Mirco Planamente
Egocentric zone-aware action recognition across environments
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:Human activities exhibit a strong correlation between actions and the places where these are performed, such as washing something at a sink. More specifically, in daily living environments we may identify particular locations, hereinafter named activity-centric zones, which may afford a set of homogeneous actions. Their knowledge can serve as a prior to favor vision models to recognize human activities. However, the appearance of these zones is scene-specific, limiting the transferability of this prior information to unfamiliar areas and domains. This problem is particularly relevant in egocentric vision, where the environment takes up most of the image, making it even more difficult to separate the action from the context. In this paper, we discuss the importance of decoupling the domain-specific appearance of activity-centric zones from their universal, domain-agnostic representations, and show how the latter can improve the cross-domain transferability of Egocentric Action Recognition (EAR) models. We validate our solution on the EPIC-Kitchens-100 and Argo1M datasets
Bringing Online Egocentric Action Recognition into the wild
Nov 06, 2022



Abstract:To enable a safe and effective human-robot cooperation, it is crucial to develop models for the identification of human activities. Egocentric vision seems to be a viable solution to solve this problem, and therefore many works provide deep learning solutions to infer human actions from first person videos. However, although very promising, most of these do not consider the major challenges that comes with a realistic deployment, such as the portability of the model, the need for real-time inference, and the robustness with respect to the novel domains (i.e., new spaces, users, tasks). With this paper, we set the boundaries that egocentric vision models should consider for realistic applications, defining a novel setting of egocentric action recognition in the wild, which encourages researchers to develop novel, applications-aware solutions. We also present a new model-agnostic technique that enables the rapid repurposing of existing architectures in this new context, demonstrating the feasibility to deploy a model on a tiny device (Jetson Nano) and to perform the task directly on the edge with very low energy consumption (2.4W on average at 50 fps).
PoliTO-IIT-CINI Submission to the EPIC-KITCHENS-100 Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Challenge for Action Recognition
Sep 09, 2022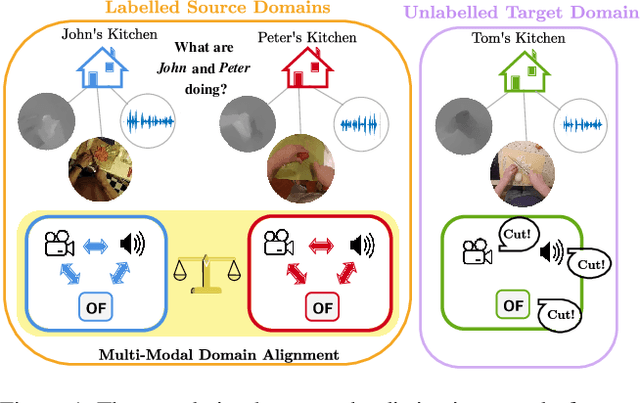
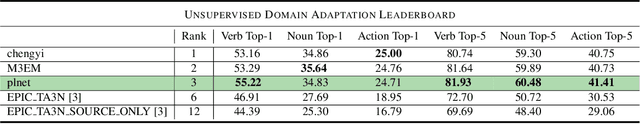
Abstract:In this report, we describe the technical details of our submission to the EPIC-Kitchens-100 Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) Challenge in Action Recognition. To tackle the domain-shift which exists under the UDA setting, we first exploited a recent Domain Generalization (DG) technique, called Relative Norm Alignment (RNA). Secondly, we extended this approach to work on unlabelled target data, enabling a simpler adaptation of the model to the target distribution in an unsupervised fashion. To this purpose, we included in our framework UDA algorithms, such as multi-level adversarial alignment and attentive entropy. By analyzing the challenge setting, we notice the presence of a secondary concurrence shift in the data, which is usually called environmental bias. It is caused by the existence of different environments, i.e., kitchens. To deal with these two shifts (environmental and temporal), we extended our system to perform Multi-Source Multi-Target Domain Adaptation. Finally, we employed distinct models in our final proposal to leverage the potential of popular video architectures, and we introduced two more losses for the ensemble adaptation. Our submission (entry 'plnet') is visible on the leaderboard and ranked in 2nd position for 'verb', and in 3rd position for both 'noun' and 'action'.
E$^2$MOTION: Motion Augmented Event Stream for Egocentric Action Recognition
Dec 07, 2021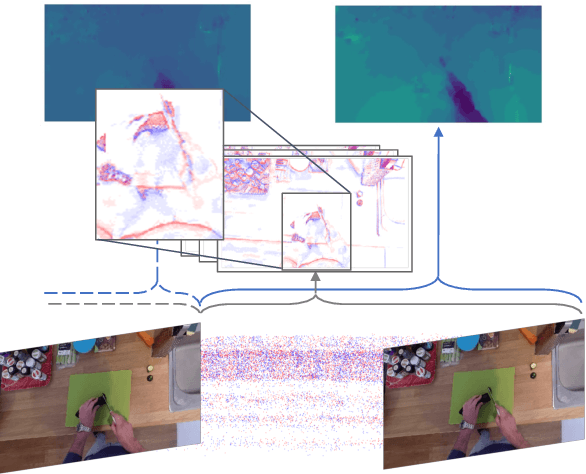
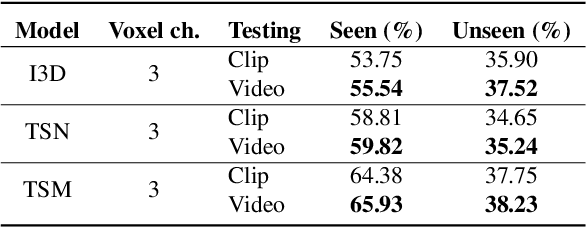
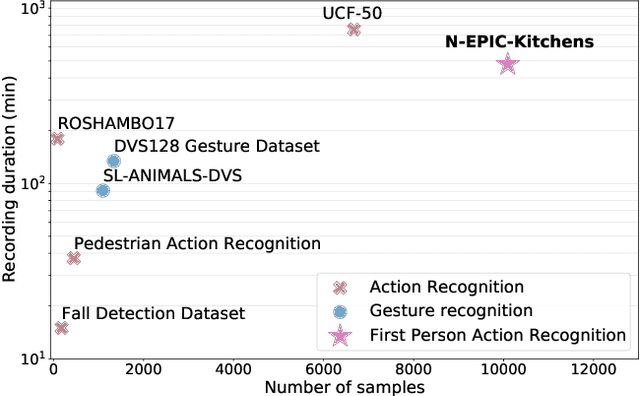
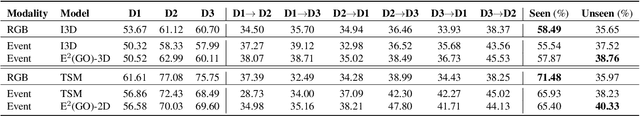
Abstract:Event cameras are novel bio-inspired sensors, which asynchronously capture pixel-level intensity changes in the form of "events". Due to their sensing mechanism, event cameras have little to no motion blur, a very high temporal resolution and require significantly less power and memory than traditional frame-based cameras. These characteristics make them a perfect fit to several real-world applications such as egocentric action recognition on wearable devices, where fast camera motion and limited power challenge traditional vision sensors. However, the ever-growing field of event-based vision has, to date, overlooked the potential of event cameras in such applications. In this paper, we show that event data is a very valuable modality for egocentric action recognition. To do so, we introduce N-EPIC-Kitchens, the first event-based camera extension of the large-scale EPIC-Kitchens dataset. In this context, we propose two strategies: (i) directly processing event-camera data with traditional video-processing architectures (E$^2$(GO)) and (ii) using event-data to distill optical flow information (E$^2$(GO)MO). On our proposed benchmark, we show that event data provides a comparable performance to RGB and optical flow, yet without any additional flow computation at deploy time, and an improved performance of up to 4% with respect to RGB only information.
Domain Generalization through Audio-Visual Relative Norm Alignment in First Person Action Recognition
Oct 19, 2021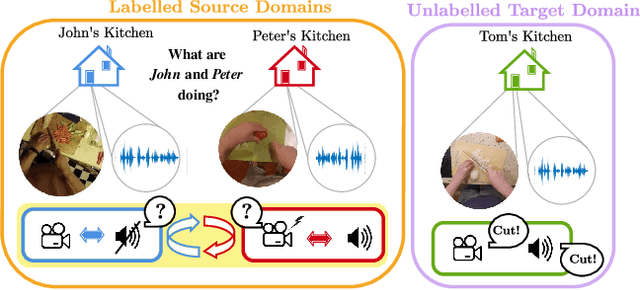
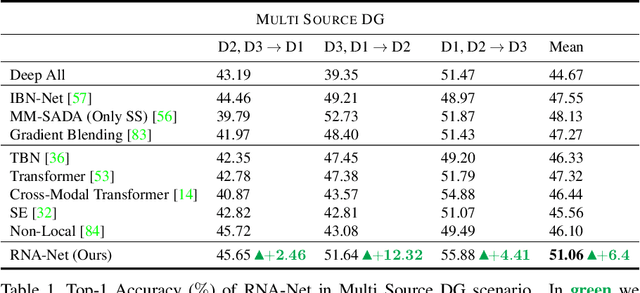
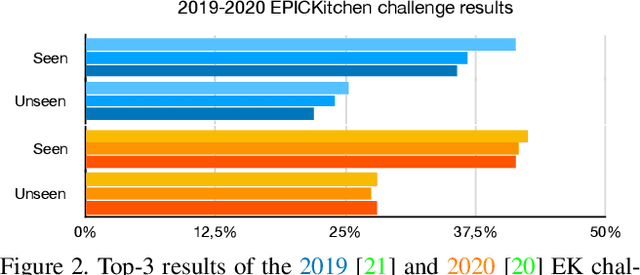
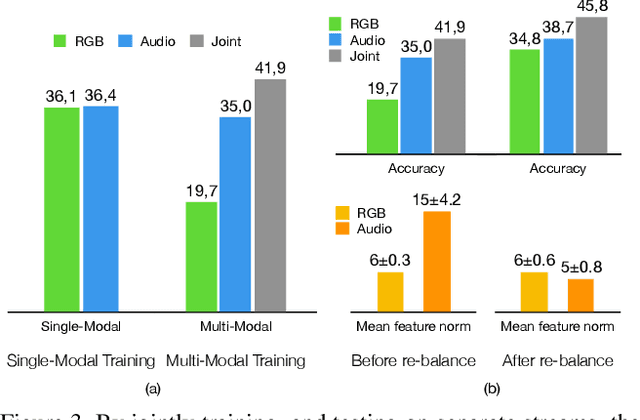
Abstract:First person action recognition is becoming an increasingly researched area thanks to the rising popularity of wearable cameras. This is bringing to light cross-domain issues that are yet to be addressed in this context. Indeed, the information extracted from learned representations suffers from an intrinsic "environmental bias". This strongly affects the ability to generalize to unseen scenarios, limiting the application of current methods to real settings where labeled data are not available during training. In this work, we introduce the first domain generalization approach for egocentric activity recognition, by proposing a new audio-visual loss, called Relative Norm Alignment loss. It re-balances the contributions from the two modalities during training, over different domains, by aligning their feature norm representations. Our approach leads to strong results in domain generalization on both EPIC-Kitchens-55 and EPIC-Kitchens-100, as demonstrated by extensive experiments, and can be extended to work also on domain adaptation settings with competitive results.
PoliTO-IIT Submission to the EPIC-KITCHENS-100 Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Challenge for Action Recognition
Jul 01, 2021


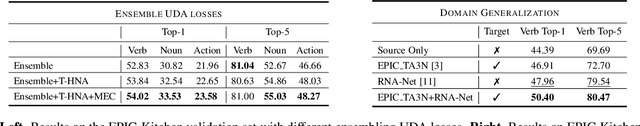
Abstract:In this report, we describe the technical details of our submission to the EPIC-Kitchens-100 Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) Challenge in Action Recognition. To tackle the domain-shift which exists under the UDA setting, we first exploited a recent Domain Generalization (DG) technique, called Relative Norm Alignment (RNA). It consists in designing a model able to generalize well to any unseen domain, regardless of the possibility to access target data at training time. Then, in a second phase, we extended the approach to work on unlabelled target data, allowing the model to adapt to the target distribution in an unsupervised fashion. For this purpose, we included in our framework existing UDA algorithms, such as Temporal Attentive Adversarial Adaptation Network (TA3N), jointly with new multi-stream consistency losses, namely Temporal Hard Norm Alignment (T-HNA) and Min-Entropy Consistency (MEC). Our submission (entry 'plnet') is visible on the leaderboard and it achieved the 1st position for 'verb', and the 3rd position for both 'noun' and 'action'.
Cross-Domain First Person Audio-Visual Action Recognition through Relative Norm Alignment
Jun 03, 2021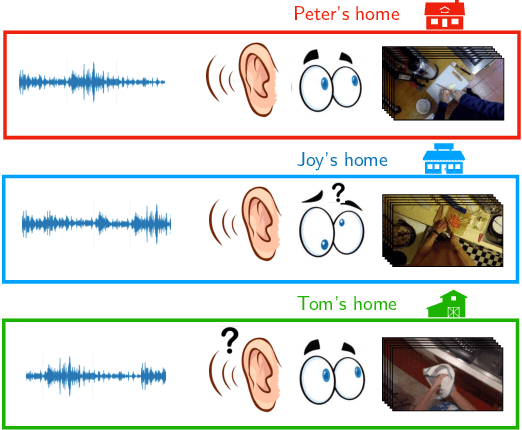
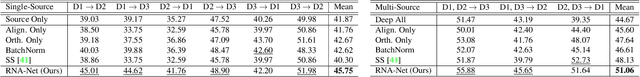
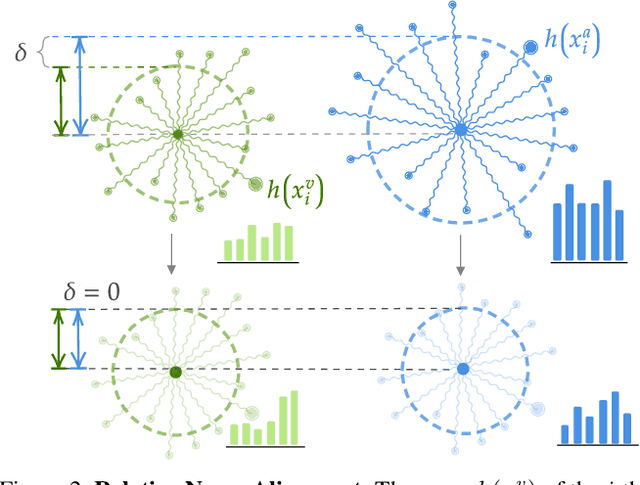
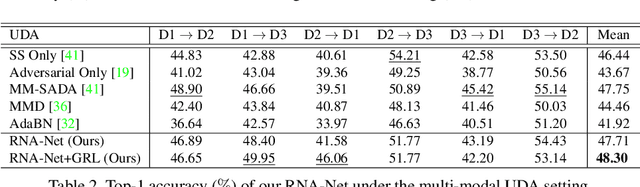
Abstract:First person action recognition is an increasingly researched topic because of the growing popularity of wearable cameras. This is bringing to light cross-domain issues that are yet to be addressed in this context. Indeed, the information extracted from learned representations suffers from an intrinsic environmental bias. This strongly affects the ability to generalize to unseen scenarios, limiting the application of current methods in real settings where trimmed labeled data are not available during training. In this work, we propose to leverage over the intrinsic complementary nature of audio-visual signals to learn a representation that works well on data seen during training, while being able to generalize across different domains. To this end, we introduce an audio-visual loss that aligns the contributions from the two modalities by acting on the magnitude of their feature norm representations. This new loss, plugged into a minimal multi-modal action recognition architecture, leads to strong results in cross-domain first person action recognition, as demonstrated by extensive experiments on the popular EPIC-Kitchens dataset.
DA4Event: towards bridging the Sim-to-Real Gap for Event Cameras using Domain Adaptation
Mar 23, 2021



Abstract:Event cameras are novel bio-inspired sensors, which asynchronously capture pixel-level intensity changes in the form of "events". The innovative way they acquire data presents several advantages over standard devices, especially in poor lighting and high-speed motion conditions. However, the novelty of these sensors results in the lack of a large amount of training data capable of fully unlocking their potential. The most common approach implemented by researchers to address this issue is to leverage simulated event data. Yet, this approach comes with an open research question: how well simulated data generalize to real data? To answer this, we propose to exploit, in the event-based context, recent Domain Adaptation (DA) advances in traditional computer vision, showing that DA techniques applied to event data help reduce the sim-to-real gap. To this purpose, we propose a novel architecture, which we call Multi-View DA4E (MV-DA4E), that better exploits the peculiarities of frame-based event representations while also promoting domain invariant characteristics in features. Through extensive experiments, we prove the effectiveness of DA methods and MV-DA4E on N-Caltech101. Moreover, we validate their soundness in a real-world scenario through a cross-domain analysis on the popular RGB-D Object Dataset (ROD), which we extended to the event modality (RGB-E).
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation through Inter-modal Rotation for RGB-D Object Recognition
Apr 21, 2020
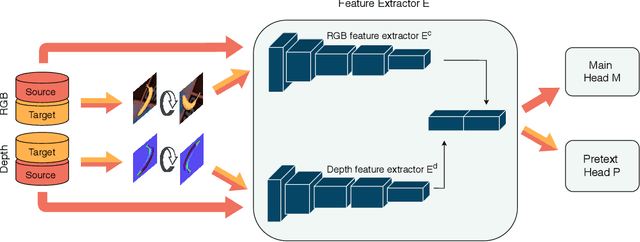
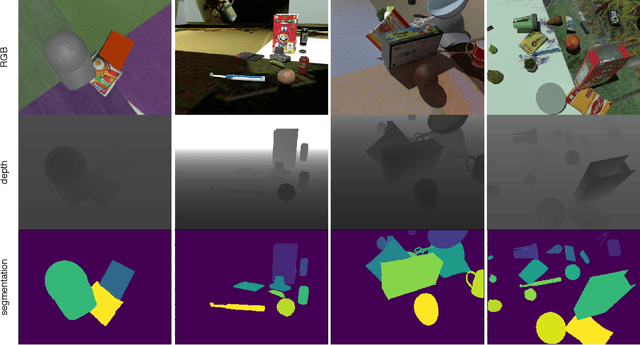

Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (DA) exploits the supervision of a label-rich source dataset to make predictions on an unlabeled target dataset by aligning the two data distributions. In robotics, DA is used to take advantage of automatically generated synthetic data, that come with "free" annotation, to make effective predictions on real data. However, existing DA methods are not designed to cope with the multi-modal nature of RGB-D data, which are widely used in robotic vision. We propose a novel RGB-D DA method that reduces the synthetic-to-real domain shift by exploiting the inter-modal relation between the RGB and depth image. Our method consists of training a convolutional neural network to solve, in addition to the main recognition task, the pretext task of predicting the relative rotation between the RGB and depth image. To evaluate our method and encourage further research in this area, we define two benchmark datasets for object categorization and instance recognition. With extensive experiments, we show the benefits of leveraging the inter-modal relations for RGB-D DA.
Joint Encoding of Appearance and Motion Features with Self-supervision for First Person Action Recognition
Feb 10, 2020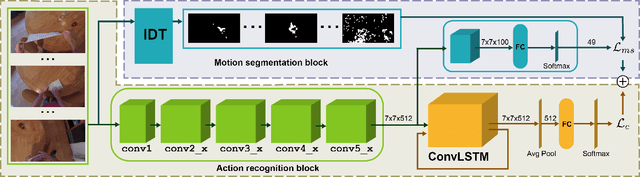

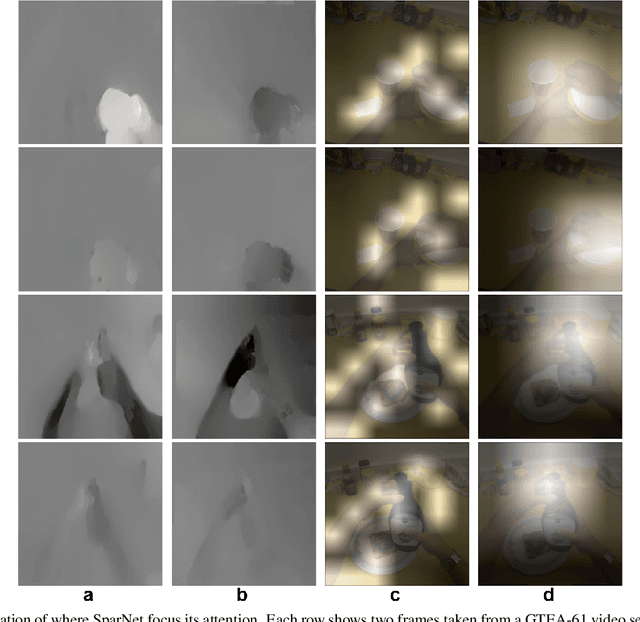

Abstract:Wearable cameras are becoming more and more popular in several applications, increasing the interest of the research community in developing approaches for recognizing actions from a first-person point of view. An open challenge is how to cope with the limited amount of motion information available about the action itself, as opposed to the more investigated third-person action recognition scenario. When focusing on manipulation tasks, videos tend to record only parts of the movement, making crucial the understanding of the objects being manipulated and of their context. Previous works addressed this issue with two-stream architectures, one dedicated to modeling the appearance of objects involved in the action, another dedicated to extracting motion features from optical flow. In this paper, we argue that features from these two information channels should be learned jointly to capture the spatio-temporal correlations between the two in a better way. To this end, we propose a single stream architecture able to do so, thanks to the addition of a self-supervised block that uses a pretext motion segmentation task to intertwine motion and appearance knowledge. Experiments on several publicly available databases show the power of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge