Bo Lu
Deep-Learning-Based Control of a Decoupled Two-Segment Continuum Robot for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Manual endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is technically demanding, and existing single-segment robotic tools offer limited dexterity. These limitations motivate the development of more advanced solutions. To address this, DESectBot, a novel dual segment continuum robot with a decoupled structure and integrated surgical forceps, enabling 6 degrees of freedom (DoFs) tip dexterity for improved lesion targeting in ESD, was developed in this work. Deep learning controllers based on gated recurrent units (GRUs) for simultaneous tip position and orientation control, effectively handling the nonlinear coupling between continuum segments, were proposed. The GRU controller was benchmarked against Jacobian based inverse kinematics, model predictive control (MPC), a feedforward neural network (FNN), and a long short-term memory (LSTM) network. In nested-rectangle and Lissajous trajectory tracking tasks, the GRU achieved the lowest position/orientation RMSEs: 1.11 mm/ 4.62° and 0.81 mm/ 2.59°, respectively. For orientation control at a fixed position (four target poses), the GRU attained a mean RMSE of 0.14 mm and 0.72°, outperforming all alternatives. In a peg transfer task, the GRU achieved a 100% success rate (120 success/120 attempts) with an average transfer time of 11.8s, the STD significantly outperforms novice-controlled systems. Additionally, an ex vivo ESD demonstration grasping, elevating, and resecting tissue as the scalpel completed the cut confirmed that DESectBot provides sufficient stiffness to divide thick gastric mucosa and an operative workspace adequate for large lesions.These results confirm that GRU-based control significantly enhances precision, reliability, and usability in ESD surgical training scenarios.
A machine learning model for skillful climate system prediction
May 06, 2025Abstract:Climate system models (CSMs), through integrating cross-sphere interactions among the atmosphere, ocean, land, and cryosphere, have emerged as pivotal tools for deciphering climate dynamics and improving forecasting capabilities. Recent breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI)-driven meteorological modeling have demonstrated remarkable success in single-sphere systems and partially spheres coupled systems. However, the development of a fully coupled AI-based climate system model encompassing atmosphere-ocean-land-sea ice interactions has remained an unresolved challenge. This paper introduces FengShun-CSM, an AI-based CSM model that provides 60-day global daily forecasts for 29 critical variables across atmospheric, oceanic, terrestrial, and cryospheric domains. The model significantly outperforms the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) subseasonal-to-seasonal (S2S) model in predicting most variables, particularly precipitation, land surface, and oceanic components. This enhanced capability is primarily attributed to its improved representation of intra-seasonal variability modes, most notably the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO). Remarkably, FengShun-CSM exhibits substantial potential in predicting subseasonal extreme events. Such breakthroughs will advance its applications in meteorological disaster mitigation, marine ecosystem conservation, and agricultural productivity enhancement. Furthermore, it validates the feasibility of developing AI-powered CSMs through machine learning technologies, establishing a transformative paradigm for next-generation Earth system modeling.
Advancing Embodied Intelligence in Robotic-Assisted Endovascular Procedures: A Systematic Review of AI Solutions
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Endovascular procedures have revolutionized the treatment of vascular diseases thanks to minimally invasive solutions that significantly reduce patient recovery time and enhance clinical outcomes. However, the precision and dexterity required during these procedures poses considerable challenges for interventionists. Robotic systems have emerged offering transformative solutions, addressing issues such as operator fatigue, radiation exposure, and the inherent limitations of human precision. The integration of Embodied Intelligence (EI) into these systems signifies a paradigm shift, enabling robots to navigate complex vascular networks and adapt to dynamic physiological conditions. Data-driven approaches, advanced computer vision, medical image analysis, and machine learning techniques, are at the forefront of this evolution. These methods augment procedural intelligence by facilitating real-time vessel segmentation, device tracking, and anatomical landmark detection. Reinforcement learning and imitation learning further refine navigation strategies and replicate experts' techniques. This review systematically examines the integration of EI principles into robotic technologies, in relation to endovascular procedures. We discuss recent advancements in intelligent perception and data-driven control, and their practical applications in robot-assisted endovascular procedures. By critically evaluating current limitations and emerging opportunities, this review establishes a framework for future developments, emphasizing the potential for greater autonomy and improved clinical outcomes. Emerging trends and specific areas of research, such as federated learning for medical data sharing, explainable AI for clinical decision support, and advanced human-robot collaboration paradigms, are also explored, offering insights into the future direction of this rapidly evolving field.
Sim4EndoR: A Reinforcement Learning Centered Simulation Platform for Task Automation of Endovascular Robotics
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Robotic-assisted percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) holds considerable promise for elevating precision and safety in cardiovascular procedures. Nevertheless, current systems heavily depend on human operators, resulting in variability and the potential for human error. To tackle these challenges, Sim4EndoR, an innovative reinforcement learning (RL) based simulation environment, is first introduced to bolster task-level autonomy in PCI. This platform offers a comprehensive and risk-free environment for the development, evaluation, and refinement of potential autonomous systems, enhancing data collection efficiency and minimizing the need for costly hardware trials. A notable aspect of the groundbreaking Sim4EndoR is its reward function, which takes into account the anatomical constraints of the vascular environment, utilizing the geometric characteristics of vessels to steer the learning process. By seamlessly integrating advanced physical simulations with neural network-driven policy learning, Sim4EndoR fosters efficient sim-to-real translation, paving the way for safer, more consistent robotic interventions in clinical practice, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Generative assimilation and prediction for weather and climate
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Machine learning models have shown great success in predicting weather up to two weeks ahead, outperforming process-based benchmarks. However, existing approaches mostly focus on the prediction task, and do not incorporate the necessary data assimilation. Moreover, these models suffer from error accumulation in long roll-outs, limiting their applicability to seasonal predictions or climate projections. Here, we introduce Generative Assimilation and Prediction (GAP), a unified deep generative framework for assimilation and prediction of both weather and climate. By learning to quantify the probabilistic distribution of atmospheric states under observational, predictive, and external forcing constraints, GAP excels in a broad range of weather-climate related tasks, including data assimilation, seamless prediction, and climate simulation. In particular, GAP is competitive with state-of-the-art ensemble assimilation, probabilistic weather forecast and seasonal prediction, yields stable millennial simulations, and reproduces climate variability from daily to decadal time scales.
FuXi-ENS: A machine learning model for medium-range ensemble weather forecasting
May 09, 2024



Abstract:Ensemble weather forecasting is essential for weather predictions and mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events. Constructing an ensemble prediction system (EPS) based on conventional numerical weather prediction (NWP) models is highly computationally expensive. Machine learning (ML) models have emerged as valuable tools for deterministic weather forecasts, providing forecasts with significantly reduced computational requirements and even surpassing the forecast performance of traditional NWP models. However, challenges arise when applying ML models to ensemble forecasting. Recent ML models, such as GenCast and SEEDS model, rely on the ERA5 Ensemble of Data Assimilations (EDA) or two operational NWP ensemble members for forecast generation. The spatial resolution of 1{\deg} or 2{\deg} in these models is often considered too coarse for many applications. To overcome these limitations, we introduce FuXi-ENS, an advanced ML model designed to deliver 6-hourly global ensemble weather forecasts up to 15 days. This model runs at a significantly improved spatial resolution of 0.25{\deg}, incorporating 5 upper-air atmospheric variables at 13 pressure levels, along with 13 surface variables. By leveraging the inherent probabilistic nature of Variational AutoEncoder (VAE), FuXi-ENS optimizes a loss function that combines the continuous ranked probability score (CRPS) and the KL divergence between the predicted and target distribution. This innovative approach represents an advancement over the traditional use of L1 loss combined with the KL loss in standard VAE models when VAE for ensemble weather forecasts. Evaluation results demonstrate that FuXi-ENS outperforms ensemble forecasts from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), a world leading NWP model, on 98.1% of 360 variable and forecast lead time combinations on CRPS.
FuXi-S2S: An accurate machine learning model for global subseasonal forecasts
Dec 15, 2023
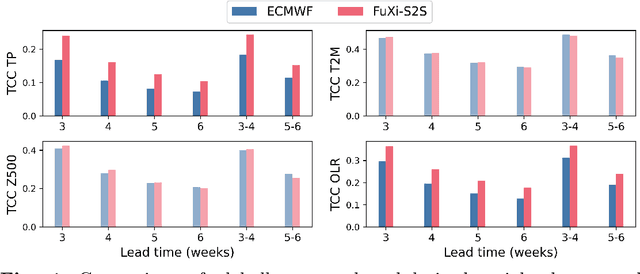
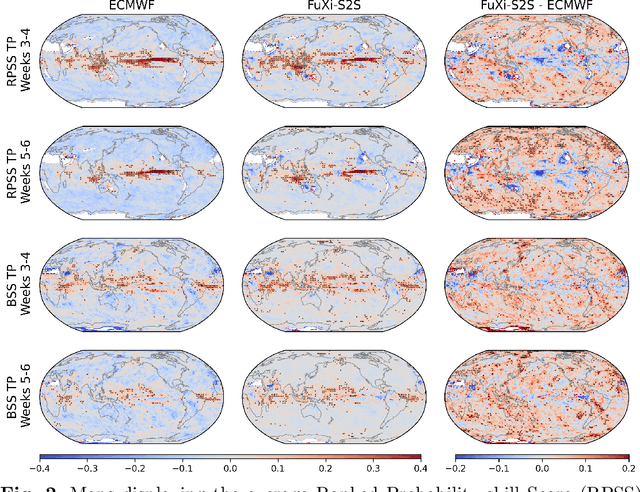
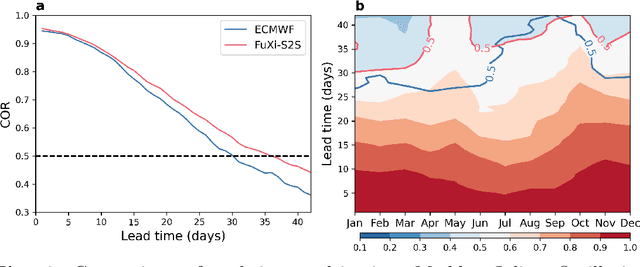
Abstract:Skillful subseasonal forecasts beyond 2 weeks are crucial for a wide range of applications across various sectors of society. Recently, state-of-the-art machine learning based weather forecasting models have made significant advancements, outperforming the high-resolution forecast (HRES) from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). However, the full potential of machine learning models in subseasonal forecasts has yet to be fully explored. In this study, we introduce FuXi Subseasonal-to-Seasonal (FuXi-S2S), a machine learning based subseasonal forecasting model that provides global daily mean forecasts up to 42 days, covering 5 upper-air atmospheric variables at 13 pressure levels and 11 surface variables. FuXi-S2S integrates an enhanced FuXi base model with a perturbation module for flow-dependent perturbations in hidden features, and incorporates Perlin noise to perturb initial conditions. The model is developed using 72 years of daily statistics from ECMWF ERA5 reanalysis data. When compared to the ECMWF Subseasonal-to-Seasonal (S2S) reforecasts, the FuXi-S2S forecasts demonstrate superior deterministic and ensemble forecasts for total precipitation (TP), outgoing longwave radiation (OLR), and geopotential at 500 hPa (Z500). Although it shows slightly inferior performance in predicting 2-meter temperature (T2M), it has clear advantages over land area. Regarding the extreme forecasts, FuXi-S2S outperforms ECMWF S2S globally for TP. Furthermore, FuXi-S2S forecasts surpass the ECMWF S2S reforecasts in predicting the Madden Julian Oscillation (MJO), a key source of subseasonal predictability. They extend the skillful prediction of MJO from 30 days to 36 days.
Robust Data-Driven 3-D Shape Servoing of Unmodeled Continuum Robots Using FBG Sensors in Unstructured Environments
Sep 12, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel and generic data-driven method to servo-control the 3-D shape of continuum robots embedded with fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors. Developments of 3-D shape perception and control technologies are crucial for continuum robots to perform the tasks autonomously in surgical interventions. However, owing to the nonlinear properties of continuum robots, one main difficulty lies in the modeling of them, especially for soft robots with variable stiffness. To address this problem, we propose a new robust adaptive controller by leveraging FBG shape feedback and neural networks (NNs) that can online estimate the unknown model of continuum robot and accounts for unexpected disturbances together with NN approximation errors, which exhibits an adaptive behavior to the unmodeled system without priori data exploration. Based on a new composite adaptation algorithm, the asymptotic convergences of the closed-loop system with NNs learning parameters have been proven by Lyapunov theory. To validate the proposed method, we present a comprehensive experimental study by using two continuum robots both integrated with multi-core FBGs, including a robotic-assisted colonoscope and multi-section extensible soft manipulators. The results demonstrate the feasibility, adaptability, and superiority of our controller in various unstructured environments as well as phantom experiments.
Combinatorial optimization solving by coherent Ising machines based on spiking neural networks
Aug 16, 2022



Abstract:Spiking neural network is a kind of neuromorphic computing which is believed to improve on the level of intelligence and provide advabtages for quantum computing. In this work, we address this issue by designing an optical spiking neural network and prove that it can be used to accelerate the speed of computation, especially on the combinatorial optimization problems. Here the spiking neural network is constructed by the antisymmetrically coupled degenerate optical parametric oscillator pulses and dissipative pulses. A nonlinear transfer function is chosen to mitigate amplitude inhomogeneities and destabilize the resulting local minima according to the dynamical behavior of spiking neurons. It is numerically proved that the spiking neural network-coherent Ising machines has excellent performance on combinatorial optimization problems, for which is expected to offer a new applications for neural computing and optical computing.
AutoLaparo: A New Dataset of Integrated Multi-tasks for Image-guided Surgical Automation in Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Aug 03, 2022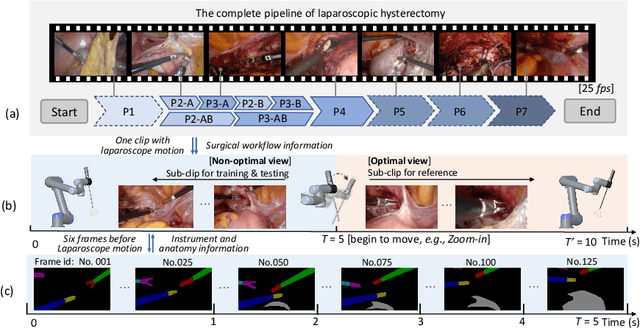
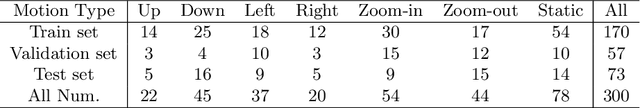
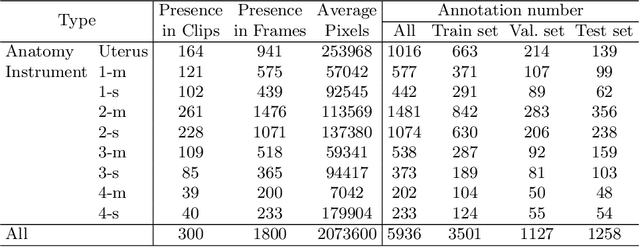
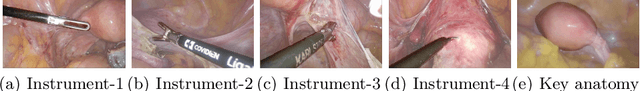
Abstract:Computer-assisted minimally invasive surgery has great potential in benefiting modern operating theatres. The video data streamed from the endoscope provides rich information to support context-awareness for next-generation intelligent surgical systems. To achieve accurate perception and automatic manipulation during the procedure, learning based technique is a promising way, which enables advanced image analysis and scene understanding in recent years. However, learning such models highly relies on large-scale, high-quality, and multi-task labelled data. This is currently a bottleneck for the topic, as available public dataset is still extremely limited in the field of CAI. In this paper, we present and release the first integrated dataset (named AutoLaparo) with multiple image-based perception tasks to facilitate learning-based automation in hysterectomy surgery. Our AutoLaparo dataset is developed based on full-length videos of entire hysterectomy procedures. Specifically, three different yet highly correlated tasks are formulated in the dataset, including surgical workflow recognition, laparoscope motion prediction, and instrument and key anatomy segmentation. In addition, we provide experimental results with state-of-the-art models as reference benchmarks for further model developments and evaluations on this dataset. The dataset is available at https://autolaparo.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge