Daniel Ho
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Deep RL at Scale: Sorting Waste in Office Buildings with a Fleet of Mobile Manipulators
May 05, 2023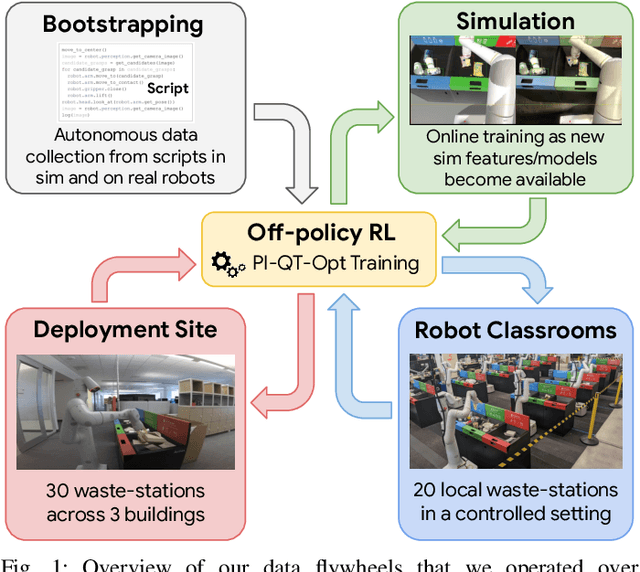
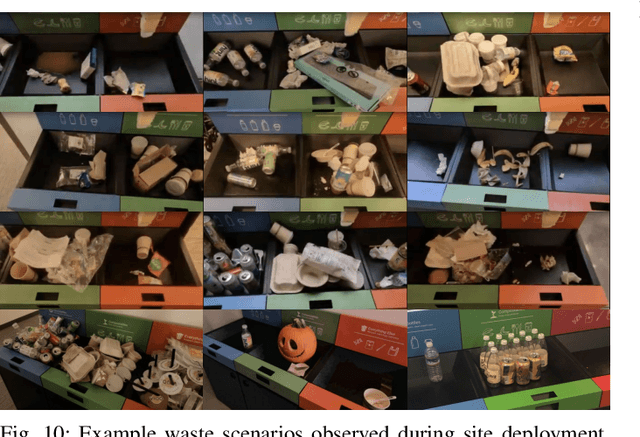

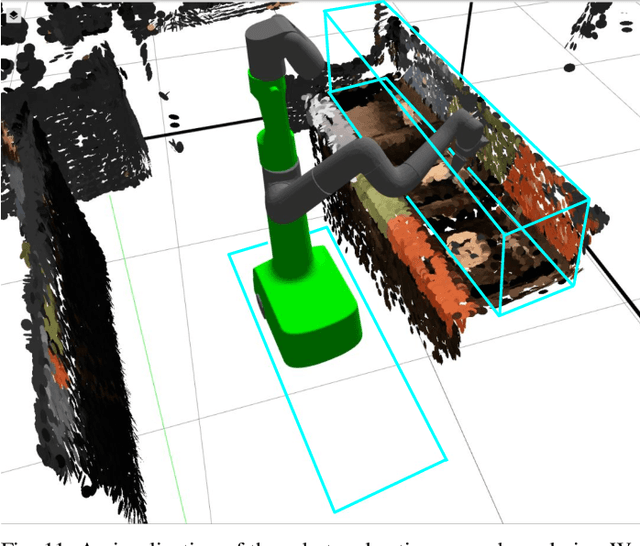
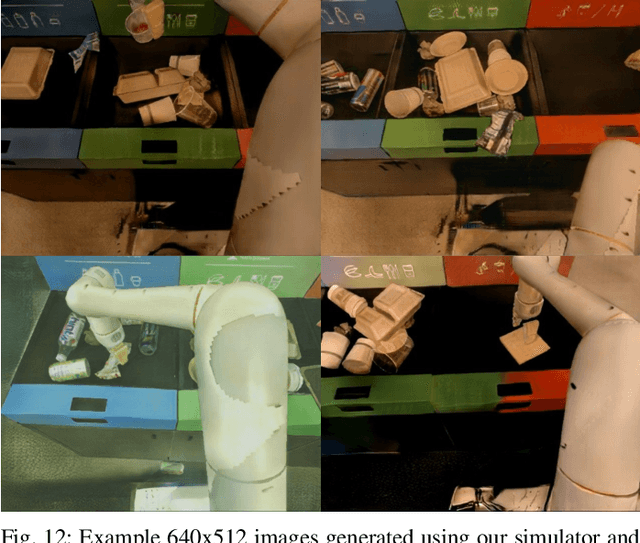
Abstract:We describe a system for deep reinforcement learning of robotic manipulation skills applied to a large-scale real-world task: sorting recyclables and trash in office buildings. Real-world deployment of deep RL policies requires not only effective training algorithms, but the ability to bootstrap real-world training and enable broad generalization. To this end, our system combines scalable deep RL from real-world data with bootstrapping from training in simulation, and incorporates auxiliary inputs from existing computer vision systems as a way to boost generalization to novel objects, while retaining the benefits of end-to-end training. We analyze the tradeoffs of different design decisions in our system, and present a large-scale empirical validation that includes training on real-world data gathered over the course of 24 months of experimentation, across a fleet of 23 robots in three office buildings, with a total training set of 9527 hours of robotic experience. Our final validation also consists of 4800 evaluation trials across 240 waste station configurations, in order to evaluate in detail the impact of the design decisions in our system, the scaling effects of including more real-world data, and the performance of the method on novel objects. The projects website and videos can be found at \href{http://rl-at-scale.github.io}{rl-at-scale.github.io}.
Asking for Help: Failure Prediction in Behavioral Cloning through Value Approximation
Feb 08, 2023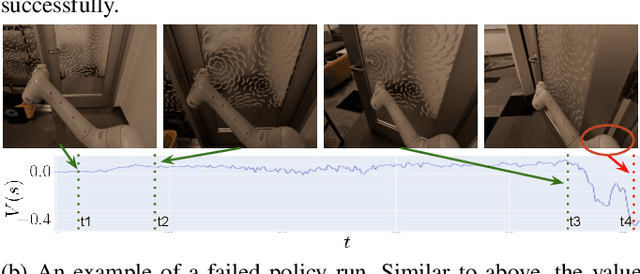
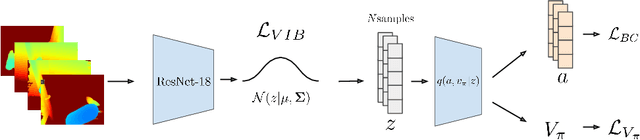
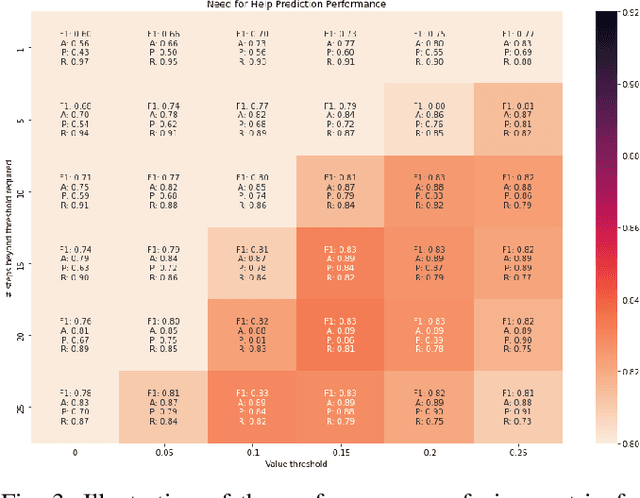
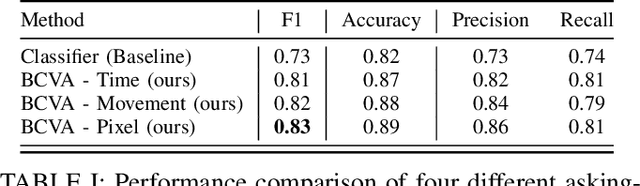
Abstract:Recent progress in end-to-end Imitation Learning approaches has shown promising results and generalization capabilities on mobile manipulation tasks. Such models are seeing increasing deployment in real-world settings, where scaling up requires robots to be able to operate with high autonomy, i.e. requiring as little human supervision as possible. In order to avoid the need for one-on-one human supervision, robots need to be able to detect and prevent policy failures ahead of time, and ask for help, allowing a remote operator to supervise multiple robots and help when needed. However, the black-box nature of end-to-end Imitation Learning models such as Behavioral Cloning, as well as the lack of an explicit state-value representation, make it difficult to predict failures. To this end, we introduce Behavioral Cloning Value Approximation (BCVA), an approach to learning a state value function based on and trained jointly with a Behavioral Cloning policy that can be used to predict failures. We demonstrate the effectiveness of BCVA by applying it to the challenging mobile manipulation task of latched-door opening, showing that we can identify failure scenarios with with 86% precision and 81% recall, evaluated on over 2000 real world runs, improving upon the baseline of simple failure classification by 10 percentage-points.
Do As I Can, Not As I Say: Grounding Language in Robotic Affordances
Apr 04, 2022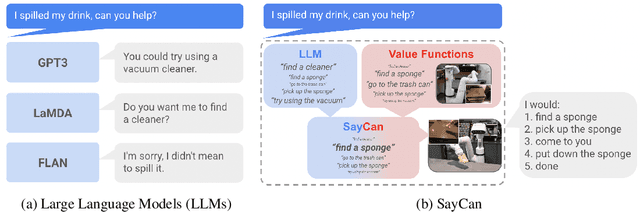
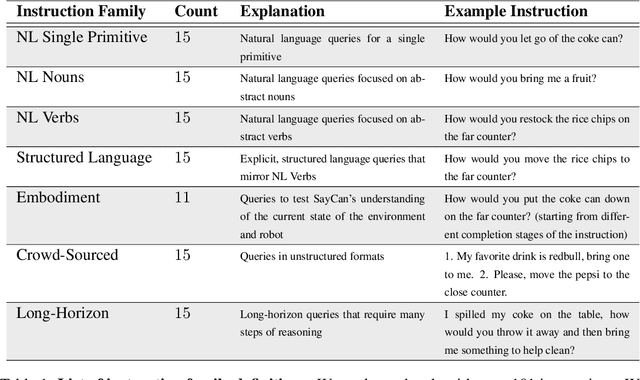
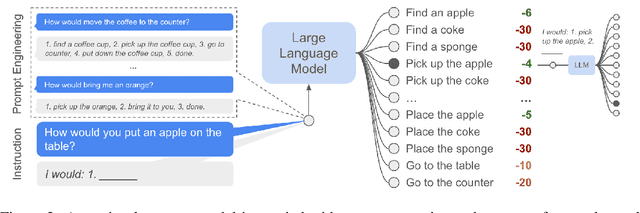
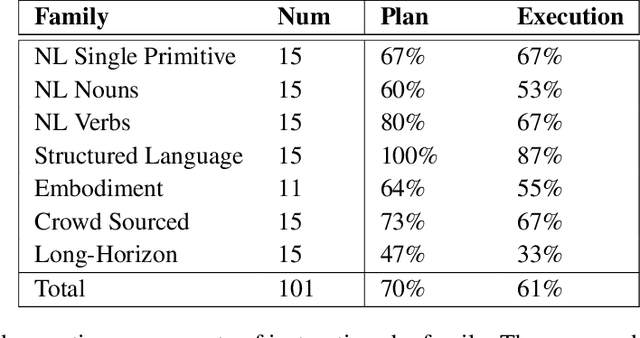
Abstract:Large language models can encode a wealth of semantic knowledge about the world. Such knowledge could be extremely useful to robots aiming to act upon high-level, temporally extended instructions expressed in natural language. However, a significant weakness of language models is that they lack real-world experience, which makes it difficult to leverage them for decision making within a given embodiment. For example, asking a language model to describe how to clean a spill might result in a reasonable narrative, but it may not be applicable to a particular agent, such as a robot, that needs to perform this task in a particular environment. We propose to provide real-world grounding by means of pretrained skills, which are used to constrain the model to propose natural language actions that are both feasible and contextually appropriate. The robot can act as the language model's "hands and eyes," while the language model supplies high-level semantic knowledge about the task. We show how low-level skills can be combined with large language models so that the language model provides high-level knowledge about the procedures for performing complex and temporally-extended instructions, while value functions associated with these skills provide the grounding necessary to connect this knowledge to a particular physical environment. We evaluate our method on a number of real-world robotic tasks, where we show the need for real-world grounding and that this approach is capable of completing long-horizon, abstract, natural language instructions on a mobile manipulator. The project's website and the video can be found at https://say-can.github.io/
Bayesian Imitation Learning for End-to-End Mobile Manipulation
Feb 15, 2022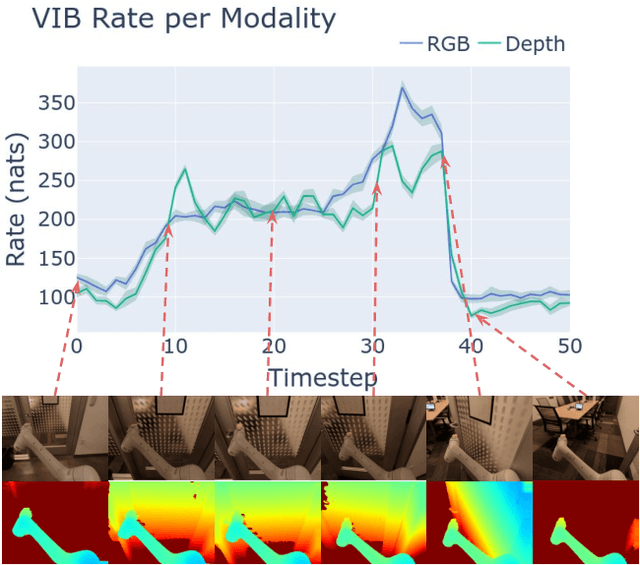
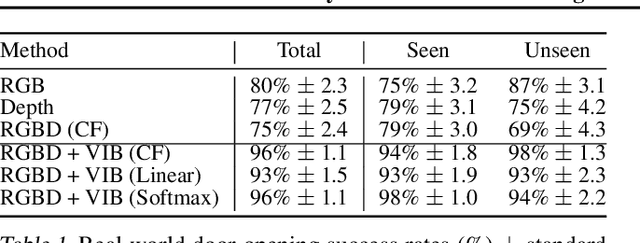
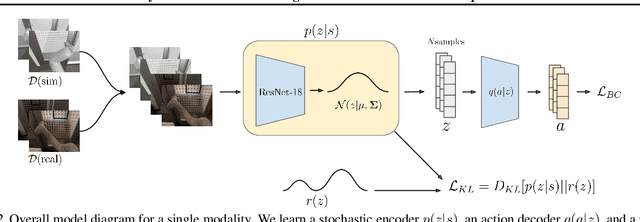
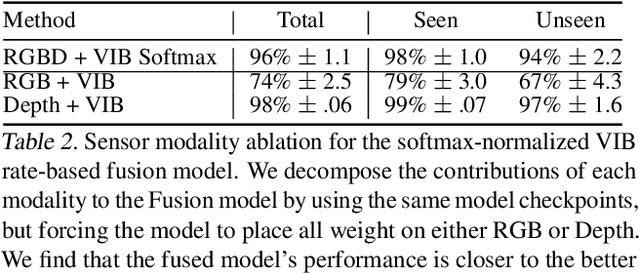
Abstract:In this work we investigate and demonstrate benefits of a Bayesian approach to imitation learning from multiple sensor inputs, as applied to the task of opening office doors with a mobile manipulator. Augmenting policies with additional sensor inputs, such as RGB + depth cameras, is a straightforward approach to improving robot perception capabilities, especially for tasks that may favor different sensors in different situations. As we scale multi-sensor robotic learning to unstructured real-world settings (e.g. offices, homes) and more complex robot behaviors, we also increase reliance on simulators for cost, efficiency, and safety. Consequently, the sim-to-real gap across multiple sensor modalities also increases, making simulated validation more difficult. We show that using the Variational Information Bottleneck (Alemi et al., 2016) to regularize convolutional neural networks improves generalization to held-out domains and reduces the sim-to-real gap in a sensor-agnostic manner. As a side effect, the learned embeddings also provide useful estimates of model uncertainty for each sensor. We demonstrate that our method is able to help close the sim-to-real gap and successfully fuse RGB and depth modalities based on understanding of the situational uncertainty of each sensor. In a real-world office environment, we achieve 96% task success, improving upon the baseline by +16%.
Practical Imitation Learning in the Real World via Task Consistency Loss
Feb 03, 2022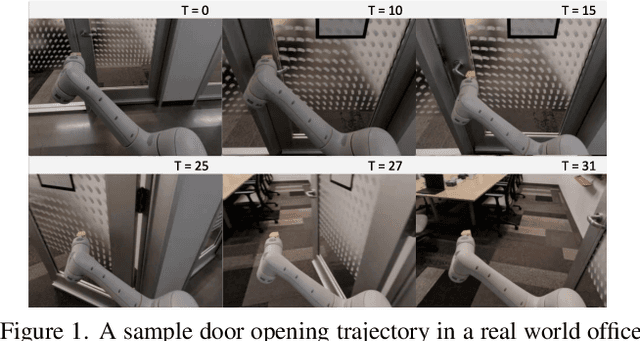
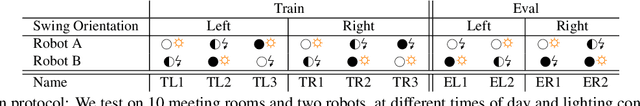
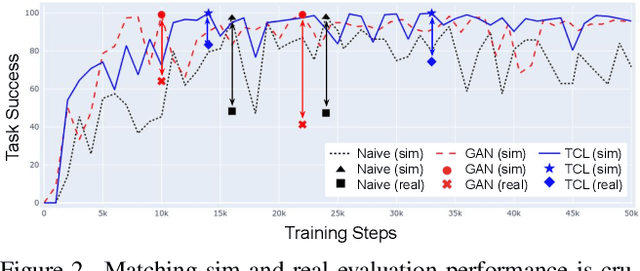
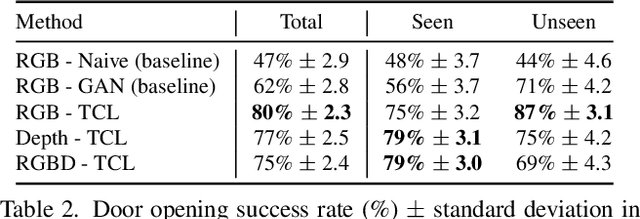
Abstract:Recent work in visual end-to-end learning for robotics has shown the promise of imitation learning across a variety of tasks. Such approaches are expensive both because they require large amounts of real world training demonstrations and because identifying the best model to deploy in the real world requires time-consuming real-world evaluations. These challenges can be mitigated by simulation: by supplementing real world data with simulated demonstrations and using simulated evaluations to identify high performing policies. However, this introduces the well-known "reality gap" problem, where simulator inaccuracies decorrelate performance in simulation from that of reality. In this paper, we build on top of prior work in GAN-based domain adaptation and introduce the notion of a Task Consistency Loss (TCL), a self-supervised loss that encourages sim and real alignment both at the feature and action-prediction levels. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by teaching a mobile manipulator to autonomously approach a door, turn the handle to open the door, and enter the room. The policy performs control from RGB and depth images and generalizes to doors not encountered in training data. We achieve 80% success across ten seen and unseen scenes using only ~16.2 hours of teleoperated demonstrations in sim and real. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to tackle latched door opening from a purely end-to-end learning approach, where the task of navigation and manipulation are jointly modeled by a single neural network.
SimGAN: Hybrid Simulator Identification for Domain Adaptation via Adversarial Reinforcement Learning
Jan 15, 2021

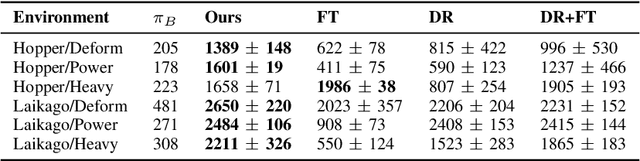
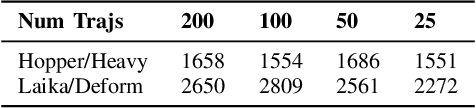
Abstract:As learning-based approaches progress towards automating robot controllers design, transferring learned policies to new domains with different dynamics (e.g. sim-to-real transfer) still demands manual effort. This paper introduces SimGAN, a framework to tackle domain adaptation by identifying a hybrid physics simulator to match the simulated trajectories to the ones from the target domain, using a learned discriminative loss to address the limitations associated with manual loss design. Our hybrid simulator combines neural networks and traditional physics simulaton to balance expressiveness and generalizability, and alleviates the need for a carefully selected parameter set in System ID. Once the hybrid simulator is identified via adversarial reinforcement learning, it can be used to refine policies for the target domain, without the need to collect more data. We show that our approach outperforms multiple strong baselines on six robotic locomotion tasks for domain adaptation.
COCOI: Contact-aware Online Context Inference for Generalizable Non-planar Pushing
Nov 23, 2020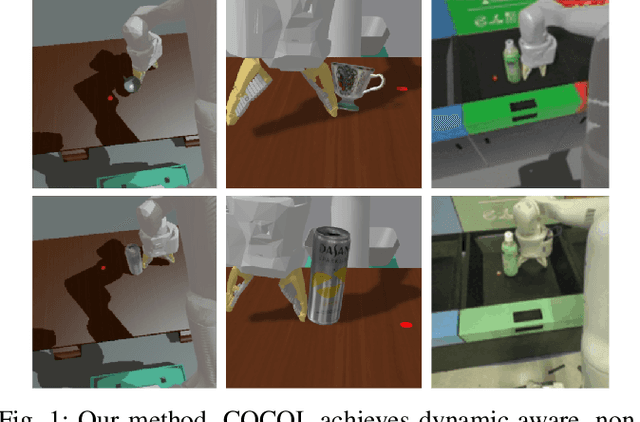
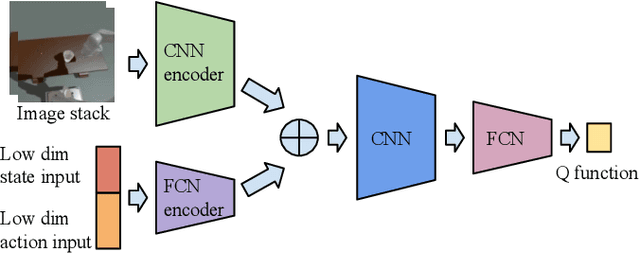
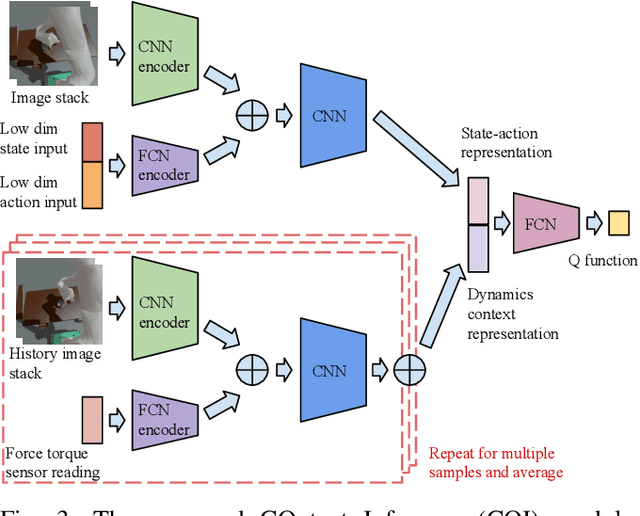
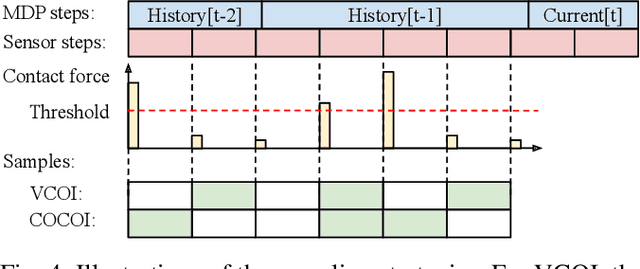
Abstract:General contact-rich manipulation problems are long-standing challenges in robotics due to the difficulty of understanding complicated contact physics. Deep reinforcement learning (RL) has shown great potential in solving robot manipulation tasks. However, existing RL policies have limited adaptability to environments with diverse dynamics properties, which is pivotal in solving many contact-rich manipulation tasks. In this work, we propose Contact-aware Online COntext Inference (COCOI), a deep RL method that encodes a context embedding of dynamics properties online using contact-rich interactions. We study this method based on a novel and challenging non-planar pushing task, where the robot uses a monocular camera image and wrist force torque sensor reading to push an object to a goal location while keeping it upright. We run extensive experiments to demonstrate the capability of COCOI in a wide range of settings and dynamics properties in simulation, and also in a sim-to-real transfer scenario on a real robot (Video: https://youtu.be/nrmJYksh1Kc)
RetinaGAN: An Object-aware Approach to Sim-to-Real Transfer
Nov 06, 2020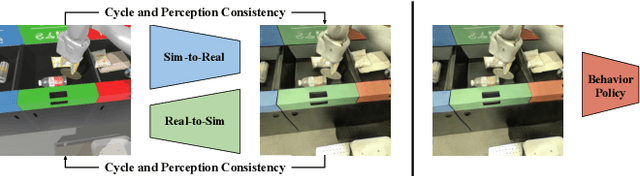

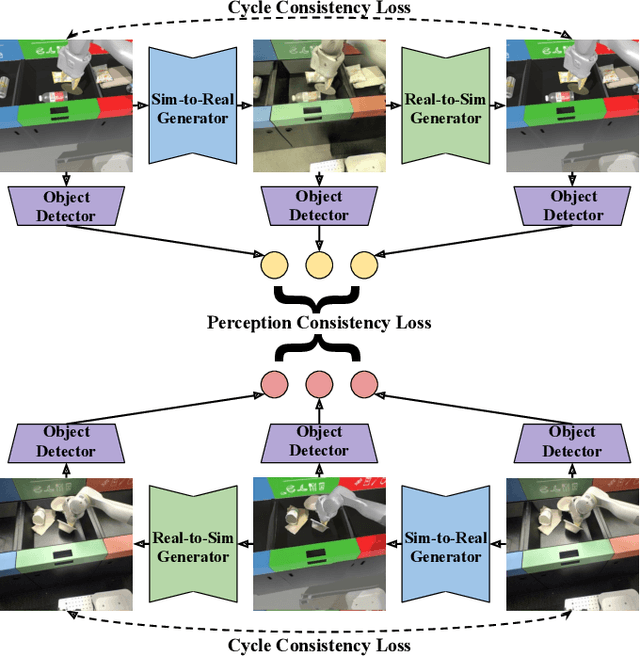
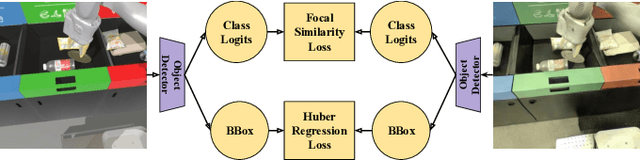
Abstract:The success of deep reinforcement learning (RL) and imitation learning (IL) in vision-based robotic manipulation typically hinges on the expense of large scale data collection. With simulation, data to train a policy can be collected efficiently at scale, but the visual gap between sim and real makes deployment in the real world difficult. We introduce RetinaGAN, a generative adversarial network (GAN) approach to adapt simulated images to realistic ones with object-detection consistency. RetinaGAN is trained in an unsupervised manner without task loss dependencies, and preserves general object structure and texture in adapted images. We evaluate our method on three real world tasks: grasping, pushing, and door opening. RetinaGAN improves upon the performance of prior sim-to-real methods for RL-based object instance grasping and continues to be effective even in the limited data regime. When applied to a pushing task in a similar visual domain, RetinaGAN demonstrates transfer with no additional real data requirements. We also show our method bridges the visual gap for a novel door opening task using imitation learning in a new visual domain. Visit the project website at https://retinagan.github.io/
SegNBDT: Visual Decision Rules for Segmentation
Jun 11, 2020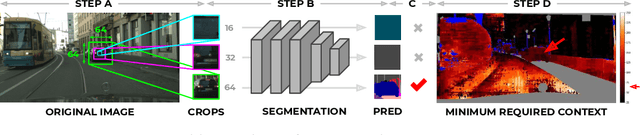

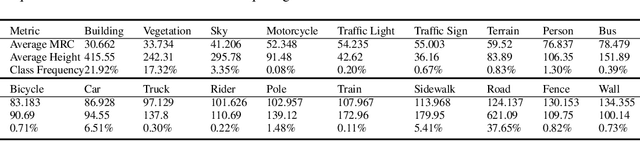

Abstract:The black-box nature of neural networks limits model decision interpretability, in particular for high-dimensional inputs in computer vision and for dense pixel prediction tasks like segmentation. To address this, prior work combines neural networks with decision trees. However, such models (1) perform poorly when compared to state-of-the-art segmentation models or (2) fail to produce decision rules with spatially-grounded semantic meaning. In this work, we build a hybrid neural-network and decision-tree model for segmentation that (1) attains neural network segmentation accuracy and (2) provides semi-automatically constructed visual decision rules such as "Is there a window?". We obtain semantic visual meaning by extending saliency methods to segmentation and attain accuracy by leveraging insights from neural-backed decision trees, a deep learning analog of decision trees for image classification. Our model SegNBDT attains accuracy within ~2-4% of the state-of-the-art HRNetV2 segmentation model while also retaining explainability; we achieve state-of-the-art performance for explainable models on three benchmark datasets -- Pascal-Context (49.12%), Cityscapes (79.01%), and Look Into Person (51.64%). Furthermore, user studies suggest visual decision rules are more interpretable, particularly for incorrect predictions. Code and pretrained models can be found at https://github.com/daniel-ho/SegNBDT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge