Valerie Shalin
A Domain-Agnostic Neurosymbolic Approach for Big Social Data Analysis: Evaluating Mental Health Sentiment on Social Media during COVID-19
Nov 11, 2024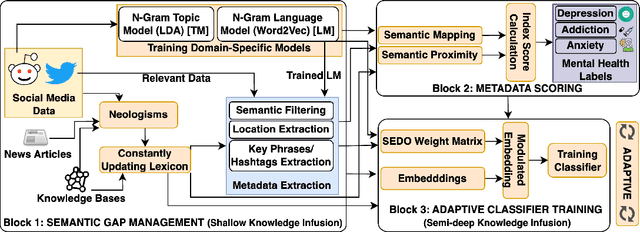
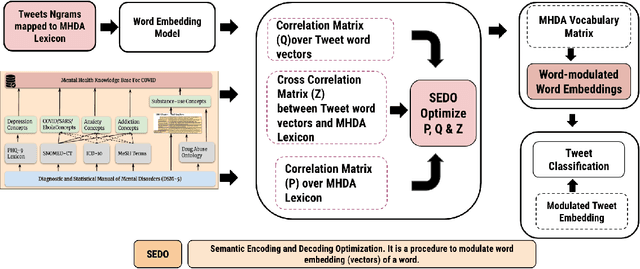
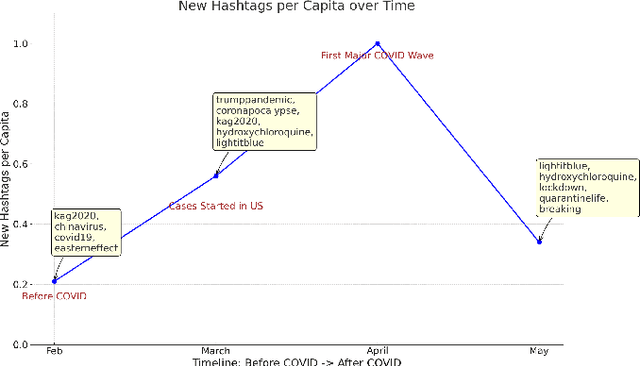
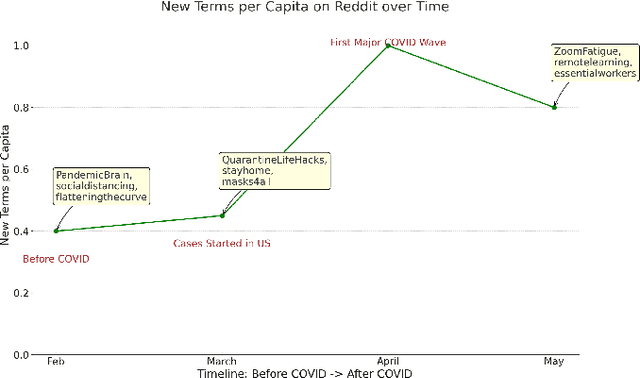
Abstract:Monitoring public sentiment via social media is potentially helpful during health crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic. However, traditional frequency-based, data-driven neural network-based approaches can miss newly relevant content due to the evolving nature of language in a dynamically evolving environment. Human-curated symbolic knowledge sources, such as lexicons for standard language and slang terms, can potentially elevate social media signals in evolving language. We introduce a neurosymbolic method that integrates neural networks with symbolic knowledge sources, enhancing the detection and interpretation of mental health-related tweets relevant to COVID-19. Our method was evaluated using a corpus of large datasets (approximately 12 billion tweets, 2.5 million subreddit data, and 700k news articles) and multiple knowledge graphs. This method dynamically adapts to evolving language, outperforming purely data-driven models with an F1 score exceeding 92\%. This approach also showed faster adaptation to new data and lower computational demands than fine-tuning pre-trained large language models (LLMs). This study demonstrates the benefit of neurosymbolic methods in interpreting text in a dynamic environment for tasks such as health surveillance.
A Cross Attention Approach to Diagnostic Explainability using Clinical Practice Guidelines for Depression
Nov 23, 2023

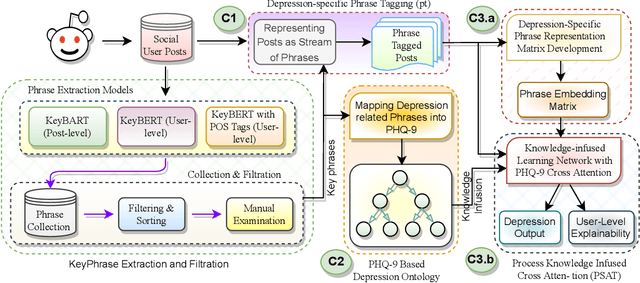
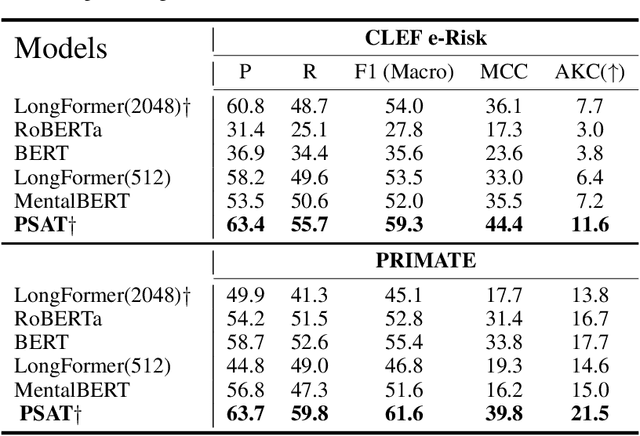
Abstract:The lack of explainability using relevant clinical knowledge hinders the adoption of Artificial Intelligence-powered analysis of unstructured clinical dialogue. A wealth of relevant, untapped Mental Health (MH) data is available in online communities, providing the opportunity to address the explainability problem with substantial potential impact as a screening tool for both online and offline applications. We develop a method to enhance attention in popular transformer models and generate clinician-understandable explanations for classification by incorporating external clinical knowledge. Inspired by how clinicians rely on their expertise when interacting with patients, we leverage relevant clinical knowledge to model patient inputs, providing meaningful explanations for classification. This will save manual review time and engender trust. We develop such a system in the context of MH using clinical practice guidelines (CPG) for diagnosing depression, a mental health disorder of global concern. We propose an application-specific language model called ProcesS knowledge-infused cross ATtention (PSAT), which incorporates CPGs when computing attention. Through rigorous evaluation on three expert-curated datasets related to depression, we demonstrate application-relevant explainability of PSAT. PSAT also surpasses the performance of nine baseline models and can provide explanations where other baselines fall short. We transform a CPG resource focused on depression, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire (e.g. PHQ-9) and related questions, into a machine-readable ontology using SNOMED-CT. With this resource, PSAT enhances the ability of models like GPT-3.5 to generate application-relevant explanations.
Knowledge Graph semantic enhancement of input data for improving AI
May 10, 2020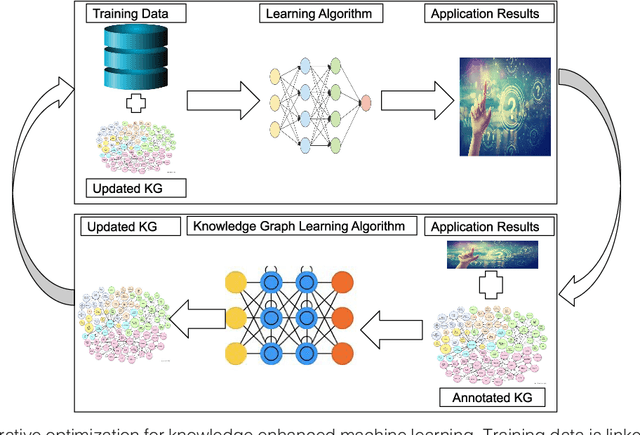
Abstract:Intelligent systems designed using machine learning algorithms require a large number of labeled data. Background knowledge provides complementary, real world factual information that can augment the limited labeled data to train a machine learning algorithm. The term Knowledge Graph (KG) is in vogue as for many practical applications, it is convenient and useful to organize this background knowledge in the form of a graph. Recent academic research and implemented industrial intelligent systems have shown promising performance for machine learning algorithms that combine training data with a knowledge graph. In this article, we discuss the use of relevant KGs to enhance input data for two applications that use machine learning -- recommendation and community detection. The KG improves both accuracy and explainability.
Modeling Islamist Extremist Communications on Social Media using Contextual Dimensions: Religion, Ideology, and Hate
Aug 20, 2019
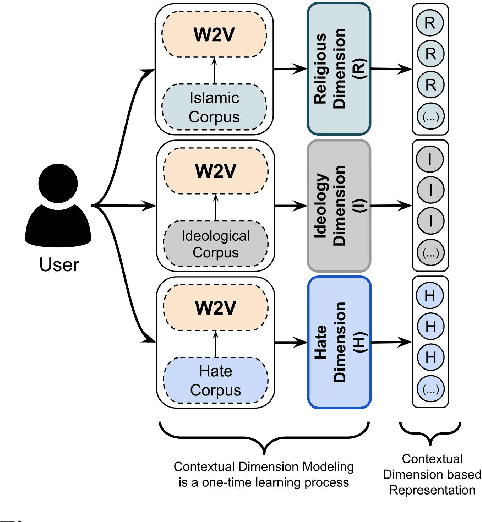
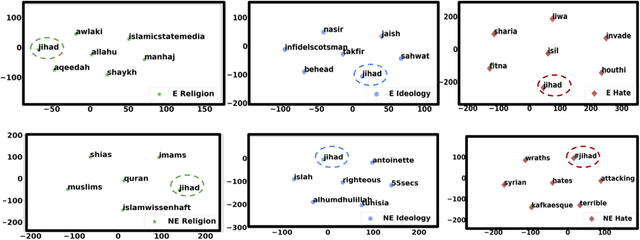
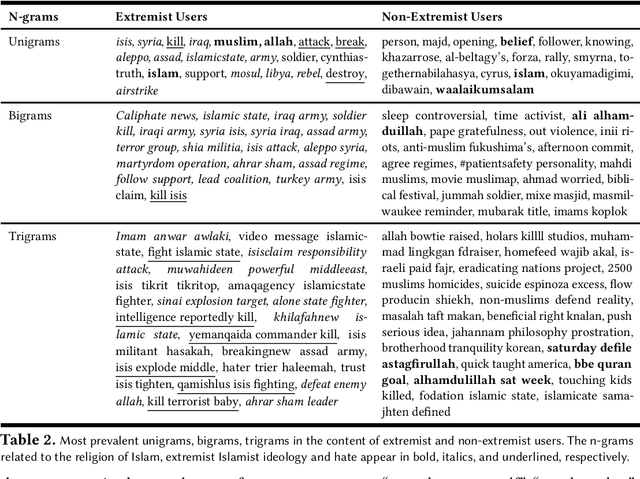
Abstract:Terror attacks have been linked in part to online extremist content. Although tens of thousands of Islamist extremism supporters consume such content, they are a small fraction relative to peaceful Muslims. The efforts to contain the ever-evolving extremism on social media platforms have remained inadequate and mostly ineffective. Divergent extremist and mainstream contexts challenge machine interpretation, with a particular threat to the precision of classification algorithms. Our context-aware computational approach to the analysis of extremist content on Twitter breaks down this persuasion process into building blocks that acknowledge inherent ambiguity and sparsity that likely challenge both manual and automated classification. We model this process using a combination of three contextual dimensions -- religion, ideology, and hate -- each elucidating a degree of radicalization and highlighting independent features to render them computationally accessible. We utilize domain-specific knowledge resources for each of these contextual dimensions such as Qur'an for religion, the books of extremist ideologues and preachers for political ideology and a social media hate speech corpus for hate. Our study makes three contributions to reliable analysis: (i) Development of a computational approach rooted in the contextual dimensions of religion, ideology, and hate that reflects strategies employed by online Islamist extremist groups, (ii) An in-depth analysis of relevant tweet datasets with respect to these dimensions to exclude likely mislabeled users, and (iii) A framework for understanding online radicalization as a process to assist counter-programming. Given the potentially significant social impact, we evaluate the performance of our algorithms to minimize mislabeling, where our approach outperforms a competitive baseline by 10.2% in precision.
CEVO: Comprehensive EVent Ontology Enhancing Cognitive Annotation
Oct 03, 2018



Abstract:While the general analysis of named entities has received substantial research attention on unstructured as well as structured data, the analysis of relations among named entities has received limited focus. In fact, a review of the literature revealed a deficiency in research on the abstract conceptualization required to organize relations. We believe that such an abstract conceptualization can benefit various communities and applications such as natural language processing, information extraction, machine learning, and ontology engineering. In this paper, we present Comprehensive EVent Ontology (CEVO), built on Levin's conceptual hierarchy of English verbs that categorizes verbs with shared meaning, and syntactic behavior. We present the fundamental concepts and requirements for this ontology. Furthermore, we present three use cases employing the CEVO ontology on annotation tasks: (i) annotating relations in plain text, (ii) annotating ontological properties, and (iii) linking textual relations to ontological properties. These use-cases demonstrate the benefits of using CEVO for annotation: (i) annotating English verbs from an abstract conceptualization, (ii) playing the role of an upper ontology for organizing ontological properties, and (iii) facilitating the annotation of text relations using any underlying vocabulary. This resource is available at https://shekarpour.github.io/cevo.io/ using https://w3id.org/cevo namespace.
Location Name Extraction from Targeted Text Streams using Gazetteer-based Statistical Language Models
Jun 07, 2018



Abstract:Extracting location names from informal and unstructured social media data requires the identification of referent boundaries and partitioning compound names. Variability, particularly systematic variability in location names (Carroll, 1983), challenges the identification task. Some of this variability can be anticipated as operations within a statistical language model, in this case drawn from gazetteers such as OpenStreetMap (OSM), Geonames, and DBpedia. This permits evaluation of an observed n-gram in Twitter targeted text as a legitimate location name variant from the same location-context. Using n-gram statistics and location-related dictionaries, our Location Name Extraction tool (LNEx) handles abbreviations and automatically filters and augments the location names in gazetteers (handling name contractions and auxiliary contents) to help detect the boundaries of multi-word location names and thereby delimit them in texts. We evaluated our approach on 4,500 event-specific tweets from three targeted streams to compare the performance of LNEx against that of ten state-of-the-art taggers that rely on standard semantic, syntactic and/or orthographic features. LNEx improved the average F-Score by 33-179%, outperforming all taggers. Further, LNEx is capable of stream processing.
A Quality Type-aware Annotated Corpus and Lexicon for Harassment Research
May 23, 2018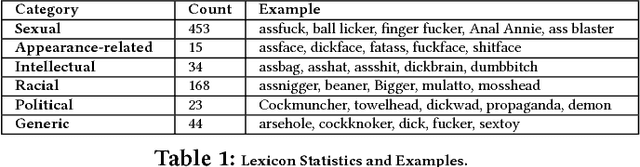
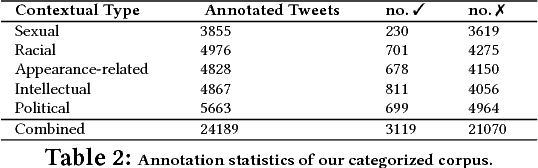

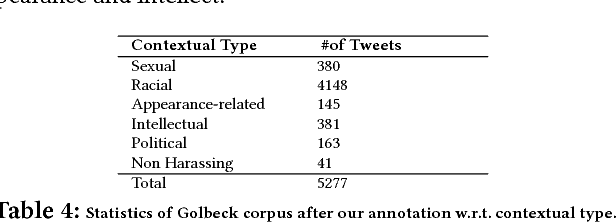
Abstract:Having a quality annotated corpus is essential especially for applied research. Despite the recent focus of Web science community on researching about cyberbullying, the community dose not still have standard benchmarks. In this paper, we publish first, a quality annotated corpus and second, an offensive words lexicon capturing different types type of harassment as (i) sexual harassment, (ii) racial harassment, (iii) appearance-related harassment, (iv) intellectual harassment, and (v) political harassment.We crawled data from Twitter using our offensive lexicon. Then relied on the human judge to annotate the collected tweets w.r.t. the contextual types because using offensive words is not sufficient to reliably detect harassment. Our corpus consists of 25,000 annotated tweets in five contextual types. We are pleased to share this novel annotated corpus and the lexicon with the research community. The instruction to acquire the corpus has been published on the Git repository.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge