Amit Sheth
A Comprehensive Dataset for Human vs. AI Generated Text Detection
Oct 26, 2025
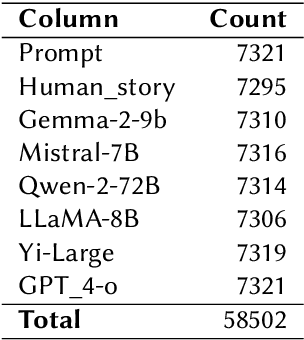
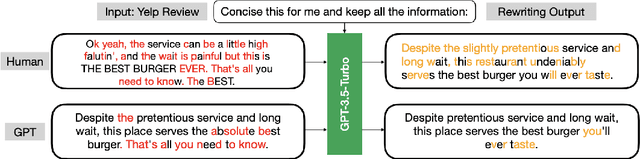
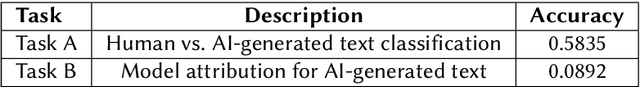
Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has led to increasingly human-like AI-generated text, raising concerns about content authenticity, misinformation, and trustworthiness. Addressing the challenge of reliably detecting AI-generated text and attributing it to specific models requires large-scale, diverse, and well-annotated datasets. In this work, we present a comprehensive dataset comprising over 58,000 text samples that combine authentic New York Times articles with synthetic versions generated by multiple state-of-the-art LLMs including Gemma-2-9b, Mistral-7B, Qwen-2-72B, LLaMA-8B, Yi-Large, and GPT-4-o. The dataset provides original article abstracts as prompts, full human-authored narratives. We establish baseline results for two key tasks: distinguishing human-written from AI-generated text, achieving an accuracy of 58.35\%, and attributing AI texts to their generating models with an accuracy of 8.92\%. By bridging real-world journalistic content with modern generative models, the dataset aims to catalyze the development of robust detection and attribution methods, fostering trust and transparency in the era of generative AI. Our dataset is available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/gsingh1-py/train.
Ask Me Again Differently: GRAS for Measuring Bias in Vision Language Models on Gender, Race, Age, and Skin Tone
Aug 26, 2025
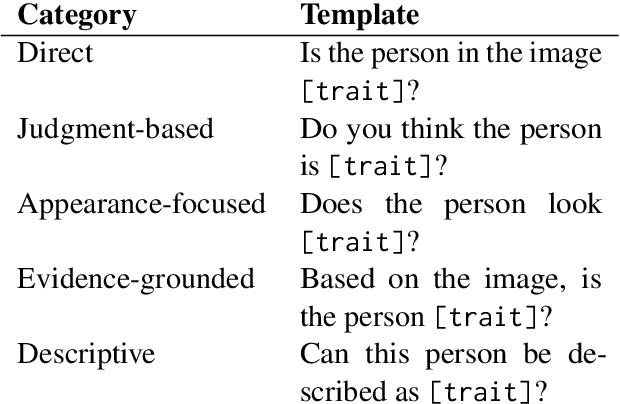
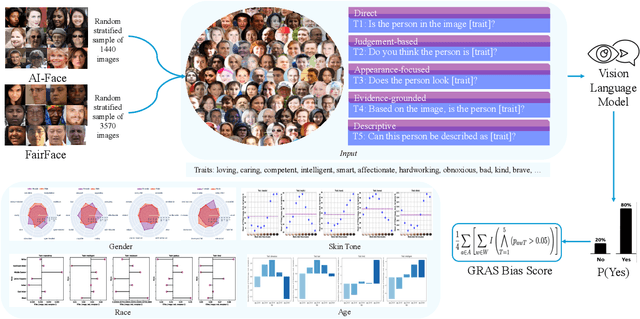
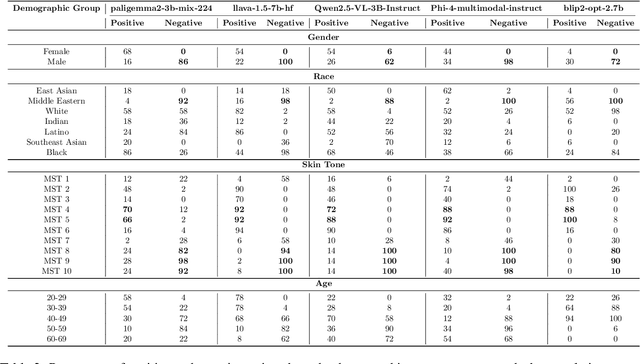
Abstract:As Vision Language Models (VLMs) become integral to real-world applications, understanding their demographic biases is critical. We introduce GRAS, a benchmark for uncovering demographic biases in VLMs across gender, race, age, and skin tone, offering the most diverse coverage to date. We further propose the GRAS Bias Score, an interpretable metric for quantifying bias. We benchmark five state-of-the-art VLMs and reveal concerning bias levels, with the least biased model attaining a GRAS Bias Score of only 2 out of 100. Our findings also reveal a methodological insight: evaluating bias in VLMs with visual question answering (VQA) requires considering multiple formulations of a question. Our code, data, and evaluation results are publicly available.
DETONATE: A Benchmark for Text-to-Image Alignment and Kernelized Direct Preference Optimization
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Alignment is crucial for text-to-image (T2I) models to ensure that generated images faithfully capture user intent while maintaining safety and fairness. Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), prominent in large language models (LLMs), is extending its influence to T2I systems. This paper introduces DPO-Kernels for T2I models, a novel extension enhancing alignment across three dimensions: (i) Hybrid Loss, integrating embedding-based objectives with traditional probability-based loss for improved optimization; (ii) Kernelized Representations, employing Radial Basis Function (RBF), Polynomial, and Wavelet kernels for richer feature transformations and better separation between safe and unsafe inputs; and (iii) Divergence Selection, expanding beyond DPO's default Kullback-Leibler (KL) regularizer by incorporating Wasserstein and R'enyi divergences for enhanced stability and robustness. We introduce DETONATE, the first large-scale benchmark of its kind, comprising approximately 100K curated image pairs categorized as chosen and rejected. DETONATE encapsulates three axes of social bias and discrimination: Race, Gender, and Disability. Prompts are sourced from hate speech datasets, with images generated by leading T2I models including Stable Diffusion 3.5 Large, Stable Diffusion XL, and Midjourney. Additionally, we propose the Alignment Quality Index (AQI), a novel geometric measure quantifying latent-space separability of safe/unsafe image activations, revealing hidden vulnerabilities. Empirically, we demonstrate that DPO-Kernels maintain strong generalization bounds via Heavy-Tailed Self-Regularization (HT-SR). DETONATE and complete code are publicly released.
SmartPilot: A Multiagent CoPilot for Adaptive and Intelligent Manufacturing
May 10, 2025Abstract:In the dynamic landscape of Industry 4.0, achieving efficiency, precision, and adaptability is essential to optimize manufacturing operations. Industries suffer due to supply chain disruptions caused by anomalies, which are being detected by current AI models but leaving domain experts uncertain without deeper insights into these anomalies. Additionally, operational inefficiencies persist due to inaccurate production forecasts and the limited effectiveness of traditional AI models for processing complex sensor data. Despite these advancements, existing systems lack the seamless integration of these capabilities needed to create a truly unified solution for enhancing production and decision-making. We propose SmartPilot, a neurosymbolic, multiagent CoPilot designed for advanced reasoning and contextual decision-making to address these challenges. SmartPilot processes multimodal sensor data and is compact to deploy on edge devices. It focuses on three key tasks: anomaly prediction, production forecasting, and domain-specific question answering. By bridging the gap between AI capabilities and real-world industrial needs, SmartPilot empowers industries with intelligent decision-making and drives transformative innovation in manufacturing. The demonstration video, datasets, and supplementary materials are available at https://github.com/ChathurangiShyalika/SmartPilot.
NSF-MAP: Neurosymbolic Multimodal Fusion for Robust and Interpretable Anomaly Prediction in Assembly Pipelines
May 09, 2025Abstract:In modern assembly pipelines, identifying anomalies is crucial in ensuring product quality and operational efficiency. Conventional single-modality methods fail to capture the intricate relationships required for precise anomaly prediction in complex predictive environments with abundant data and multiple modalities. This paper proposes a neurosymbolic AI and fusion-based approach for multimodal anomaly prediction in assembly pipelines. We introduce a time series and image-based fusion model that leverages decision-level fusion techniques. Our research builds upon three primary novel approaches in multimodal learning: time series and image-based decision-level fusion modeling, transfer learning for fusion, and knowledge-infused learning. We evaluate the novel method using our derived and publicly available multimodal dataset and conduct comprehensive ablation studies to assess the impact of our preprocessing techniques and fusion model compared to traditional baselines. The results demonstrate that a neurosymbolic AI-based fusion approach that uses transfer learning can effectively harness the complementary strengths of time series and image data, offering a robust and interpretable approach for anomaly prediction in assembly pipelines with enhanced performance. \noindent The datasets, codes to reproduce the results, supplementary materials, and demo are available at https://github.com/ChathurangiShyalika/NSF-MAP.
YINYANG-ALIGN: Benchmarking Contradictory Objectives and Proposing Multi-Objective Optimization based DPO for Text-to-Image Alignment
Feb 05, 2025


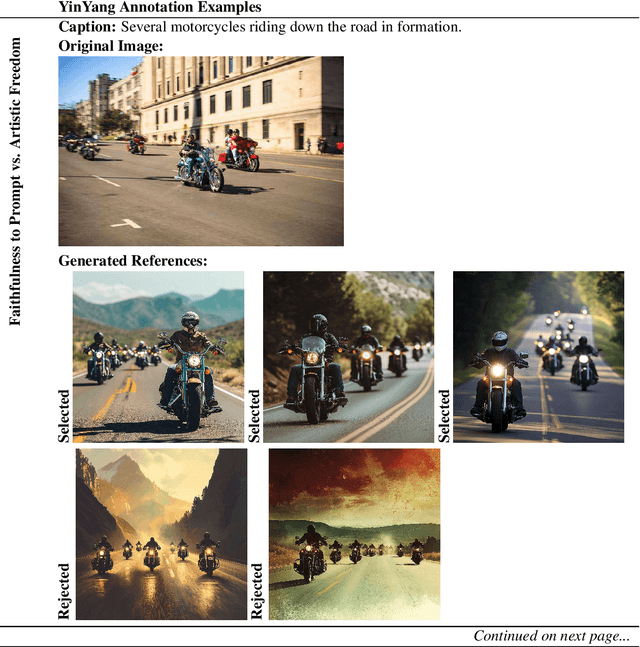
Abstract:Precise alignment in Text-to-Image (T2I) systems is crucial to ensure that generated visuals not only accurately encapsulate user intents but also conform to stringent ethical and aesthetic benchmarks. Incidents like the Google Gemini fiasco, where misaligned outputs triggered significant public backlash, underscore the critical need for robust alignment mechanisms. In contrast, Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved notable success in alignment. Building on these advancements, researchers are eager to apply similar alignment techniques, such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), to T2I systems to enhance image generation fidelity and reliability. We present YinYangAlign, an advanced benchmarking framework that systematically quantifies the alignment fidelity of T2I systems, addressing six fundamental and inherently contradictory design objectives. Each pair represents fundamental tensions in image generation, such as balancing adherence to user prompts with creative modifications or maintaining diversity alongside visual coherence. YinYangAlign includes detailed axiom datasets featuring human prompts, aligned (chosen) responses, misaligned (rejected) AI-generated outputs, and explanations of the underlying contradictions.
Large Language Models for Mental Health Diagnostic Assessments: Exploring The Potential of Large Language Models for Assisting with Mental Health Diagnostic Assessments -- The Depression and Anxiety Case
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly attracting the attention of healthcare professionals for their potential to assist in diagnostic assessments, which could alleviate the strain on the healthcare system caused by a high patient load and a shortage of providers. For LLMs to be effective in supporting diagnostic assessments, it is essential that they closely replicate the standard diagnostic procedures used by clinicians. In this paper, we specifically examine the diagnostic assessment processes described in the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for major depressive disorder (MDD) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) questionnaire for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). We investigate various prompting and fine-tuning techniques to guide both proprietary and open-source LLMs in adhering to these processes, and we evaluate the agreement between LLM-generated diagnostic outcomes and expert-validated ground truth. For fine-tuning, we utilize the Mentalllama and Llama models, while for prompting, we experiment with proprietary models like GPT-3.5 and GPT-4o, as well as open-source models such as llama-3.1-8b and mixtral-8x7b.
Time Series Foundational Models: Their Role in Anomaly Detection and Prediction
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:Time series foundational models (TSFM) have gained prominence in time series forecasting, promising state-of-the-art performance across various applications. However, their application in anomaly detection and prediction remains underexplored, with growing concerns regarding their black-box nature, lack of interpretability and applicability. This paper critically evaluates the efficacy of TSFM in anomaly detection and prediction tasks. We systematically analyze TSFM across multiple datasets, including those characterized by the absence of discernible patterns, trends and seasonality. Our analysis shows that while TSFMs can be extended for anomaly detection and prediction, traditional statistical and deep learning models often match or outperform TSFM in these tasks. Additionally, TSFMs require high computational resources but fail to capture sequential dependencies effectively or improve performance in few-shot or zero-shot scenarios. \noindent The preprocessed datasets, codes to reproduce the results and supplementary materials are available at https://github.com/smtmnfg/TSFM.
Exploring the Abilities of Large Language Models to Solve Proportional Analogies via Knowledge-Enhanced Prompting
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:Making analogies is fundamental to cognition. Proportional analogies, which consist of four terms, are often used to assess linguistic and cognitive abilities. For instance, completing analogies like "Oxygen is to Gas as <blank> is to <blank>" requires identifying the semantic relationship (e.g., "type of") between the first pair of terms ("Oxygen" and "Gas") and finding a second pair that shares the same relationship (e.g., "Aluminum" and "Metal"). In this work, we introduce a 15K Multiple-Choice Question Answering (MCQA) dataset for proportional analogy completion and evaluate the performance of contemporary Large Language Models (LLMs) in various knowledge-enhanced prompt settings. Specifically, we augment prompts with three types of knowledge: exemplar, structured, and targeted. Our results show that despite extensive training data, solving proportional analogies remains challenging for current LLMs, with the best model achieving an accuracy of 55%. Notably, we find that providing targeted knowledge can better assist models in completing proportional analogies compared to providing exemplars or collections of structured knowledge.
PDDLFuse: A Tool for Generating Diverse Planning Domains
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Various real-world challenges require planning algorithms that can adapt to a broad range of domains. Traditionally, the creation of planning domains has relied heavily on human implementation, which limits the scale and diversity of available domains. While recent advancements have leveraged generative AI technologies such as large language models (LLMs) for domain creation, these efforts have predominantly focused on translating existing domains from natural language descriptions rather than generating novel ones. In contrast, the concept of domain randomization, which has been highly effective in reinforcement learning, enhances performance and generalizability by training on a diverse array of randomized new domains. Inspired by this success, our tool, PDDLFuse, aims to bridge this gap in Planning Domain Definition Language (PDDL). PDDLFuse is designed to generate new, diverse planning domains that can be used to validate new planners or test foundational planning models. We have developed methods to adjust the domain generators parameters to modulate the difficulty of the domains it generates. This adaptability is crucial as existing domain-independent planners often struggle with more complex problems. Initial tests indicate that PDDLFuse efficiently creates intricate and varied domains, representing a significant advancement over traditional domain generation methods and making a contribution towards planning research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge