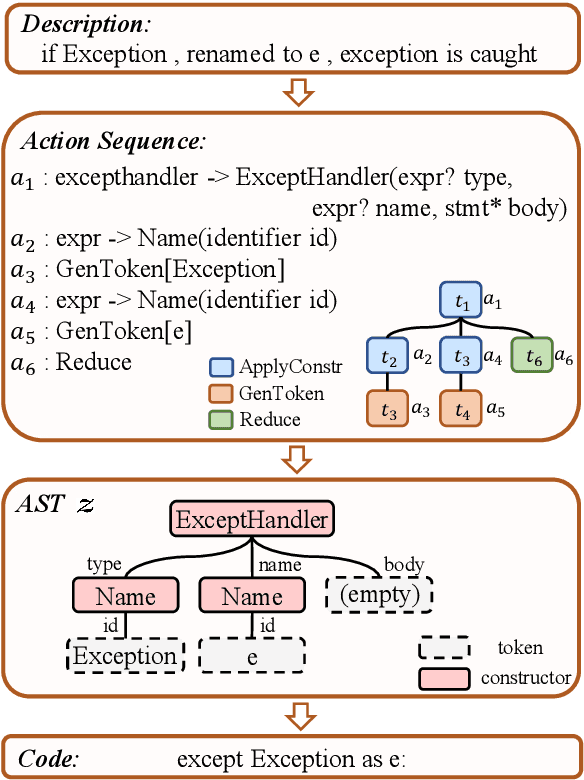
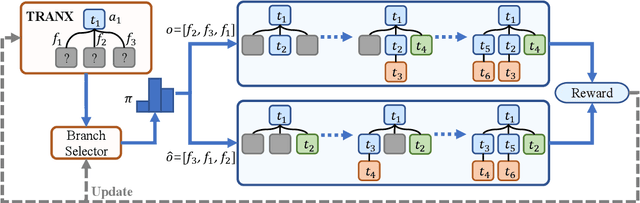
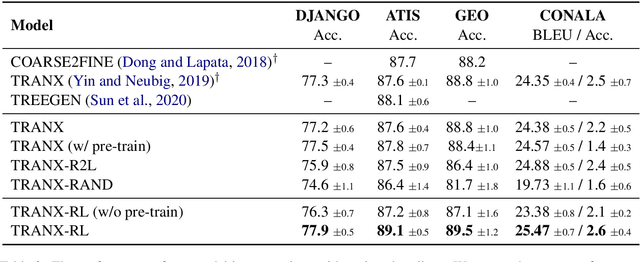
Abstract:Due to the great potential in facilitating software development, code generation has attracted increasing attention recently. Generally, dominant models are Seq2Tree models, which convert the input natural language description into a sequence of tree-construction actions corresponding to the pre-order traversal of an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST). However, such a traversal order may not be suitable for handling all multi-branch nodes. In this paper, we propose to equip the Seq2Tree model with a context-based Branch Selector, which is able to dynamically determine optimal expansion orders of branches for multi-branch nodes. Particularly, since the selection of expansion orders is a non-differentiable multi-step operation, we optimize the selector through reinforcement learning, and formulate the reward function as the difference of model losses obtained through different expansion orders. Experimental results and in-depth analysis on several commonly-used datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of our approach. We have released our code at https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/CG-RL.
Combining Context and Knowledge Representations for Chemical-Disease Relation Extraction
Dec 23, 2019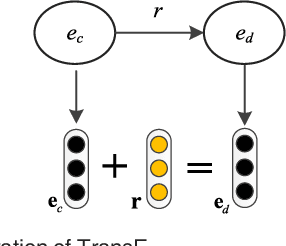
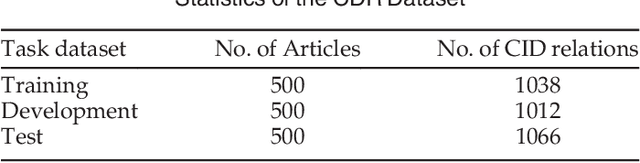
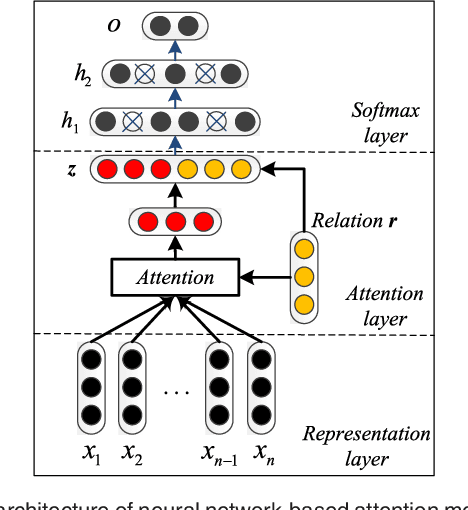
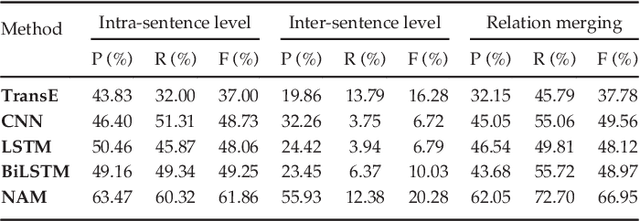
Abstract:Automatically extracting the relationships between chemicals and diseases is significantly important to various areas of biomedical research and health care. Biomedical experts have built many large-scale knowledge bases (KBs) to advance the development of biomedical research. KBs contain huge amounts of structured information about entities and relationships, therefore plays a pivotal role in chemical-disease relation (CDR) extraction. However, previous researches pay less attention to the prior knowledge existing in KBs. This paper proposes a neural network-based attention model (NAM) for CDR extraction, which makes full use of context information in documents and prior knowledge in KBs. For a pair of entities in a document, an attention mechanism is employed to select important context words with respect to the relation representations learned from KBs. Experiments on the BioCreative V CDR dataset show that combining context and knowledge representations through the attention mechanism, could significantly improve the CDR extraction performance while achieve comparable results with state-of-the-art systems.
* Published on IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 11 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge