Gharib Gharibi
Split Learning for Distributed Collaborative Training of Deep Learning Models in Health Informatics
Aug 21, 2023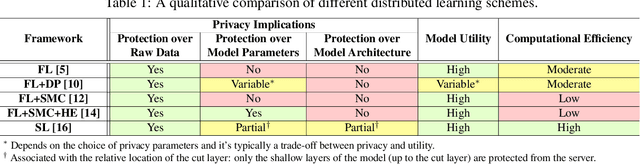
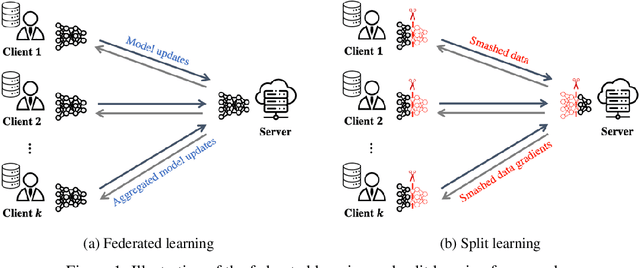
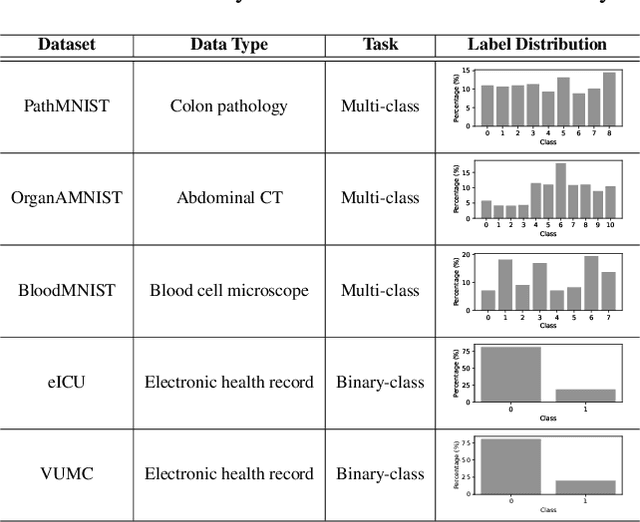
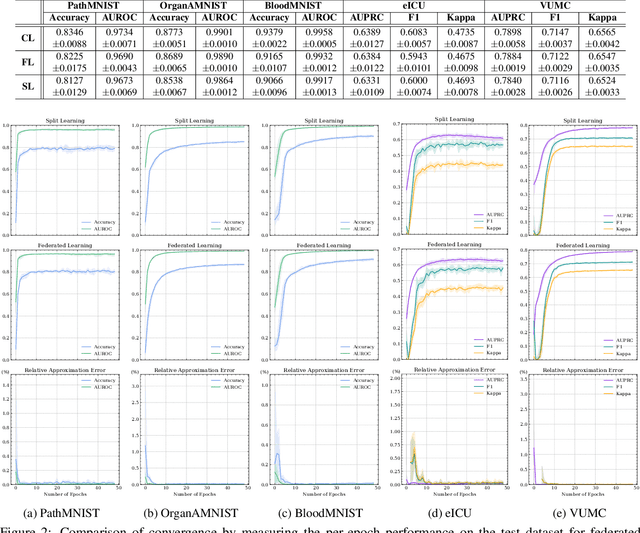
Abstract:Deep learning continues to rapidly evolve and is now demonstrating remarkable potential for numerous medical prediction tasks. However, realizing deep learning models that generalize across healthcare organizations is challenging. This is due, in part, to the inherent siloed nature of these organizations and patient privacy requirements. To address this problem, we illustrate how split learning can enable collaborative training of deep learning models across disparate and privately maintained health datasets, while keeping the original records and model parameters private. We introduce a new privacy-preserving distributed learning framework that offers a higher level of privacy compared to conventional federated learning. We use several biomedical imaging and electronic health record (EHR) datasets to show that deep learning models trained via split learning can achieve highly similar performance to their centralized and federated counterparts while greatly improving computational efficiency and reducing privacy risks.
SCAT: Second Chance Autoencoder for Textual Data
May 11, 2020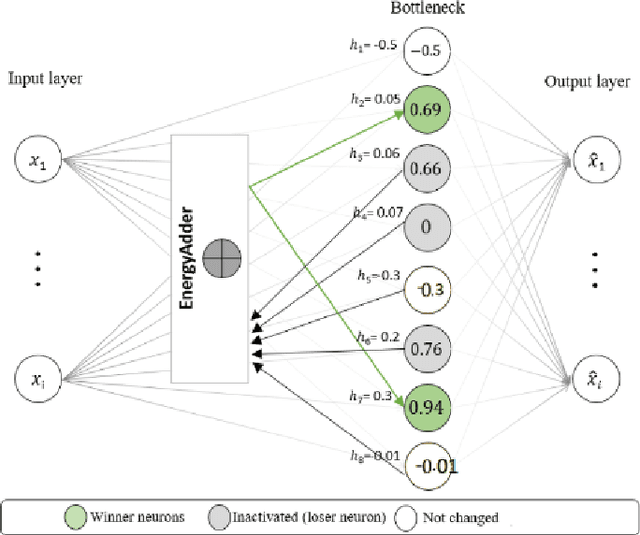
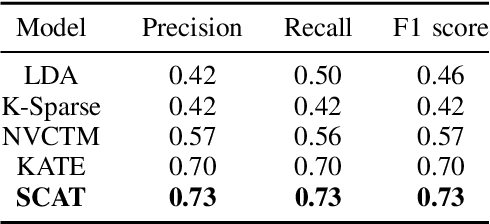
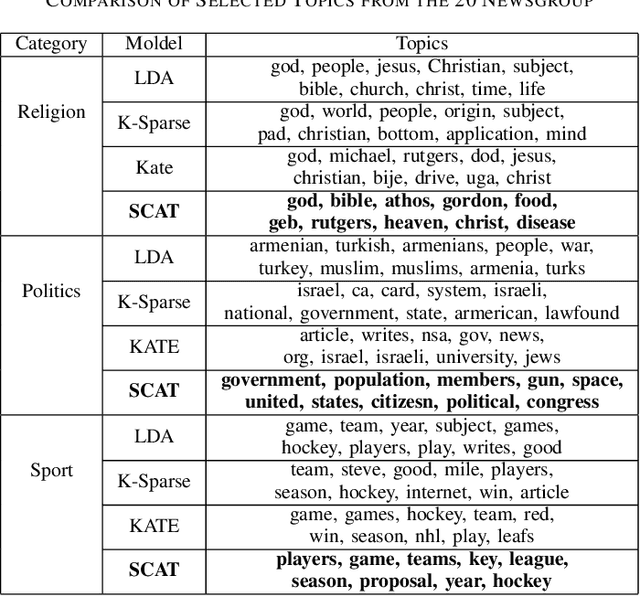
Abstract:We present a k-competitive learning approach for textual autoencoders named Second Chance Autoencoder (SCAT). SCAT selects the $k$ largest and smallest positive activations as the winner neurons, which gain the activation values of the loser neurons during the learning process, and thus focus on retrieving well-representative features for topics. Our experiments show that SCAT achieves outstanding performance in classification, topic modeling, and document visualization compared to LDA, K-Sparse, NVCTM, and KATE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge