Something Something 100
Papers and Code
Where to Explore: A Reach and Cost-Aware Approach for Unbiased Data Collection in Recommender Systems
Dec 11, 2025Exploration is essential to improve long-term recommendation quality, but it often degrades short-term business performance, especially in remote-first TV environments where users engage passively, expect instant relevance, and offer few chances for correction. This paper introduces an approach for delivering content-level exploration safely and efficiently by optimizing its placement based on reach and opportunity cost. Deployed on a large-scale streaming platform with over 100 million monthly active users, our approach identifies scroll-depth regions with lower engagement and strategically introduces a dedicated container, the "Something Completely Different" row containing randomized content. Rather than enforcing exploration uniformly across the user interface (UI), we condition its appearance on empirically low-cost, high-reach positions to ensure minimal tradeoff against platform-level watch time goals. Extensive A/B testing shows that this strategy preserves business metrics while collecting unbiased interaction data. Our method complements existing intra-row diversification and bandit-based exploration techniques by introducing a deployable, behaviorally informed mechanism for surfacing exploratory content at scale. Moreover, we demonstrate that the collected unbiased data, integrated into downstream candidate generation, significantly improves user engagement, validating its value for recommender systems.
V-JEPA 2: Self-Supervised Video Models Enable Understanding, Prediction and Planning
Jun 11, 2025A major challenge for modern AI is to learn to understand the world and learn to act largely by observation. This paper explores a self-supervised approach that combines internet-scale video data with a small amount of interaction data (robot trajectories), to develop models capable of understanding, predicting, and planning in the physical world. We first pre-train an action-free joint-embedding-predictive architecture, V-JEPA 2, on a video and image dataset comprising over 1 million hours of internet video. V-JEPA 2 achieves strong performance on motion understanding (77.3 top-1 accuracy on Something-Something v2) and state-of-the-art performance on human action anticipation (39.7 recall-at-5 on Epic-Kitchens-100) surpassing previous task-specific models. Additionally, after aligning V-JEPA 2 with a large language model, we demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on multiple video question-answering tasks at the 8 billion parameter scale (e.g., 84.0 on PerceptionTest, 76.9 on TempCompass). Finally, we show how self-supervised learning can be applied to robotic planning tasks by post-training a latent action-conditioned world model, V-JEPA 2-AC, using less than 62 hours of unlabeled robot videos from the Droid dataset. We deploy V-JEPA 2-AC zero-shot on Franka arms in two different labs and enable picking and placing of objects using planning with image goals. Notably, this is achieved without collecting any data from the robots in these environments, and without any task-specific training or reward. This work demonstrates how self-supervised learning from web-scale data and a small amount of robot interaction data can yield a world model capable of planning in the physical world.
CA^2ST: Cross-Attention in Audio, Space, and Time for Holistic Video Recognition
Mar 30, 2025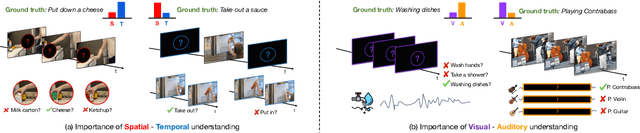
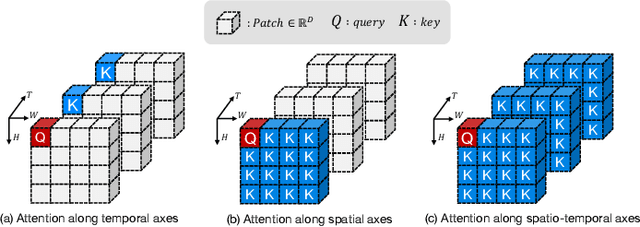
We propose Cross-Attention in Audio, Space, and Time (CA^2ST), a transformer-based method for holistic video recognition. Recognizing actions in videos requires both spatial and temporal understanding, yet most existing models lack a balanced spatio-temporal understanding of videos. To address this, we propose a novel two-stream architecture, called Cross-Attention in Space and Time (CAST), using only RGB input. In each layer of CAST, Bottleneck Cross-Attention (B-CA) enables spatial and temporal experts to exchange information and make synergistic predictions. For holistic video understanding, we extend CAST by integrating an audio expert, forming Cross-Attention in Visual and Audio (CAVA). We validate the CAST on benchmarks with different characteristics, EPIC-KITCHENS-100, Something-Something-V2, and Kinetics-400, consistently showing balanced performance. We also validate the CAVA on audio-visual action recognition benchmarks, including UCF-101, VGG-Sound, KineticsSound, and EPIC-SOUNDS. With a favorable performance of CAVA across these datasets, we demonstrate the effective information exchange among multiple experts within the B-CA module. In summary, CA^2ST combines CAST and CAVA by employing spatial, temporal, and audio experts through cross-attention, achieving balanced and holistic video understanding.
Real-time Planning of Minimum-time Trajectories for Agile UAV Flight
Sep 24, 2024We address the challenge of real-time planning of minimum-time trajectories over multiple waypoints, onboard multirotor UAVs. Previous works demonstrated that achieving a truly time-optimal trajectory is computationally too demanding to enable frequent replanning during agile flight, especially on less powerful flight computers. Our approach overcomes this stumbling block by utilizing a point-mass model with a novel iterative thrust decomposition algorithm, enabling the UAV to use all of its collective thrust, something previous point-mass approaches could not achieve. The approach enables gravity and drag modeling integration, significantly reducing tracking errors in high-speed trajectories, which is proven through an ablation study. When combined with a new multi-waypoint optimization algorithm, which uses a gradient-based method to converge to optimal velocities in waypoints, the proposed method generates minimum-time multi-waypoint trajectories within milliseconds. The proposed approach, which we provide as open-source package, is validated both in simulation and in real-world, using Nonlinear Model Predictive Control. With accelerations of up to 3.5g and speeds over 100 km/h, trajectories generated by the proposed method yield similar or even smaller tracking errors than the trajectories generated for a full multirotor model.
Egocentric zone-aware action recognition across environments
Sep 21, 2024



Human activities exhibit a strong correlation between actions and the places where these are performed, such as washing something at a sink. More specifically, in daily living environments we may identify particular locations, hereinafter named activity-centric zones, which may afford a set of homogeneous actions. Their knowledge can serve as a prior to favor vision models to recognize human activities. However, the appearance of these zones is scene-specific, limiting the transferability of this prior information to unfamiliar areas and domains. This problem is particularly relevant in egocentric vision, where the environment takes up most of the image, making it even more difficult to separate the action from the context. In this paper, we discuss the importance of decoupling the domain-specific appearance of activity-centric zones from their universal, domain-agnostic representations, and show how the latter can improve the cross-domain transferability of Egocentric Action Recognition (EAR) models. We validate our solution on the EPIC-Kitchens-100 and Argo1M datasets
CAST: Cross-Attention in Space and Time for Video Action Recognition
Nov 30, 2023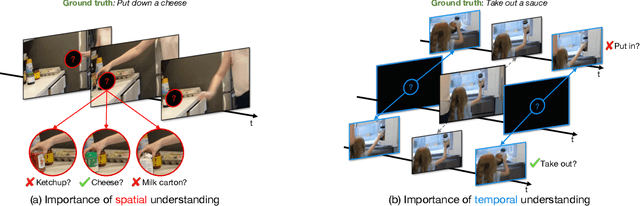
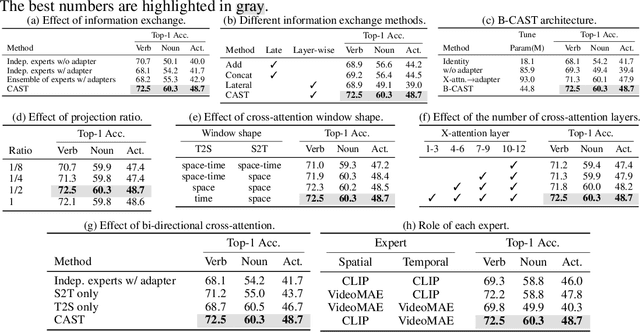
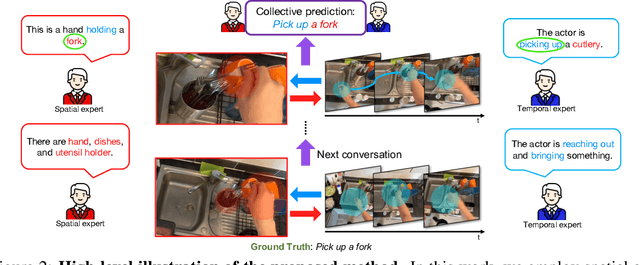
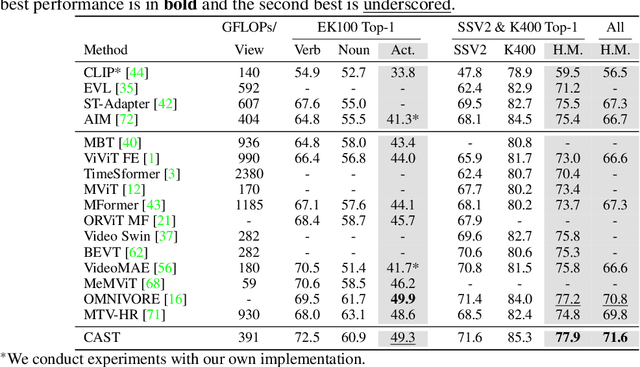
Recognizing human actions in videos requires spatial and temporal understanding. Most existing action recognition models lack a balanced spatio-temporal understanding of videos. In this work, we propose a novel two-stream architecture, called Cross-Attention in Space and Time (CAST), that achieves a balanced spatio-temporal understanding of videos using only RGB input. Our proposed bottleneck cross-attention mechanism enables the spatial and temporal expert models to exchange information and make synergistic predictions, leading to improved performance. We validate the proposed method with extensive experiments on public benchmarks with different characteristics: EPIC-KITCHENS-100, Something-Something-V2, and Kinetics-400. Our method consistently shows favorable performance across these datasets, while the performance of existing methods fluctuates depending on the dataset characteristics.
Free-Form Composition Networks for Egocentric Action Recognition
Jul 13, 2023Egocentric action recognition is gaining significant attention in the field of human action recognition. In this paper, we address data scarcity issue in egocentric action recognition from a compositional generalization perspective. To tackle this problem, we propose a free-form composition network (FFCN) that can simultaneously learn disentangled verb, preposition, and noun representations, and then use them to compose new samples in the feature space for rare classes of action videos. First, we use a graph to capture the spatial-temporal relations among different hand/object instances in each action video. We thus decompose each action into a set of verb and preposition spatial-temporal representations using the edge features in the graph. The temporal decomposition extracts verb and preposition representations from different video frames, while the spatial decomposition adaptively learns verb and preposition representations from action-related instances in each frame. With these spatial-temporal representations of verbs and prepositions, we can compose new samples for those rare classes in a free-form manner, which is not restricted to a rigid form of a verb and a noun. The proposed FFCN can directly generate new training data samples for rare classes, hence significantly improve action recognition performance. We evaluated our method on three popular egocentric action recognition datasets, Something-Something V2, H2O, and EPIC-KITCHENS-100, and the experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method for handling data scarcity problems, including long-tailed and few-shot egocentric action recognition.
Modelling Spatio-Temporal Interactions for Compositional Action Recognition
May 04, 2023



Humans have the natural ability to recognize actions even if the objects involved in the action or the background are changed. Humans can abstract away the action from the appearance of the objects and their context which is referred to as compositionality of actions. Compositional action recognition deals with imparting human-like compositional generalization abilities to action-recognition models. In this regard, extracting the interactions between humans and objects forms the basis of compositional understanding. These interactions are not affected by the appearance biases of the objects or the context. But the context provides additional cues about the interactions between things and stuff. Hence we need to infuse context into the human-object interactions for compositional action recognition. To this end, we first design a spatial-temporal interaction encoder that captures the human-object (things) interactions. The encoder learns the spatio-temporal interaction tokens disentangled from the background context. The interaction tokens are then infused with contextual information from the video tokens to model the interactions between things and stuff. The final context-infused spatio-temporal interaction tokens are used for compositional action recognition. We show the effectiveness of our interaction-centric approach on the compositional Something-Else dataset where we obtain a new state-of-the-art result of 83.8% top-1 accuracy outperforming recent important object-centric methods by a significant margin. Our approach of explicit human-object-stuff interaction modeling is effective even for standard action recognition datasets such as Something-Something-V2 and Epic-Kitchens-100 where we obtain comparable or better performance than state-of-the-art.
Finetuning for Sarcasm Detection with a Pruned Dataset
Dec 23, 2022Sarcasm is a form of irony that involves saying or writing something that is opposite or opposite to what one really means, often in a humorous or mocking way. It is often used to mock or mock someone or something, or to be humorous or amusing. Sarcasm is usually conveyed through tone of voice, facial expressions, or other forms of nonverbal communication, but it can also be indicated by the use of certain words or phrases that are typically associated with irony or humor. Sarcasm detection is difficult because it relies on context and non-verbal cues. It can also be culturally specific, subjective and ambiguous. In this work, we fine-tune the RoBERTa based sarcasm detection model presented in Abaskohi et al. [2022] to get to within 0.02 F1 of the state-of-the-art (Hercog et al. [2022]) on the iSarcasm dataset (Oprea and Magdy [2019]). This performance is achieved by augmenting iSarcasm with a pruned version of the Self Annotated Reddit Corpus (SARC) (Khodak et al. [2017]). Our pruned version is 100 times smaller than the subset of SARC used to train the state-of-the-art model.
Fixing Model Bugs with Natural Language Patches
Nov 20, 2022Current approaches for fixing systematic problems in NLP models (e.g. regex patches, finetuning on more data) are either brittle, or labor-intensive and liable to shortcuts. In contrast, humans often provide corrections to each other through natural language. Taking inspiration from this, we explore natural language patches -- declarative statements that allow developers to provide corrective feedback at the right level of abstraction, either overriding the model (``if a review gives 2 stars, the sentiment is negative'') or providing additional information the model may lack (``if something is described as the bomb, then it is good''). We model the task of determining if a patch applies separately from the task of integrating patch information, and show that with a small amount of synthetic data, we can teach models to effectively use real patches on real data -- 1 to 7 patches improve accuracy by ~1-4 accuracy points on different slices of a sentiment analysis dataset, and F1 by 7 points on a relation extraction dataset. Finally, we show that finetuning on as many as 100 labeled examples may be needed to match the performance of a small set of language patches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge