John G. Rogers III
Deep Bayesian Future Fusion for Self-Supervised, High-Resolution, Off-Road Mapping
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:The limited sensing resolution of resource-constrained off-road vehicles poses significant challenges towards reliable off-road autonomy. To overcome this limitation, we propose a general framework based on fusing the future information (i.e. future fusion) for self-supervision. Recent approaches exploit this future information alongside the hand-crafted heuristics to directly supervise the targeted downstream tasks (e.g. traversability estimation). However, in this paper, we opt for a more general line of development - time-efficient completion of the highest resolution (i.e. 2cm per pixel) BEV map in a self-supervised manner via future fusion, which can be used for any downstream tasks for better longer range prediction. To this end, first, we create a high-resolution future-fusion dataset containing pairs of (RGB / height) raw sparse and noisy inputs and map-based dense labels. Next, to accommodate the noise and sparsity of the sensory information, especially in the distal regions, we design an efficient realization of the Bayes filter onto the vanilla convolutional network via the recurrent mechanism. Equipped with the ideas from SOTA generative models, our Bayesian structure effectively predicts high-quality BEV maps in the distal regions. Extensive evaluation on both the quality of completion and downstream task on our future-fusion dataset demonstrates the potential of our approach.
PIAug -- Physics Informed Augmentation for Learning Vehicle Dynamics for Off-Road Navigation
Nov 01, 2023



Abstract:Modeling the precise dynamics of off-road vehicles is a complex yet essential task due to the challenging terrain they encounter and the need for optimal performance and safety. Recently, there has been a focus on integrating nominal physics-based models alongside data-driven neural networks using Physics Informed Neural Networks. These approaches often assume the availability of a well-distributed dataset; however, this assumption may not hold due to regions in the physical distribution that are hard to collect, such as high-speed motions and rare terrains. Therefore, we introduce a physics-informed data augmentation methodology called PIAug. We show an example use case of the same by modeling high-speed and aggressive motion predictions, given a dataset with only low-speed data. During the training phase, we leverage the nominal model for generating target domain (medium and high velocity) data using the available source data (low velocity). Subsequently, we employ a physics-inspired loss function with this augmented dataset to incorporate prior knowledge of physics into the neural network. Our methodology results in up to 67% less mean error in trajectory prediction in comparison to a standalone nominal model, especially during aggressive maneuvers at speeds outside the training domain. In real-life navigation experiments, our model succeeds in 4x tighter waypoint tracking constraints than the Kinematic Bicycle Model (KBM) at out-of-domain velocities.
Robust Incremental Smoothing and Mapping (riSAM)
Sep 28, 2022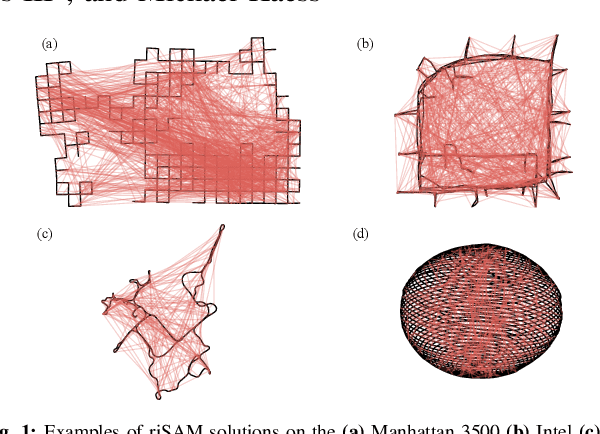
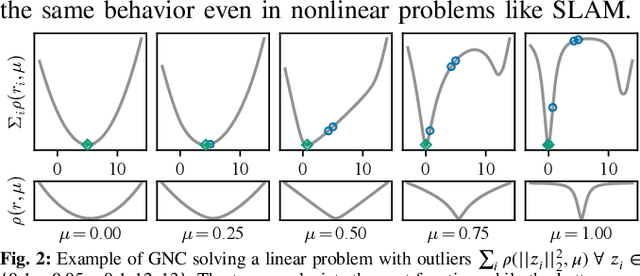
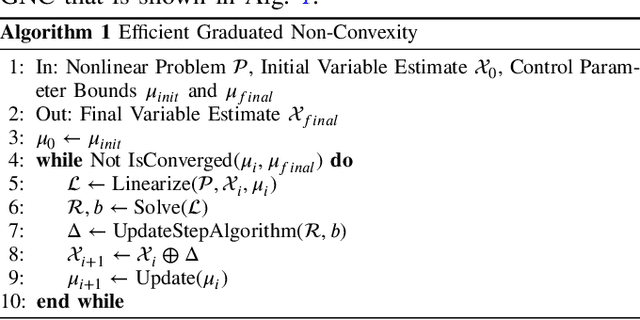
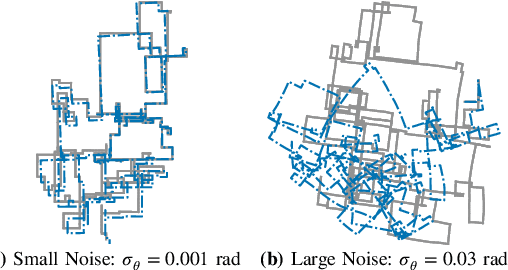
Abstract:This paper presents a method for robust optimization for online incremental Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). Due to the NP-Hardness of data association in the presence of perceptual aliasing, tractable (approximate) approaches to data association will produce erroneous measurements. We require SLAM back-ends that can converge to accurate solutions in the presence of outlier measurements while meeting online efficiency constraints. Existing robust SLAM methods either remain sensitive to outliers, become increasingly sensitive to initialization, or fail to provide online efficiency. We present the robust incremental Smoothing and Mapping (riSAM) algorithm, a robust back-end optimizer for incremental SLAM based on Graduated Non-Convexity. We demonstrate on benchmarking datasets that our algorithm achieves online efficiency, outperforms existing online approaches, and matches or improves the performance of existing offline methods.
How Does It Feel? Self-Supervised Costmap Learning for Off-Road Vehicle Traversability
Sep 22, 2022
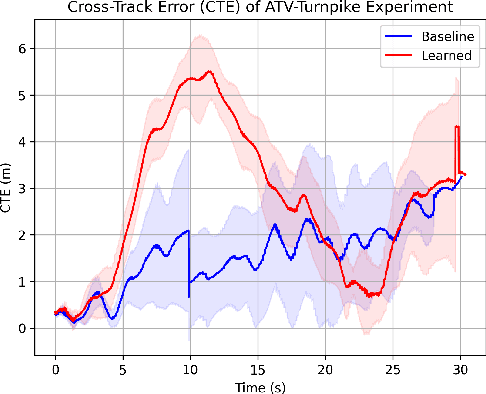
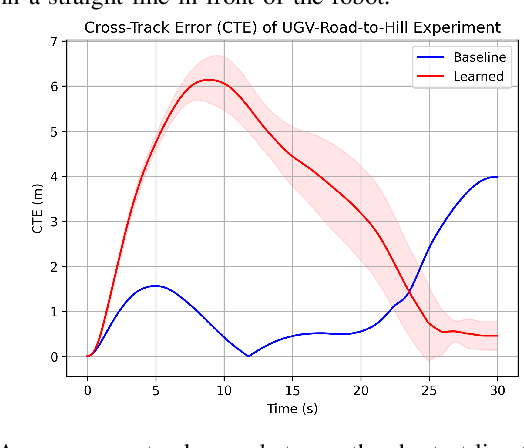
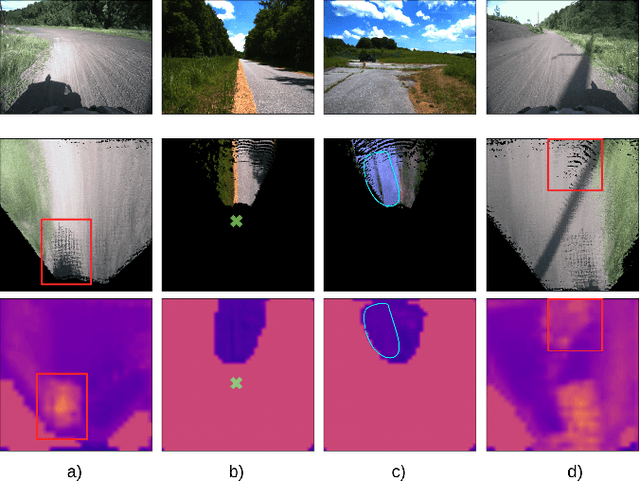
Abstract:Estimating terrain traversability in off-road environments requires reasoning about complex interaction dynamics between the robot and these terrains. However, it is challenging to build an accurate physics model, or create informative labels to learn a model in a supervised manner, for these interactions. We propose a method that learns to predict traversability costmaps by combining exteroceptive environmental information with proprioceptive terrain interaction feedback in a self-supervised manner. Additionally, we propose a novel way of incorporating robot velocity in the costmap prediction pipeline. We validate our method in multiple short and large-scale navigation tasks on a large, autonomous all-terrain vehicle (ATV) on challenging off-road terrains, and demonstrate ease of integration on a separate large ground robot. Our short-scale navigation results show that using our learned costmaps leads to overall smoother navigation, and provides the robot with a more fine-grained understanding of the interactions between the robot and different terrain types, such as grass and gravel. Our large-scale navigation trials show that we can reduce the number of interventions by up to 57% compared to an occupancy-based navigation baseline in challenging off-road courses ranging from 400 m to 3150 m.
Robot navigation from human demonstration: learning control behaviors with environment feature maps
May 06, 2022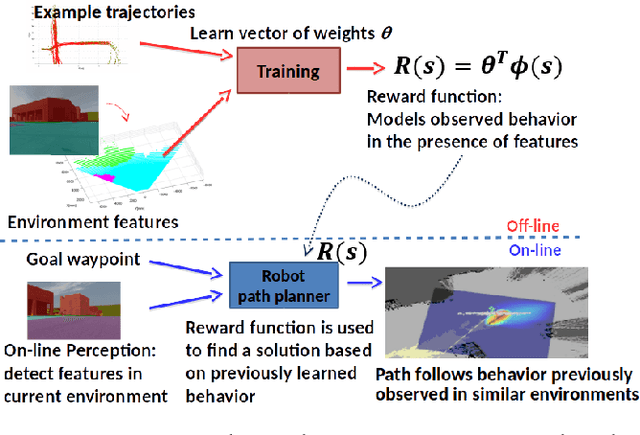

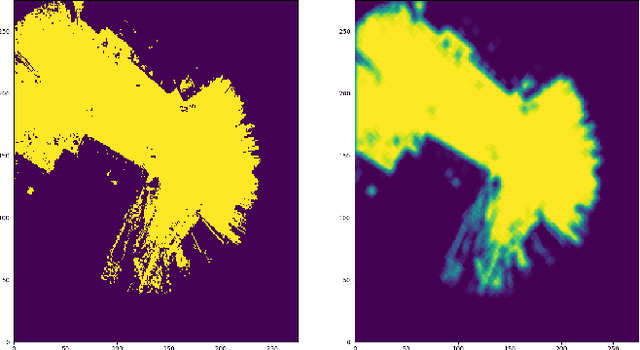
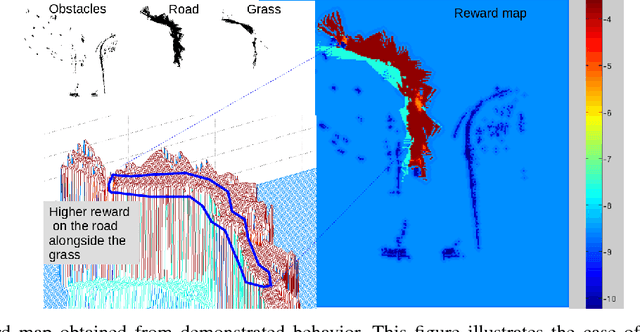
Abstract:When working alongside human collaborators in dynamic and unstructured environments, such as disaster recovery or military operation, fast field adaptation is necessary for an unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) to perform its duties or learn novel tasks. In these scenarios, personnel and equipment are constrained, making training with minimal human supervision a desirable learning attribute. We address the problem of making UGVs more reliable and adaptable teammates with a novel framework that uses visual perception and inverse optimal control to learn traversal costs for environment features. Through extensive evaluation in a real-world environment, we show that our framework requires few human demonstrated trajectory exemplars to learn feature costs that reliably encode several different traversal behaviors. Additionally, we present an on-line version of the framework that allows a human teammate to intervene during live operation to correct deteriorated behavior or to adapt behavior to dynamic changes in complex and unstructured environments.
Risk Averse Bayesian Reward Learning for Autonomous Navigation from Human Demonstration
Jul 31, 2021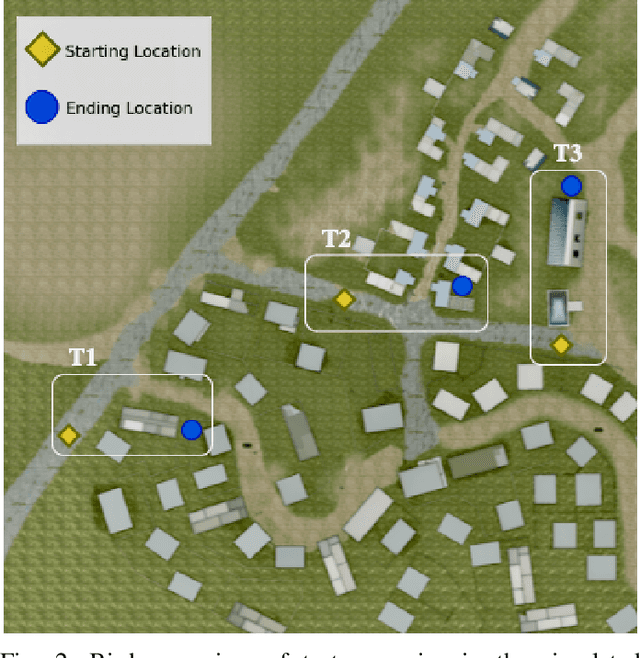

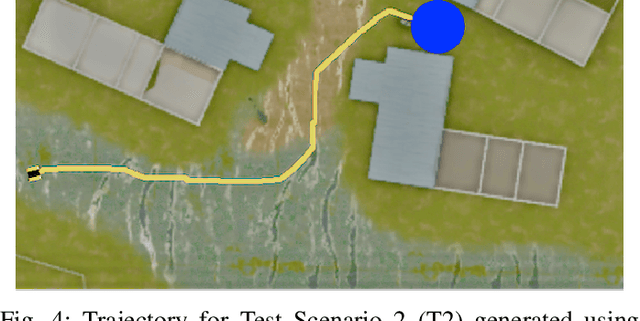
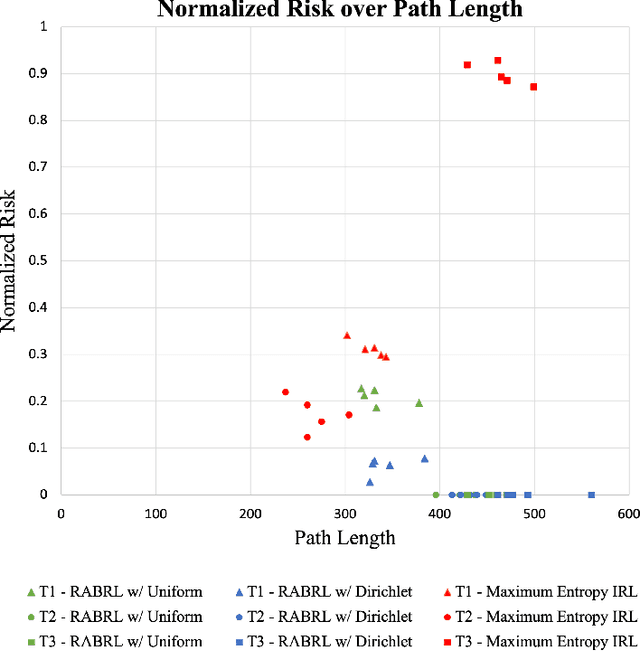
Abstract:Traditional imitation learning provides a set of methods and algorithms to learn a reward function or policy from expert demonstrations. Learning from demonstration has been shown to be advantageous for navigation tasks as it allows for machine learning non-experts to quickly provide information needed to learn complex traversal behaviors. However, a minimal set of demonstrations is unlikely to capture all relevant information needed to achieve the desired behavior in every possible future operational environment. Due to distributional shift among environments, a robot may encounter features that were rarely or never observed during training for which the appropriate reward value is uncertain, leading to undesired outcomes. This paper proposes a Bayesian technique which quantifies uncertainty over the weights of a linear reward function given a dataset of minimal human demonstrations to operate safely in dynamic environments. This uncertainty is quantified and incorporated into a risk averse set of weights used to generate cost maps for planning. Experiments in a 3-D environment with a simulated robot show that our proposed algorithm enables a robot to avoid dangerous terrain completely in two out of three test scenarios and accumulates a lower amount of risk than related approaches in all scenarios without requiring any additional demonstrations.
ScoutBot: A Dialogue System for Collaborative Navigation
Jul 21, 2018
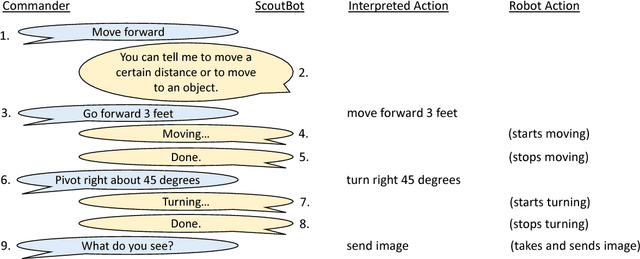
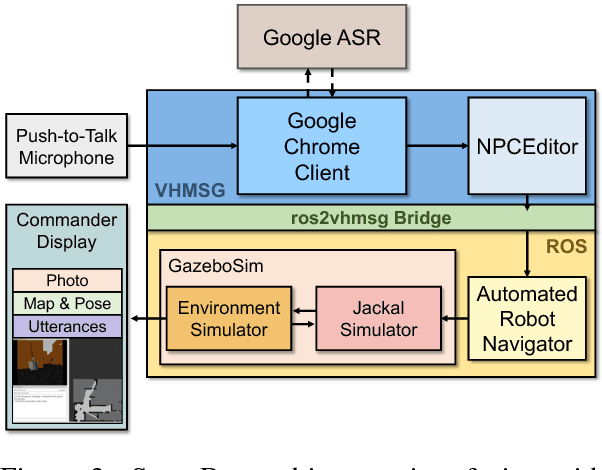

Abstract:ScoutBot is a dialogue interface to physical and simulated robots that supports collaborative exploration of environments. The demonstration will allow users to issue unconstrained spoken language commands to ScoutBot. ScoutBot will prompt for clarification if the user's instruction needs additional input. It is trained on human-robot dialogue collected from Wizard-of-Oz experiments, where robot responses were initiated by a human wizard in previous interactions. The demonstration will show a simulated ground robot (Clearpath Jackal) in a simulated environment supported by ROS (Robot Operating System).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge