Qingxia Chen
Catalysts of Conversation: Examining Interaction Dynamics Between Topic Initiators and Commentors in Alzheimer's Disease Online Communities
Dec 18, 2024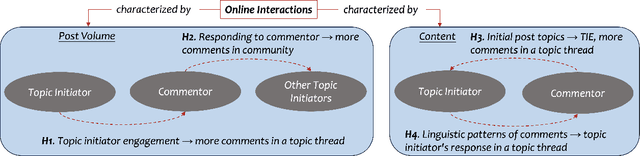
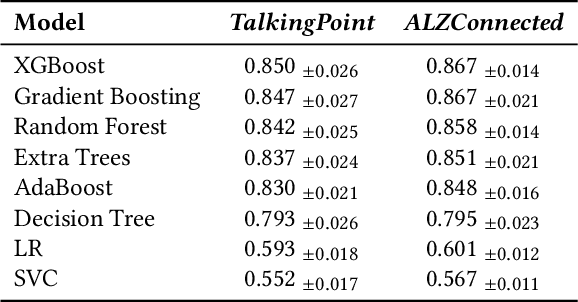
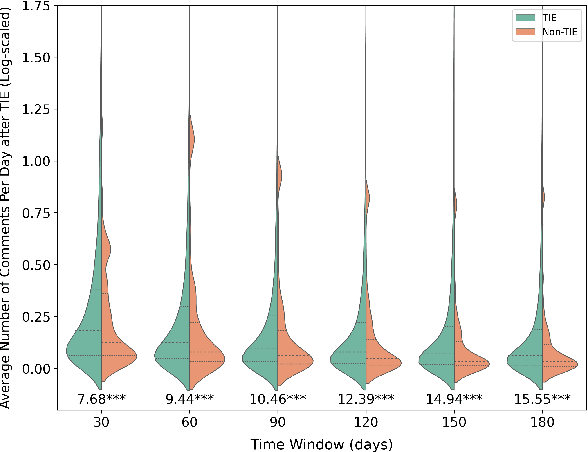
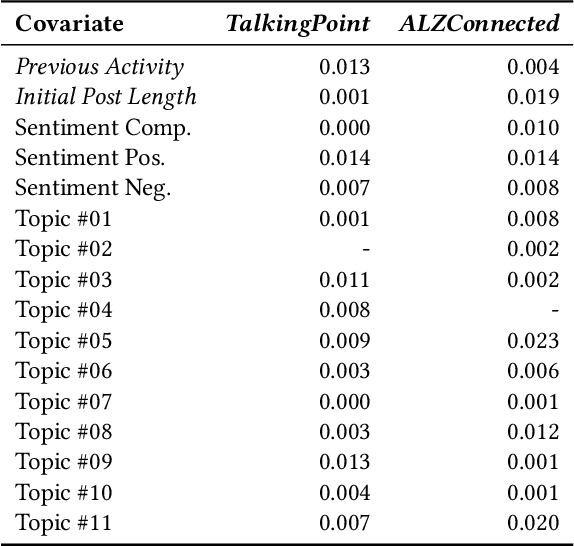
Abstract:Informal caregivers (e.g.,family members or friends) of people living with Alzheimers Disease and Related Dementias (ADRD) face substantial challenges and often seek informational or emotional support through online communities. Understanding the factors that drive engagement within these platforms is crucial, as it can enhance their long-term value for caregivers by ensuring that these communities effectively meet their needs. This study investigated the user interaction dynamics within two large, popular ADRD communities, TalkingPoint and ALZConnected, focusing on topic initiator engagement, initial post content, and the linguistic patterns of comments at the thread level. Using analytical methods such as propensity score matching, topic modeling, and predictive modeling, we found that active topic initiator engagement drives higher comment volumes, and reciprocal replies from topic initiators encourage further commentor engagement at the community level. Practical caregiving topics prompt more re-engagement of topic initiators, while emotional support topics attract more comments from other commentors. Additionally, the linguistic complexity and emotional tone of a comment influence its likelihood of receiving replies from topic initiators. These findings highlight the importance of fostering active and reciprocal engagement and providing effective strategies to enhance sustainability in ADRD caregiving and broader health-related online communities.
Adaptive Task Offloading for Space Missions: A State-Graph-Based Approach
Nov 16, 2022Abstract:Advances in space exploration have led to an explosion of tasks. Conventionally, these tasks are offloaded to ground servers for enhanced computing capability, or to adjacent low-earth-orbit satellites for reduced transmission delay. However, the overall delay is determined by both computation and transmission costs. The existing offloading schemes, while being highly-optimized for either costs, can be abysmal for the overall performance. The computation-transmission cost dilemma is yet to be solved. In this paper, we propose an adaptive offloading scheme to reduce the overall delay. The core idea is to jointly model and optimize the transmission-computation process over the entire network. Specifically, to represent the computation state migrations, we generalize graph nodes with multiple states. In this way, the joint optimization problem is transformed into a shortest path problem over the state graph. We further provide an extended Dijkstra's algorithm for efficient path finding. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme outperforms the ground and one-hop offloading schemes by up to 37.56% and 39.35% respectively on SpaceCube v2.0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge