Chaoyang Wang
V-Retrver: Evidence-Driven Agentic Reasoning for Universal Multimodal Retrieval
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have recently been applied to universal multimodal retrieval, where Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning improves candidate reranking. However, existing approaches remain largely language-driven, relying on static visual encodings and lacking the ability to actively verify fine-grained visual evidence, which often leads to speculative reasoning in visually ambiguous cases. We propose V-Retrver, an evidence-driven retrieval framework that reformulates multimodal retrieval as an agentic reasoning process grounded in visual inspection. V-Retrver enables an MLLM to selectively acquire visual evidence during reasoning via external visual tools, performing a multimodal interleaved reasoning process that alternates between hypothesis generation and targeted visual verification.To train such an evidence-gathering retrieval agent, we adopt a curriculum-based learning strategy combining supervised reasoning activation, rejection-based refinement, and reinforcement learning with an evidence-aligned objective. Experiments across multiple multimodal retrieval benchmarks demonstrate consistent improvements in retrieval accuracy (with 23.0% improvements on average), perception-driven reasoning reliability, and generalization.
Revisiting Diffusion Model Predictions Through Dimensionality
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion and flow matching models have highlighted a shift in the preferred prediction target -- moving from noise ($\varepsilon$) and velocity (v) to direct data (x) prediction -- particularly in high-dimensional settings. However, a formal explanation of why the optimal target depends on the specific properties of the data remains elusive. In this work, we provide a theoretical framework based on a generalized prediction formulation that accommodates arbitrary output targets, of which $\varepsilon$-, v-, and x-prediction are special cases. We derive the analytical relationship between data's geometry and the optimal prediction target, offering a rigorous justification for why x-prediction becomes superior when the ambient dimension significantly exceeds the data's intrinsic dimension. Furthermore, while our theory identifies dimensionality as the governing factor for the optimal prediction target, the intrinsic dimension of manifold-bound data is typically intractable to estimate in practice. To bridge this gap, we propose k-Diff, a framework that employs a data-driven approach to learn the optimal prediction parameter k directly from data, bypassing the need for explicit dimension estimation. Extensive experiments in both latent-space and pixel-space image generation demonstrate that k-Diff consistently outperforms fixed-target baselines across varying architectures and data scales, providing a principled and automated approach to enhancing generative performance.
A DeepSeek-Powered AI System for Automated Chest Radiograph Interpretation in Clinical Practice
Dec 23, 2025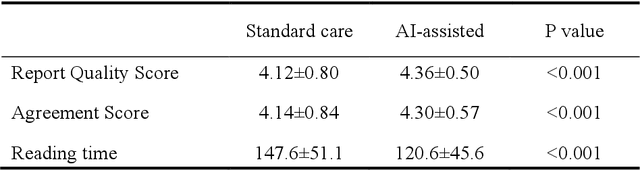
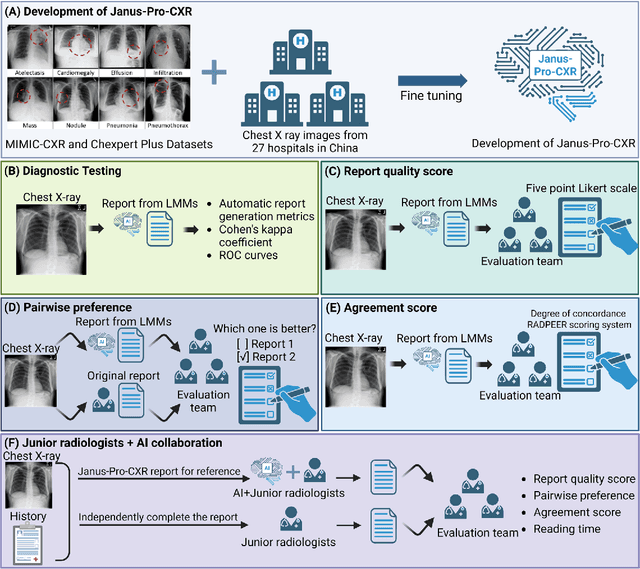
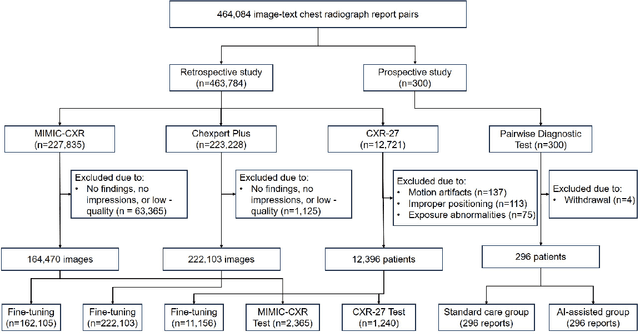
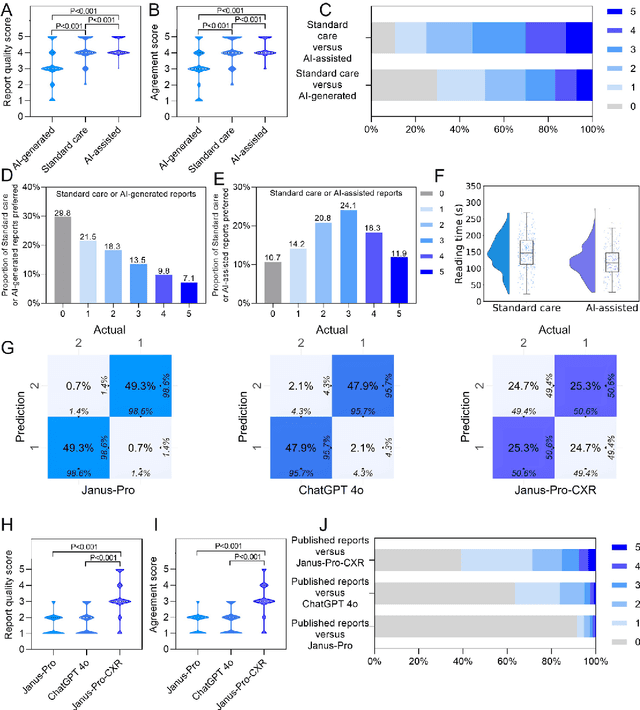
Abstract:A global shortage of radiologists has been exacerbated by the significant volume of chest X-ray workloads, particularly in primary care. Although multimodal large language models show promise, existing evaluations predominantly rely on automated metrics or retrospective analyses, lacking rigorous prospective clinical validation. Janus-Pro-CXR (1B), a chest X-ray interpretation system based on DeepSeek Janus-Pro model, was developed and rigorously validated through a multicenter prospective trial (NCT07117266). Our system outperforms state-of-the-art X-ray report generation models in automated report generation, surpassing even larger-scale models including ChatGPT 4o (200B parameters), while demonstrating reliable detection of six clinically critical radiographic findings. Retrospective evaluation confirms significantly higher report accuracy than Janus-Pro and ChatGPT 4o. In prospective clinical deployment, AI assistance significantly improved report quality scores, reduced interpretation time by 18.3% (P < 0.001), and was preferred by a majority of experts in 54.3% of cases. Through lightweight architecture and domain-specific optimization, Janus-Pro-CXR improves diagnostic reliability and workflow efficiency, particularly in resource-constrained settings. The model architecture and implementation framework will be open-sourced to facilitate the clinical translation of AI-assisted radiology solutions.
AdaTooler-V: Adaptive Tool-Use for Images and Videos
Dec 19, 2025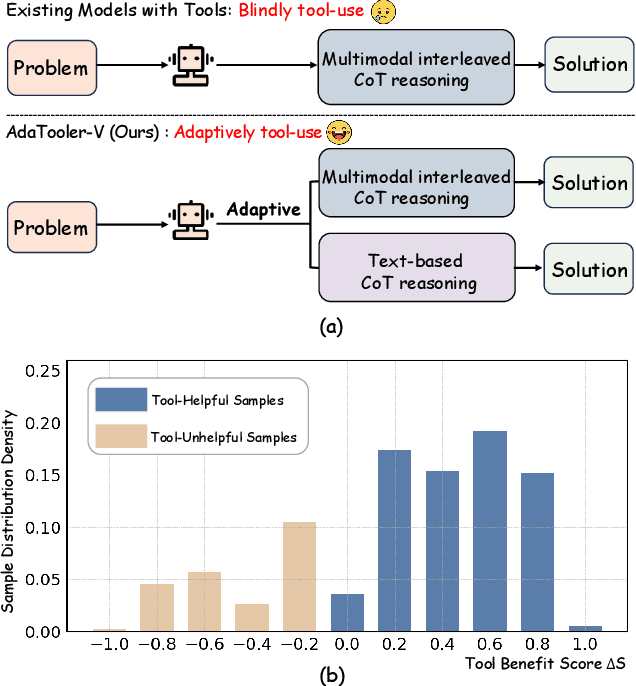
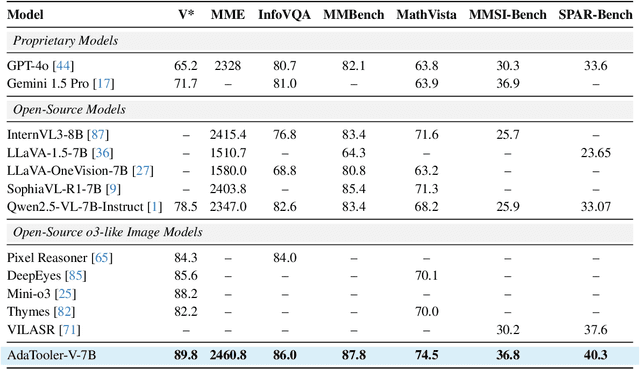
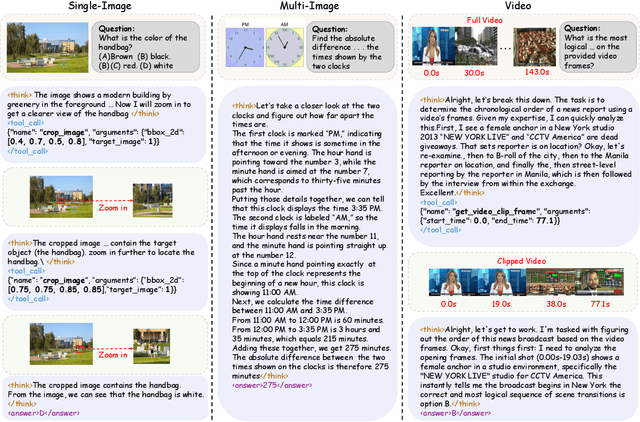
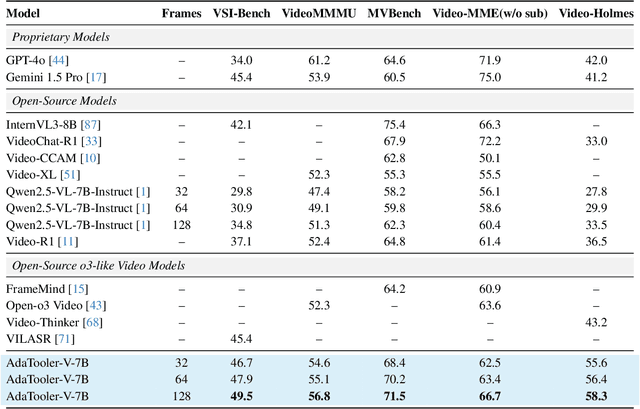
Abstract:Recent advances have shown that multimodal large language models (MLLMs) benefit from multimodal interleaved chain-of-thought (CoT) with vision tool interactions. However, existing open-source models often exhibit blind tool-use reasoning patterns, invoking vision tools even when they are unnecessary, which significantly increases inference overhead and degrades model performance. To this end, we propose AdaTooler-V, an MLLM that performs adaptive tool-use by determining whether a visual problem truly requires tools. First, we introduce AT-GRPO, a reinforcement learning algorithm that adaptively adjusts reward scales based on the Tool Benefit Score of each sample, encouraging the model to invoke tools only when they provide genuine improvements. Moreover, we construct two datasets to support training: AdaTooler-V-CoT-100k for SFT cold start and AdaTooler-V-300k for RL with verifiable rewards across single-image, multi-image, and video data. Experiments across twelve benchmarks demonstrate the strong reasoning capability of AdaTooler-V, outperforming existing methods in diverse visual reasoning tasks. Notably, AdaTooler-V-7B achieves an accuracy of 89.8\% on the high-resolution benchmark V*, surpassing the commercial proprietary model GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro. All code, models, and data are released.
EasyV2V: A High-quality Instruction-based Video Editing Framework
Dec 18, 2025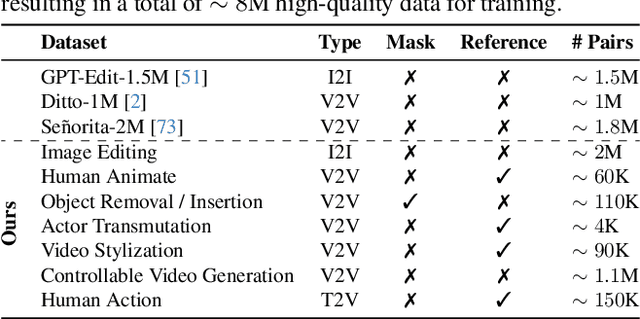

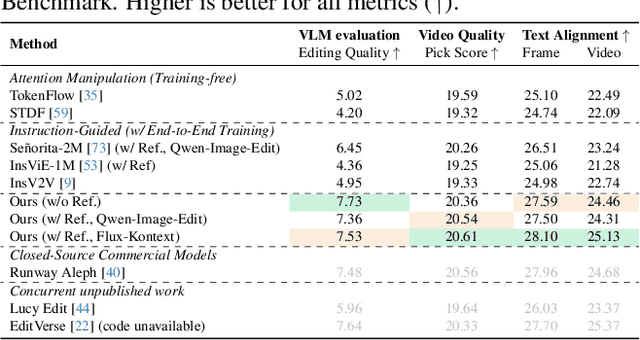
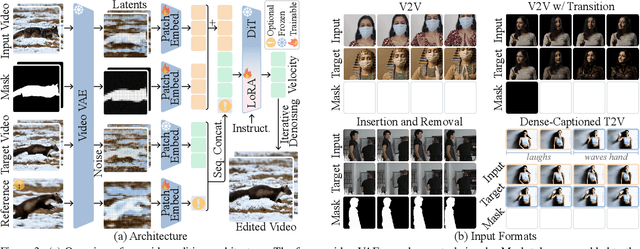
Abstract:While image editing has advanced rapidly, video editing remains less explored, facing challenges in consistency, control, and generalization. We study the design space of data, architecture, and control, and introduce \emph{EasyV2V}, a simple and effective framework for instruction-based video editing. On the data side, we compose existing experts with fast inverses to build diverse video pairs, lift image edit pairs into videos via single-frame supervision and pseudo pairs with shared affine motion, mine dense-captioned clips for video pairs, and add transition supervision to teach how edits unfold. On the model side, we observe that pretrained text-to-video models possess editing capability, motivating a simplified design. Simple sequence concatenation for conditioning with light LoRA fine-tuning suffices to train a strong model. For control, we unify spatiotemporal control via a single mask mechanism and support optional reference images. Overall, EasyV2V works with flexible inputs, e.g., video+text, video+mask+text, video+mask+reference+text, and achieves state-of-the-art video editing results, surpassing concurrent and commercial systems. Project page: https://snap-research.github.io/easyv2v/
OmniView: An All-Seeing Diffusion Model for 3D and 4D View Synthesis
Dec 11, 2025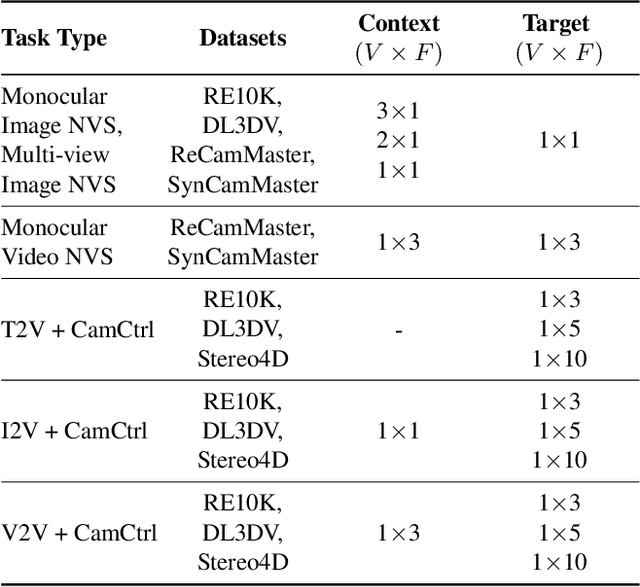
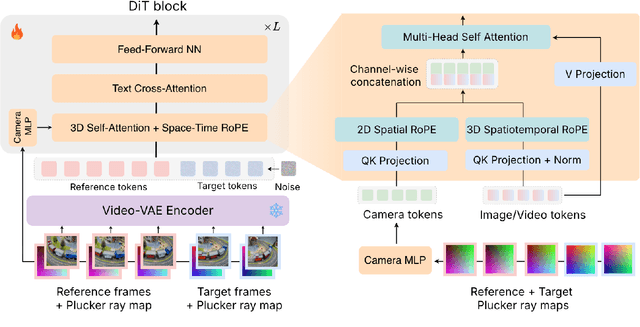
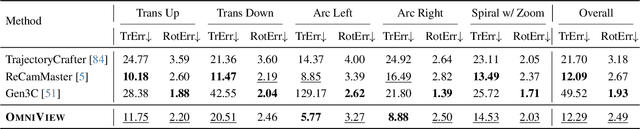

Abstract:Prior approaches injecting camera control into diffusion models have focused on specific subsets of 4D consistency tasks: novel view synthesis, text-to-video with camera control, image-to-video, amongst others. Therefore, these fragmented approaches are trained on disjoint slices of available 3D/4D data. We introduce OmniView, a unified framework that generalizes across a wide range of 4D consistency tasks. Our method separately represents space, time, and view conditions, enabling flexible combinations of these inputs. For example, OmniView can synthesize novel views from static, dynamic, and multiview inputs, extrapolate trajectories forward and backward in time, and create videos from text or image prompts with full camera control. OmniView is competitive with task-specific models across diverse benchmarks and metrics, improving image quality scores among camera-conditioned diffusion models by up to 33\% in multiview NVS LLFF dataset, 60\% in dynamic NVS Neural 3D Video benchmark, 20\% in static camera control on RE-10K, and reducing camera trajectory errors by 4x in text-conditioned video generation. With strong generalizability in one model, OmniView demonstrates the feasibility of a generalist 4D video model. Project page is available at https://snap-research.github.io/OmniView/
OracleAgent: A Multimodal Reasoning Agent for Oracle Bone Script Research
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:As one of the earliest writing systems, Oracle Bone Script (OBS) preserves the cultural and intellectual heritage of ancient civilizations. However, current OBS research faces two major challenges: (1) the interpretation of OBS involves a complex workflow comprising multiple serial and parallel sub-tasks, and (2) the efficiency of OBS information organization and retrieval remains a critical bottleneck, as scholars often spend substantial effort searching for, compiling, and managing relevant resources. To address these challenges, we present OracleAgent, the first agent system designed for the structured management and retrieval of OBS-related information. OracleAgent seamlessly integrates multiple OBS analysis tools, empowered by large language models (LLMs), and can flexibly orchestrate these components. Additionally, we construct a comprehensive domain-specific multimodal knowledge base for OBS, which is built through a rigorous multi-year process of data collection, cleaning, and expert annotation. The knowledge base comprises over 1.4M single-character rubbing images and 80K interpretation texts. OracleAgent leverages this resource through its multimodal tools to assist experts in retrieval tasks of character, document, interpretation text, and rubbing image. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OracleAgent achieves superior performance across a range of multimodal reasoning and generation tasks, surpassing leading mainstream multimodal large language models (MLLMs) (e.g., GPT-4o). Furthermore, our case study illustrates that OracleAgent can effectively assist domain experts, significantly reducing the time cost of OBS research. These results highlight OracleAgent as a significant step toward the practical deployment of OBS-assisted research and automated interpretation systems.
Vision-EKIPL: External Knowledge-Infused Policy Learning for Visual Reasoning
Jun 07, 2025


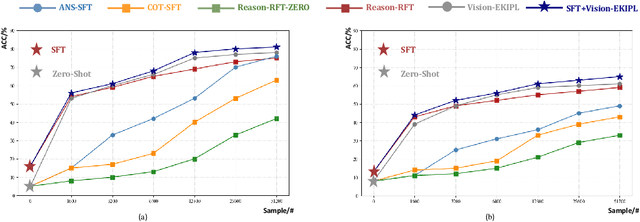
Abstract:Visual reasoning is crucial for understanding complex multimodal data and advancing Artificial General Intelligence. Existing methods enhance the reasoning capability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) through Reinforcement Learning (RL) fine-tuning (e.g., GRPO). However, current RL approaches sample action groups solely from the policy model itself, which limits the upper boundary of the model's reasoning capability and leads to inefficient training. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel RL framework called \textbf{Vision-EKIPL}. The core of this framework lies in introducing high-quality actions generated by external auxiliary models during the RL training process to guide the optimization of the policy model. The policy learning with knowledge infusion from external models significantly expands the model's exploration space, effectively improves the reasoning boundary, and substantially accelerates training convergence speed and efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed Vision-EKIPL achieved up to a 5\% performance improvement on the Reason-RFT-CoT Benchmark compared to the state-of-the-art (SOTA). It reveals that Vision-EKIPL can overcome the limitations of traditional RL methods, significantly enhance the visual reasoning performance of MLLMs, and provide a new effective paradigm for research in this field.
Grounding Chest X-Ray Visual Question Answering with Generated Radiology Reports
May 22, 2025Abstract:We present a novel approach to Chest X-ray (CXR) Visual Question Answering (VQA), addressing both single-image image-difference questions. Single-image questions focus on abnormalities within a specific CXR ("What abnormalities are seen in image X?"), while image-difference questions compare two longitudinal CXRs acquired at different time points ("What are the differences between image X and Y?"). We further explore how the integration of radiology reports can enhance the performance of VQA models. While previous approaches have demonstrated the utility of radiology reports during the pre-training phase, we extend this idea by showing that the reports can also be leveraged as additional input to improve the VQA model's predicted answers. First, we propose a unified method that handles both types of questions and auto-regressively generates the answers. For single-image questions, the model is provided with a single CXR. For image-difference questions, the model is provided with two CXRs from the same patient, captured at different time points, enabling the model to detect and describe temporal changes. Taking inspiration from 'Chain-of-Thought reasoning', we demonstrate that performance on the CXR VQA task can be improved by grounding the answer generator module with a radiology report predicted for the same CXR. In our approach, the VQA model is divided into two steps: i) Report Generation (RG) and ii) Answer Generation (AG). Our results demonstrate that incorporating predicted radiology reports as evidence to the AG model enhances performance on both single-image and image-difference questions, achieving state-of-the-art results on the Medical-Diff-VQA dataset.
Conditional Panoramic Image Generation via Masked Autoregressive Modeling
May 22, 2025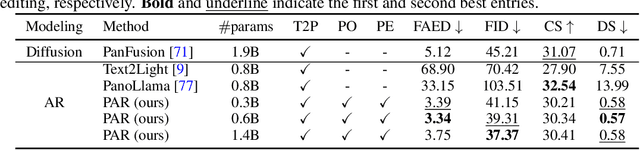
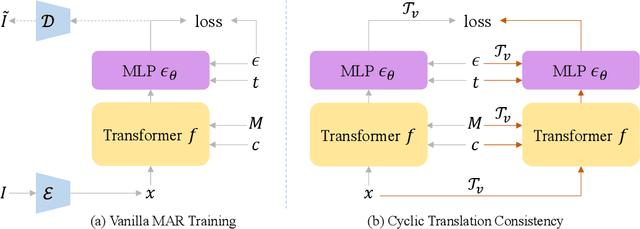
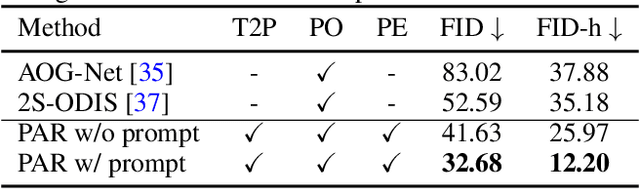

Abstract:Recent progress in panoramic image generation has underscored two critical limitations in existing approaches. First, most methods are built upon diffusion models, which are inherently ill-suited for equirectangular projection (ERP) panoramas due to the violation of the identically and independently distributed (i.i.d.) Gaussian noise assumption caused by their spherical mapping. Second, these methods often treat text-conditioned generation (text-to-panorama) and image-conditioned generation (panorama outpainting) as separate tasks, relying on distinct architectures and task-specific data. In this work, we propose a unified framework, Panoramic AutoRegressive model (PAR), which leverages masked autoregressive modeling to address these challenges. PAR avoids the i.i.d. assumption constraint and integrates text and image conditioning into a cohesive architecture, enabling seamless generation across tasks. To address the inherent discontinuity in existing generative models, we introduce circular padding to enhance spatial coherence and propose a consistency alignment strategy to improve generation quality. Extensive experiments demonstrate competitive performance in text-to-image generation and panorama outpainting tasks while showcasing promising scalability and generalization capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge