Long Quang
GO: The Great Outdoors Multimodal Dataset
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:The Great Outdoors (GO) dataset is a multi-modal annotated data resource aimed at advancing ground robotics research in unstructured environments. This dataset provides the most comprehensive set of data modalities and annotations compared to existing off-road datasets. In total, the GO dataset includes six unique sensor types with high-quality semantic annotations and GPS traces to support tasks such as semantic segmentation, object detection, and SLAM. The diverse environmental conditions represented in the dataset present significant real-world challenges that provide opportunities to develop more robust solutions to support the continued advancement of field robotics, autonomous exploration, and perception systems in natural environments. The dataset can be downloaded at: https://www.unmannedlab.org/the-great-outdoors-dataset/
CoPeD-Advancing Multi-Robot Collaborative Perception: A Comprehensive Dataset in Real-World Environments
May 23, 2024



Abstract:In the past decade, although single-robot perception has made significant advancements, the exploration of multi-robot collaborative perception remains largely unexplored. This involves fusing compressed, intermittent, limited, heterogeneous, and asynchronous environmental information across multiple robots to enhance overall perception, despite challenges like sensor noise, occlusions, and sensor failures. One major hurdle has been the lack of real-world datasets. This paper presents a pioneering and comprehensive real-world multi-robot collaborative perception dataset to boost research in this area. Our dataset leverages the untapped potential of air-ground robot collaboration featuring distinct spatial viewpoints, complementary robot mobilities, coverage ranges, and sensor modalities. It features raw sensor inputs, pose estimation, and optional high-level perception annotation, thus accommodating diverse research interests. Compared to existing datasets predominantly designed for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), our setup ensures a diverse range and adequate overlap of sensor views to facilitate the study of multi-robot collaborative perception algorithms. We demonstrate the value of this dataset qualitatively through multiple collaborative perception tasks. We believe this work will unlock the potential research of high-level scene understanding through multi-modal collaborative perception in multi-robot settings.
Real-World Deployment of a Hierarchical Uncertainty-Aware Collaborative Multiagent Planning System
Apr 26, 2024Abstract:We would like to enable a collaborative multiagent team to navigate at long length scales and under uncertainty in real-world environments. In practice, planning complexity scales with the number of agents in the team, with the length scale of the environment, and with environmental uncertainty. Enabling tractable planning requires developing abstract models that can represent complex, high-quality plans. However, such models often abstract away information needed to generate directly-executable plans for real-world agents in real-world environments, as planning in such detail, especially in the presence of real-world uncertainty, would be computationally intractable. In this paper, we describe the deployment of a planning system that used a hierarchy of planners to execute collaborative multiagent navigation tasks in real-world, unknown environments. By developing a planning system that was robust to failures at every level of the planning hierarchy, we enabled the team to complete collaborative navigation tasks, even in the presence of imperfect planning abstractions and real-world uncertainty. We deployed our approach on a Clearpath Husky-Jackal team navigating in a structured outdoor environment, and demonstrated that the system enabled the agents to successfully execute collaborative plans.
Resilient and Distributed Multi-Robot Visual SLAM: Datasets, Experiments, and Lessons Learned
Apr 10, 2023



Abstract:This paper revisits Kimera-Multi, a distributed multi-robot Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) system, towards the goal of deployment in the real world. In particular, this paper has three main contributions. First, we describe improvements to Kimera-Multi to make it resilient to large-scale real-world deployments, with particular emphasis on handling intermittent and unreliable communication. Second, we collect and release challenging multi-robot benchmarking datasets obtained during live experiments conducted on the MIT campus, with accurate reference trajectories and maps for evaluation. The datasets include up to 8 robots traversing long distances (up to 8 km) and feature many challenging elements such as severe visual ambiguities (e.g., in underground tunnels and hallways), mixed indoor and outdoor trajectories with different lighting conditions, and dynamic entities (e.g., pedestrians and cars). Lastly, we evaluate the resilience of Kimera-Multi under different communication scenarios, and provide a quantitative comparison with a centralized baseline system. Based on the results from both live experiments and subsequent analysis, we discuss the strengths and weaknesses of Kimera-Multi, and suggest future directions for both algorithm and system design. We release the source code of Kimera-Multi and all datasets to facilitate further research towards the reliable real-world deployment of multi-robot SLAM systems.
NAUTS: Negotiation for Adaptation to Unstructured Terrain Surfaces
Jul 28, 2022
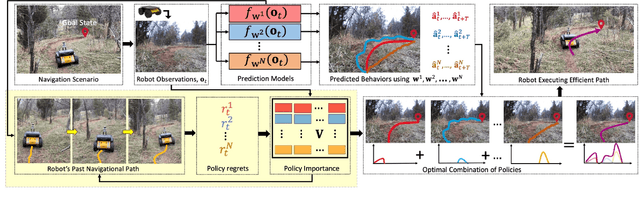

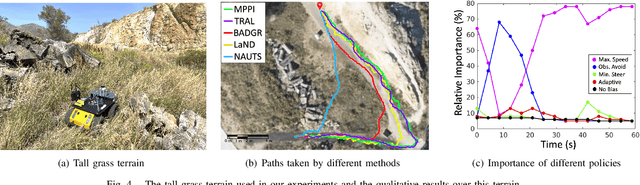
Abstract:When robots operate in real-world off-road environments with unstructured terrains, the ability to adapt their navigational policy is critical for effective and safe navigation. However, off-road terrains introduce several challenges to robot navigation, including dynamic obstacles and terrain uncertainty, leading to inefficient traversal or navigation failures. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel approach for adaptation by negotiation that enables a ground robot to adjust its navigational behaviors through a negotiation process. Our approach first learns prediction models for various navigational policies to function as a terrain-aware joint local controller and planner. Then, through a new negotiation process, our approach learns from various policies' interactions with the environment to agree on the optimal combination of policies in an online fashion to adapt robot navigation to unstructured off-road terrains on the fly. Additionally, we implement a new optimization algorithm that offers the optimal solution for robot negotiation in real-time during execution. Experimental results have validated that our method for adaptation by negotiation outperforms previous methods for robot navigation, especially over unseen and uncertain dynamic terrains.
Self-Reflective Terrain-Aware Robot Adaptation for Consistent Off-Road Ground Navigation
Nov 12, 2021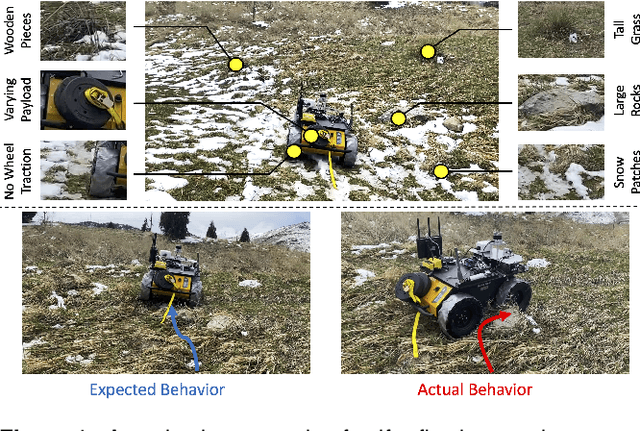

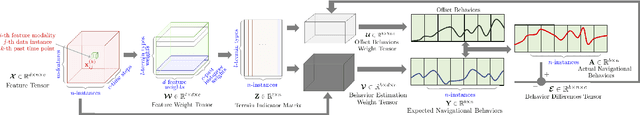
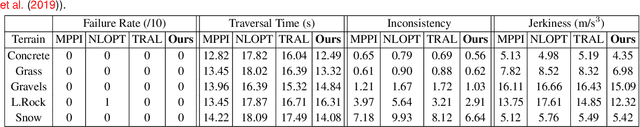
Abstract:Ground robots require the crucial capability of traversing unstructured and unprepared terrains and avoiding obstacles to complete tasks in real-world robotics applications such as disaster response. When a robot operates in off-road field environments such as forests, the robot's actual behaviors often do not match its expected or planned behaviors, due to changes in the characteristics of terrains and the robot itself. Therefore, the capability of robot adaptation for consistent behavior generation is essential for maneuverability on unstructured off-road terrains. In order to address the challenge, we propose a novel method of self-reflective terrain-aware adaptation for ground robots to generate consistent controls to navigate over unstructured off-road terrains, which enables robots to more accurately execute the expected behaviors through robot self-reflection while adapting to varying unstructured terrains. To evaluate our method's performance, we conduct extensive experiments using real ground robots with various functionality changes over diverse unstructured off-road terrains. The comprehensive experimental results have shown that our self-reflective terrain-aware adaptation method enables ground robots to generate consistent navigational behaviors and outperforms the compared previous and baseline techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge