Adria Mallol-Ragolta
Reading Smiles: Proxy Bias in Foundation Models for Facial Emotion Recognition
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Foundation Models (FMs) are rapidly transforming Affective Computing (AC), with Vision Language Models (VLMs) now capable of recognising emotions in zero shot settings. This paper probes a critical but underexplored question: what visual cues do these models rely on to infer affect, and are these cues psychologically grounded or superficially learnt? We benchmark varying scale VLMs on a teeth annotated subset of AffectNet dataset and find consistent performance shifts depending on the presence of visible teeth. Through structured introspection of, the best-performing model, i.e., GPT-4o, we show that facial attributes like eyebrow position drive much of its affective reasoning, revealing a high degree of internal consistency in its valence-arousal predictions. These patterns highlight the emergent nature of FMs behaviour, but also reveal risks: shortcut learning, bias, and fairness issues especially in sensitive domains like mental health and education.
Affective Computing Has Changed: The Foundation Model Disruption
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:The dawn of Foundation Models has on the one hand revolutionised a wide range of research problems, and, on the other hand, democratised the access and use of AI-based tools by the general public. We even observe an incursion of these models into disciplines related to human psychology, such as the Affective Computing domain, suggesting their affective, emerging capabilities. In this work, we aim to raise awareness of the power of Foundation Models in the field of Affective Computing by synthetically generating and analysing multimodal affective data, focusing on vision, linguistics, and speech (acoustics). We also discuss some fundamental problems, such as ethical issues and regulatory aspects, related to the use of Foundation Models in this research area.
HEAR4Health: A blueprint for making computer audition a staple of modern healthcare
Jan 25, 2023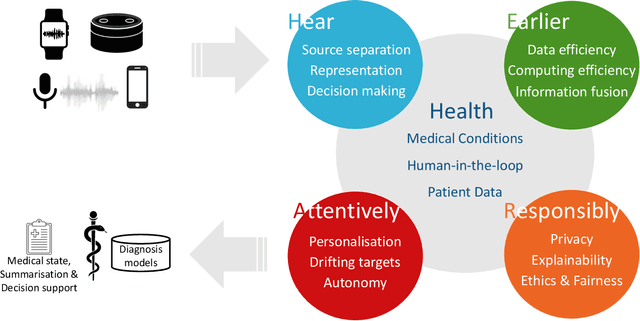

Abstract:Recent years have seen a rapid increase in digital medicine research in an attempt to transform traditional healthcare systems to their modern, intelligent, and versatile equivalents that are adequately equipped to tackle contemporary challenges. This has led to a wave of applications that utilise AI technologies; first and foremost in the fields of medical imaging, but also in the use of wearables and other intelligent sensors. In comparison, computer audition can be seen to be lagging behind, at least in terms of commercial interest. Yet, audition has long been a staple assistant for medical practitioners, with the stethoscope being the quintessential sign of doctors around the world. Transforming this traditional technology with the use of AI entails a set of unique challenges. We categorise the advances needed in four key pillars: Hear, corresponding to the cornerstone technologies needed to analyse auditory signals in real-life conditions; Earlier, for the advances needed in computational and data efficiency; Attentively, for accounting to individual differences and handling the longitudinal nature of medical data; and, finally, Responsibly, for ensuring compliance to the ethical standards accorded to the field of medicine.
The ACM Multimedia 2022 Computational Paralinguistics Challenge: Vocalisations, Stuttering, Activity, & Mosquitoes
May 13, 2022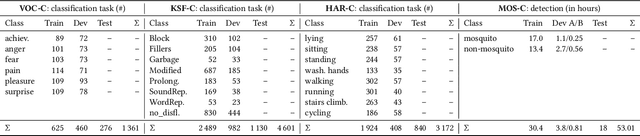
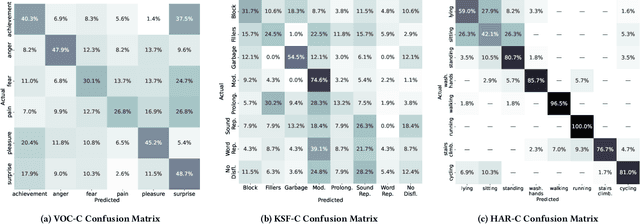
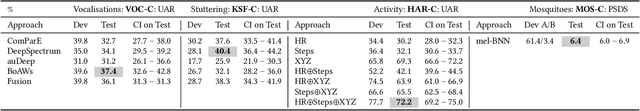
Abstract:The ACM Multimedia 2022 Computational Paralinguistics Challenge addresses four different problems for the first time in a research competition under well-defined conditions: In the Vocalisations and Stuttering Sub-Challenges, a classification on human non-verbal vocalisations and speech has to be made; the Activity Sub-Challenge aims at beyond-audio human activity recognition from smartwatch sensor data; and in the Mosquitoes Sub-Challenge, mosquitoes need to be detected. We describe the Sub-Challenges, baseline feature extraction, and classifiers based on the usual ComPaRE and BoAW features, the auDeep toolkit, and deep feature extraction from pre-trained CNNs using the DeepSpectRum toolkit; in addition, we add end-to-end sequential modelling, and a log-mel-128-BNN.
Continuous-Time Audiovisual Fusion with Recurrence vs. Attention for In-The-Wild Affect Recognition
Mar 29, 2022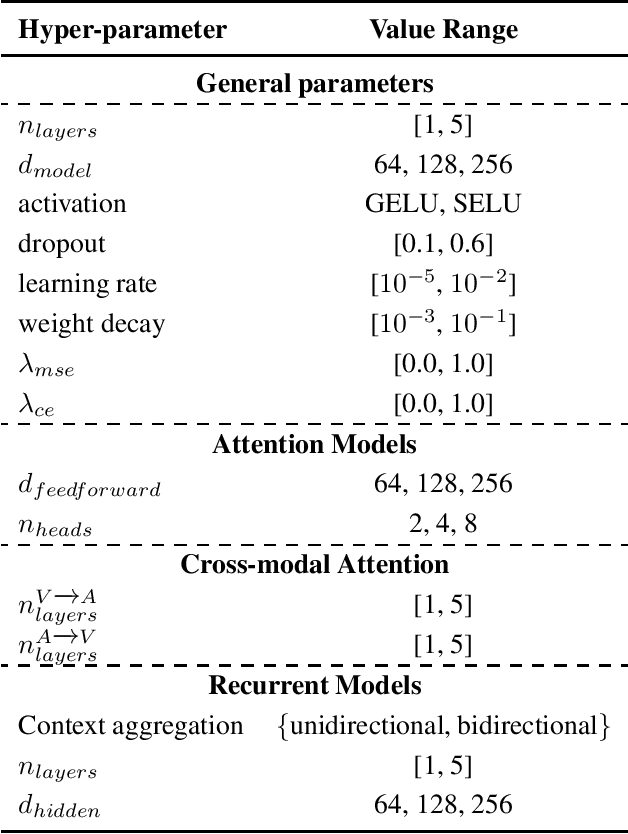
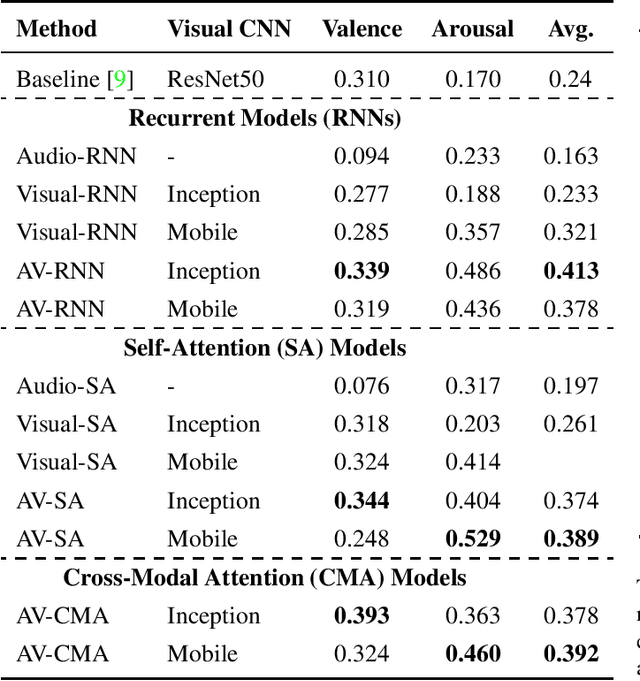
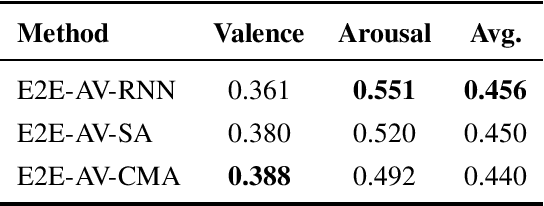
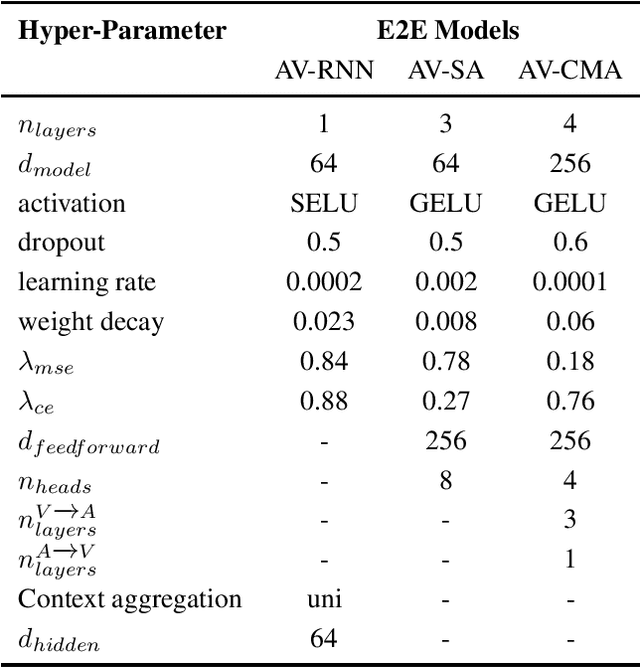
Abstract:In this paper, we present our submission to 3rd Affective Behavior Analysis in-the-wild (ABAW) challenge. Learningcomplex interactions among multimodal sequences is critical to recognise dimensional affect from in-the-wild audiovisual data. Recurrence and attention are the two widely used sequence modelling mechanisms in the literature. To clearly understand the performance differences between recurrent and attention models in audiovisual affect recognition, we present a comprehensive evaluation of fusion models based on LSTM-RNNs, self-attention and cross-modal attention, trained for valence and arousal estimation. Particularly, we study the impact of some key design choices: the modelling complexity of CNN backbones that provide features to the the temporal models, with and without end-to-end learning. We trained the audiovisual affect recognition models on in-the-wild ABAW corpus by systematically tuning the hyper-parameters involved in the network architecture design and training optimisation. Our extensive evaluation of the audiovisual fusion models shows that LSTM-RNNs can outperform the attention models when coupled with low-complex CNN backbones and trained in an end-to-end fashion, implying that attention models may not necessarily be the optimal choice for continuous-time multimodal emotion recognition.
Audio Self-supervised Learning: A Survey
Mar 02, 2022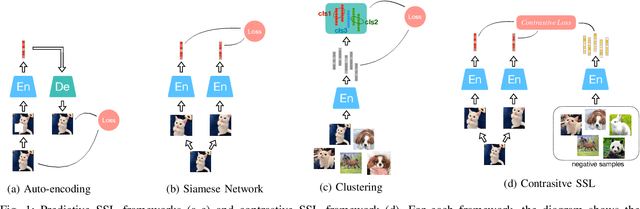
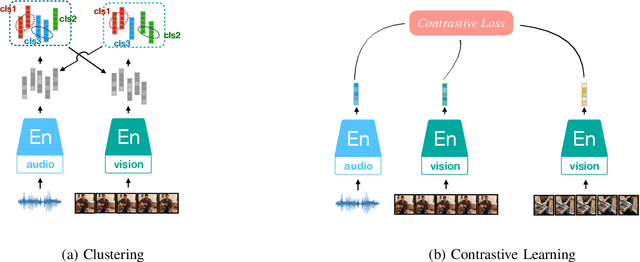
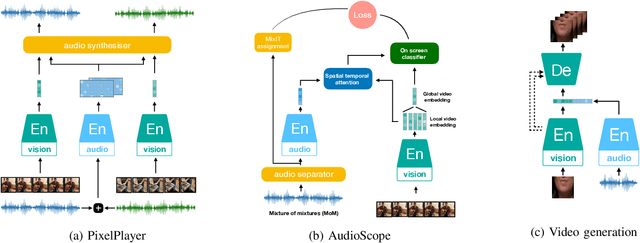
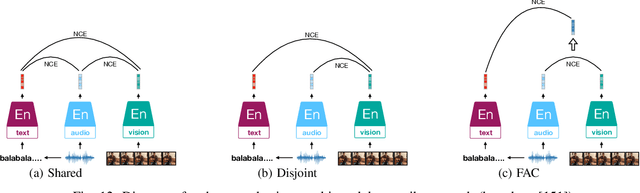
Abstract:Inspired by the humans' cognitive ability to generalise knowledge and skills, Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) targets at discovering general representations from large-scale data without requiring human annotations, which is an expensive and time consuming task. Its success in the fields of computer vision and natural language processing have prompted its recent adoption into the field of audio and speech processing. Comprehensive reviews summarising the knowledge in audio SSL are currently missing. To fill this gap, in the present work, we provide an overview of the SSL methods used for audio and speech processing applications. Herein, we also summarise the empirical works that exploit the audio modality in multi-modal SSL frameworks, and the existing suitable benchmarks to evaluate the power of SSL in the computer audition domain. Finally, we discuss some open problems and point out the future directions on the development of audio SSL.
EIHW-MTG: Second DiCOVA Challenge System Report
Oct 18, 2021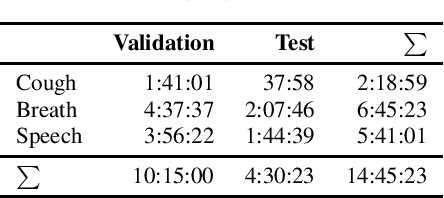
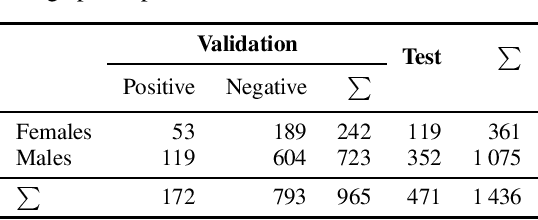
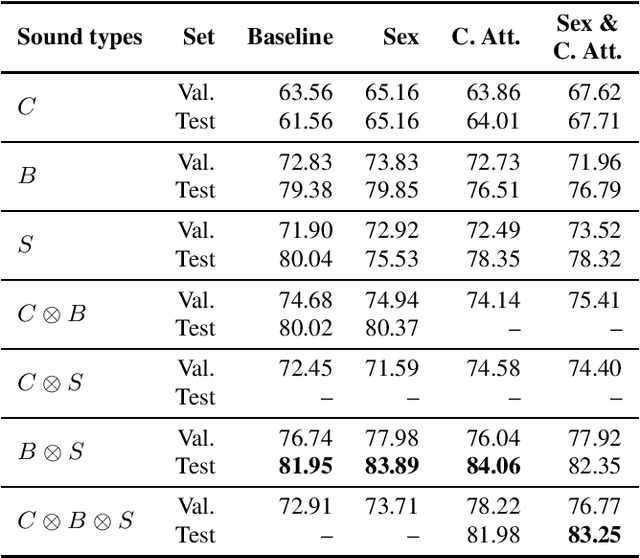
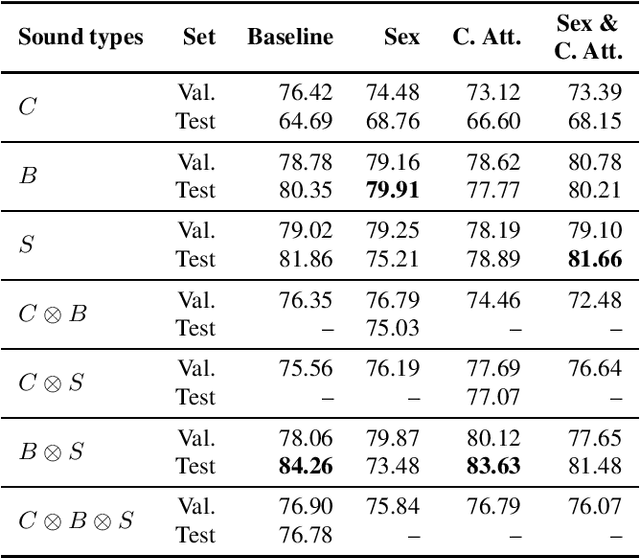
Abstract:This work presents an outer product-based approach to fuse the embedded representations generated from the spectrograms of cough, breath, and speech samples for the automatic detection of COVID-19. To extract deep learnt representations from the spectrograms, we compare the performance of a CNN trained from scratch and a ResNet18 architecture fine-tuned for the task at hand. Furthermore, we investigate whether the patients' sex and the use of contextual attention mechanisms is beneficial. Our experiments use the dataset released as part of the Second Diagnosing COVID-19 using Acoustics (DiCOVA) Challenge. The results suggest the suitability of fusing breath and speech information to detect COVID-19. An Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 84.06% is obtained on the test partition when using a CNN trained from scratch with contextual attention mechanisms. When using the ResNet18 architecture for feature extraction, the baseline model scores the highest performance with an AUC of 84.26%.
EIHW-MTG DiCOVA 2021 Challenge System Report
Oct 13, 2021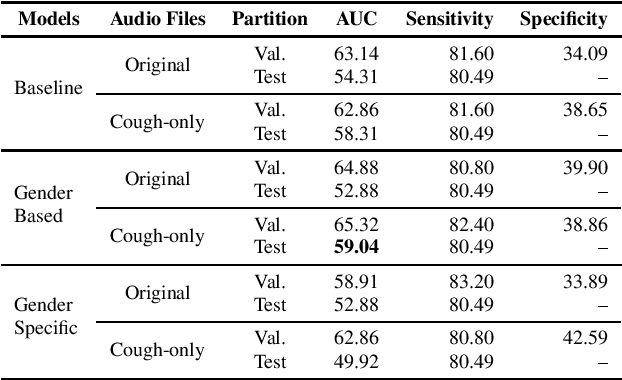
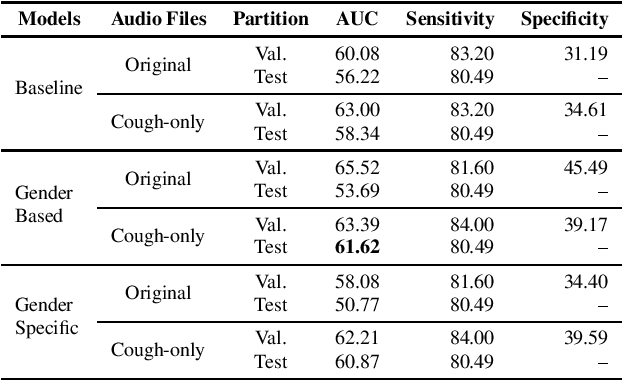
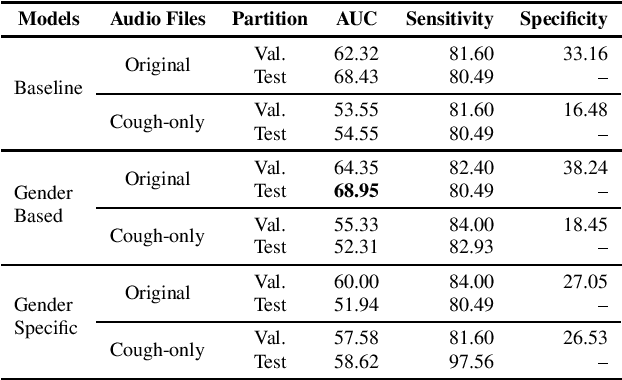
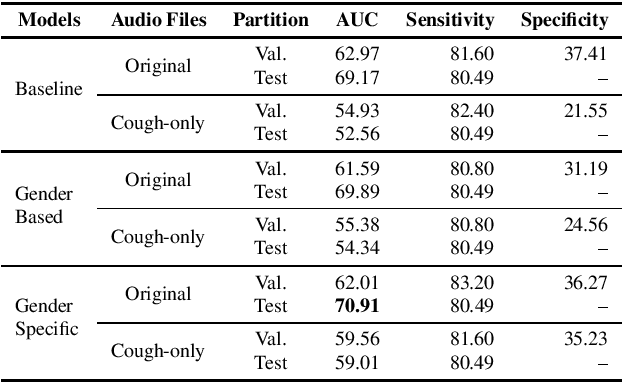
Abstract:This paper aims to automatically detect COVID-19 patients by analysing the acoustic information embedded in coughs. COVID-19 affects the respiratory system, and, consequently, respiratory-related signals have the potential to contain salient information for the task at hand. We focus on analysing the spectrogram representations of coughing samples with the aim to investigate whether COVID-19 alters the frequency content of these signals. Furthermore, this work also assesses the impact of gender in the automatic detection of COVID-19. To extract deep learnt representations of the spectrograms, we compare the performance of a cough-specific, and a Resnet18 pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). Additionally, our approach explores the use of contextual attention, so the model can learn to highlight the most relevant deep learnt features extracted by the CNN. We conduct our experiments on the dataset released for the Cough Sound Track of the DiCOVA 2021 Challenge. The best performance on the test set is obtained using the Resnet18 pre-trained CNN with contextual attention, which scored an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 70.91 at 80% sensitivity.
MuSe 2020 -- The First International Multimodal Sentiment Analysis in Real-life Media Challenge and Workshop
Apr 30, 2020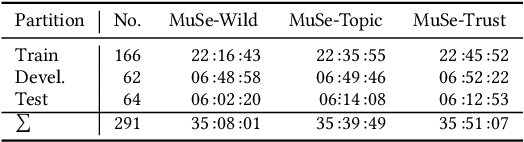
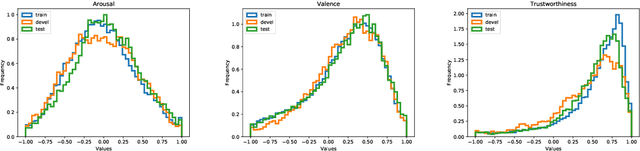
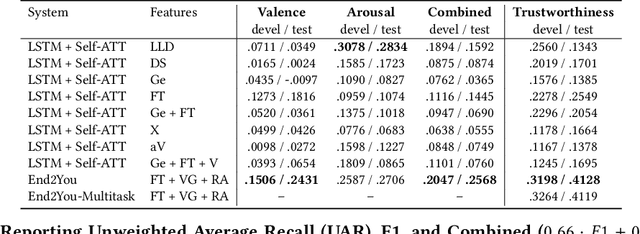
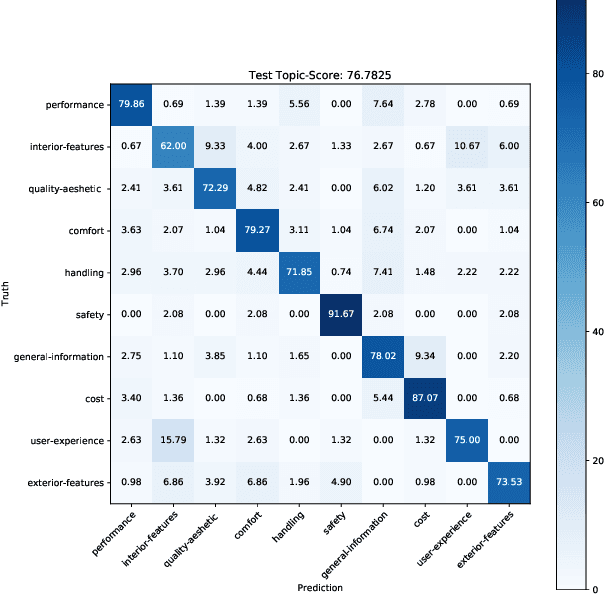
Abstract:Multimodal Sentiment Analysis in Real-life Media (MuSe) 2020 is a Challenge-based Workshop focusing on the tasks of sentiment recognition, as well as emotion-target engagement and trustworthiness detection by means of more comprehensively integrating the audio-visual and language modalities. The purpose of MuSe 2020 is to bring together communities from different disciplines; mainly, the audio-visual emotion recognition community (signal-based), and the sentiment analysis community (symbol-based). We present three distinct sub-challenges: MuSe-Wild, which focuses on continuous emotion (arousal and valence) prediction; MuSe-Topic, in which participants recognise domain-specific topics as the target of 3-class (low, medium, high) emotions; and MuSe-Trust, in which the novel aspect of trustworthiness is to be predicted. In this paper, we provide detailed information on MuSe-CaR, the first of its kind in-the-wild database, which is utilised for the challenge, as well as the state-of-the-art features and modelling approaches applied. For each sub-challenge, a competitive baseline for participants is set; namely, on test we report for MuSe-Wild a combined (valence and arousal) CCC of .2568, for MuSe-Topic a score (computed as 0.34$\cdot$ UAR + 0.66$\cdot$F1) of 76.78 % on the 10-class topic and 40.64 % on the 3-class emotion prediction, and for MuSe-Trust a CCC of .4359.
Adversarial-based neural networks for affect estimations in the wild
Feb 09, 2020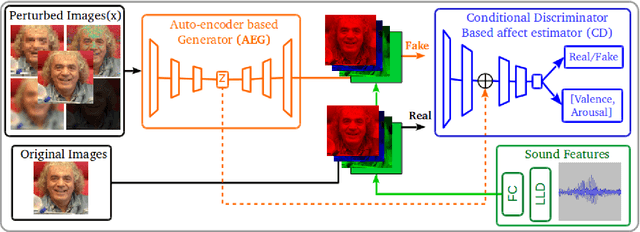

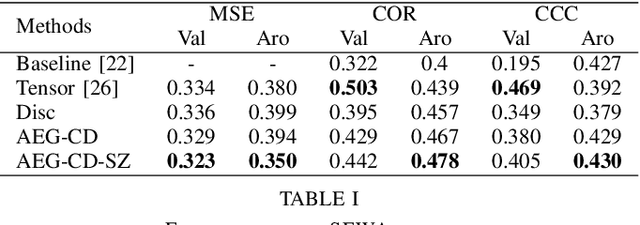
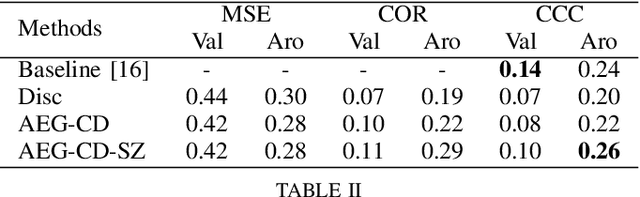
Abstract:There is a growing interest in affective computing research nowadays given its crucial role in bridging humans with computers. This progress has been recently accelerated due to the emergence of bigger data. One recent advance in this field is the use of adversarial learning to improve model learning through augmented samples. However, the use of latent features, which is feasible through adversarial learning, is not largely explored, yet. This technique may also improve the performance of affective models, as analogously demonstrated in related fields, such as computer vision. To expand this analysis, in this work, we explore the use of latent features through our proposed adversarial-based networks for valence and arousal recognition in the wild. Specifically, our models operate by aggregating several modalities to our discriminator, which is further conditioned to the extracted latent features by the generator. Our experiments on the recently released SEWA dataset suggest the progressive improvements of our results. Finally, we show our competitive results on the Affective Behavior Analysis in-the-Wild (ABAW) challenge dataset
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge