Bradley A. Malin
Risk-Equalized Differentially Private Synthetic Data: Protecting Outliers by Controlling Record-Level Influence
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:When synthetic data is released, some individuals are harder to protect than others. A patient with a rare disease combination or a transaction with unusual characteristics stands out from the crowd. Differential privacy provides worst-case guarantees, but empirical attacks -- particularly membership inference -- succeed far more often against such outliers, especially under moderate privacy budgets and with auxiliary information. This paper introduces risk-equalized DP synthesis, a framework that prioritizes protection for high-risk records by reducing their influence on the learned generator. The mechanism operates in two stages: first, a small privacy budget estimates each record's "outlierness"; second, a DP learning procedure weights each record inversely to its risk score. Under Gaussian mechanisms, a record's privacy loss is proportional to its influence on the output -- so deliberately shrinking outliers' contributions yields tighter per-instance privacy bounds for precisely those records that need them most. We prove end-to-end DP guarantees via composition and derive closed-form per-record bounds for the synthesis stage (the scoring stage adds a uniform per-record term). Experiments on simulated data with controlled outlier injection show that risk-weighting substantially reduces membership inference success against high-outlierness records; ablations confirm that targeting -- not random downweighting -- drives the improvement. On real-world benchmarks (Breast Cancer, Adult, German Credit), gains are dataset-dependent, highlighting the interplay between scorer quality and synthesis pipeline.
PRISM: Differentially Private Synthetic Data with Structure-Aware Budget Allocation for Prediction
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Differential privacy (DP) provides a mathematical guarantee limiting what an adversary can learn about any individual from released data. However, achieving this protection typically requires adding noise, and noise can accumulate when many statistics are measured. Existing DP synthetic data methods treat all features symmetrically, spreading noise uniformly even when the data will serve a specific prediction task. We develop a prediction-centric approach operating in three regimes depending on available structural knowledge. In the causal regime, when the causal parents of $Y$ are known and distribution shift is expected, we target the parents for robustness. In the graphical regime, when a Bayesian network structure is available and the distribution is stable, the Markov blanket of $Y$ provides a sufficient feature set for optimal prediction. In the predictive regime, when no structural knowledge exists, we select features via differentially private methods without claiming to recover causal or graphical structure. We formalize this as PRISM, a mechanism that (i) identifies a predictive feature subset according to the appropriate regime, (ii) constructs targeted summary statistics, (iii) allocates budget to minimize an upper bound on prediction error, and (iv) synthesizes data via graphical-model inference. We prove end-to-end privacy guarantees and risk bounds. Empirically, task-aware allocation improves prediction accuracy compared to generic synthesizers. Under distribution shift, targeting causal parents achieves AUC $\approx 0.73$ while correlation-based selection collapses to chance ($\approx 0.49$).
What Really is a Member? Discrediting Membership Inference via Poisoning
Jun 06, 2025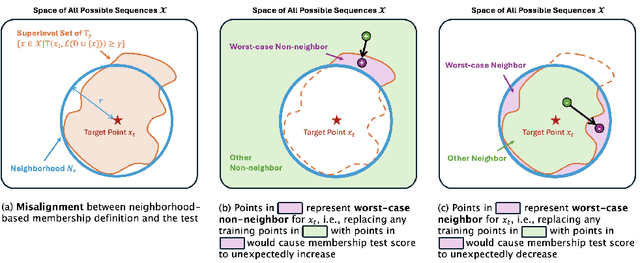
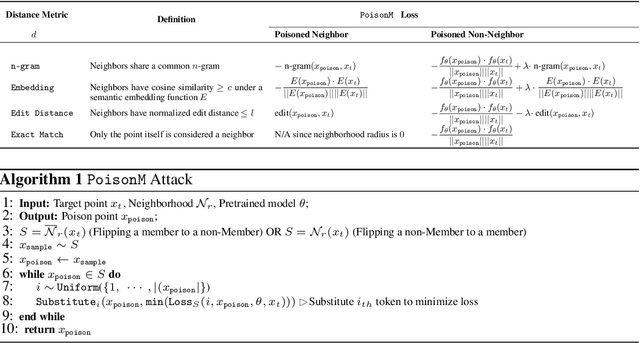
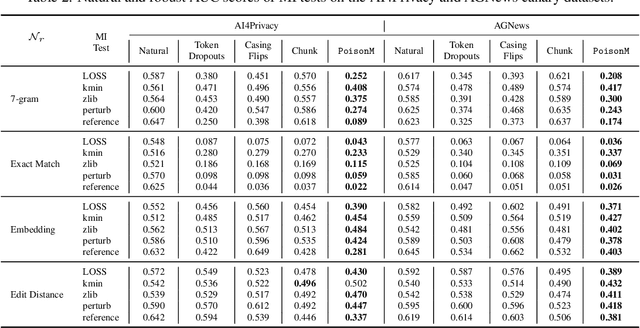
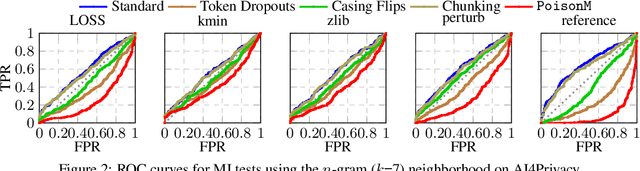
Abstract:Membership inference tests aim to determine whether a particular data point was included in a language model's training set. However, recent works have shown that such tests often fail under the strict definition of membership based on exact matching, and have suggested relaxing this definition to include semantic neighbors as members as well. In this work, we show that membership inference tests are still unreliable under this relaxation - it is possible to poison the training dataset in a way that causes the test to produce incorrect predictions for a target point. We theoretically reveal a trade-off between a test's accuracy and its robustness to poisoning. We also present a concrete instantiation of this poisoning attack and empirically validate its effectiveness. Our results show that it can degrade the performance of existing tests to well below random.
Role and Use of Race in AI/ML Models Related to Health
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:The role and use of race within health-related artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) models has sparked increasing attention and controversy. Despite the complexity and breadth of related issues, a robust and holistic framework to guide stakeholders in their examination and resolution remains lacking. This perspective provides a broad-based, systematic, and cross-cutting landscape analysis of race-related challenges, structured around the AI/ML lifecycle and framed through "points to consider" to support inquiry and decision-making.
Towards Statistical Factuality Guarantee for Large Vision-Language Models
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Advancements in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated promising performance in a variety of vision-language tasks involving image-conditioned free-form text generation. However, growing concerns about hallucinations in LVLMs, where the generated text is inconsistent with the visual context, are becoming a major impediment to deploying these models in applications that demand guaranteed reliability. In this paper, we introduce a framework to address this challenge, ConfLVLM, which is grounded on conformal prediction to achieve finite-sample distribution-free statistical guarantees on the factuality of LVLM output. This framework treats an LVLM as a hypothesis generator, where each generated text detail (or claim) is considered an individual hypothesis. It then applies a statistical hypothesis testing procedure to verify each claim using efficient heuristic uncertainty measures to filter out unreliable claims before returning any responses to users. We conduct extensive experiments covering three representative application domains, including general scene understanding, medical radiology report generation, and document understanding. Remarkably, ConfLVLM reduces the error rate of claims generated by LLaVa-1.5 for scene descriptions from 87.8\% to 10.0\% by filtering out erroneous claims with a 95.3\% true positive rate. Our results further demonstrate that ConfLVLM is highly flexible, and can be applied to any black-box LVLMs paired with any uncertainty measure for any image-conditioned free-form text generation task while providing a rigorous guarantee on controlling the risk of hallucination.
Automatic Prompt Optimization via Heuristic Search: A Survey
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models have led to remarkable achievements across a variety of Natural Language Processing tasks, making prompt engineering increasingly central to guiding model outputs. While manual methods can be effective, they typically rely on intuition and do not automatically refine prompts over time. In contrast, automatic prompt optimization employing heuristic-based search algorithms can systematically explore and improve prompts with minimal human oversight. This survey proposes a comprehensive taxonomy of these methods, categorizing them by where optimization occurs, what is optimized, what criteria drive the optimization, which operators generate new prompts, and which iterative search algorithms are applied. We further highlight specialized datasets and tools that support and accelerate automated prompt refinement. We conclude by discussing key open challenges pointing toward future opportunities for more robust and versatile LLM applications.
Implementing Trust in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis with a Conformalized Uncertainty-Aware AI Framework in Whole-Slide Images
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:Ensuring trustworthiness is fundamental to the development of artificial intelligence (AI) that is considered societally responsible, particularly in cancer diagnostics, where a misdiagnosis can have dire consequences. Current digital pathology AI models lack systematic solutions to address trustworthiness concerns arising from model limitations and data discrepancies between model deployment and development environments. To address this issue, we developed TRUECAM, a framework designed to ensure both data and model trustworthiness in non-small cell lung cancer subtyping with whole-slide images. TRUECAM integrates 1) a spectral-normalized neural Gaussian process for identifying out-of-scope inputs and 2) an ambiguity-guided elimination of tiles to filter out highly ambiguous regions, addressing data trustworthiness, as well as 3) conformal prediction to ensure controlled error rates. We systematically evaluated the framework across multiple large-scale cancer datasets, leveraging both task-specific and foundation models, illustrate that an AI model wrapped with TRUECAM significantly outperforms models that lack such guidance, in terms of classification accuracy, robustness, interpretability, and data efficiency, while also achieving improvements in fairness. These findings highlight TRUECAM as a versatile wrapper framework for digital pathology AI models with diverse architectural designs, promoting their responsible and effective applications in real-world settings.
Catalysts of Conversation: Examining Interaction Dynamics Between Topic Initiators and Commentors in Alzheimer's Disease Online Communities
Dec 18, 2024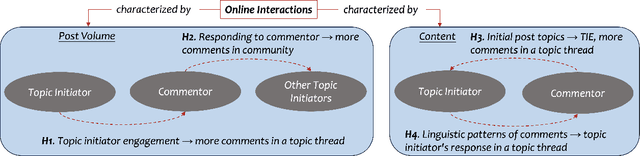
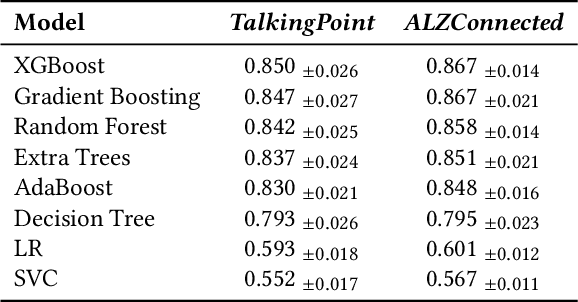
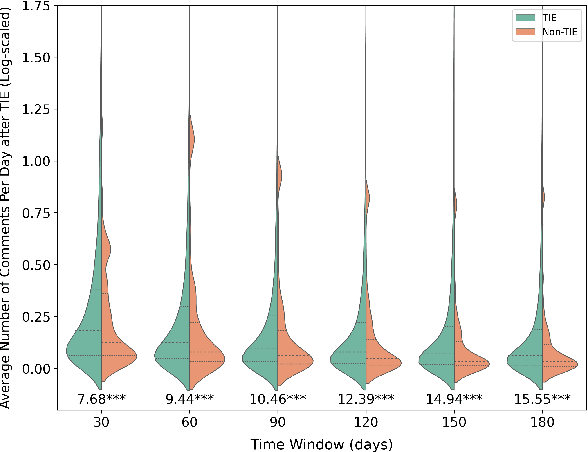
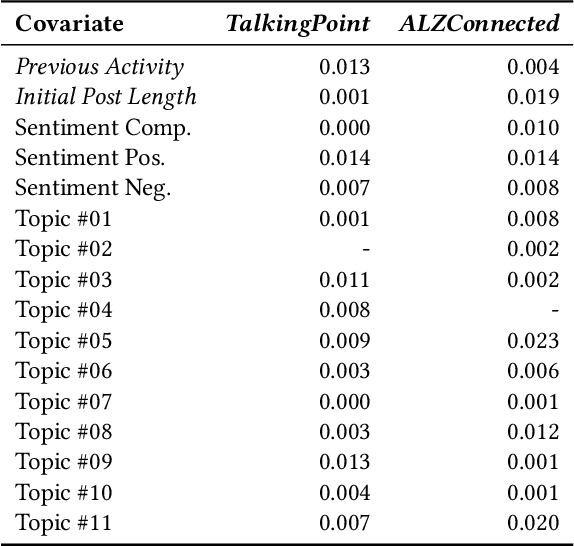
Abstract:Informal caregivers (e.g.,family members or friends) of people living with Alzheimers Disease and Related Dementias (ADRD) face substantial challenges and often seek informational or emotional support through online communities. Understanding the factors that drive engagement within these platforms is crucial, as it can enhance their long-term value for caregivers by ensuring that these communities effectively meet their needs. This study investigated the user interaction dynamics within two large, popular ADRD communities, TalkingPoint and ALZConnected, focusing on topic initiator engagement, initial post content, and the linguistic patterns of comments at the thread level. Using analytical methods such as propensity score matching, topic modeling, and predictive modeling, we found that active topic initiator engagement drives higher comment volumes, and reciprocal replies from topic initiators encourage further commentor engagement at the community level. Practical caregiving topics prompt more re-engagement of topic initiators, while emotional support topics attract more comments from other commentors. Additionally, the linguistic complexity and emotional tone of a comment influence its likelihood of receiving replies from topic initiators. These findings highlight the importance of fostering active and reciprocal engagement and providing effective strategies to enhance sustainability in ADRD caregiving and broader health-related online communities.
Do You Know What You Are Talking About? Characterizing Query-Knowledge Relevance For Reliable Retrieval Augmented Generation
Oct 10, 2024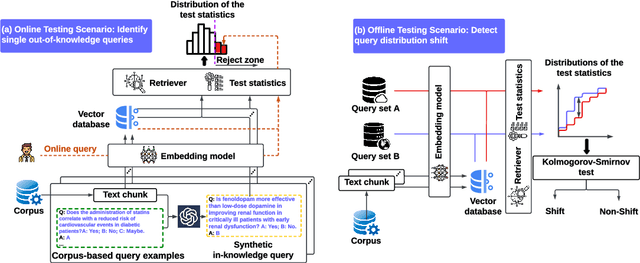
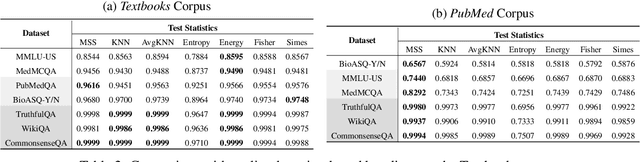
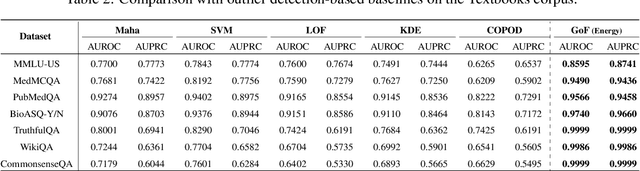
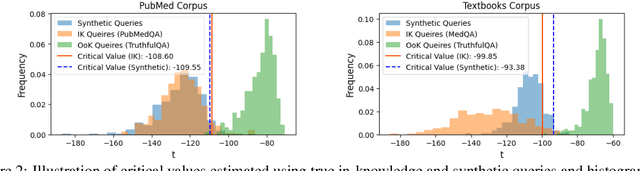
Abstract:Language models (LMs) are known to suffer from hallucinations and misinformation. Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) that retrieves verifiable information from an external knowledge corpus to complement the parametric knowledge in LMs provides a tangible solution to these problems. However, the generation quality of RAG is highly dependent on the relevance between a user's query and the retrieved documents. Inaccurate responses may be generated when the query is outside of the scope of knowledge represented in the external knowledge corpus or if the information in the corpus is out-of-date. In this work, we establish a statistical framework that assesses how well a query can be answered by an RAG system by capturing the relevance of knowledge. We introduce an online testing procedure that employs goodness-of-fit (GoF) tests to inspect the relevance of each user query to detect out-of-knowledge queries with low knowledge relevance. Additionally, we develop an offline testing framework that examines a collection of user queries, aiming to detect significant shifts in the query distribution which indicates the knowledge corpus is no longer sufficiently capable of supporting the interests of the users. We demonstrate the capabilities of these strategies through a systematic evaluation on eight question-answering (QA) datasets, the results of which indicate that the new testing framework is an efficient solution to enhance the reliability of existing RAG systems.
Leveraging Generative AI for Clinical Evidence Summarization Needs to Achieve Trustworthiness
Nov 19, 2023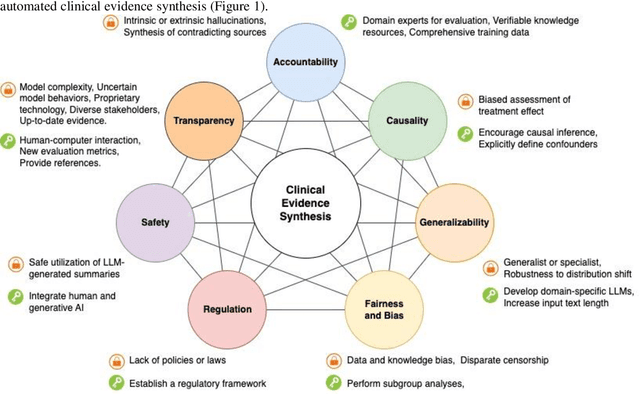
Abstract:Evidence-based medicine aims to improve the quality of healthcare by empowering medical decisions and practices with the best available evidence. The rapid growth of medical evidence, which can be obtained from various sources, poses a challenge in collecting, appraising, and synthesizing the evidential information. Recent advancements in generative AI, exemplified by large language models, hold promise in facilitating the arduous task. However, developing accountable, fair, and inclusive models remains a complicated undertaking. In this perspective, we discuss the trustworthiness of generative AI in the context of automated summarization of medical evidence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge