Christian Ellis
Efficiently Solving Mixed-Hierarchy Games with Quasi-Policy Approximations
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Multi-robot coordination often exhibits hierarchical structure, with some robots' decisions depending on the planned behaviors of others. While game theory provides a principled framework for such interactions, existing solvers struggle to handle mixed information structures that combine simultaneous (Nash) and hierarchical (Stackelberg) decision-making. We study N-robot forest-structured mixed-hierarchy games, in which each robot acts as a Stackelberg leader over its subtree while robots in different branches interact via Nash equilibria. We derive the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) first-order optimality conditions for this class of games and show that they involve increasingly high-order derivatives of robots' best-response policies as the hierarchy depth grows, rendering a direct solution intractable. To overcome this challenge, we introduce a quasi-policy approximation that removes higher-order policy derivatives and develop an inexact Newton method for efficiently solving the resulting approximated KKT systems. We prove local exponential convergence of the proposed algorithm for games with non-quadratic objectives and nonlinear constraints. The approach is implemented in a highly optimized Julia library (MixedHierarchyGames.jl) and evaluated in simulated experiments, demonstrating real-time convergence for complex mixed-hierarchy information structures.
BEV-Patch-PF: Particle Filtering with BEV-Aerial Feature Matching for Off-Road Geo-Localization
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:We propose BEV-Patch-PF, a GPS-free sequential geo-localization system that integrates a particle filter with learned bird's-eye-view (BEV) and aerial feature maps. From onboard RGB and depth images, we construct a BEV feature map. For each 3-DoF particle pose hypothesis, we crop the corresponding patch from an aerial feature map computed from a local aerial image queried around the approximate location. BEV-Patch-PF computes a per-particle log-likelihood by matching the BEV feature to the aerial patch feature. On two real-world off-road datasets, our method achieves 7.5x lower absolute trajectory error (ATE) on seen routes and 7.0x lower ATE on unseen routes than a retrieval-based baseline, while maintaining accuracy under dense canopy and shadow. The system runs in real time at 10 Hz on an NVIDIA Tesla T4, enabling practical robot deployment.
Zero to Autonomy in Real-Time: Online Adaptation of Dynamics in Unstructured Environments
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:Autonomous robots must go from zero prior knowledge to safe control within seconds to operate in unstructured environments. Abrupt terrain changes, such as a sudden transition to ice, create dynamics shifts that can destabilize planners unless the model adapts in real-time. We present a method for online adaptation that combines function encoders with recursive least squares, treating the function encoder coefficients as latent states updated from streaming odometry. This yields constant-time coefficient estimation without gradient-based inner-loop updates, enabling adaptation from only a few seconds of data. We evaluate our approach on a Van der Pol system to highlight algorithmic behavior, in a Unity simulator for high-fidelity off-road navigation, and on a Clearpath Jackal robot, including on a challenging terrain at a local ice rink. Across these settings, our method improves model accuracy and downstream planning, reducing collisions compared to static and meta-learning baselines.
Temporally Consistent Unsupervised Segmentation for Mobile Robot Perception
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Rapid progress in terrain-aware autonomous ground navigation has been driven by advances in supervised semantic segmentation. However, these methods rely on costly data collection and labor-intensive ground truth labeling to train deep models. Furthermore, autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in unrehearsed, unstructured environments where no labeled data exists and semantic categories may be ambiguous or domain-specific. Recent zero-shot approaches to unsupervised segmentation have shown promise in such settings but typically operate on individual frames, lacking temporal consistency-a critical property for robust perception in unstructured environments. To address this gap we introduce Frontier-Seg, a method for temporally consistent unsupervised segmentation of terrain from mobile robot video streams. Frontier-Seg clusters superpixel-level features extracted from foundation model backbones-specifically DINOv2-and enforces temporal consistency across frames to identify persistent terrain boundaries or frontiers without human supervision. We evaluate Frontier-Seg on a diverse set of benchmark datasets-including RUGD and RELLIS-3D-demonstrating its ability to perform unsupervised segmentation across unstructured off-road environments.
Foundation Models for Logistics: Toward Certifiable, Conversational Planning Interfaces
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:Logistics operators, from battlefield coordinators rerouting airlifts ahead of a storm to warehouse managers juggling late trucks, often face life-critical decisions that demand both domain expertise and rapid and continuous replanning. While popular methods like integer programming yield logistics plans that satisfy user-defined logical constraints, they are slow and assume an idealized mathematical model of the environment that does not account for uncertainty. On the other hand, large language models (LLMs) can handle uncertainty and promise to accelerate replanning while lowering the barrier to entry by translating free-form utterances into executable plans, yet they remain prone to misinterpretations and hallucinations that jeopardize safety and cost. We introduce a neurosymbolic framework that pairs the accessibility of natural-language dialogue with verifiable guarantees on goal interpretation. It converts user requests into structured planning specifications, quantifies its own uncertainty at the field and token level, and invokes an interactive clarification loop whenever confidence falls below an adaptive threshold. A lightweight model, fine-tuned on just 100 uncertainty-filtered examples, surpasses the zero-shot performance of GPT-4.1 while cutting inference latency by nearly 50%. These preliminary results highlight a practical path toward certifiable, real-time, and user-aligned decision-making for complex logistics.
Spatiotemporal Contrastive Learning for Cross-View Video Localization in Unstructured Off-road Terrains
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Robust cross-view 3-DoF localization in GPS-denied, off-road environments remains challenging due to (1) perceptual ambiguities from repetitive vegetation and unstructured terrain, and (2) seasonal shifts that significantly alter scene appearance, hindering alignment with outdated satellite imagery. To address this, we introduce MoViX, a self-supervised cross-view video localization framework that learns viewpoint- and season-invariant representations while preserving directional awareness essential for accurate localization. MoViX employs a pose-dependent positive sampling strategy to enhance directional discrimination and temporally aligned hard negative mining to discourage shortcut learning from seasonal cues. A motion-informed frame sampler selects spatially diverse frames, and a lightweight temporal aggregator emphasizes geometrically aligned observations while downweighting ambiguous ones. At inference, MoViX runs within a Monte Carlo Localization framework, using a learned cross-view matching module in place of handcrafted models. Entropy-guided temperature scaling enables robust multi-hypothesis tracking and confident convergence under visual ambiguity. We evaluate MoViX on the TartanDrive 2.0 dataset, training on under 30 minutes of data and testing over 12.29 km. Despite outdated satellite imagery, MoViX localizes within 25 meters of ground truth 93% of the time, and within 50 meters 100% of the time in unseen regions, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines without environment-specific tuning. We further demonstrate generalization on a real-world off-road dataset from a geographically distinct site with a different robot platform.
Online Adaptation of Terrain-Aware Dynamics for Planning in Unstructured Environments
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Autonomous mobile robots operating in remote, unstructured environments must adapt to new, unpredictable terrains that can change rapidly during operation. In such scenarios, a critical challenge becomes estimating the robot's dynamics on changing terrain in order to enable reliable, accurate navigation and planning. We present a novel online adaptation approach for terrain-aware dynamics modeling and planning using function encoders. Our approach efficiently adapts to new terrains at runtime using limited online data without retraining or fine-tuning. By learning a set of neural network basis functions that span the robot dynamics on diverse terrains, we enable rapid online adaptation to new, unseen terrains and environments as a simple least-squares calculation. We demonstrate our approach for terrain adaptation in a Unity-based robotics simulator and show that the downstream controller has better empirical performance due to higher accuracy of the learned model. This leads to fewer collisions with obstacles while navigating in cluttered environments as compared to a neural ODE baseline.
PSN Game: Game-theoretic Planning via a Player Selection Network
Apr 30, 2025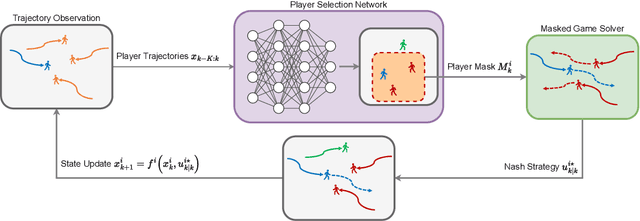
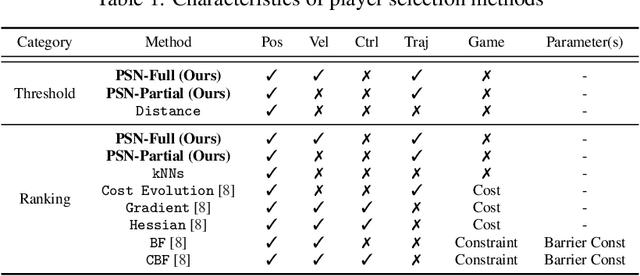
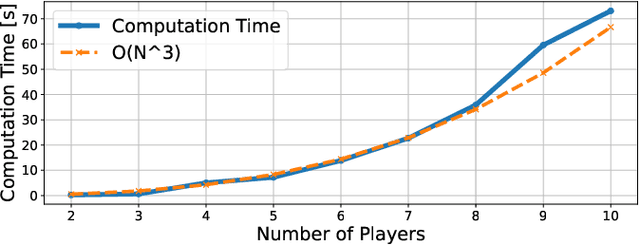
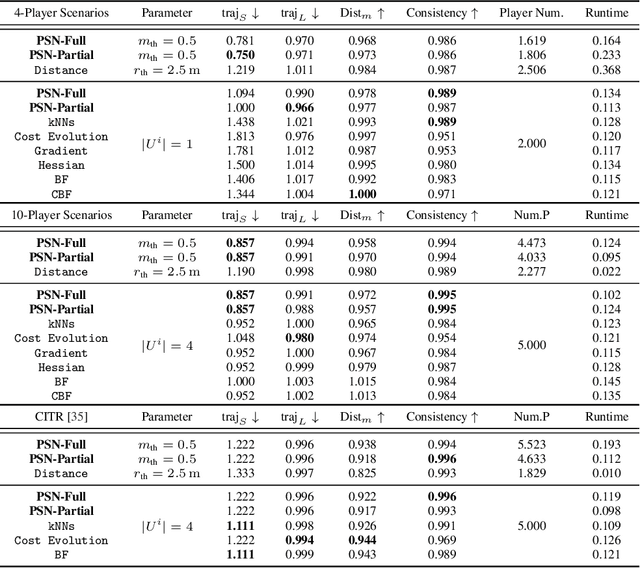
Abstract:While game-theoretic planning frameworks are effective at modeling multi-agent interactions, they require solving optimization problems with hundreds or thousands of variables, resulting in long computation times that limit their use in large-scale, real-time systems. To address this issue, we propose PSN Game: a novel game-theoretic planning framework that reduces runtime by learning a Player Selection Network (PSN). A PSN outputs a player selection mask that distinguishes influential players from less relevant ones, enabling the ego player to solve a smaller, masked game involving only selected players. By reducing the number of variables in the optimization problem, PSN directly lowers computation time. The PSN Game framework is more flexible than existing player selection methods as it i) relies solely on observations of players' past trajectories, without requiring full state, control, or other game-specific information; and ii) requires no online parameter tuning. We train PSNs in an unsupervised manner using a differentiable dynamic game solver, with reference trajectories from full-player games guiding the learning. Experiments in both simulated scenarios and human trajectory datasets demonstrate that i) PSNs outperform baseline selection methods in trajectory smoothness and length, while maintaining comparable safety and achieving a 10x speedup in runtime; and ii) PSNs generalize effectively to real-world scenarios without fine-tuning. By selecting only the most relevant players for decision-making, PSNs offer a general mechanism for reducing planning complexity that can be seamlessly integrated into existing multi-agent planning frameworks.
Multi-Fidelity Policy Gradient Algorithms
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Many reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms require large amounts of data, prohibiting their use in applications where frequent interactions with operational systems are infeasible, or high-fidelity simulations are expensive or unavailable. Meanwhile, low-fidelity simulators--such as reduced-order models, heuristic reward functions, or generative world models--can cheaply provide useful data for RL training, even if they are too coarse for direct sim-to-real transfer. We propose multi-fidelity policy gradients (MFPGs), an RL framework that mixes a small amount of data from the target environment with a large volume of low-fidelity simulation data to form unbiased, reduced-variance estimators (control variates) for on-policy policy gradients. We instantiate the framework by developing multi-fidelity variants of two policy gradient algorithms: REINFORCE and proximal policy optimization. Experimental results across a suite of simulated robotics benchmark problems demonstrate that when target-environment samples are limited, MFPG achieves up to 3.9x higher reward and improves training stability when compared to baselines that only use high-fidelity data. Moreover, even when the baselines are given more high-fidelity samples--up to 10x as many interactions with the target environment--MFPG continues to match or outperform them. Finally, we observe that MFPG is capable of training effective policies even when the low-fidelity environment is drastically different from the target environment. MFPG thus not only offers a novel paradigm for efficient sim-to-real transfer but also provides a principled approach to managing the trade-off between policy performance and data collection costs.
GO: The Great Outdoors Multimodal Dataset
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:The Great Outdoors (GO) dataset is a multi-modal annotated data resource aimed at advancing ground robotics research in unstructured environments. This dataset provides the most comprehensive set of data modalities and annotations compared to existing off-road datasets. In total, the GO dataset includes six unique sensor types with high-quality semantic annotations and GPS traces to support tasks such as semantic segmentation, object detection, and SLAM. The diverse environmental conditions represented in the dataset present significant real-world challenges that provide opportunities to develop more robust solutions to support the continued advancement of field robotics, autonomous exploration, and perception systems in natural environments. The dataset can be downloaded at: https://www.unmannedlab.org/the-great-outdoors-dataset/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge